OVERVIEW
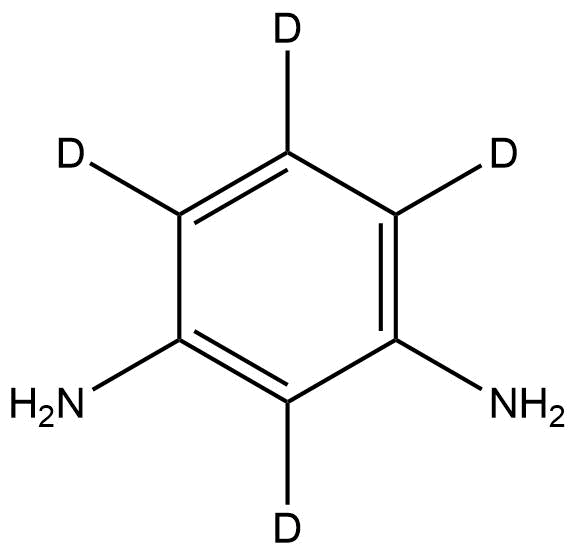
1,3-Benzene-d₄-diamine is a deuterium-labeled analog of m-phenylenediamine (m-PDA), where four hydrogen atoms on the benzene ring are replaced with deuterium atoms. This isotopic modification increases the molecular weight by 4 Da without altering the molecular structure or chemical reactivity of the parent compound. The compound serves as a valuable stable isotope-labeled reagent in analytical chemistry, synthetic chemistry, and materials science, particularly for use in mechanistic studies, tracer experiments, and the synthesis of deuterated polymers and dyes.
Due to its isotopic labeling, 1,3-benzene-d₄-diamine provides improved analytical clarity in NMR and mass spectrometry (MS) applications. Its aromatic amine structure makes it a key intermediate for preparing deuterated arylamines, polymers, and fine chemicals used in pharmaceutical and materials research.
CHEMICAL INFORMATION
-
Name: 1,3-Benzene-d₄-diamine
-
Molecular Formula: C₆D₄(NH₂)₂
-
Molecular Weight: 112.17 g/mol
-
Isotopic Enrichment: ≥ 98 atom % D
-
Chemical Class: Deuterated aromatic diamine; stable isotope-labeled compound
-
Stability: Stable under normal laboratory conditions; may gradually oxidize and darken upon prolonged exposure to air or light
APPLICATIONS of 1,3-Benzene-d4-diamine
-
Stable Isotope Labeling and Tracer Studies:
1,3-Benzene-d₄-diamine is used as a labeled analog of m-phenylenediamine in isotopic tracing to investigate reaction mechanisms, oxidation pathways, and catalytic transformations involving aromatic amines. -
Analytical Chemistry and Mass Spectrometry:
Serves as a reference material and internal standard for MS analyses. Its +4 Da isotopic mass shift allows accurate quantification and clear differentiation from non-deuterated species. -
NMR Spectroscopy:
Utilized in studying isotope effects on aromatic proton relaxation, chemical shifts, and substitution dynamics. The presence of deuterium in the aromatic ring provides cleaner NMR spectra and facilitates mechanistic studies. -
Polymer and Material Science:
Functions as an isotopically labeled monomer for synthesizing deuterated poly(m-phenylenediamine) and related materials. Such polymers are used in studies of electrical conductivity, thermal stability, and structural characterization by neutron scattering. -
Pharmaceutical and Cosmetic Research:
Used in the synthesis of deuterated intermediates for compounds containing aromatic amine groups. Its deuterium labeling aids in metabolic tracing, degradation studies, and comparative pharmacokinetic analysis.
ADVANTAGES of 1,3-Benzene-d4-diamine
-
High isotopic enrichment (≥ 98 atom % D) ensures precise and reproducible isotopic labeling.
-
Chemically identical to non-deuterated m-phenylenediamine, enabling direct substitution in synthetic and analytical applications.
-
Non-radioactive and safe for long-term storage and laboratory use.
-
Enhances spectral resolution and simplifies interpretation in both NMR and MS analyses.
-
Ideal for investigating isotope effects and tracking chemical transformations in aromatic amine systems.
HANDLING
-
Hazards: Toxic and potentially sensitizing; may cause irritation or allergic reactions upon skin contact or inhalation. Harmful if ingested or absorbed through the skin.
-
Precautions: Handle in a well-ventilated fume hood while wearing suitable PPE including gloves, goggles, and a lab coat. Avoid exposure to air and light to prevent oxidation.
-
Storage: Keep in a tightly closed, inertly sealed container. Store in a cool, dry, and dark place under nitrogen or argon atmosphere.
-
Disposal: Dispose of material in accordance with local and federal regulations. Prevent release into waterways or soil.
Safety Note: Although relatively stable, aromatic diamines can undergo oxidation forming dark-colored degradation products; hence minimal air exposure is recommended.
QUALITY & SPECIFICATION
-
Chemical Purity: ≥ 98 %
-
Isotopic Enrichment: ≥ 98 atom % D
-
Water Content: ≤ 0.05 %
-
Analytical Verification: Confirmed by ¹H NMR, ²H NMR, IR spectroscopy, and LC-MS
-
Appearance: White crystalline or off-white powder
-
COA Availability: Each batch is accompanied by a Certificate of Analysis verifying isotopic enrichment and chemical purity
SUMMARY
1,3-Benzene-d₄-diamine is a deuterated form of m-phenylenediamine, serving as a vital reagent for isotopic labeling, analytical chemistry, and polymer research. Its substitution of four deuterium atoms in the aromatic ring enhances isotopic stability and facilitates clear identification in spectroscopic and mass spectrometric analyses. This compound is indispensable for studying reaction kinetics, isotope effects, and molecular transformations involving aromatic amines, making it a cornerstone material for advanced chemical and materials research.
learn more about,
Deuterated Polymers: A Cornerstone Guide to Synthesis, Applications, and Future Trends
Availability of All the Deuterated Chemicals at ResolveMass Laboratories Inc.
ResolveMass Laboratories: Leading Deuterated Chemical Synthesis Company in the United States.
Deuterated Internal Standards for LC-MS: Selection & Custom Synthesis
How to Choose the Right Deuterated Labelled Chemical Synthesis Company in Canada
How to Choose the Right Deuterium Labelled Compounds Supplier for Your Lab
Deuterium-Labelled Compounds — Synthesis, Applications & Ordering
Reviews
There are no reviews yet.