INTRODUCTION: PLA SUPPLIER IN CANADA AND U.S — WHY IT MATTERS
A PLA supplier in Canada and U.S plays a critical role in ensuring consistent polymer quality, regulatory compliance, and performance across pharmaceutical, biomedical, and industrial applications. PLA (Polylactic Acid) is not just a biodegradable polymer—it is a highly tunable material whose properties depend heavily on supplier expertise, grade control, and analytical validation.
For pharmaceutical scientists, medical device manufacturers, and R&D teams, selecting a trusted PLA supplier in Canada and U.S directly impacts product safety, scalability, and approval timelines.
Polylactic Acid (PLA) has revolutionized industries ranging from 3D printing to packaging, biomedicine, and sustainable manufacturing. As a biodegradable and bio-based thermoplastic, PLA is rapidly becoming the material of choice for companies aiming to reduce their environmental footprint. With growing demand in Canada and the United States, sourcing high-quality PLA suppliers is essential for businesses and individuals seeking reliable and sustainable solutions.
In this guide, we will explore:
- The properties and benefits of PLA
- Applications of PLA in various industries
- The manufacturing process of PLA
- How to evaluate and choose a reliable supplier
- The future of PLA in North America
SUMMARY
- PLA (Polylactic Acid) is a biodegradable, bio-based polymer widely used in pharmaceuticals, medical devices, packaging, and R&D.
- Choosing the right PLA supplier in Canada and U.S is critical for quality, regulatory compliance, and reproducibility.
- ResolveMass Laboratories Inc. supports PLA sourcing, characterization, reverse engineering, and regulatory-ready analytics.
- This guide explains applications, grades, selection criteria, regulations, and why supplier expertise matters.
1: What is PLA (Polylactic Acid)?
PLA is a biodegradable, thermoplastic polyester derived from renewable resources such as corn starch, sugarcane, or other plant-based materials. Unlike traditional petroleum-based plastics, PLA offers a sustainable alternative that can decompose under industrial composting conditions.
Key Characteristics of PLA:
- Renewable Origin: Made from plant-based feedstocks rather than fossil fuels
- Biodegradability: Breaks down into water, carbon dioxide, and organic matter under proper conditions
- Biocompatibility: Safe for medical and food-contact applications with appropriate certifications
- Mechanical Properties: Good tensile strength, low shrinkage, and excellent printability
- Thermal Properties: Melting point typically between 150-160°C, glass transition around 60°C
- Environmental Profile: Lower carbon footprint compared to conventional plastics
Types of PLA Available:
| PLA Grade | Properties | Primary Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Standard PLA | Good stiffness, easy processing | 3D printing, general packaging |
| High-Heat PLA | Enhanced temperature resistance | Food containers, automotive parts |
| Impact-Modified PLA | Improved toughness and flexibility | Durable goods, protective cases |
| Medical-Grade PLA | Biocompatible, sterilizable | Surgical implants, drug delivery |
| Filled PLA | Reinforced with fibers or minerals | Engineering applications, composites |
PLA is a biodegradable polymer derived primarily from renewable resources such as corn starch, sugarcane, or cassava. It is widely recognized as an eco-friendly alternative to petroleum-based plastics due to its:
✅ Biodegradability – Breaks down under industrial composting conditions
✅ Renewability – Derived from plant-based sources
✅ Low carbon footprint – Lower greenhouse gas emissions compared to fossil-based plastics
✅ Versatility – Used in industries like packaging, biomedical, textiles, and 3D printing
Chemical Structure of PLA
PLA is a linear aliphatic polyester composed of lactic acid monomers. Its molecular structure provides high mechanical strength and optical clarity, making it suitable for diverse applications.
2: Manufacturing Process of PLA
The production of PLA involves several key steps:
1. Fermentation of Raw Materials
Corn starch, sugarcane, or other biomass undergoes fermentation, producing lactic acid. This step is crucial, as the purity of lactic acid determines the quality of the final PLA product.
2. Polymerization Process
Lactic acid is converted into lactide, which then undergoes ring-opening polymerization to form PLA chains. Depending on the polymerization method, manufacturers can control molecular weight, crystallinity, and mechanical properties of PLA.
3. Compounding and Processing
PLA can be modified with plasticizers, fillers, or blended with other biodegradable materials to enhance flexibility, durability, and processability.
4. Granulation and Filament Production
PLA resin is transformed into pellets, which can be further processed into 3D printing filaments, injection-molded parts, and packaging films.
3: Applications of PLA in Various Industries
1. 3D Printing
PLA is the most popular filament material for Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) 3D printers due to its:
✅ Low printing temperature (180-220°C)
✅ Minimal warping & ease of use
✅ Eco-friendliness & recyclability
2. Medical & Biomedical Applications
Due to its biocompatibility and biodegradability, PLA is widely used in:
✔ Surgical sutures
✔ Drug delivery systems
✔ Tissue engineering scaffolds
3. Sustainable Packaging
PLA-based packaging solutions are increasingly replacing petroleum-based plastics in:
✔ Food containers & disposable cutlery
✔ Compostable bags & films
✔ Eco-friendly cosmetic packaging
4. Textiles & Fibers
PLA fibers offer an alternative to synthetic materials in:
✔ Eco-friendly apparel
✔ Biodegradable fabrics
5. PHARMACEUTICAL APPLICATIONS
PLA is used in drug delivery systems due to its predictable biodegradation and safety profile.
Common applications include:
- Long-acting injectable microspheres
- Controlled-release implants
- Depot formulations
6. MEDICAL DEVICE APPLICATIONS
Medical-grade PLA is used for resorbable devices where controlled mechanical strength and degradation are required.
Examples include:
- Sutures
- Orthopedic fixation devices
- Tissue engineering scaffolds
7. R&D AND INDUSTRIAL APPLICATIONS
In research and specialty manufacturing, PLA is used for:
- Prototyping
- Biodegradable packaging validation
- Polymer blending studies
Each application demands specific PLA characteristics that only experienced suppliers can reliably provide.
4: How to Evaluate and Choose a Reliable PLA Supplier?
When sourcing PLA suppliers in Canada and the United States, consider the following factors:
1. Purity & Certification
Ensure the supplier provides high-purity PLA resins with certifications such as:
- ASTM D6400 (Compostability Standard)
- EN 13432 (European Biodegradability Standard)
2. Customization & Product Range
Reliable suppliers should offer different grades of PLA, including:
✔ Standard PLA – For general applications
✔ High-impact PLA (PLA+) – For tougher, more durable products
✔ Medical-grade PLA – For biomedical and pharmaceutical uses
3. Sustainability Commitment
Look for suppliers who adhere to sustainable practices, such as:
✔ Carbon-neutral production
✔ Use of renewable energy in manufacturing
✔ Recycled or bio-based feedstocks
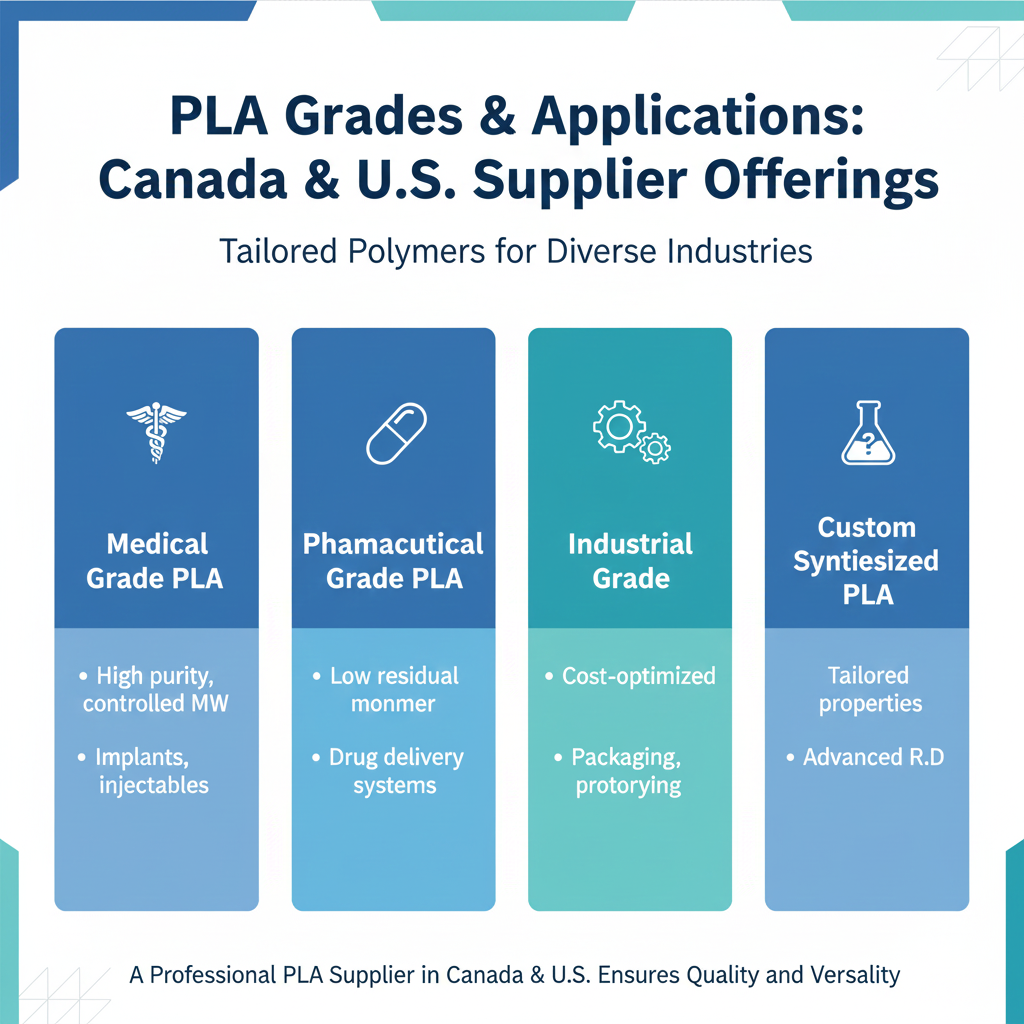
5: TYPES AND GRADES OFFERED BY A PLA SUPPLIER IN CANADA AND U.S
A professional PLA supplier in Canada and U.S typically offers multiple grades tailored for different applications.
| PLA Grade Type | Key Characteristics | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Medical Grade PLA | High purity, controlled MW | Implants, injectables |
| Pharmaceutical Grade PLA | Low residual monomer | Drug delivery systems |
| Industrial Grade PLA | Cost-optimized | Packaging, prototyping |
| Custom Synthesized PLA | Tailored properties | Advanced R&D |
Understanding these distinctions is essential for selecting the right material.
6: The Future of PLA in North America
1. Rising Demand for Biodegradable Plastics
The global market for PLA is expected to grow due to increasing bans on single-use plastics and consumer demand for sustainable alternatives.
2. Advancements in PLA Blends & Composites
Research is focusing on enhancing mechanical properties, thermal stability, and biodegradability by blending PLA with other bio-based materials.
3. Expansion of Recycling & Composting Infrastructure
To maximize PLA’s environmental benefits, investments in industrial composting and advanced recycling technologies are needed.
Conclusion
PLA is a game-changer in sustainable plastics, offering a biodegradable, renewable, and versatile alternative to fossil-based polymers. As demand grows in Canada and the United States, selecting a reliable supplier with high-quality PLA resins and eco-friendly practices is essential.
By choosing certified PLA materials, businesses and consumers can contribute to a greener, more sustainable future.
Reference
- Sin LT, Tueen BS. Polylactic acid: a practical guide for the processing, manufacturing, and applications of PLA. William Andrew; 2019 Jun 15.
- Jamshidian M, Tehrany EA, Imran M, Jacquot M, Desobry S. Poly‐lactic acid: production, applications, nanocomposites, and release studies. Comprehensive reviews in food science and food safety. 2010 Sep;9(5):552-71.
- Sin LT. Polylactic acid: PLA biopolymer technology and applications. William Andrew; 2012 Dec 31.
- Joseph TM, Kallingal A, Suresh AM, Mahapatra DK, Hasanin MS, Haponiuk J, Thomas S. 3D printing of polylactic acid: recent advances and opportunities. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology. 2023 Mar;125(3):1015-35.

LET’S CONNECT
If you are looking for high-quality PLA (Polylactic Acid) materials for 3D printing, packaging, medical applications, or industrial use, ResolveMass Laboratories Inc. is here to help!
We provide custom PLA solutions, including:
✅ High-purity PLA resins for specialized applications
✅ Custom PLA blends for enhanced durability and performance
✅ Bulk ordering options for industrial and commercial needs
End-to-End Biomarker Bioanalytical Services Offered by a CRO: Capabilities and Expectations
Introduction Biomarker bioanalytical services CRO partnerships have become indispensable in modern pharmaceutical development, providing the…
Regulatory-Compliant Biomarker Bioanalytical Services for FDA and Health Canada Submissions
Introduction Biomarker bioanalytical services for FDA and Health Canada submissions require rigorous compliance with regulatory…
Outsourced Medicinal Chemistry for Startups: Cost, Speed, and Scientific Advantages
🔍 Summary (Key Takeaways) Outsourced medicinal chemistry for startups offers a strategic advantage by minimizing…
Why Early-Stage Biotech Companies Outsource Chemistry Services to Drug Discovery CROs
Introduction Early-stage biotech companies are increasingly adopting Outsourced Chemistry Services for Biotech to stay competitive…
Why Early-Stage Biotech Companies Outsource Bioanalytical Services to CROs
Introduction Outsourced bioanalytical services play a critical role in helping early-stage biotech companies overcome scientific,…
7 Questions to Ask Before Collaborating with a Full Service Drug Discovery CRO
Summary Before partnering with a Full Service Drug Discovery CRO, the following key questions can…