Introduction
The decision between Bioanalytical CRO vs In-house labs is one of the most important strategic choices a biotech company makes during drug development. This choice influences development timelines, regulatory success, data credibility, and long-term scalability.
As drug modalities become more complex—ranging from oligonucleotides and peptides to ADCs and biologics—the need for advanced bioanalytical expertise has never been higher. Many biotechs struggle to determine whether building internal bioanalytical capabilities or partnering with a specialized CRO is the right path.
This article provides a clear, experience-driven comparison of Bioanalytical CRO vs In-house labs, helping biotech leaders make informed, risk-aware decisions.
Summary
Bioanalytical CRO vs In-house labs is a strategic decision that directly impacts cost, speed, compliance, and data quality.
- CROs provide specialized expertise, scalability, regulatory readiness, and faster turnaround.
- In-house labs offer control and proximity, but require heavy capital investment and ongoing operational burden.
- For early-stage and mid-size biotechs, outsourcing to a Bioanalytical CRO is often more cost-effective and lower risk.
- Hybrid models are increasingly popular, combining internal oversight with CRO execution.
ResolveMass Laboratories Inc. supports biotechs with advanced LC-MS bioanalysis, regulatory-grade validation, and real-world development experience.
1: What Is a Bioanalytical CRO?
A Bioanalytical Contract Research Organization (CRO) is a specialized external scientific partner that provides regulated, validated, and compliance-ready bioanalysis services to support preclinical, clinical, and post-marketing drug development programs.
In short, a Bioanalytical CRO enables biotechs and pharmaceutical companies to generate regulatory-acceptable bioanalytical data without building and maintaining expensive internal laboratory infrastructure.
Unlike general CROs, bioanalytical CROs focus specifically on quantitative and qualitative analysis of drugs, metabolites, biomarkers, and biological matrices, operating under GLP, GCP, and regulatory authority expectations.
Core Role of a Bioanalytical CRO
A Bioanalytical CRO acts as an extension of the sponsor’s scientific and regulatory team, ensuring that:
- Bioanalytical methods are fit-for-purpose and scientifically justified
- Data is accurate, reproducible, and inspection-ready
- Studies remain aligned with global regulatory guidance
- Analytical challenges are proactively identified and resolved
This role becomes increasingly critical as drug modalities grow more complex and regulatory scrutiny intensifies.
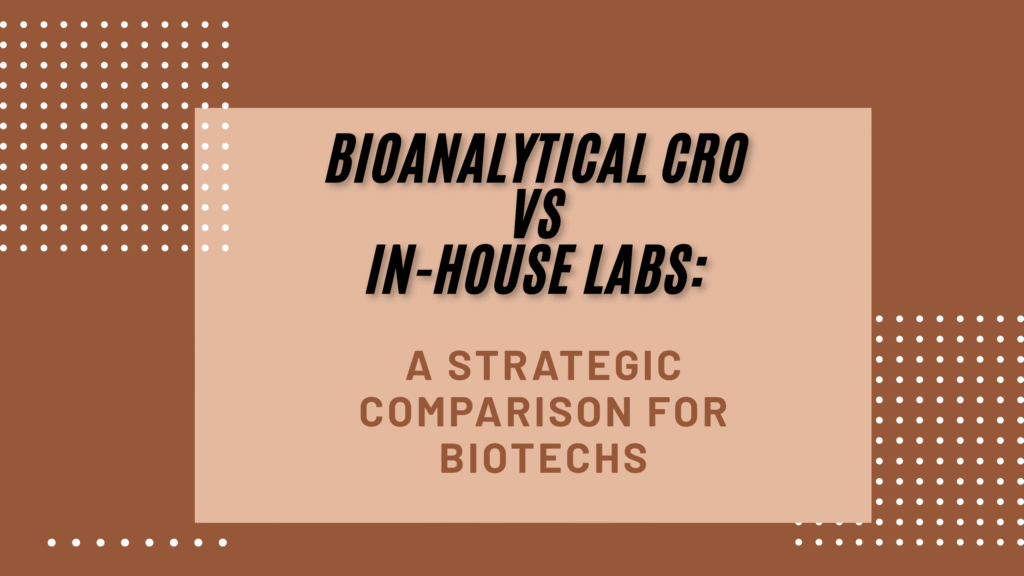
2: Typical Services Offered by a Bioanalytical CRO
Bioanalytical CROs offer a broad and integrated service portfolio designed to support drug development across all stages.
2.1 LC-MS/MS Method Development and Validation
Bioanalytical CROs specialize in robust LC-MS/MS method development, tailored to:
- Specific drug modalities
- Complex biological matrices (plasma, serum, tissue, CSF, urine)
- Sensitivity requirements for low-dose or long-half-life compounds
Validation activities follow FDA, EMA, and ICH guidance, ensuring:
- Accuracy, precision, selectivity, and sensitivity
- Stability under multiple conditions
- Reproducibility across analysts and instruments
2.2 Pharmacokinetic (PK), Toxicokinetic (TK), and ADA Analysis
CROs support quantitative exposure assessment critical for decision-making by providing:
- PK profiling for dose optimization
- TK analysis to support safety studies
- Anti-drug antibody (ADA) assessments for biologics
These analyses directly impact dose selection, safety margins, and regulatory submissions.
2.3 Large Molecule and Small Molecule Bioanalysis
Bioanalytical CROs are equipped to handle both:
- Small molecules using LC-MS/MS platforms
- Large molecules using ligand-binding assays, hybrid LC-MS, or advanced workflows
- LC-MS for large molecules
This flexibility allows CROs to support diverse and evolving pipelines without requiring sponsors to build separate internal capabilities.
2.4 Oligonucleotide, Peptide, and ADC Bioanalysis
Advanced modalities introduce unique analytical challenges, such as:
- Low ionization efficiency
- Non-specific binding
- Metabolite complexity
- Conjugate stability issues
Specialized CROs develop custom strategies for:
- Intact and metabolite analysis
- Conjugated and unconjugated payload quantification
- Sensitivity enhancement and matrix interference control
Learn more about cell and gene therapy bioanalysis and biomarker bioanalytical services for advanced modalities.
2.5 Sample Analysis Under GLP/GCP Compliance
Bioanalytical CROs operate under regulated environments that ensure:
- Full sample traceability
- Chain-of-custody documentation
- Validated systems and SOPs
- Audit-ready data packages
Compliance is embedded into daily operations, not treated as a one-time activity.
2.6 Regulatory Documentation and Audit Support
CROs provide comprehensive regulatory support, including:
- Bioanalytical method validation reports
- Study reports suitable for IND, NDA, and BLA submissions
- Responses to regulatory queries
- Support during inspections and audits
This significantly reduces regulatory risk for sponsors.
2.7 Scientific Depth at ResolveMass Laboratories Inc.
At ResolveMass Laboratories Inc., bioanalysis is led by scientists with hands-on, real-world experience across multiple drug modalities, rather than teams focused only on theoretical compliance.
This ensures that analytical strategies are practical, defensible, and optimized for real regulatory expectations. Learn more about bioanalytical services in drug development.
3: What Are In-House Bioanalytical Labs?
An in-house bioanalytical lab is an internal laboratory facility owned and operated by a biotech or pharmaceutical company to support its own development programs.
In short, in-house labs provide direct operational control, but require significant capital investment, specialized staffing, and continuous regulatory maintenance.
These labs are often built to support long-term pipelines, but may struggle to adapt as analytical needs evolve.
3.1 Typical Characteristics of In-House Bioanalytical Labs
3.1.1 Dedicated Analytical Instruments
In-house labs require:
- High-end LC-MS/MS systems
- Sample preparation platforms
- Software licenses and data systems
These assets demand ongoing maintenance, upgrades, and validation, regardless of utilization levels.
3.1.2 Internal Bioanalytical Scientists
Running an in-house lab depends on:
- Highly trained analysts
- Method development specialists
- QA and compliance personnel
Recruiting, retaining, and training such talent represents a long-term operational commitment.
3.1.3 Custom Workflows Aligned to Company Pipelines
In-house labs often develop pipeline-specific workflows, which can be efficient for routine assays but may become limiting when:
- New drug modalities are introduced
- Sensitivity requirements increase
- Regulatory expectations change
3.1.4 Long-Term Operational Commitments
Once established, in-house labs require continuous investment in:
- Compliance updates
- SOP maintenance
- Instrument lifecycle management
- Regulatory readiness
This creates fixed costs that persist even during pipeline pauses.
4: Bioanalytical CRO vs In-House Labs: Cost Comparison
Bioanalytical CROs typically reduce overall cost and financial risk, particularly for early- and mid-stage biotechs.
The Bioanalytical CRO vs In-house labs decision often comes down to variable versus fixed cost structures. Detailed cost comparisons are outlined in cost-effective bioanalytical services.
Detailed Cost Comparison
| Cost Component | Bioanalytical CRO | In-House Lab |
|---|---|---|
| Capital equipment | Not required | High upfront investment |
| Method development | Included in service | Salaries + training |
| Validation & compliance | Built into operations | Continuous internal expense |
| Staff training | CRO responsibility | Ongoing burden |
| Idle capacity cost | None | High during low utilization |
Why CROs Are More Cost-Efficient
- No capital expenditure for instruments
- Pay-per-study or milestone-based pricing
- No idle lab capacity during development pauses
- No long-term staffing liabilities
For many organizations, the Bioanalytical CRO vs In-house labs choice favors CROs due to financial flexibility, lower risk, and faster return on investment.
5: Expertise & Scientific Depth: CRO vs In-House
CROs offer broader, deeper, and more current expertise.
Why Bioanalytical CROs Excel in Expertise
- Exposure to multiple sponsors and modalities
- Continuous method optimization experience
- Cross-study learning and troubleshooting
- Advanced instrumentation specialization (HRMS, hybrid LC-MS)
In contrast, in-house teams often focus on a narrow set of assays, which can limit innovation and problem-solving capacity.
ResolveMass Laboratories Inc. builds methods informed by real-world regulatory feedback, not textbook assumptions. Explore bioanalytical CRO for drug discovery for more.
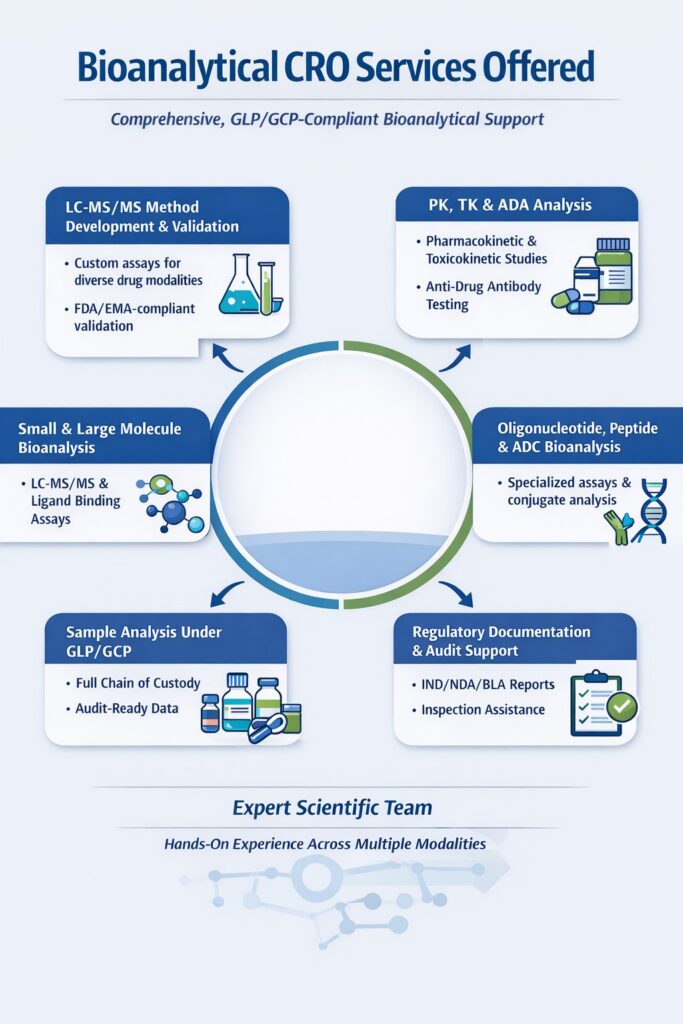
6: Regulatory Readiness: Bioanalytical CRO vs In-House Labs
CROs are purpose-built for inspections.
Regulatory Considerations
- GLP/GCP compliance
- FDA, EMA, and Health Canada inspection readiness
- Complete audit trails and SOP systems
- Data integrity (ALCOA+)
Bioanalytical CROs operate under constant inspection preparedness, while in-house labs often scramble when regulatory scrutiny begins.
Why CROs Outperform In-House Labs in Regulatory Readiness
| Factor | Bioanalytical CRO | In-House Lab |
|---|---|---|
| Inspection preparedness | Continuous and systematic | Often reactive |
| SOP adherence | Strict and audited | Variable |
| Data traceability | Full audit trails | Partial or inconsistent |
| Regulatory risk | Low | Moderate to high |
For biotech companies, this operational readiness translates to reduced regulatory risk and faster approvals.
Learn More About Regulated Bioanalytical Services
To better understand compliance and inspection-ready bioanalysis, explore:
- Regulated Bioanalytical Services – Explore CRO solutions that meet FDA, EMA, and Health Canada standards
- GLP Bioanalytical Services – Learn how GLP ensures data integrity in preclinical studies
7: Speed & Scalability: Which Model Delivers Faster?
Bioanalytical CROs scale faster and respond better to study changes.
CRO Advantages in Speed
- Parallel assay development and validation
- Rapid sample throughput
- Flexible resourcing during peak studies
- No delays due to hiring or procurement
In-house labs frequently face bottlenecks related to instrument availability, staffing gaps, and validation timelines.
8: Data Quality & Reliability
Data quality depends on systems, not ownership—but CROs are optimized for it.
CRO Strengths in Data Quality
- Dedicated QA oversight
- Validated systems and workflows
- Independent scientific review
- Proven reproducibility across studies
A well-established CRO like ResolveMass Laboratories Inc. delivers regulatory-defensible data designed to stand up during submissions and audits.
Learn more about high-throughput bioanalysis and bioanalytical quantification.
9: When In-House Labs Make Sense
While CROs offer many advantages, in-house labs can be strategic in specific scenarios:
- Large pharma with stable pipelines
- High-volume, routine assays
- Proprietary platform technologies
- Long-term internal analytics strategy
Even in these cases, many organizations adopt a hybrid model—outsourcing complex bioanalysis while retaining internal oversight.
Many organizations adopt a hybrid model—outsourcing complex bioanalysis while retaining internal oversight.
10: Hybrid Model: The Best of Both Worlds?
Yes, for many biotechs.
Hybrid Strategy Benefits
- Internal scientific control
- CRO execution for complex assays
- Reduced capital risk
- Faster regulatory alignment
In modern development programs, Bioanalytical CRO vs In-house labs is no longer binary—it’s strategic.
11: Why Biotechs Choose ResolveMass Laboratories Inc.
ResolveMass Laboratories Inc. supports biotechs at every stage by offering:
- Advanced LC-MS bioanalysis expertise
- Deep experience with complex modalities
- Regulatory-ready validation strategies
- Transparent scientific communication
- Partner-level collaboration, not vendor-only service
Our team brings hands-on experience, not just compliance checklists, ensuring data that accelerates confident decision-making.
Conclusion
The Bioanalytical CRO vs In-house labs decision ultimately depends on company stage, pipeline complexity, regulatory exposure, and long-term strategy.
For most biotechs, especially in early and mid-development, partnering with a specialized CRO offers speed, flexibility, expertise, and reduced risk. In-house labs may provide control, but often at a significantly higher operational cost.
By choosing the right bioanalytical partner, biotechs can focus on what matters most—advancing therapies safely and efficiently. Explore outsourced bioanalysis for drug development and bioanalytical CRO services for PK and TK for more guidance.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Outsourcing is suitable when:
-Internal labs lack specific instruments or expertise
-Regulatory-grade assay development is required
-Faster turnaround or scalability is needed
-Regulatory scrutiny demands rigorous validation
In-house labs may still make sense for ongoing routine assays if internal capability exists.
-Control vs. scalability: In-house labs have direct control but limited resources; CROs offer scalable expertise.
-Cost structure: In-house labs carry fixed costs, while CROs use pay-per-project models.
-Expertise and equipment: CROs typically offer broader instruments and deeper regulatory familiarity.
Bioanalytical CROs provide:
-Method development and validation
-High-sensitivity LC-MS/MS bioanalysis
-Pharmacokinetic (PK), toxicokinetic (TK), and biomarker quantification
-Regulatory documentation for IND/NDA/BLA submissions
-GLP and GCP compliance workflows
Possible risks include:
-Reduced direct control over daily analysis
-Dependence on external timelines and communication
-Need for strong quality and contract management
Strong project oversight and clear agreements can mitigate these risks.
Reference
- Stephen Lowes.Outsourcing in Bioanalysis: A CRO Perspective.https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.4155/bio-2017-4994
- Xiaojing Yu &Arkady I Gusev.CRO Benchmarking for Clinical Biomarker Analysis Outsourcing.https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.4155/bio-2019-0123
- Roger Hayes.Bioanalytical Outsourcing: Transitioning from Pharma to Cro.https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.4155/bio-2017-4996
- Neil Spooner, Melanie Anderson, Lieve Dillen, Luca Ferrari, Martijn Hilhorst, Zamas Lam.The Changing World of Bioanalysis: Summary of Panel Discussions.https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.4155/bio-2017-4993
- Ming Li.Automation in Chinese Bioanalytical Cros for Sustained Competitiveness and Growth.https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.4155/bio.16.29

