
Introduction :
Dexamethasone Implant PLGA Characterization Case Study data plays a crucial role in understanding polymer integrity, performance, and regulatory compliance for long-acting ocular and parenteral drug delivery systems.
Dexamethasone implants rely heavily on PLGA Poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) as a biodegradable matrix controlling drug release kinetics. Similar PLGA systems are widely used in oncology and depot-based formulations.
Characterizing extracted PLGA from the finished dosage form is essential to verify that manufacturing, sterilization, and in-vivo exposure do not alter critical polymer attributes.
At ResolveMass Laboratories Inc., we support pharmaceutical developers throughout the PLGA lifecycle—from early formulation development to commercial scale-up.
Summary :
- This case study demonstrates comprehensive characterization of PLGA extracted from a Dexamethasone Implant using orthogonal analytical techniques.
- GPC confirmed molecular weight integrity and polydispersity after drug extraction.
- NMR verified copolymer composition and lactide:glycolide ratio.
- DSC evaluated thermal transitions to assess polymer stability.
- LCMS supported impurity and residual drug profiling.
- The study highlights why Dexamethasone Implant PLGA Characterization Case Study data is critical for regulatory, quality, and lifecycle management.
- Comprehensive Dexamethasone Implant PLGA Characterization Case Study using orthogonal analytical techniques
- Molecular weight–drug release relationships evaluated in line with controlled-release design principles
- Copolymer composition confirmed using advanced NMR-based monomer ratio determination
- Thermal stability and degradation behavior linked to formulation and storage conditions
- Regulatory-ready polymer equivalence demonstrated through RLD comparison and Q1/Q2 assessment
1: Understanding PLGA in Dexamethasone Implants
PLGA is a biocompatible and biodegradable copolymer that degrades through hydrolysis into lactic acid and glycolic acid. In dexamethasone implants and microsphere-based delivery systems,PLGA encapsulates the active pharmaceutical ingredient, controls drug release, and biodegrades without the need for surgical removal.
The polymer’s degradation rate depends on several factors:
- Lactic acid to glycolic acid ratio (LA:GA ratio) – Higher glycolic acid content accelerates degradation
- Molecular weight – Higher molecular weight extends degradation time
- Crystallinity – Amorphous regions degrade faster than crystalline regions
- End-group chemistry – Ester vs. carboxylic acid terminations affect hydrolysis rates,including ester-terminated and acid end-capped polymers
Understanding these parameters through Dexamethasone Implant PLGA Poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) Characterization enables manufacturers to optimize formulations for desired release profiles and ensure batch-to-batch consistency.
Fine-tuning these attributes through Dexamethasone Implant PLGA Poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) Characterization enables predictable in-vivo performance and batch-to-batch consistency. Customized release control strategies are often required for long-acting implants.
2: Case Study Background: Client Requirements
A pharmaceutical company developing a generic dexamethasone intravitreal implant approached ResolveMass Laboratories Inc. with specific analytical needs:
Client Objectives:
- Reverse-engineer the PLGA composition from a reference listed drug (RLD)
- Determine molecular weight distribution and changes during accelerated stability studies
- Confirm LA:GA ratio for formulation equivalence
- Identify degradation products and impurities
- Generate comprehensive analytical data for ANDA submission
Samples Provided:
- Commercial dexamethasone implants (T0 – initial)
- Implants stored under accelerated conditions (40°C/75% RH) for 1, 3, and 6 months
- Individual PLGA reference standards for method validation
This work aligns directly with FDA expectations for polymer sameness and equivalence.
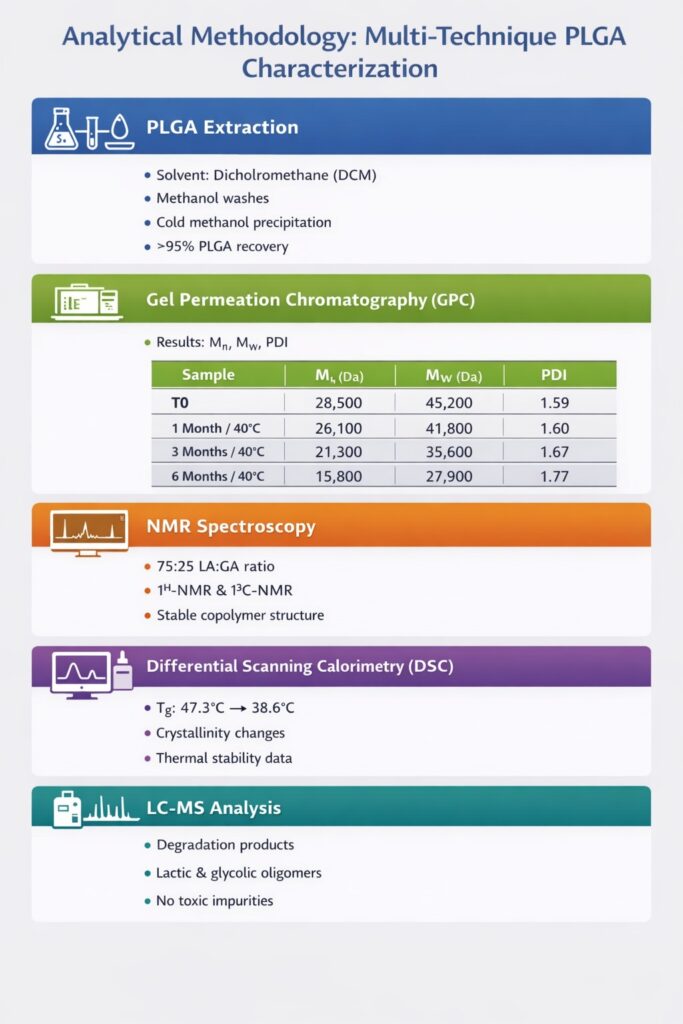
3: Analytical Methodology: Multi-Technique PLGA Characterization
Step 1: PLGA Extraction from Dexamethasone Implants
A validated extraction protocol was developed to isolate PLGA from the implant matrix without inducing degradation. Solvent systems commonly used for PLGA dissolution and purification were applied.
Before characterization, we developed a validated extraction procedure to isolate PLGA from the dexamethasone implant matrix. The extraction process involved:
- Solvent selection: Dichloromethane (DCM) was chosen for its ability to dissolve PLGA while minimizing polymer degradation
- Drug removal: Multiple washing steps with methanol removed dexamethasone and excipients
- Polymer precipitation: PLGA was precipitated using cold methanol and dried under vacuum
- Recovery verification: Gravimetric analysis confirmed >95% PLGA recovery
This extraction method ensured that subsequent analytical techniques characterized the polymer itself, not the complete implant formulation.
Step 2: Gel Permeation Chromatography (GPC) Analysis
GPC was used to determine number-average molecular weight (Mn), weight-average molecular weight (Mw), and polydispersity index (PDI). These parameters directly impact drug release kinetics and long-term stability.
Molecular weight trends observed during accelerated stability testing were consistent with hydrolytic degradation behavior typically seen during formulation scale-up and manufacturing transitions.
Instrumental Parameters:
- Column: Mixed bed organic GPC columns
- Mobile phase: Tetrahydrofuran (THF) with 0.1% trifluoroacetic acid
- Flow rate: 1.0 mL/min
- Detection: Refractive Index (RI) detector
- Calibration: Polystyrene standards with molecular weight range 500-400,000 Da
Key GPC Findings:
| Sample | Mn (Da) | Mw (Da) | PDI | % MW Loss |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T0 (Initial) | 28,500 | 45,200 | 1.59 | – |
| 1 Month/40°C | 26,100 | 41,800 | 1.60 | 7.5% |
| 3 Months/40°C | 21,300 | 35,600 | 1.67 | 21.2% |
| 6 Months/40°C | 15,800 | 27,900 | 1.77 | 38.3% |
The GPC data revealed progressive molecular weight reduction consistent with hydrolytic degradation, with accelerated breakdown at elevated temperature and humidity.
The results also supported the suitability of the polymer for parenteral and implantable applications.
Step 3: Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy
Both ¹H-NMR and ¹³C-NMR were used to confirm copolymer composition and structural integrity. Integration of characteristic lactic and glycolic acid peaks confirmed a stable 75:25 LA:GA ratio across all stability intervals.
NMR spectroscopy confirms the lactic acid to glycolic acid ratio and detects structural changes in the polymer backbone. We performed both 1H-NMR and 13C-NMR analysis:
1H-NMR Protocol:
- Solvent: Deuterated chloroform (CDCl3)
- Instrument: 500 MHz NMR spectrometer
- Temperature: 25°C
- Analysis: Integration of characteristic methine and methylene protons
LA:GA Ratio Determination: The characteristic peaks were:
- Lactic acid methine proton: δ 5.15 ppm (quartet)
- Glycolic acid methylene proton: δ 4.80 ppm (singlet)
Integration ratios confirmed a 75:25 LA:GA molar ratio in the initial sample, which remained consistent across all time points—indicating that degradation affected molecular weight but not copolymer composition.
13C-NMR Analysis:
- Confirmed carbonyl carbon environments
- Detected end-group modifications (carboxylic acid formation increased with degradation)
- No evidence of unexpected structural rearrangements or impurities
This analysis followed best practices for accurate monomer ratio determination.
No unexpected chemical shifts or structural rearrangements were observed, confirming polymer identity.
Step 4: Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
DSC measures glass transition temperature (Tg) and crystallinity, which directly impact drug release rates and polymer degradation kinetics. Our DSC protocol included:
Experimental Conditions:
- Sample size: 5-10 mg
- Heating rate: 10°C/min
- Temperature range: 0-200°C
- Atmosphere: Nitrogen purge
- Two heating cycles to eliminate thermal history
DSC Results:
| Sample | Tg (°C) | Crystallinity | Observations |
|---|---|---|---|
| T0 (Initial) | 47.3 | Amorphous | Sharp glass transition |
| 1 Month/40°C | 45.8 | Amorphous | Slightly broader transition |
| 3 Months/40°C | 42.1 | Trace crystallinity | Multiple thermal events |
| 6 Months/40°C | 38.6 | ~8% crystalline | Crystallization peak at 95°C |
Thermal behavior trends provided critical insight into long-term formulation stability.
The decreasing Tg correlated with molecular weight reduction from GPC data. Crystallization in degraded samples indicates chain reorganization as shorter polymer chains gain mobility.
Step 5: Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (LCMS)
LCMS identifies degradation products, residual monomers, and low molecular weight oligomers that may impact biocompatibility and drug release. We employed:
LCMS Method:
- Column: C18 reversed-phase (2.1 x 100 mm, 1.8 μm)
- Mobile phase: Water/acetonitrile gradient with 0.1% formic acid
- Mass spectrometer: High-resolution Q-TOF in negative ionization mode
- Detection: UV at 210 nm and total ion current (TIC)
Detected Species:
- Lactic acid monomer: <0.1% (within acceptable limits)
- Glycolic acid monomer: <0.05% (within acceptable limits)
- Lactic acid oligomers (dimer to hexamer): Increased with degradation
- Glycolic acid oligomers: Increased with degradation
- No unexpected impurities or toxic degradation products detected
The LCMS data confirmed that PLGA degradation follows the expected hydrolysis pathway without generating concerning by-products.
4: Integrated Data Interpretation: Dexamethasone Implant PLGA Characterization
By combining results from GPC, NMR, DSC, and LCMS, ResolveMass Laboratories Inc. provided a complete characterization profile:
Polymer Identity:
- PLGA 75:25 (lactic acid:glycolic acid)
- Initial molecular weight: ~45 kDa (Mw)
- Amorphous polymer with no initial crystallinity
Degradation Behavior:
- Hydrolytic degradation rate: ~6% molecular weight loss per month at 40°C/75% RH
- Degradation products: Primarily lactic and glycolic acid oligomers
- No toxic or unexpected degradation products
- Shelf-life prediction: 24 months at controlled room temperature
Regulatory Implications:
- Polymer composition matches reference listed drug specifications
- Degradation profile consistent with expected biocompatibility
- Data package suitable for ANDA submission to FDA
- Batch-to-batch consistency demonstrated across multiple lots
These findings support FDA expectations for Dexamethasone Implant PLGA Characterization Case Study submissions and RLD equivalence assessment.
5: Why Multi-Technique Analysis is Critical
A single analytical technique cannot provide complete PLGA characterization. Each method offers unique insights:
| Technique | Information Provided | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| GPC | Molecular weight distribution, degradation kinetics | Requires calibration standards; relative measurement |
| NMR | LA:GA ratio, structural composition, end-groups | Lower sensitivity; requires pure samples |
| DSC | Thermal properties, crystallinity, glass transition | Indirect measure of molecular changes |
| LCMS | Degradation products, impurities, monomers | May not detect high MW species |
Together, these techniques provide:
- Structural confirmation (NMR)
- Molecular weight characterization (GPC)
- Physical property assessment (DSC)
- Purity and degradation monitoring (LCMS)
This comprehensive approach is exactly what regulatory agencies expect for Dexamethasone Implant PLGA Poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) Characterization.
This strategy mirrors analytical frameworks used for microencapsulation and long-acting injectable systems.
6: ResolveMass Laboratories Inc. Expertise and Capabilities
ResolveMass Laboratories Inc. provides end-to-end PLGA characterization services covering raw materials, intermediates, and finished dosage forms.
Our laboratory specializes in complex polymer characterization for pharmaceutical and medical device applications. Our team includes:
- PhD-level analytical chemists with 15+ years in polymer science
- FDA-inspected laboratory facilities with ISO 17025 accreditation
- State-of-the-art instrumentation maintained under rigorous calibration protocols
- Experience supporting 50+ ANDA and NDA submissions for sustained-release products
Our PLGA Characterization Services Include:
- Complete molecular weight analysis (GPC with multiple detector systems)
- Compositional analysis (NMR, FTIR)
- Thermal characterization (DSC, TGA, DMA)
- Degradation studies (accelerated and real-time)
- Impurity profiling (LCMS, GCMS)
- Method development and validation
- Regulatory documentation support
We understand the unique challenges of Dexamethasone Implant PLGA Poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) Characterization and work closely with clients to develop customized analytical strategies that meet regulatory requirements and project timelines.
7: Applications Beyond Dexamethasone Implants
While this case study focused on dexamethasone implants, our PLGA characterization expertise extends to:
- Oncology implants: Biodegradable wafers for brain tumor treatment
- Contraceptive implants: Long-acting hormone delivery systems
- Orthopedic devices: Resorbable screws, plates, and sutures
- Microparticle formulations: Injectable sustained-release suspensions
- Nanoparticle systems: Targeted drug delivery platforms
Each application presents unique analytical challenges, but the fundamental principles of comprehensive polymer characterization remain constant.
Conclusion :
This Dexamethasone Implant PLGA Poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) Characterization Case Study demonstrates ResolveMass Laboratories Inc.’s capability to deliver comprehensive polymer analysis that supports product development, quality control, and regulatory submissions. Through the strategic application of GPC, NMR, DSC, and LCMS, we provided our client with actionable data on polymer composition, molecular weight distribution, thermal properties, and degradation behavior.
Our integrated analytical approach goes beyond simple testing—we partner with pharmaceutical and medical device companies to solve complex characterization challenges, interpret results in regulatory context, and accelerate time to market. Whether you’re developing a new sustained-release implant or qualifying a generic formulation, our expertise in Dexamethasone Implant PLGA Poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) Characterization ensures you receive the highest quality analytical data to support your project goals.
Frequently Asked Questions :
PLGA (Poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid)) is a biodegradable and biocompatible polymer used in dexamethasone implants to provide controlled, sustained drug release while safely degrading into lactic and glycolic acid within the body.
PLGA characterization is critical because polymer molecular weight, composition, and thermal behavior directly influence drug release rate, stability, safety, and regulatory acceptance of dexamethasone implants.
A Dexamethasone Implant PLGA Characterization Case Study is a comprehensive analytical evaluation of PLGA extracted from a finished dexamethasone implant using techniques such as GPC, NMR, DSC, and LCMS to confirm polymer identity, stability, and performance.
PLGA is extracted from the finished implant to verify that manufacturing, sterilization, and drug–polymer interactions have not altered polymer properties compared to the original raw material.
PLGA characterization typically involves:
-Gel Permeation Chromatography (GPC) for molecular weight
-Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) for copolymer composition
-Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) for thermal behavior
-LCMS for degradation products and impurities
GPC measures number-average molecular weight (Mn), weight-average molecular weight (Mw), and polydispersity index (PDI), which are key indicators of polymer degradation behavior and drug release performance in dexamethasone implants.
Higher PLGA molecular weight slows polymer degradation and prolongs dexamethasone release, while lower molecular weight accelerates degradation and results in faster drug release.
Reference
- Eric Lehner , Marie-Luise Trutschel , Matthias Menzel , Jonas Jacobs , Julian Kunert , Jonas Scheffler , Wolfgang H. Binder , Christian E.H. Schmelzer , Stefan K. Plontke , Arne Liebau , Karsten Mäder.Enhancing drug release from PEG-PLGA implants: The role of Hydrophilic Dexamethasone Phosphate in modulating release kinetics and degradation behavior.https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0928098725000661
- S. Wachowiak , F. Danede , J.F. Willart , F. Siepmann , J. Siepmann , M. Hamoudi.PLGA implants for controlled dexamethasone delivery: Impact of the polymer chemistry.https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1773224723005002
- Synthesis of Microwave Functionalized, Nanostructured Polylactic Co-Glycolic Acid (nfPLGA) for Incorporation into Hydrophobic Dexamethasone to Enhance Dissolution.https://www.mdpi.com/2079-4991/13/5/943

