Introduction
The custom polymer synthesis process has revolutionized material science, enabling researchers and manufacturers to create precisely tailored polymeric materials for specific applications. Whether you’re developing advanced drug delivery systems, creating high-performance coatings, or engineering specialized electronic materials, understanding the systematic approach to polymer synthesis is essential for achieving optimal results.
At ResolveMass Laboratories Inc., we’ve refined our polymer synthesis methodology over years of serving diverse industries—from pharmaceuticals to aerospace. This guide walks you through each critical phase of the custom polymer synthesis journey, providing insights drawn from thousands of successful projects and backed by rigorous scientific protocols.
Custom polymer synthesis plays a pivotal role in a wide range of applications, including drug delivery systems, advanced materials, and nanotechnology. Whether you’re developing new materials for industrial use or creating specific polymers for pharmaceutical applications, understanding the step-by-step process of custom polymer synthesis is essential for achieving high-quality results. In this guide, we will walk you through the key stages of the custom polymer synthesis process, from design to final product, highlighting the key considerations for success
Before diving into the steps, understand what custom polymer synthesis really means 👉 What Is Custom Polymer Synthesis? An In-Depth Guide
Summary
This comprehensive guide covers the complete custom polymer synthesis process from initial consultation to final delivery. Key takeaways include:
- Identifying critical quality parameters that ensure product consistency and performance
- Understanding the fundamental steps of custom polymer synthesis from concept to production
- Learning about monomer selection, polymerization techniques, and quality control measures
- Exploring advanced characterization methods including NMR, GPC, and thermal analysis
- Discovering how professional laboratories ensure precise molecular weight control and purity
- Recognizing the importance of scalability planning and regulatory compliance
- Understanding typical timelines ranging from 2-12 weeks depending on complexity
1: Understanding Custom Polymer Synthesis
Custom polymer synthesis is the controlled creation of polymeric materials with specific molecular structures, properties, and functionalities. Unlike off-the-shelf polymers, custom synthesis allows for precise control over molecular weight, architecture, composition, and end-group functionalities to meet exact application requirements.
Why Custom Synthesis Matters
Standard commercial polymers often cannot meet the specialized demands of cutting-edge research and industrial applications. Custom synthesis provides:
- Molecular precision: Control over molecular weight distribution (PDI < 1.2)
- Functional customization: Integration of specific reactive groups or side chains
- Property optimization: Tailored thermal, mechanical, and chemical characteristics
- Application-specific solutions: Materials designed for unique performance requirements
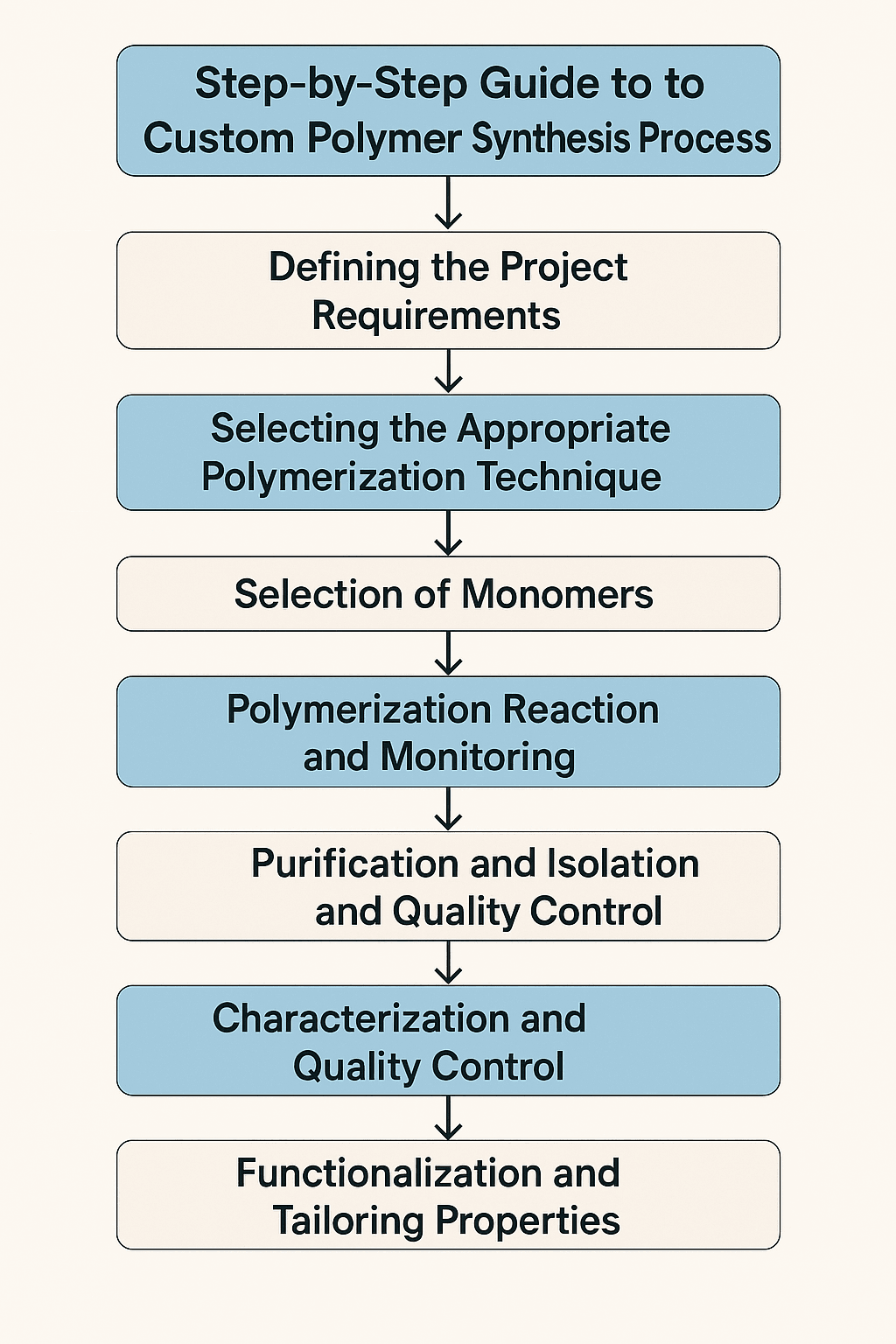
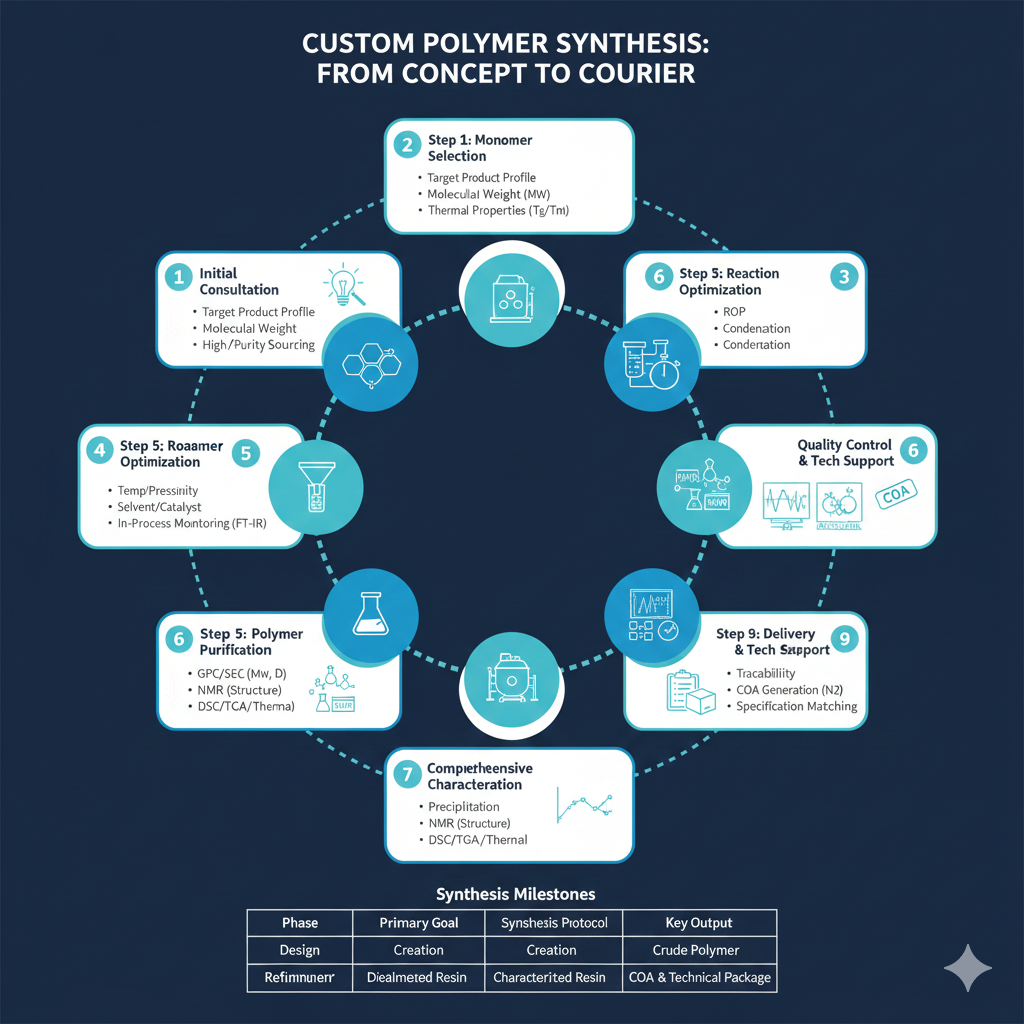
Step 1: Initial Consultation and Project Assessment
The custom polymer synthesis process begins with a thorough understanding of your requirements. This critical first step determines the feasibility, timeline, and approach for your project.
What We Evaluate
During the initial consultation, several key factors are assessed:
| Assessment Area | Key Considerations |
|---|---|
| Target Properties | Molecular weight, polydispersity, thermal stability, solubility |
| Application Requirements | End-use conditions, regulatory needs, performance specifications |
| Scale Requirements | Research quantities (grams) vs. production scale (kilograms) |
| Timeline Constraints | Standard delivery (4-8 weeks) vs. expedited projects |
| Budget Parameters | Complexity, scale, and analytical requirements |
Our team conducts a comprehensive technical review to identify potential synthetic challenges, recommend optimal approaches, and establish realistic project milestones. This upfront investment in planning significantly increases success rates and reduces costly iterations.
How Will You Use the Polymer?
The right polymer for your project depends on what you need it to do. Are you developing something for:
- Drug Delivery? → You’ll need a polymer that’s biocompatible and possibly biodegradable, so it safely releases medication in the body.
- Medical Devices? → Focus on mechanical strength and long-term stability to ensure durability and safety.
- Materials Science? → Your polymer may need specialized properties like flexibility, heat resistance, or conductivity, depending on the application.
Step 2: Monomer Selection and Sourcing
Selecting appropriate monomers is fundamental to successful polymer synthesis. The monomer choice directly impacts the polymer’s structure, properties, and synthesis efficiency.
Monomer Selection Criteria
The choice of monomers is one of the most critical steps in the custom polymer synthesis process. Monomers serve as the building blocks of the polymer and define the chemical and physical properties of the final product.
Considerations for Monomer Selection:
- Functionality: Choose monomers with specific functional groups that align with your desired polymer properties, such as hydrophobicity, hydrophilicity, or chemical reactivity.
- Compatibility: Ensure the monomers are compatible with the selected polymerization method. Some monomers may require special conditions for polymerization or may not be compatible with certain catalysts or solvents.
- Availability and Cost: Consider the availability of monomers and their cost-effectiveness, especially for large-scale production.
In pharmaceutical applications, it is also important to select monomers that are non-toxic and biocompatible, ensuring safety in medical or drug delivery systems.
Learn what factors matters most when selecting monomers for efficient synthesis Monomer Selection Strategies for Custom Polymer Synthesis
When choosing monomers for your custom polymer synthesis process, consider:
- Reactivity profiles: Polymerization kinetics and compatibility with chosen methods
- Purity requirements: Pharmaceutical-grade (>99.5%) vs. industrial-grade materials
- Functional group compatibility: Protecting group strategies when necessary
- Availability and cost: Custom synthesis vs. commercial sources
- Safety profiles: Handling requirements and hazard classifications
Quality Verification
All monomers undergo rigorous verification before synthesis:
- Identity confirmation: NMR spectroscopy and mass spectrometry
- Purity analysis: HPLC or GC with quantification of impurities
- Water content: Karl Fischer titration (critical for many polymerizations)
- Inhibitor removal: When required for radical polymerizations
This quality-first approach prevents common synthesis failures caused by impure starting materials.
Step 3: Synthesis Method Selection
Choosing the right polymerization technique is crucial for achieving desired polymer characteristics. The custom polymer synthesis process employs various methodologies depending on target specifications.
Common Polymerization Techniques
The next step in the process is selecting the right polymerization technique based on the project’s requirements. Several polymerization methods are used in custom polymer synthesis, each offering distinct advantages for specific applications.
Understand how new methods are changing the way custom polymers are made – Emerging Trends in Custom Polymer Synthesis for 2025 and Beyond
Common Polymerization Methods:
- Radical Polymerization: Suitable for synthesizing a wide variety of polymers, especially those that are used in coatings, adhesives, and drug delivery systems. It’s highly versatile but may lead to broad molecular weight distributions.
- Living/Controlled Radical Polymerization (e.g., ATRP, RAFT): These methods provide better control over molecular weight and the distribution of polymer chains, which is crucial for creating uniform materials for pharmaceutical applications.
- Ring-Opening Polymerization (ROP): Ideal for synthesizing cyclic or biodegradable polymers, commonly used in drug delivery and medical devices.
- Step-Growth Polymerization: Involves the reaction of bifunctional monomers to form high-molecular-weight polymers, often used for creating polyesters, polyamides, and polyurethanes.
The choice of polymerization method will depend on factors such as the desired polymer structure, molecular weight, and functionalization.
Living/Controlled Radical Polymerization (CRP)
- RAFT (Reversible Addition-Fragmentation chain Transfer)
- ATRP (Atom Transfer Radical Polymerization)
- NMP (Nitroxide-Mediated Polymerization)
- Best for: Narrow molecular weight distributions, block copolymers
Ionic Polymerization
- Anionic and cationic mechanisms
- Best for: Ultra-low PDI (<1.1), controlled architectures
Ring-Opening Polymerization (ROP)
- Suitable for: Cyclic monomers, biocompatible polymers
Condensation Polymerization
- Step-growth mechanisms
- Best for: Polyesters, polyamides, high-performance materials
Method Selection Factors
The optimal technique depends on:
- Target molecular weight and distribution
- Monomer functional group tolerance
- Required end-group fidelity
- Temperature sensitivity
- Scale-up considerations
Step 4: Reaction Setup and Optimization
Proper reaction setup is where theory meets practice in the custom polymer synthesis process. Meticulous attention to reaction conditions ensures reproducibility and success.
Critical Reaction Parameters
Once the monomers are selected, polymerization begins. During this phase, the monomers undergo a chemical reaction to form polymer chains. The process may take place under different conditions, such as temperature control, solvent choice, and pressure, depending on the polymerization technique.
Key Considerations During Polymerization:
- Reaction Conditions: Control factors such as temperature, pressure, and time to ensure proper polymerization. The conditions should be optimized to achieve the desired molecular weight and narrow polydispersity.
- Catalysts and Initiators: Depending on the polymerization method, catalysts (for step-growth or ROP) or initiators (for radical polymerization) are required to kick-start the polymerization reaction. Their concentration and activity should be carefully controlled.
- Monitoring the Reaction: During polymerization, it is important to monitor the progress of the reaction to ensure the desired degree of polymerization is achieved. Techniques such as size-exclusion chromatography (SEC), Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR), and Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy can be used to track the polymerization process and verify molecular weight and composition.
At this stage, some CROs may employ real-time monitoring techniques or automated systems for precise control over the polymerization process.
Temperature Control Temperature directly affects polymerization kinetics, molecular weight, and side reactions. Our systems maintain ±0.5°C precision using:
- Programmable heating/cooling systems
- Real-time temperature monitoring
- Safety interlocks for runaway reaction prevention
Atmosphere Control Many polymerizations require inert atmospheres:
- Schlenk line techniques for air-sensitive reactions
- Glove box operations for ultra-sensitive systems
- Vacuum-backfill cycles to remove oxygen and moisture
Mixing and Agitation Proper mixing ensures:
- Homogeneous monomer distribution
- Efficient heat transfer
- Consistent molecular weight distribution
Reagent Addition Protocols Controlled addition techniques include:
- Slow addition for exothermic reactions
- Continuous feed for living polymerizations
- Sequential addition for block copolymers
Reaction Monitoring
Real-time monitoring provides crucial data:
- In-situ sampling: Periodic aliquot withdrawal for analysis
- Conversion tracking: Monomer consumption via NMR or GC
- Molecular weight evolution: Offline GPC analysis
- Calorimetry: Heat flow monitoring for kinetic studies
Step 5: Polymer Purification
Purification removes unreacted monomers, initiators, catalysts, and oligomers to yield high-purity polymer products suitable for demanding applications.
Purification Techniques
Purification eliminates residual monomers, solvents, and low molecular weight by-products to guarantee the polymer’s safety and efficacy.
Purification Methods:
- Precipitation: One common method is to precipitate the polymer from a solvent using a non-solvent. This is especially useful for purifying polymers synthesized by radical polymerization.
- Dialysis: For water-soluble polymers, dialysis can help remove low molecular weight impurities and solvents.
- Chromatography: Techniques like gel permeation chromatography (GPC) or flash chromatography are used for high-purity polymers, ensuring that the product is free from contaminants.
Explore practical ways to achieve high purity in custom polymers through smart purification
Drying Methods:
- Vacuum Drying: Gentle and avoids thermal degradation.
- Freeze-Drying (Lyophilization): Used for sensitive or thermolabile polymers.
Precipitation The most common method involves:
- Dissolution in good solvent
- Precipitation into non-solvent
- Multiple cycles for high purity (typically 3-5 times)
- Suitable for most polymer types
Dialysis Membrane-based separation removes:
- Low molecular weight impurities
- Salts and small molecules
- Ideal for water-soluble polymers
- MWCO selection based on target polymer size
Column Chromatography For specialized applications:
- Size exclusion chromatography (SEC) for fractionation
- Silica gel for removing catalysts
- Ion exchange for charged polymers
Solvent Extraction Removes specific impurities through:
- Selective solubility differences
- Liquid-liquid phase separation
- Soxhlet extraction for stubborn contaminants
Drying and Storage
Final drying protocols ensure stability:
- Vacuum oven drying (typically 40-60°C)
- Freeze-drying for heat-sensitive materials
- Residual solvent quantification (<0.1% by NMR)
- Storage under inert atmosphere with desiccants
Step 6: Comprehensive Characterization
Thorough characterization validates that the synthesized polymer meets all specifications. This is a cornerstone of the custom polymer synthesis process.
Molecular Weight Analysis
Gel Permeation Chromatography (GPC/SEC) Provides critical information:
- Number-average molecular weight (Mn)
- Weight-average molecular weight (Mw)
- Polydispersity index (PDI = Mw/Mn)
- Molecular weight distribution curves
Our multi-detector GPC systems include:
- Refractive index detection
- Light scattering for absolute molecular weight
- Viscometry for structural insights
Structural Characterization
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) ¹H-NMR and ¹³C-NMR confirm:
- Chemical structure and composition
- Copolymer ratios and sequence distribution
- End-group analysis
- Tacticity and stereochemistry
Mass Spectrometry MALDI-TOF and ESI-MS provide:
- Precise molecular weight determination
- End-group identification
- Oligomer distribution analysis
Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) Identifies:
- Functional groups
- Purity indicators
- Chemical modifications
Thermal Analysis
Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) Measures thermal transitions:
- Glass transition temperature (Tg)
- Melting point (Tm)
- Crystallization behavior
- Thermal history effects
Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA) Assesses thermal stability:
- Decomposition temperatures
- Residual solvent content
- Filler/additive content
- Multi-step degradation profiles
Physical Property Testing
Additional analyses include:
- Viscosity measurements (solution or melt)
- Mechanical testing (tensile, compression)
- Solubility testing in various solvents
- Optical properties (UV-Vis, refractive index)
Step 7: Scale-Up Considerations
Transitioning from research-scale to production quantities requires careful planning within the custom polymer synthesis process.
Scale-Up Challenges
Heat Transfer Management Larger reaction volumes create heat dissipation challenges:
- Surface-area-to-volume ratios decrease
- Requires enhanced cooling systems
- May necessitate semi-batch operation
Mixing Efficiency Maintaining homogeneity at scale:
- Reynolds number considerations
- Impeller design optimization
- Power input calculations
Safety Considerations Larger quantities amplify risks:
- Comprehensive thermal hazard analysis
- Emergency cooling capabilities
- Containment protocols for runaway reactions
Phased Scale-Up Approach
We recommend:
- Bench scale (1-100g): Method development and optimization
- Pilot scale (100g-1kg): Process validation and troubleshooting
- Production scale (1kg+): Full-scale manufacturing with validated protocols
This staged approach minimizes risk and ensures consistent quality across scales.
Step 8: Quality Control and Documentation
Rigorous quality control ensures every batch meets specifications. Our custom polymer synthesis process includes comprehensive documentation for traceability and regulatory compliance.
After the polymer has been purified, it is critical to characterize its properties to ensure it meets the predefined specifications. Characterization provides detailed information about the polymer’s structure, molecular weight, and performance characteristics.
Common Characterization Techniques:
- Gel Permeation Chromatography (GPC): Used to determine the molecular weight distribution (Mw, Mn) and polydispersity index (PDI) of the polymer.
- Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR): Provides detailed information about the chemical structure of the polymer, confirming the monomer units and any functional groups present.
- Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR): Used to identify functional groups and monitor chemical changes in the polymer structure.
- Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC): Provides information on the polymer’s thermal properties, including melting temperature, glass transition temperature, and crystallinity.
- Mechanical Testing: For applications in materials science, mechanical tests such as tensile strength, modulus, and elongation are performed to determine the physical properties of the polymer.
Want in-depth view at these techniques and their importance in ensuring polymer quality, check out our detailed blog on Characterization of Polymers.
Quality Assurance Protocols
Batch Records Complete documentation includes:
- Raw material lot numbers and certificates of analysis
- Step-by-step synthesis procedures with timestamps
- In-process monitoring data
- Deviation reports and corrective actions
Certificate of Analysis (CoA) Each batch includes:
- Molecular weight data (Mn, Mw, PDI)
- NMR spectra confirming structure
- Thermal analysis results
- Purity assessment
- Appearance and solubility
Regulatory Compliance For regulated industries:
- GMP-compliant synthesis when required
- ISO-certified quality systems
- Regulatory filing support (DMF, REACH)
- Stability studies and shelf-life determination
📚 Want to dive deeper? Explore our blog for more expert insights on polymer science and drug delivery innovations
Step 9: Delivery and Technical Support
The final phase ensures successful transfer of materials and knowledge.
Packaging and Shipping
The polymer is put through final testing to make sure it meets the desired quality standards after it has been synthesized, purified, characterized, and functionalized. it undergoes final testing to ensure that it meets the desired quality standards. In many situations, final product testing is necessary to confirm biocompatibility, safety, and efficacy, particularly for pharmaceutical or medical uses.
This phase ensures the synthesized polymer is safe, stable, and functional for its intended use.
Before packaging, purity checks are a must – see how to ensure high purity in polymers here
Types of Testing:
- Biological Testing: Includes cytotoxicity, hemolysis, genotoxicity, and in vivo studies.
- Stability Testing: Conduct under different environmental conditions (temperature, humidity, light).
- Performance Testing: Application-specific testing like drug release profile, adhesive strength, or biodegradation rate.
Packaging Considerations:
- Contamination Protection: Use cleanroom conditions and sterile containers.
- Moisture & Light Protection: Use barrier materials to maintain stability.
- Labeling & Traceability: Ensure compliance with regulatory standards and facilitate traceability.
Documentation: Include Certificate of Analysis (CoA), Batch Manufacturing Record (BMR), Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS), and stability reports.
Polymers are packaged to maintain quality:
- Inert atmosphere packaging (nitrogen or argon)
- Amber glass or specialized containers for light-sensitive materials
- Temperature-controlled shipping when required
- Clear labeling with safety information
Comprehensive Documentation
Each shipment includes:
- Certificate of Analysis
- Detailed synthesis report
- Handling and storage recommendations
- MSDS/SDS documentation
- Recommended dissolution protocols
Ongoing Support
Our commitment extends beyond delivery:
- Technical consultation for application development
- Troubleshooting assistance
- Replication protocols for future batches
- Method transfer support for in-house synthesis
Typical Project Timelines
Understanding timeframes helps with project planning:
| Project Complexity | Timeline | Typical Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Simple Homopolymers | 2-4 weeks | Well-established methods, standard monomers |
| Block Copolymers | 4-6 weeks | Sequential polymerization, multiple purifications |
| Novel Structures | 6-10 weeks | Method development, optimization cycles |
| Complex Architectures | 8-12 weeks | Star polymers, grafts, multi-block systems |
| Scale-Up Projects | 10-16 weeks | Pilot batching, process validation |
Rush timelines may be accommodated depending on project specifics and laboratory capacity.
Choosing the Right Polymer for Your Application
Selecting the ideal polymer depends heavily on its intended use—whether it’s for drug delivery, medical devices, or advanced materials science. Each application demands a unique combination of properties to ensure optimal performance.
For drug delivery systems, polymers must be biocompatible and biodegradable, with controlled degradation rates to release therapeutics effectively. Materials like PLGA (poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) and PEG (polyethylene glycol) are popular due to their tunable molecular weights (typically Mₙ 10–50 kDa for PLGA), solubility in water or organic solvents, and moderate mechanical strength. These polymers often have a low glass transition temperature (T₉) for flexibility and degrade over weeks to months, making them ideal for temporary implants or injectable formulations.
In medical device manufacturing, durability and stability are key. Polymers like PEEK (polyether ether ketone) and UHMWPE (ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene) offer high tensile strength, thermal resistance (PEEK’s Tₘ ~340°C), and oxidative stability, ensuring they withstand sterilization and long-term use in the body. Silicone rubber, with its high elongation (up to 800%) and biocompatibility, is another favorite for flexible implants. Unlike drug delivery polymers, medical-grade plastics often prioritize high crystallinity for structural integrity and low solubility to prevent degradation in bodily fluids.
For materials science applications, the requirements vary widely. Some projects need high-temperature resistance (e.g., PTFE, polyimides), while others prioritize electrical conductivity or optical clarity. Biodegradability may or may not be necessary, depending on environmental or industrial use cases.
Ultimately, the right polymer balances molecular weight, solubility, thermal properties (T₉ and Tₘ), mechanical strength, and degradation behavior to match the application’s demands. Whether you need a flexible, absorbable stent material or a rigid, heat-resistant coating, understanding these parameters ensures the best performance for your project. Let me know your specific needs—I’d be happy to recommend tailored options!
Ensuring Regulatory Compliance for Polymer Applications
When developing polymers for pharmaceutical or medical applications, regulatory compliance is just as critical as material performance. The polymer must meet stringent safety and quality standards to ensure patient safety and gain approval for clinical or commercial use.
- Key Regulatory Considerations
- FDA Approval (U.S.) & EMA Compliance (EU)
For drug delivery, polymers must be GRAS (Generally Recognized as Safe) or listed in the FDA’s Inactive Ingredient Database (IID).
Explore how polymer synthesis supports drug delivery systems and why it must meet high standards The Importance of Polymer Synthesis in Modern Science and Technology
Medical devices require FDA 510(k) clearance or PMA (Premarket Approval) depending on risk classification (Class I-III).
ISO 10993 (Biocompatibility Testing) is mandatory for implants and devices contacting bodily tissues.
- Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP)
Ensures consistent production under controlled conditions.
Required for pharmaceutical excipients (e.g., polymer coatings, hydrogels) and implantable materials.
- ISO Certifications
ISO 13485 (Medical Devices Quality Management) is essential for device manufacturing.
ISO 9001 (General Quality Management) may apply for non-medical polymers.
- USP/EP/JP Monographs
If the polymer is used in drug formulations, it must meet pharmacopeial standards (e.g., USP-NF, European Pharmacopoeia).
- Biocompatibility & Toxicity Testing
ISO 10993-1 outlines required tests (cytotoxicity, sensitization, systemic toxicity, etc.).
OECD Guidelines – may apply for environmental safety in biodegradable polymers.
Sterilization Compatibility – Must validate stability under autoclaving, gamma irradiation, or ethylene oxide (EtO) sterilization.
Conclusion
Custom polymer synthesis is a highly specialized and multi-step process that requires careful planning, expertise, and precision at each stage. From defining the project requirements to final product testing, each step plays a crucial role in creating high-quality, functional polymers for various applications. By understanding the key stages and considerations involved in custom polymer synthesis, you can better navigate the complexities of polymer design and achieve your project goals efficiently.
At ResolveMass Laboratories Inc., we offer expert custom polymer synthesis services tailored to your specific needs. Whether you’re looking for advanced drug delivery systems, specialized materials, or novel polymer architectures, our team has the experience and capabilities to bring your vision to life.
FAQs on Custom Polymer Synthesis Process
Q1: What is the difference between free radical and controlled radical polymerization? Free radical polymerization is fast and simple but results in polymers with broad molecular weight distribution. Controlled radical methods like RAFT or ATRP allow for precision control over chain length and structure.
Q2: Which polymers are best suited for drug delivery applications? Biocompatible and biodegradable polymers such as PLGA, PEG, PCL, and amphiphilic block copolymers like PEG-PLA or PEG-PCL are commonly used.
Q3: How do you choose between step-growth and chain-growth polymerization? Step-growth is ideal for polyesters and polyamides with high strength, while chain-growth (especially controlled methods) is used for precision polymers and complex architectures.
Q4: Can I perform custom polymer synthesis at a small scale for research? Yes. Many CROs and academic labs offer small-batch synthesis with detailed control and analytical support.
Q5: What are the critical documents required for regulatory submission? Typical documentation includes CoA, MSDS, BMR, process validation, analytical reports, and stability data.
Q6: What are stimuli-responsive polymers? These are smart materials that change their physical or chemical properties in response to external stimuli like pH, temperature, or enzymatic activity. They’re used in targeted drug delivery and diagnostics.
ResolveMass Laboratories Inc.: Your Trusted Partner in Polymer Synthesis and Characterization
ResolveMass Laboratories Inc. is a leading contract research organization in Canada, recognized for its excellence in custom polymer synthesis and advanced polymer characterization. With over a decade of experience, we have successfully delivered high-performance polymer solutions for applications in pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, medical devices, and advanced materials. Our multidisciplinary team of polymer chemists and materials scientists holds extensive expertise in designing, synthesizing, and characterizing complex polymer systems—including block copolymers, functionalized bioconjugates, and PEGylated compounds.
What sets us apart is our ability to provide end-to-end support—from molecular design and synthesis to structural validation using techniques like NMR, GPC, MALDI-TOF, DSC, TGA, LCMS, GCMS, and FTIR. Whether you require custom polymers for research or GMP-grade materials for product development, we tailor every project to your specifications while ensuring regulatory compliance and quality assurance.
Clients across North America trust ResolveMass for our scientific rigor, transparency, and commitment to delivering reproducible results. Partner with ResolveMass Laboratories for polymer synthesis and characterization—where innovation meets dependability.
Ready to Get Started?
📩 Contact our expert team
📞 Request a quote for method development
📅 Book a consultation with our scientists
🧪 Submit your sample for testing
References
- Lengwan LiJacek JakowskiChangwoo DoKunlun Hong, Deuteration and Polymers: Rich History with Great Potentia, Macromolecules 2021, 54, 8, 3555–3584
https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.macromol.0c02284 - Meifang Liu, Qiang Chen, Yiyang Liu, Jie Li, Xiaoyu Yang, Jie Du, Xinxin Tan, Fabrication and characterization of deuteration-rich polymer microsphere for high-yield neutron source, Polymer Engineering and Science, Volume64, Issue11, November 2024, https://doi.org/10.1002/pen.26925
- \Moad, G., Rizzardo, E., & Thang, S. H. (2008). Living radical polymerization by the RAFT process—A second update. Australian Journal of Chemistry, 61(10), 772–778. https://doi.org/10.1071/CH08172
- Lutz, J. F. (2013). Sequence-controlled polymerizations: The next Holy Grail in polymer science? Polymers, 5(3), 981–1005. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym5030981
🛠️ How to Troubleshoot Common Polymerization Issues
Even with perfect planning, polymer synthesis can fail or result in poor yields. Here’s how to fix it:
| Issue | Likely Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Polymer too low in molecular weight | Incomplete initiation or short reaction time | Use fresh initiators, increase reaction time, or raise temp |
| Broad polydispersity (high PDI) | Uncontrolled chain growth | Shift to RAFT or ATRP techniques for control |
| Cloudy or impure product | Incomplete purification or phase separation | Use multi-step purification: dialysis + precipitation |
| Monomer not reacting | Low reactivity or wrong conditions | Verify pH, solvent polarity, initiator choice |
💡 Tip: Always perform a small-scale pilot synthesis before scaling up.
High-Purity Deuterated Benzene-d6 for OLED Applications: Specifications, Purity & Bulk Supply
Introduction: High-purity Deuterated Benzene-d6 for OLED Application plays a key role in the development of…
Case Study: Identifying Unknown Impurities using High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry
Introduction: Identifying Unknown Impurities by HRMS is one of the most powerful analytical approaches in…
Advanced Technical Strategies in the Contract Manufacturing of Peptide-Oligonucleotide Conjugates
Introduction: Peptide Oligonucleotide Conjugate Manufacturing is a highly specialized process that combines peptide chemistry with…
Peptide-Oligonucleotide Conjugates (POC) Synthesis and Characterization for Drug Discovery Programs
Introduction: The development of Peptide-Oligonucleotide Conjugates (POCs) depends on the careful integration of advanced chemistry…
Peptide-Oligonucleotide Conjugation Services for Therapeutic Development
Summary Two core synthesis strategies—stepwise solid-phase assembly and post-synthetic parallel conjugation—enable flexible design based on…
CRO Services for Peptide-Oligonucleotide Conjugates (POCs)
Executive Summary Peptide-Oligonucleotide Conjugates (POCs) combine targeting peptides with antisense or siRNA to improve delivery,…