Introduction: Why Monomer Selection Is Critical in Custom Polymer Synthesis
Custom Polymer Synthesis relies heavily on intelligent monomer selection to design polymers with precise structural, mechanical, and functional characteristics. The choice of monomers determines everything from polymer stability and reactivity to biocompatibility and regulatory acceptance.
Monomers are the foundational building blocks of polymers, determining their structural, mechanical, and functional properties. The success of custom polymer synthesis hinges on choosing the right monomers that align with the desired application. Whether for industrial-grade materials or biocompatible polymers, strategic monomer selection drives the innovation and efficacy of the final product.
This guide delves into the critical strategies for selecting monomers, shedding light on factors, techniques, and real-world applications that underscore their importance.
At ResolveMass Laboratories Inc., monomer selection is treated as a science-driven, application-focused strategy—ensuring polymers are not only innovative but also scalable, reproducible, and compliant with global standards.
Summary
- Custom Polymer Synthesis begins with strategic monomer selection to achieve targeted physical, chemical, and biological properties
- Monomer chemistry directly influences polymer performance, scalability, and regulatory compliance
- Functional groups, molecular weight control, and end-use application drive monomer decisions
- Expert-led monomer selection minimizes development risk and accelerates commercialization
- ResolveMass Laboratories Inc. applies advanced scientific expertise to deliver reliable, application-specific polymers
1: What Is Monomer Selection in Custom Polymer Synthesis?
Monomer selection in Custom Polymer Synthesis refers to choosing the appropriate molecular building blocks that will define the polymer’s final properties and performance.
Monomers are evaluated based on chemical structure, reactivity, compatibility, and intended application.
Key Objectives of Monomer Selection
- Achieve desired polymer functionality
- Control molecular weight and architecture
- Ensure process scalability
- Meet regulatory and safety requirements
2: Why Monomer Selection Directly Impacts Polymer Performance
Monomer chemistry dictates polymer behavior at both molecular and macroscopic levels.
Even small variations in monomer structure can dramatically change:
- Mechanical strength
- Thermal stability
- Chemical resistance
- Degradation profile
Performance Factors Influenced by Monomers
- Glass transition temperature (Tg)
- Hydrophobicity or hydrophilicity
- Crystallinity
- Elasticity and toughness
This is why Custom Polymer Synthesis demands expert-driven monomer screening rather than trial-and-error approaches.
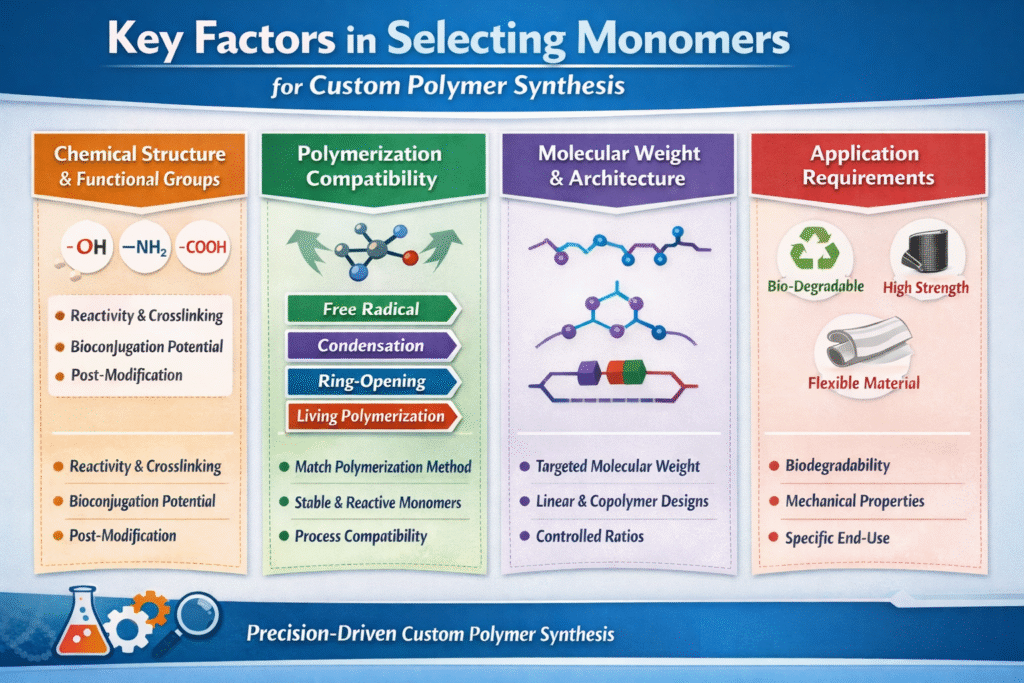
3: Key Factors to Consider When Selecting Monomers for Custom Polymer Synthesis
1. Chemical Structure and Functional Groups
Functional groups determine polymer reactivity, crosslinking ability, and post-synthesis modifications.
Common functional considerations include:
- Hydroxyl (–OH) for hydrophilicity
- Amine (–NH₂) for biofunctionalization
- Carboxyl (–COOH) for conjugation chemistry
Monomers must possess reactive groups conducive to the desired polymerization process. Examples include:
- Double bonds: Common in free radical polymerization (e.g., styrene, acrylic acid).
- Cyclic structures: Used in ring-opening polymerization (e.g., lactides for biodegradable polymers).
- Specific functional groups: Tailored for post-polymerization modifications (e.g., amines, carboxyl groups).
Curious how monomer structure affects biodegradability and function? Read this – Introduction to Poly(β-amino esters): Structure and Properties
Selecting the right functional group ensures compatibility with downstream applications such as drug delivery or surface coatings.
2. Polymerization Mechanism Compatibility
Monomers must be compatible with the intended polymerization technique.
| Polymerization Type | Suitable Monomer Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Free radical | Vinyl groups, acrylates |
| Condensation | Diols, diacids |
| Ring-opening | Cyclic esters, lactones |
| Controlled/living | High purity, low inhibitor content |
Different polymerization methods require specific monomer properties:
- Radical Polymerization: Requires stable monomers with nonpolar functional groups.
- Living Polymerization: Needs monomers with controlled reactivity for precise molecular weight regulation.
- Emulsion Polymerization: Hydrophilic or amphiphilic monomers are ideal.
Monomer compatibility starts with knowing your technique, here’s a breakdown – A Comprehensive Guide to Polymerization Techniques: Step-Growth vs Chain-Growth
ResolveMass Laboratories Inc. aligns monomer selection with controlled polymerization strategies to ensure consistency and predictability.
3. Desired Molecular Weight and Architecture
Monomer purity and reactivity influence molecular weight control in Custom Polymer Synthesis.
Architectural considerations include:
- Linear polymers
- Branched polymers
- Block copolymers
- Graft copolymers
Precise monomer ratios and reactivity profiles are essential to achieving these structures reliably.
4. Application Requirements
Monomer properties must align with the target application:
- Biodegradability: Lactide and glycolide for medical sutures.
- High strength: Acrylonitrile for carbon fiber precursors.
- Flexibility: Ethylene for packaging materials.
From drug delivery to electronics, see how polymers support modern tech – The Importance of Polymer Synthesis in Modern Science and Technology
4: Importance of Monomer Selection in Custom Polymer Synthesis
The choice of monomers directly influences:
- Polymer properties: Thermal stability, flexibility, solubility, and mechanical strength.
- Functional characteristics: Hydrophilicity, biodegradability, and conductivity.
- Application suitability: Medical, industrial, or environmental use cases.
Case Example:
In drug delivery, hydrophilic monomers like polyethylene glycol (PEG) derivatives are often selected for biocompatibility and reduced immunogenicity, ensuring patient safety.
Wondering how monomer selection fits into the full process? Step-by-Step Guide to Custom Polymer Synthesis Process, this article shows you.
5: Strategies for Monomer Selection
5.1 Assessing Material Properties
Understanding the material’s intended use guides monomer selection.
Key Material Properties:
- Thermal Stability: For high-temperature applications, select monomers with aromatic groups.
- Elasticity: Rubber-like polymers require monomers with low glass transition temperatures (e.g., butadiene).
- Chemical Resistance: Monomers with halogen or fluorine groups (e.g., tetrafluoroethylene) enhance resistance to chemicals.
Thermal stability starts with your polymer type, here’s the difference – Thermoplastic vs. Thermosetting Polymers: Insights for Custom Polymer Synthesis
5.2 Leveraging Computational Tools
Advanced tools predict polymer behavior based on monomer properties:
- Molecular simulations: Evaluate polymer structure and reactivity.
- Predictive algorithms: Suggest optimal monomers for desired properties.
How AI Is Revolutionizing Custom Polymer Synthesis, this guide shows how digital tools boost accuracy in polymer science.
5.3 Incorporating Functionalization Potential
Monomers with modifiable functional groups allow post-polymerization modifications:
- Applications: Adding hydrophilic groups for water solubility or attaching drug molecules for targeted delivery.
6: Monomer Selection for Specific Applications
6.1 Biodegradable Polymers
Monomers:
- Lactides, glycolides, caprolactones.
Applications: - Biodegradable plastics, medical implants, and tissue engineering scaffolds.
6.2 Conductive Polymers
Monomers:
- Aniline, thiophene, pyrrole.
Applications: - Flexible electronics, sensors, and solar cells.
6.3 Drug Delivery Systems
Monomers:
- PEG derivatives, acrylic acids.
Applications: - Hydrogels, nanoparticles, and micelles for controlled drug release.
7. Challenges in Monomer Selection
7.1 Balancing Multiple Properties
It is challenging to find a single monomer that satisfies all requirements:
- Example: High-strength polymers may lack flexibility, necessitating copolymerization.
7.2 Environmental and Economic Considerations
Sustainable synthesis requires monomers that:
- Are derived from renewable resources.
- Exhibit low toxicity and minimal environmental impact.
- Are cost-effective for large-scale production.
Top Challenges and Opportunities in Custom Polymer Synthesis this article explores the real challenges behind smart polymer design.
8. Trends in Monomer Development
8.1 Bio-Based Monomers
Derived from natural sources, bio-based monomers are increasingly popular:
- Examples: Polylactic acid (PLA) from corn, polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA) from bacteria.
- Advantages: Renewable and biodegradable.
8.2 Smart Monomers
These monomers enable polymers to respond to environmental stimuli:
- Examples: Temperature-sensitive N-isopropylacrylamide (NIPAAm).
- Applications: Smart coatings and biomedical devices.
Want to see what’s next in monomer design? Check out how deuterated polymers are shaping the future.
9. Techniques to Evaluate Monomer Suitability
9.1 Spectroscopic Analysis
- FTIR: Identifies functional groups.
- NMR: Determines chemical structure.
9.2 Thermal Analysis
- DSC: Measures melting and glass transition temperatures.
- TGA: Assesses thermal stability.
9.3 Mechanical Testing
- Evaluates polymer strength and elasticity after polymerization.
Want to know how experts test monomers before using them? How to Ensure High Purity in Custom Polymer Synthesis, this article covers the methods used to ensure high purity.
10: Why Choose ResolveMass Laboratories for Custom Polymer Synthesis?
At ResolveMass Laboratories, we specialize in custom polymer synthesis tailored to your needs.
Our Advantages:
- Extensive monomer library: Choose from a wide range of monomers for specific applications.
- Expert guidance: Collaborate with scientists to optimize monomer selection.
- Advanced analysis: Ensure polymer performance with cutting-edge testing facilities.
Wondering why ResolveMass is trusted by so many? Custom Organic Synthesis in Montreal, Canada or United States, this explains it in simple terms.
Future Trends in Monomer Selection for Custom Polymer Synthesis
Innovation in Custom Polymer Synthesis is driven by smarter monomer design.
Emerging trends include:
- AI-assisted monomer prediction
- Precision macromolecular engineering
- Sustainable and biodegradable monomers
ResolveMass remains at the forefront by continuously adapting to these advancements.
Conclusion
Custom Polymer Synthesis succeeds or fails based on the quality of monomer selection.
By aligning chemistry, application needs, regulatory expectations, and scalability, organizations can achieve high-performance, reliable polymer solutions.
With its deep scientific expertise and advanced analytical capabilities, ResolveMass Laboratories Inc. stands as a trusted partner for precision-driven Custom Polymer Synthesis.
Explore More:
Contact Us today to learn how we can help with your custom polymer projects.
FAQs
Monomer evaluation ensures that the selected monomers have the correct chemical structure, purity, and stability required to produce polymers with consistent performance, safety, and scalability.
The most commonly used techniques include spectroscopic analysis (FTIR, NMR), thermal analysis (DSC, TGA), and mechanical testing after polymerization to confirm performance.
FTIR identifies functional groups present in monomers, helping confirm chemical identity and detect impurities that may interfere with polymerization.
NMR determines the detailed chemical structure of monomers, including molecular framework and purity, which is critical for controlled and reproducible polymer synthesis.
Thermal analysis techniques such as DSC and TGA assess melting behavior, glass transition temperature, and thermal stability, ensuring monomers can withstand processing conditions.
References
- Challenges for Natural Monomers and Polymers: Novel Design Strategies and Engineering to Develop Advanced Polymers.https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1163/138577210X12634696333190
- Combinatorial Methods, Automated Synthesis and High-Throughput Screening in Polymer Research: The Evolution Continues.https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/marc.200300147
- Precise Polymer Synthesis by Autonomous Self-Optimizing Flow Reactors.https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/anie.201810384
- Exploring Strategies To Bias Sequence in Natural and Synthetic Oligomers and Polymers.https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/acs.accounts.7b00495

