Introduction:
AI in bioanalysis is no longer a futuristic concept—it’s the present reality transforming how bioanalytical laboratories operate, analyze data, and deliver critical insights for pharmaceutical development, clinical diagnostics, and research. Artificial intelligence technologies are fundamentally changing the landscape of bioanalytical science by introducing unprecedented levels of automation, accuracy, and analytical power that were unimaginable just a decade ago.
At ResolveMass Laboratories Inc., our AI-enabled platforms support a wide range of regulated and discovery-stage programs through comprehensive bioanalytical services, including bioanalytical services in drug development and customized strategies for emerging modalities.
This transformation is particularly impactful for organizations leveraging bioanalytical CRO services and bioanalytical outsourcing models to accelerate development while maintaining regulatory compliance.
The bioanalytical industry stands at an inflection point where AI adoption is transitioning from competitive advantage to operational necessity. This article explores the transformative future of artificial intelligence in bioanalytical laboratories and what it means for pharmaceutical companies, research institutions, and clinical laboratories worldwide.
Summary:
The future of AI in bioanalysis is transforming bioanalytical laboratories through automation, enhanced accuracy, and unprecedented data processing capabilities. This comprehensive guide explores how artificial intelligence is reshaping the bioanalytical landscape.
Key Takeaways:
- AI in bioanalysis is revolutionizing drug development timelines by reducing analysis time by up to 70%
- Machine learning algorithms now detect molecular patterns with 95%+ accuracy in mass spectrometry data
- Predictive analytics powered by AI anticipate equipment failures before they occur, reducing downtime by 60%
- Real-time quality control systems ensure compliance with regulatory standards automatically
- Integration of AI tools reduces operational costs while improving research outcomes
- The bioanalytical market is projected to reach $15.8 billion by 2030, with AI as a primary growth driver
1: Understanding AI in Bioanalysis: Current Applications
AI in bioanalysis encompasses the application of machine learning algorithms, neural networks, and computational intelligence to biological sample analysis, data interpretation, and laboratory workflow optimization. Currently, AI is being deployed across multiple bioanalytical domains with measurable impact.
1.1 Mass Spectrometry Data Analysis
Machine learning algorithms excel at pattern recognition in complex mass spectrometry datasets. AI systems can identify and quantify compounds in biological matrices with remarkable precision, processing data that would take human analysts days to complete in mere minutes.
Advanced AI-driven interpretation is especially valuable for complex studies such as LC-MS bioanalysis for oligonucleotides, LC-MS/MS bioanalysis of xenobiotics, and LC-MS for large molecules.
Current AI applications in MS include:
- Automated peak detection and integration
- Spectral library matching and compound identification
- Matrix effect prediction and compensation
- Quality control outlier detection
- Retention time prediction for method development
1.2 Chromatography Optimization
AI-powered chromatography optimization platforms use predictive modeling to determine optimal separation conditions. These systems analyze thousands of potential parameter combinations to identify the most efficient method conditions.
| AI Application | Traditional Approach | AI-Enhanced Approach | Time Savings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Method Development | 2-4 weeks | 3-5 days | 70-85% |
| Peak Resolution Optimization | Manual iteration | Automated prediction | 80% |
| Mobile Phase Selection | Trial and error | Computational modeling | 75% |
| Column Selection | Experience-based | Data-driven prediction | 60% |
These AI-enhanced workflows directly support faster and more reliable bioanalytical method development while addressing common challenges in bioanalytical method development.
1.3 Predictive Maintenance and Laboratory Operations
Predictive maintenance systems powered by AI monitor instrument performance in real-time, identifying potential failures before they impact laboratory operations. This proactive approach minimizes downtime and ensures consistent analytical quality.
2: How AI in Bioanalysis is Transforming Drug Development
The pharmaceutical industry is experiencing a paradigm shift as AI in bioanalysis accelerates drug development timelines and reduces costs. From early discovery through clinical trials, artificial intelligence is optimizing every stage of the bioanalytical workflow.
2.1 Accelerated Bioanalytical Method Development
AI algorithms can predict optimal analytical conditions based on molecular structure and physicochemical properties, dramatically reducing method development time. What traditionally required weeks of experimental optimization can now be accomplished in days through computational modeling and machine learning predictions.
This acceleration is especially beneficial during bioanalytical method development and validation programs required for IND- and NDA-enabling studies.
AI also shortens timelines for bioanalytical method validation while improving consistency across laboratories.
2.2 Enhanced Pharmacokinetic Studies
Artificial intelligence systems analyze PK/PD data with unprecedented speed and accuracy, identifying subtle patterns in drug metabolism and distribution that might escape human observation. These insights enable more informed decision-making in early-phase clinical development.AI-driven analysis strengthens decision-making across PK/PD bioanalysis, toxicokinetic bioanalysis, and clinical bioanalytical services.
2.3 Real-Time Biomarker Discovery
Machine learning algorithms process multi-omics data from bioanalytical platforms to identify novel biomarkers for disease diagnosis and treatment monitoring. AI systems can correlate thousands of molecular features with clinical outcomes, revealing biomarker candidates that traditional statistical approaches might miss.
AI-driven biomarker discovery advantages:
- Analysis of high-dimensional datasets (proteomics, metabolomics, genomics)
- Pattern recognition across multiple biological matrices
- Integration of clinical and analytical data
- Validation through predictive modeling
- Reduced time from discovery to clinical application
These capabilities are increasingly applied within advanced biomarker bioanalytical services and next-generation biomarker bioanalytical strategies supporting precision medicine initiatives.

3: The Role of Machine Learning in Bioanalytical Quality Control
Machine learning algorithms are revolutionizing quality control processes in bioanalytical laboratories by providing real-time monitoring, automated deviation detection, and predictive quality assurance.
AI-powered QC frameworks reinforce bioanalytical data integrity requirements while ensuring inspection readiness under GLP and regulatory expectations.
3.1 Automated Quality Assessment
AI-powered quality control systems continuously monitor analytical runs, instantly flagging deviations from established acceptance criteria. These systems learn from historical data to refine their detection algorithms, becoming more accurate over time.
3.2 Calibration Curve Optimization
Machine learning models optimize calibration curve fitting, selecting the most appropriate regression model based on data characteristics. This ensures accurate quantification across the entire analytical range while minimizing bias.
3.3 Cross-Validation and Method Transfer
AI systems facilitate method transfer between laboratories by predicting how analytical methods will perform in different environments. This capability is particularly valuable for global pharmaceutical companies operating multiple bioanalytical facilities.
These systems align with GLP bioanalytical services and broader regulated bioanalytical services.
4: Advanced AI Technologies Shaping Bioanalytical Innovation
The future of AI in bioanalysis will be defined by emerging technologies that push the boundaries of what’s possible in biological sample analysis.
4.1 Deep Learning for Spectral Interpretation
Deep neural networks process spectral data with human-like pattern recognition capabilities, identifying subtle spectral features that indicate molecular structure and composition. These systems continuously improve through exposure to larger datasets.
4.2 Natural Language Processing for Laboratory Documentation
NLP technologies automate laboratory documentation, extracting relevant information from scientific literature, method protocols, and regulatory guidance documents. This capability ensures laboratories remain current with best practices and regulatory requirements.
4.3 Computer Vision for Sample Analysis
Computer vision systems monitor sample preparation procedures, ensuring consistency and identifying potential contamination or handling errors. These AI systems provide an additional layer of quality assurance in pre-analytical workflows.
4.4 Reinforcement Learning for Method Optimization
Reinforcement learning algorithms optimize complex multi-parameter analytical methods through iterative experimentation and learning. These systems autonomously explore parameter space to identify optimal conditions.
5: AI-Driven Automation in Bioanalytical Workflows
Automation powered by artificial intelligence is transforming bioanalytical laboratory operations, increasing throughput while reducing human error and operational costs.
5.1 Intelligent Sample Management
AI systems optimize sample routing, prioritization, and storage based on stability requirements, analysis timelines, and resource availability. This ensures efficient laboratory operations and sample integrity.
5.2 Robotic Process Automation
AI-controlled robotic systems perform sample preparation with precision and consistency that exceeds human capability. These systems adapt to different sample types and analytical requirements through machine learning.
Benefits of AI-driven automation:
- 24/7 laboratory operations without fatigue-related errors
- Consistent sample preparation across thousands of samples
- Real-time adjustment to unexpected conditions
- Comprehensive data capture and traceability
- Reduced reagent consumption through optimization
- Scalability to handle increasing sample volumes
Automation is particularly impactful for high-throughput bioanalysis and scalable bioanalytical laboratory services supporting large clinical programs.
5.3 Workflow Orchestration
AI orchestration platforms coordinate multiple instruments, automation systems, and data processing workflows to maximize laboratory efficiency. These systems dynamically adjust resource allocation based on sample priorities and instrument availability.
6: Regulatory Considerations for AI in Bioanalytical Laboratories
As AI in bioanalysis becomes more prevalent, regulatory agencies are developing frameworks to ensure these technologies meet rigorous quality and reliability standards.
6.1 Validation Requirements
AI systems used in regulated bioanalytical testing must undergo thorough validation demonstrating accuracy, precision, and reliability. This includes documentation of algorithm training, validation datasets, and performance characteristics.
AI validation frameworks must support submissions for bioanalytical services for IND and NDA submissions and global regulatory filings.
6.2 Data Integrity and Audit Trails
AI systems must maintain comprehensive audit trails documenting all decisions, predictions, and data transformations. This ensures regulatory compliance and enables thorough investigation of any anomalies.
6.3 FDA and EMA Guidance
Regulatory agencies are issuing guidance documents addressing AI implementation in pharmaceutical development and bioanalytical testing. Laboratories must stay current with evolving regulatory expectations.
| Regulatory Aspect | Current Requirement | AI Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Method Validation | ICH M10 guidelines | AI algorithm validation |
| Data Integrity | 21 CFR Part 11 | AI decision audit trails |
| Quality Control | GLP/GMP compliance | AI system qualification |
| Documentation | Complete traceability | Algorithm versioning |
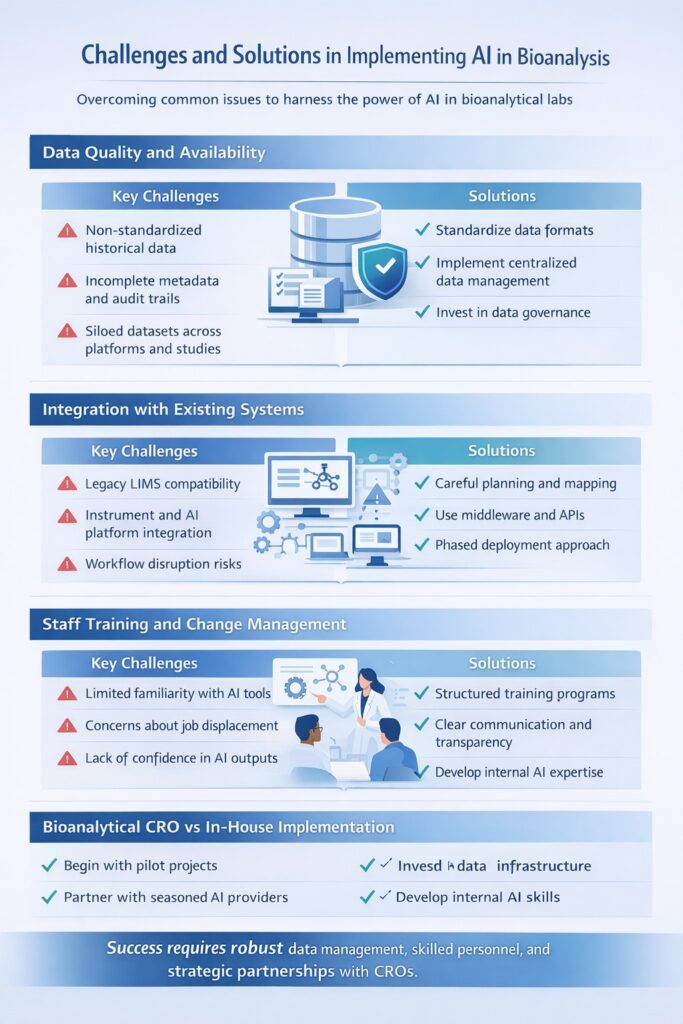
7: Challenges and Solutions in Implementing AI in Bioanalysis
Despite its transformative potential, implementing AI in Bioanalysis comes with practical, technical, and organizational challenges. Successful adoption requires more than technology—it demands high-quality data, system integration, skilled personnel, and strong governance frameworks.
Below are the most common challenges laboratories face and proven solutions to overcome them.
7.1 Data Quality and Availability
The effectiveness of AI in Bioanalysis depends heavily on access to large, high-quality, and well-structured datasets. Many laboratories struggle with inconsistent data formats, incomplete historical records, and limited data accessibility across systems.
Key Challenges
- Non-standardized historical data
- Incomplete metadata and audit trails
- Siloed datasets across platforms and studies
Solutions
- Establish standardized data formats and naming conventions
- Implement centralized data management systems
- Invest in data governance aligned with GxP and ALCOA+ principles
Robust data infrastructure is the foundation for reliable and explainable AI-driven bioanalytical workflows.
7.2 Integration with Existing Systems
Integrating AI in Bioanalysis with legacy LIMS, CDS, and analytical instruments is often technically complex. Many laboratories operate heterogeneous systems that were not designed for advanced analytics or machine learning.
Key Challenges
- Compatibility issues with legacy LIMS
- Limited interoperability between instruments and AI platforms
- Risk of workflow disruption during implementation
Solutions
- Careful system mapping and implementation planning
- Use of middleware and APIs to bridge systems
- Phased deployment to minimize operational risk
Successful integration ensures AI enhances workflows without compromising compliance or productivity.
7.3 Staff Training and Change Management
Human expertise remains critical in AI in Bioanalysis, making staff training and change management essential. Resistance to new technologies and lack of AI literacy can slow adoption.
Key Challenges
- Limited familiarity with AI-driven tools
- Concerns about job displacement
- Lack of confidence in AI outputs
Solutions
- Structured training programs for scientists and analysts
- Clear communication that AI supports—not replaces—expert judgment
- Development of internal AI champions and cross-functional teams
A culture that embraces innovation enables sustainable AI adoption.
Key strategies for successful AI implementation:
Organizations that successfully implement AI in Bioanalysis typically follow these best practices:
- Start with pilot projects that demonstrate clear scientific and operational value
- Invest in data infrastructure before deploying AI solutions
- Partner with experienced AI and bioanalytical solution providers
- Develop internal AI expertise through continuous training
- Maintain human oversight of AI-driven decisions
- Establish clear governance, validation, and documentation frameworks
Many organizations adopt AI by partnering with experienced CROs offering bioanalytical outsourcing for pharma, outsourced bioanalysis for drug development, and bioanalytical CRO services for PK and TK.
Choosing between bioanalytical CRO vs in-house models requires careful evaluation of timelines, cost, and internal expertise.
8: The Economic Impact of AI in Bioanalytical Services
The integration of artificial intelligence into bioanalytical operations delivers measurable economic benefits through increased efficiency, reduced costs, and enhanced analytical capabilities.
8.1 Cost Reduction Through Efficiency
AI-optimized workflows reduce reagent consumption, minimize instrument downtime, and decrease the time required for method development and validation. These efficiencies translate directly to cost savings.
AI-driven efficiencies are especially attractive for organizations seeking cost-effective bioanalytical services, affordable bioanalytical services for biotech startups, and transparent bioanalytical testing services cost structures.
8.2 Increased Laboratory Throughput
AI-powered automation enables laboratories to process more samples with the same resources, improving revenue potential and reducing per-sample costs.
8.3 Competitive Advantage
Laboratories implementing AI capabilities can offer faster turnaround times, more comprehensive data analysis, and superior quality assurance—differentiating themselves in a competitive market.
9: Future Trends: What’s Next for AI in Bioanalysis?
The future of AI in bioanalysis promises even more transformative capabilities as technology continues to evolve.
9.1 Federated Learning for Multi-Site Studies
Federated learning will enable AI systems to learn from data across multiple laboratories without compromising data privacy or security, accelerating algorithm improvement.
9.2 Quantum Computing Integration
Quantum computing will enable AI systems to solve complex molecular modeling and data analysis problems that are currently intractable, opening new possibilities in bioanalytical science.
These advancements are accelerating innovation across cell and gene therapy bioanalysis, biosimilar bioanalysis, and antibody-drug conjugate bioanalytical services.
AI will be central to advanced bioanalytical strategies for complex drug modalities and virtual bioanalytical strategy models.
9.3 Personalized Medicine and Real-Time Analytics
AI will enable real-time bioanalytical monitoring for personalized medicine applications, adjusting treatment protocols based on continuous biomarker analysis.
9.4 Autonomous Laboratories
Fully autonomous laboratories powered by AI will conduct experiments, analyze results, and generate hypotheses with minimal human intervention, dramatically accelerating research timelines.
Projected AI capabilities by 2030:
- Fully automated method development in under 24 hours
- Real-time adaptive quality control systems
- AI-designed analytical methods optimized for specific applications
- Predictive biomarker discovery from multi-omics integration
- Self-optimizing laboratory workflows
- Autonomous regulatory report generation
Conclusion:
The future of AI in bioanalysis is not just promising—it’s already here, transforming how bioanalytical laboratories operate and deliver value to the pharmaceutical industry. Artificial intelligence technologies are enabling faster drug development, more accurate analytical results, and unprecedented insights into biological systems. These innovations are fully supported by ResolveMass’ comprehensive bioanalytical services overview, spanning discovery through clinical development.
At ResolveMass Laboratories Inc., we recognize that AI in bioanalysis represents more than just technological advancement; it’s a fundamental shift in how bioanalytical science is practiced. By embracing artificial intelligence while maintaining the scientific rigor and regulatory compliance that define our industry, we’re helping our clients accelerate their research and development programs while ensuring the highest quality standards.
The laboratories that thrive in this new era will be those that successfully integrate AI capabilities with domain expertise, regulatory knowledge, and a commitment to scientific excellence. As AI technologies continue to evolve, the possibilities for innovation in bioanalytical science are limitless. Whether supporting startups through bioanalytical CRO for virtual biotech or global programs via bioanalytical CRO for drug discovery, ResolveMass delivers AI-powered excellence across the bioanalytical lifecycle.
Frequently Asked Questions:
AI in Bioanalysis refers to the use of artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies to support data processing, method development, quality control, and interpretation in bioanalytical laboratories. It helps scientists analyze complex datasets more accurately and efficiently.
AI in Bioanalysis is used for automated peak integration, anomaly detection, predictive method optimization, data quality checks, and trend analysis. These applications reduce manual effort while improving consistency and compliance.
The main benefits of AI in Bioanalysis include faster data analysis, improved accuracy, enhanced data integrity, reduced human bias, and better decision-making in drug development programs.
Yes, regulatory agencies accept AI in Bioanalysis when it is properly validated, documented, and used with human oversight. AI tools must comply with GxP principles, data integrity requirements, and audit trail expectations.
No, AI in Bioanalysis does not replace scientists; it supports them. Expert bioanalytical professionals are essential for method design, data interpretation, validation, and regulatory decision-making.
AI in Bioanalysis improves data integrity by automatically detecting anomalies, missing data, inconsistent trends, and potential errors. This strengthens compliance with ALCOA+ principles and regulatory expectations.
AI in Bioanalysis is especially valuable for LC-MS/MS, HRMS, ligand-binding assays, ADC bioanalysis, oligonucleotide analysis, and biologics characterization due to the complexity and volume of data generated.
Reference
- Ming Li. Automation in The Bioanalytical Laboratory: What is The Future?https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.4155/bio.13.263
- Ming Li. The case for bioanalytical analyzer.https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/17576180.2024.2344328
- Artificial Intelligence Approaches in Drug Discovery: Towards the Laboratory of the Future.https://www.benthamdirect.com/content/journals/ctmc/10.2174/1568026622666221006140825
- Artificial intelligence in the pre-analytical phase: State-of-the art and future perspectives.https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10943465/
- John F. Place , Alain Truchaud, Kyoichi Ozawa , Harry Pardue, Paul Schnipelsky.Use of artificial intelligence in analytical systems for the clinical laboratory.https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/000991209500002Q

