PLGA (Poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) | CAS 26780-50-7)
Overview
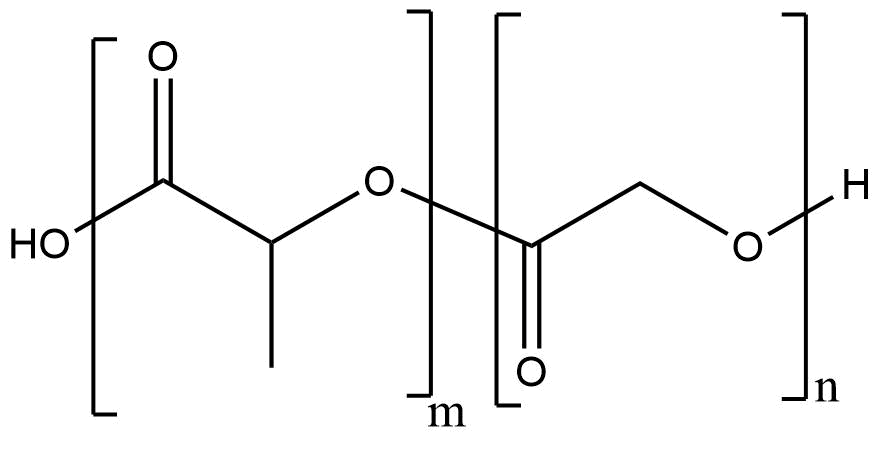
PLGA Poly(lactic-co-glycolic) acid | CAS 26780-50-7 is a well-established biodegradable copolymer synthesized through the random ring-opening copolymerization of lactide (cyclic dimer of lactic acid) and glycolide (cyclic dimer of glycolic acid). Known for its biocompatibility, tunable degradation rate, and versatility, PLGA has become one of the most widely used polymers in pharmaceutical formulations, controlled drug delivery systems, and biomedical devices.
The polymer’s CAS number 26780-50-7 identifies it as a family of copolymers with varying ratios of lactic acid and glycolic acid units. By adjusting this ratio, manufacturers can precisely control the mechanical properties, degradation profile, and hydrophilicity of the material, making PLGA an ideal choice for diverse applications in drug delivery, tissue engineering, and absorbable sutures.
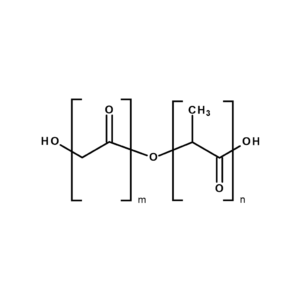
Chemical Structure and Composition of PLGA Poly(lactic-co-glycolic) acid | CAS 26780-50-7
PLGA is represented by the general formula:
–[C₃H₄O₂]_m – [C₂H₂O₂]_n–
where m and n denote the molar ratios of lactic and glycolic acid monomeric units, respectively. The copolymer can be synthesized in various compositions such as PLGA 50:50, 65:35, 75:25, or 85:15, each exhibiting distinct degradation kinetics and physical characteristics.
-
Lactic acid component introduces hydrophobicity and crystalline behavior.
-
Glycolic acid component contributes to hydrophilicity and faster hydrolytic degradation.
The ester linkages between the monomers are hydrolytically unstable, allowing the polymer to degrade into lactic acid and glycolic acid, both of which enter the natural Krebs metabolic cycle, resulting in non-toxic and biocompatible degradation products.
Synthesis Process of PLGA Poly(lactic-co-glycolic) acid | CAS 26780-50-7
PLGA is typically synthesized via ring-opening polymerization (ROP) of lactide and glycolide in the presence of catalysts such as stannous octoate (Sn(Oct)₂) or other organometallic initiators. The polymerization reaction conditions—temperature, monomer ratio, and catalyst concentration—directly affect the molecular weight, crystallinity, and polydispersity of the final polymer.
Common synthesis parameters:
-
Temperature: 120–180°C
-
Catalyst concentration: 0.01–0.1% (w/w)
-
Monomer ratio: 50:50 to 85:15 (lactide:glycolide)
-
Reaction environment: Inert (argon or nitrogen) to prevent oxidation
Post-synthesis, the polymer is purified by precipitation and vacuum-dried to remove residual monomers or catalysts, ensuring high purity suitable for biomedical or pharmaceutical use.
Physicochemical Properties of PLGA Poly(lactic-co-glycolic) acid | CAS 26780-50-7
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Appearance | White to off-white solid or powder |
| CAS Number | 26780-50-7 |
| Molecular Weight (Mw) | 7k–240k g/mol (variable) |
| Glass Transition Temperature (Tg) | 40–60°C |
| Degradation Time | Weeks to months (depending on composition) |
| Solubility | Soluble in acetone, dichloromethane, ethyl acetate; insoluble in water |
| Biodegradability | Fully biodegradable via hydrolysis into lactic and glycolic acids |
Degradation Mechanism
The degradation of PLGA occurs primarily through bulk hydrolysis of ester bonds. The rate depends on several parameters:
-
Lactide-to-glycolide ratio: Higher glycolic content → faster degradation
-
Molecular weight: Lower Mw → faster hydrolysis
-
Crystallinity and morphology: Amorphous polymers degrade faster than crystalline ones
-
Environmental conditions: pH, temperature, and water availability significantly influence the process
PLGA 50:50 typically exhibits the fastest degradation rate, often completing in 1–2 months, while PLGA 85:15 may take several months for complete resorption.
Applications PLGA Poly(lactic-co-glycolic) acid | CAS 26780-50-7
1. Drug Delivery Systems
PLGA is extensively used in controlled and sustained-release formulations. Its degradation-controlled release mechanism enables precise drug release profiles for small molecules, peptides, and proteins.
-
Microspheres and nanoparticles (e.g., depot formulations of leuprolide acetate)
-
Implantable drug delivery systems
-
Targeted delivery vehicles for anticancer drugs, vaccines, and antibiotics
2. Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine
Due to its biocompatibility and resorbability, PLGA serves as a scaffold material for bone, cartilage, and soft tissue regeneration. The polymer can be fabricated into porous matrices, electrospun fibers, or 3D-printed scaffolds that support cell adhesion, proliferation, and differentiation.
3. Surgical Sutures and Implants
PLGA is a key component in absorbable sutures and temporary implants, offering mechanical strength during tissue healing and gradual degradation thereafter, eliminating the need for surgical removal.
4. Biomedical Devices and Coatings
PLGA is used as a biodegradable coating material for stents and medical devices to deliver therapeutic agents locally or control surface properties.
Quality and Regulatory Standards
At ResolveMass Laboratories Inc., we supply high-purity PLGA (CAS 26780-50-7) synthesized under controlled conditions to meet stringent pharmaceutical and biomedical quality standards. Our PLGA is characterized for:
-
Molecular weight distribution (by GPC)
-
Monomer ratio (by NMR spectroscopy)
-
Residual solvent and monomer content
-
Thermal behavior (by DSC and TGA)
We ensure compliance with ISO 9001:2015 standards and provide analytical documentation including Certificate of Analysis (CoA), Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS), and NMR/GPC profiles upon request.
Key Advantages
-
Tunable degradation and release profiles
-
Excellent biocompatibility and safety record
-
Proven track record in FDA-approved formulations
-
Versatile for nanoparticles, scaffolds, and coatings
-
Available in custom molecular weights and monomer ratios
Conclusion
PLGA (Poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid), CAS 26780-50-7) continues to be the gold standard biodegradable polymer for drug delivery and tissue engineering. Its customizable composition, predictable degradation, and regulatory acceptance make it indispensable for developing next-generation biomedical and pharmaceutical innovations.
At ResolveMass Laboratories Inc., we provide research-grade and GMP-grade PLGA tailored to your specific application—whether for formulation development, polymer research, or scalable production.
Refer full product list at resolvemass.ca : Products
Read below Learn with Us Articles:
PLGA Nanoparticles Synthesis: A Step-by-Step Guide for Beginners
PLGA 50:50 Poly(D L-lactide-co-glycolide) Supplier Guide: What to Look for in a Reliable Provider
The Science Behind GPC: A Deep Dive into Analyzing PLA, PLGA, and PCL for Research

Reviews
There are no reviews yet.