Gel Permeation Chromatography (GPC) is a powerful analytical technique widely used for polymer characterization, particularly in determining molecular weight distribution. Understanding molecular weight distribution is crucial for predicting polymer behavior, processing conditions, and final application properties. This article explores the fundamentals of GPC, its significance in polymer science, and why it remains a preferred technique for polymer characterization.
Article Summary
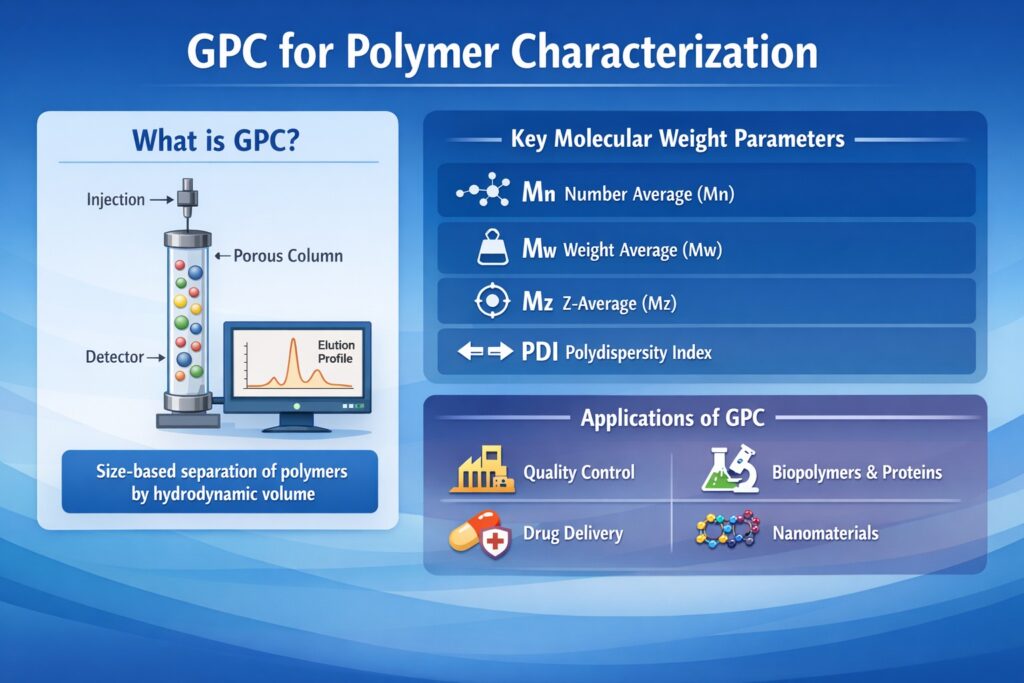
- Gel Permeation Chromatography (GPC), also known as Size Exclusion Chromatography (SEC), is a key analytical technique used to determine polymer molecular weight distribution and related parameters critical to material performance.
- GPC separates macromolecules based on hydrodynamic volume, enabling detailed analysis of polymer architecture, including linearity, branching, and degradation behavior.
- The technique provides essential molecular weight parameters such as Mn, Mw, Mz, and polydispersity index (PDI), which are vital for quality control, regulatory compliance, and product consistency.
- Advanced GPC systems combined with multi-detector technologies allow accurate data interpretation, improved chromatogram analysis, and absolute molecular weight determination.
- GPC is widely applied across industries including polymer manufacturing, pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, nanotechnology, and biomedical research.
- Ongoing advancements in instrumentation and sustainable materials research ensure GPC remains a foundational tool in modern polymer characterization.
Video Guide: Gel Permeation Chromatography (GPC) Explained – Principle, Working, and Applications
What is GPC?
Gel Permeation Chromatography (GPC), also known as Size Exclusion Chromatography (SEC), is a liquid chromatographic method used to separate macromolecules based on their hydrodynamic volume. It is primarily utilized to analyze polymers, proteins, and other high-molecular-weight compounds. By passing the polymer solution through a porous column, smaller molecules penetrate deeper into the pores, while larger molecules elute faster, resulting in a size-based separation.
Role of GPC in Understanding Polymer Architecture
Beyond basic molecular weight separation, GPC plays a crucial role in revealing polymer architecture such as linearity, branching, and crosslinking tendencies. While polymers may share similar average molecular weights, differences in architecture can significantly influence viscosity, melt strength, and mechanical performance. GPC profiles help scientists distinguish subtle variations by observing changes in elution behavior and distribution shape.
When combined with advanced detectors, GPC allows deeper insight into how polymer chains are built and how they interact in solution. Branched polymers, for example, often exhibit smaller hydrodynamic volumes compared to linear polymers of the same molecular weight, leading to different retention times. This makes GPC an essential technique for correlating molecular structure with real-world material performance.
Why is GPC Important for Polymer Characterization?
GPC provides critical information on polymer properties, including:
- Molecular weight distribution (Mw, Mn, Mz, and polydispersity index)
- Polymer branching and structure
- Degradation analysis
- Batch-to-batch consistency
- Polymer purity
These parameters help industries develop high-performance materials, ensuring quality control and regulatory compliance.
Working Principle of GPC
- Sample Preparation: The polymer sample is dissolved in a suitable solvent (e.g., tetrahydrofuran, chloroform, or water) and filtered to remove particulates.
- Injection: A small volume of the prepared solution is injected into the chromatographic system.
- Separation Process: The sample passes through a column filled with porous beads that separate molecules based on their size.
- Detection and Analysis: A detector (typically a Refractive Index (RI) or UV detector) records the elution profile, which is then analyzed to determine molecular weight distribution.
Importance of Column Chemistry and Packing Materials
The performance of GPC analysis heavily depends on column chemistry and the nature of the packing material used. Columns are typically packed with porous polymeric or silica-based beads that are chemically compatible with the mobile phase. Selecting the correct column ensures minimal interaction between the polymer and stationary phase, preserving the size-based separation principle.
Improper column selection can result in adsorption effects, peak broadening, or inaccurate molecular weight measurements. Modern GPC columns are engineered with narrow pore size distributions and enhanced mechanical stability, allowing consistent performance over repeated runs. This makes column selection a critical factor in achieving reproducible and reliable polymer characterization results.
Molecular Weight Parameters in GPC
- Number Average Molecular Weight (Mn): The total weight of all polymer molecules divided by the number of molecules.
- Weight Average Molecular Weight (Mw): Weighs larger molecules more heavily as they contribute more to total polymer weight.
- Z-Average Molecular Weight (Mz): Considers the highest molecular weight fractions.
- Polydispersity Index (PDI = Mw/Mn): Indicates the molecular weight distribution breadth.
Data Interpretation and Chromatogram Analysis in GPC
Interpreting GPC data requires careful analysis of chromatograms, which represent detector response as a function of elution volume or time. The shape of the chromatographic curve provides valuable information about polymer uniformity and distribution breadth. Narrow peaks typically indicate uniform polymers, while broader peaks suggest higher polydispersity or mixed populations.
Accurate data interpretation also depends on proper baseline correction, calibration curve selection, and detector alignment. Software tools integrated with modern GPC systems assist analysts in converting raw detector signals into meaningful molecular weight values. Skilled interpretation ensures that GPC results translate into actionable insights for material development and quality assurance.
Key Applications of GPC in Polymer Analysis
1. Quality Control in Polymer Manufacturing
GPC is essential in ensuring polymer production consistency by monitoring molecular weight and polydispersity across different batches.
2. Biopolymer and Protein Characterization
GPC is used in pharmaceutical and biotech industries to study proteins, polysaccharides, and other macromolecules.
3. Degradation and Stability Studies
Understanding polymer degradation helps industries assess material lifetime, recyclability, and performance under various conditions.
4. Drug Delivery and Biomedical Applications
Polymers used in drug delivery systems (e.g., PLGA, PEG) require precise molecular weight characterization for controlled release properties.
5. Nanotechnology and Advanced Materials
GPC is employed in research and development of nanomaterials, composites, and smart polymers to optimize their molecular architecture.
Advantages of GPC
- High-resolution separation
- Non-destructive analysis
- Provides absolute molecular weight data (with multi-angle light scattering detectors)
- Fast and reproducible results
GPC vs Other Polymer Characterization Techniques
While several analytical techniques are available for polymer analysis, GPC remains unique in its ability to directly measure molecular weight distribution. Techniques such as viscometry, rheology, and spectroscopy provide complementary information but often lack the resolution needed to distinguish individual molecular fractions. GPC fills this gap by offering size-based separation with high precision.
Compared to mass spectrometry or thermal analysis, GPC is non-destructive and suitable for routine quality control. It also supports a wide variety of polymer types, from synthetic plastics to biopolymers. For comprehensive polymer characterization, GPC is frequently used alongside other techniques to provide a complete molecular and structural profile.
Agilent and Malvern GPC for Polymer Characterization
Gel Permeation Chromatography (GPC), also known as Size Exclusion Chromatography (SEC), is a powerful analytical technique widely used in polymer characterization to determine molecular weight distribution, average molecular weights (Mn, Mw), and polydispersity index (PDI). Agilent Technologies and Malvern Panalytical are two leading providers of advanced GPC solutions that cater to diverse polymer analysis needs.
Agilent GPC systems, such as the 1260 Infinity II Multi-Detector GPC/SEC System, are known for their precision, modular flexibility, and ease of use. These systems support multi-detector setups including refractive index (RI), light scattering (LS), and viscometry to deliver comprehensive data for synthetic and natural polymers. Agilent’s systems are especially suited for laboratories seeking high-throughput and reliable polymer profiling across a wide molecular weight range.
Malvern Panalytical’s OMNISEC platform is an advanced multi-detector GPC/SEC system offering unparalleled sensitivity and detailed polymer insight. OMNISEC integrates detectors for RI, light scattering, UV/Vis, and intrinsic viscosity in one compact unit. This system enables absolute molecular weight determination without relying solely on calibration standards, ideal for both research and quality control environments.
Together, Agilent and Malvern provide robust GPC tools that empower researchers and manufacturers to fully understand and optimize polymer properties for diverse industrial applications.
Challenges and Considerations in GPC Analysis
- Choice of Solvent: The polymer must be fully soluble in the chosen solvent.
- Column Selection: Different pore sizes affect separation efficiency.
- Detector Sensitivity: The type of detector used can impact accuracy and resolution.
- Calibration Standards: GPC relies on calibration with known standards, typically polystyrene.
Regulatory and Industrial Significance of GPC Data
In regulated industries such as pharmaceuticals, medical devices, and food packaging, GPC data plays a vital role in meeting compliance standards. Molecular weight distribution directly influences product safety, efficacy, and consistency. Regulatory agencies often require detailed polymer characterization data as part of product approval and validation processes.
From an industrial perspective, GPC supports process optimization and cost control by identifying variations in raw materials and production conditions. Early detection of molecular weight deviations helps manufacturers prevent defects and ensure consistent product performance. As a result, GPC is deeply embedded in both regulatory frameworks and industrial quality systems.
Future of GPC in Polymer Characterization
Advancements in multi-detection GPC, including light scattering (MALS), viscometry, and mass spectrometry coupling, have significantly enhanced the accuracy of polymer characterization. Emerging trends in sustainable polymer research also emphasize the role of GPC in biodegradable polymers, recyclable materials, and green chemistry applications.
Conclusion
Gel Permeation Chromatography remains a cornerstone technique in polymer characterization due to its ability to deliver detailed molecular weight distribution data with high accuracy and reliability. From understanding polymer architecture to supporting regulatory compliance, GPC provides insights that directly impact material design, processing, and performance. Its compatibility with advanced detectors further enhances its analytical power.
As polymer science continues to evolve toward sustainable and high-performance materials, the importance of precise molecular characterization will only grow. GPC, supported by continuous technological advancements and robust instrumentation, will remain an indispensable tool for researchers, manufacturers, and quality control laboratories worldwide.
REFERENCES
- Matson, J. B., Steele, A. Q., Mase, J. D., & Schulz, M. D. (2023). Polymer characterization by size-exclusion chromatography with multi-angle light scattering (SEC-MALS): A tutorial review. Polymer Chemistry, 15(3), 127–142. https://doi.org/10.1039/d3py01181j
- Li, X. (2025). Techniques in Polymer Characterization: Bridging Structure with Performance. Research & Reviews in Polymer, 16(1), Article 160. Retrieved from https://www.tsijournals.com/articles/techniques-in-polymer-characterization-bridging-structure-with-performance.pdf
- Advincula, R., Yuan, J., & Brittain, W. J. (2021). Molecular characterization of polymer networks. Chemical Reviews, 121(8), 5042–5092. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.0c01304
LET’S CONNECT
Ready to Elevate Your Polymer Research? Let’s transform your polymer projects together!
Unlock the full potential of your materials with ResolveMass Laboratories’ advanced GPC analysis. Our cutting-edge techniques and expert team are here to help you achieve precision and innovation in polymer characterization.
Case Study: Sameness Evaluation of Octreotide Generic project submission to USFDA
Introduction: The Octreotide Sameness Study for ANDA submission is a critical regulatory requirement when filing…
Case Study: Sameness Evaluation of Liraglutide Generic project submission to USFDA
Introduction: The Liraglutide Sameness Study for ANDA submission is a critical regulatory requirement when filing…
CRO Checklist: How to Select the Best Lab for Peptide Sameness Study
Introduction: Choosing the Best CRO for Peptide Sameness Study is one of the most critical…
Common Deficiencies in Peptide Sameness Study During ANDA Review
Introduction: Peptide Sameness Study Deficiencies are a leading cause of regulatory delays during ANDA review…
Peptide Sequencing, Peptide Mapping and NMR in Sameness Studies: Why Orthogonal Methods Matter
Introduction: Peptide Sequencing and Mapping for Sameness Study is the foundation for demonstrating structural identity…
Regulatory Requirements for Peptide Sameness Study (FDA & Health Canada)
Introduction: FDA Peptide Sameness Study Requirements define the scientific and regulatory framework needed to demonstrate…