Introduction:
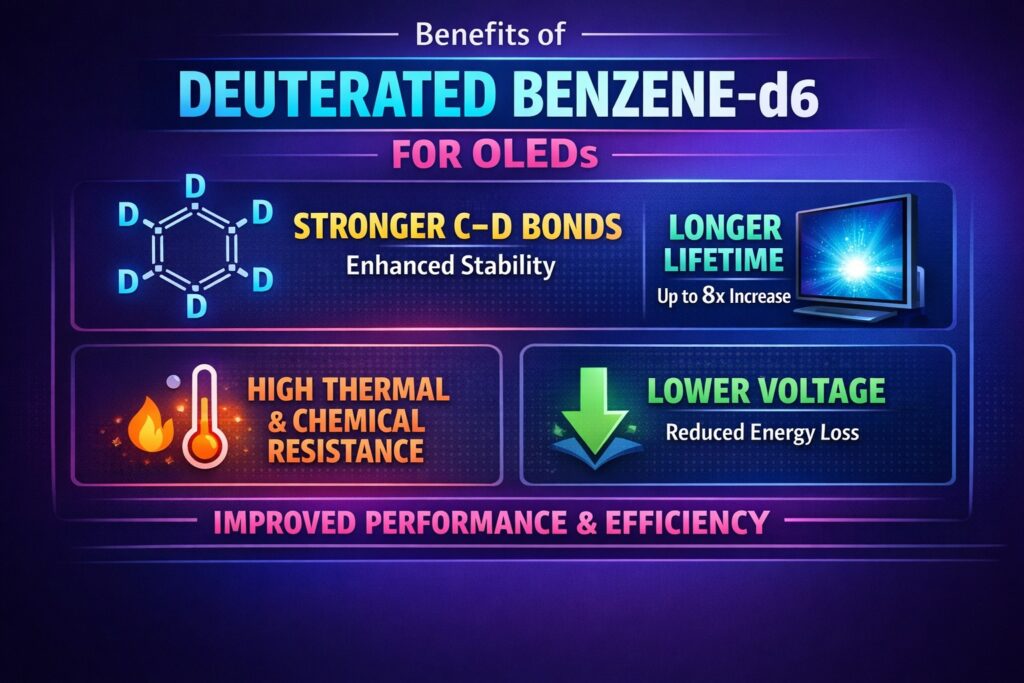
High-purity Deuterated Benzene-d6 for OLED Application plays a key role in the development of advanced organic electronic devices, especially in improving the lifetime of blue OLED emitters. Blue OLED materials operate at higher energy levels, which makes them more prone to chemical breakdown during long-term use. By replacing hydrogen atoms with deuterium through the Kinetic Isotope Effect, the molecular structure becomes stronger and more stable. This change increases bond strength and improves both thermal and chemical resistance. As a result, OLED devices show longer operating life and more consistent performance under electrical stress.
In modern display technology, stability is one of the biggest challenges. Materials used in emitting layers must handle high brightness and continuous operation without degrading. The use of Deuterated Benzene-d6 for OLED Application helps reduce molecular damage that normally happens in blue emitters. This makes it a preferred starting material for host and dopant synthesis in high-performance OLED systems.
Explore our comprehensive catalog of isotopic solutions: Check the availability of all the deuterated chemicals
Summary
- Extends blue OLED lifetime by strengthening C–D bonds through the Kinetic Isotope Effect, reducing bond cleavage and molecular degradation.
- Improves device efficiency with better exciton confinement, lower non-radiative energy loss, reduced operating voltage, and EQE up to 27.4%.
- Enhances thermal and thin-film stability with higher molecular packing density, improved Tg and Td, and better resistance to crystallization.
- Meets strict electronic-grade purity standards requiring ≥99.96 atom % D enrichment and ≥99.9% chemical purity with tight impurity control.
- Enables scalable production through advanced microwave-assisted flow synthesis with up to 91% reaction efficiency and consistent enrichment levels.
- Supports sustainability through recovery and re-enrichment programs that reduce cost, conserve deuterium resources, and stabilize supply chains.
The Physicochemical Advantages of Deuterated Benzene-d6 for OLED Application in Host Synthesis
The use of Deuterated Benzene-d6 for OLED Application in host synthesis provides a stronger molecular framework compared to standard benzene. When deuterium (D) replaces hydrogen (H), the resulting C–D bond vibrates at a lower frequency and requires more energy to break. This directly improves chemical stability in OLED devices, where materials are exposed to constant electrical excitation. The stronger bond reduces the chance of bond cleavage during charge recombination. Over time, this leads to better luminance stability and longer device lifetime.
When $C_6D_6$ is used to build host materials such as carbazole, fluorene, and phenylbenzene derivatives, it helps solve the well-known “blue emitter problem.” Blue OLEDs face higher energy stress than red or green devices. These higher energies can break weak C–H bonds and create radicals that damage the material. Starting with a fully deuterated benzene core protects these sensitive positions. Because deuterium is heavier than hydrogen, the C–D bond has lower zero-point energy, making bond breaking less likely during operation.
Learn more about the role of isotopes in material science: Deuterated polymers: A cornerstone guide to synthesis and applications
In addition to chemical strength, $C_6D_6$ also improves thin-film properties. Deuterated materials often show higher molecular packing density, such as $1.139$ g/$cm^3$ compared to $1.114$ g/$cm^3$ for non-deuterated versions. A denser structure creates a more rigid environment for dopants and reduces non-radiative energy loss. The shift from C–H stretching at $3203$ $cm^{-1}$ to C–D stretching at $2376$ $cm^{-1}$ lowers vibrational energy loss. This improves exciton confinement and enhances color purity in OLED devices.
| Property | Benzene-h6 (C6H6) | Benzene-d6 (C6D6) |
|---|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | $78.11$ g/mol | $84.15$ g/mol |
| Boiling Point | $80.1^\circ$C | $79.1^\circ$C |
| Melting Point | $5.5^\circ$C | $6.0 – 7.0^\circ$C |
| Density | $0.876$ g/mL | $0.950$ g/mL |
| Refractive Index ($n^{20}_D$) | $1.501$ | $1.497 – 1.499$ |
| Isotopic Mass Shift | $M$ | $M+6$ |
| Zero-Point Energy | Baseline | $\sim 1.2 – 1.5$ kcal/mol lower |
Deuterated intermediates also show improved thermal behavior. Materials derived from $C_6D_6$ often have higher glass transition temperatures ($T_g$) and decomposition temperatures ($T_d$). These properties are important for maintaining stable amorphous films during vacuum deposition and long-term device operation. For example, some exciplex hosts made from $C_6D_6$ show $T_d$ values up to $432^\circ$C. Higher $T_g$ reduces the risk of crystallization and maintains uniform light emission across the display.
Need specialized materials for your electronics project? Browse high-purity deuterated reagents for electronics
Stringent Purity Standards for Deuterated Benzene-d6 for OLED Application in High-Resolution Displays
For Deuterated Benzene-d6 for OLED Application, purity is critical. Electronic-grade material typically requires isotopic enrichment of at least $99.96$ atom % D and chemical purity of $\ge 99.9%$. Even small amounts of hydrogen or other impurities can reduce device efficiency. In high-resolution displays, trace contamination may cause uneven brightness or early failure. Strict quality control ensures reliable OLED manufacturing.
Isotopic purity is verified using $^1H$-NMR spectroscopy. The residual proton signal at $7.16$ ppm must be extremely low. Studies show that higher deuteration levels directly improve device lifetime. A host made from $99.96$ atom % D performs much better than one made from $98%$ enrichment. This highlights the importance of precise isotopic control.
Ensure the integrity of your research with expert analysis: Learn about the analytical characterization of deuterated compounds
Chemical impurities such as halogenated compounds, trace metals, and moisture must also be tightly controlled. Advanced analytical tools like HPLC-MS and GC-MS detect impurities down to ppm levels. Moisture content is usually kept at $\le 0.01%$ using Karl Fischer titration. These strict standards protect catalysts and ensure consistent thin-film performance.
| Impurity Type | Impact on OLED Performance | Specification (Electronic Grade) |
|---|---|---|
| Residual Protons ($^1H$) | Increases vibrational quenching | $< 0.04$ atom % |
| Halogenated Species | Accelerates chemical degradation | $< 1$ ppm |
| Trace Metals (Fe, Cu, Ni) | Forms mass adducts/charge traps | $< 50$ ppb total |
| Moisture ($H_2O$) | Interferes with catalysts/degrades films | $< 100$ ppm |
| Organic Contaminants | Quenches electroluminescence | $< 50$ ppb |
Maintaining ultra-high purity helps prevent non-radiative recombination centers. Multiple distillation steps and clean vacuum systems are used to avoid contamination. These practices support stable light output and long device lifetime in demanding applications.
Advancements in Flow Synthesis for Deuterated Benzene-d6 for OLED Application Production
The production of Deuterated Benzene-d6 for OLED Application has moved from traditional batch reactors to advanced microwave-assisted flow systems. This modern method increases reaction efficiency up to $91%$ and reduces reaction time significantly. Continuous flow reactors allow better temperature control and consistent enrichment levels. This shift supports large-scale OLED manufacturing with improved reliability.
Older batch processes required long heating cycles and manual catalyst handling. In contrast, microwave flow reactors can reach $200^\circ$C in just $90$ seconds. This reduces energy use and improves catalyst life. Faster reactions also lower production costs and increase throughput.
Looking for a reliable manufacturing partner? Partner with a leading deuterated labelled synthesis company in Canada
Multi-stage flow systems allow gradual hydrogen-to-deuterium exchange. This improves enrichment efficiency while reducing $D_2O$ consumption. Automated separation systems maintain chemical purity at $\ge 99.7%$. These improvements ensure a stable supply chain for global OLED manufacturers.
| Synthesis Parameter | Conventional Batch Reactor | Microwave Flow Reactor |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Method | Thermal Conduction | Microwave Irradiation |
| Time to $200^\circ$C | $60$ minutes | $90$ seconds |
| Reaction Efficiency | $\sim 27%$ (in $10$ min) | $91%$ (in $3$ min) |
| Catalyst Type | Various (Pt, Pd, Ni) | Fixed-bed Pt/Alumina |
| Scalability | Volume-limited | Series-stage expansion |
| Automation | Manual filtration | Integrated separation |
Impact of Deuterated Benzene-d6 for OLED Application on T90 Lifetime and Efficiency
The use of Deuterated Benzene-d6 for OLED Application in emitting layers can increase T90 lifetime by up to eight times in blue OLED devices. This improvement comes from reduced bond breaking and lower non-radiative energy loss. Deuteration also improves charge mobility by lowering reorganization energy. As a result, operating voltage can decrease by around $0.3$ V at $1000$ cd/$m^2$. Lower voltage reduces heat generation and improves overall stability.
In phosphorescent OLED systems, combining deuterated host and transport layers creates cumulative stability benefits. Interface protection reduces radical formation and slows luminance decay. External quantum efficiency (EQE) can reach $27.4%$, with power efficiency around $41.2$ lm/W. These performance gains make $C_6D_6$ an important structural component in advanced OLED stacks.
Optimize your laboratory standards and analytical processes: Purchase high-quality stable isotope labeled compounds
| Device Metric | Protonated Host (Control) | Deuterated Host (C6D6 derived) |
|---|---|---|
| T90 Lifetime (at $1000$ cd/$m^2$) | Baseline ($100$ h) | $370 – 800$ h |
| Operation Voltage | $V_{ref}$ | $V_{ref} – 0.3$ V |
| Max External Quantum Efficiency (EQE) | $\sim 20 – 24%$ | $27.4%$ |
| Power Efficiency | $\sim 30$ lm/W | $41.2$ lm/W |
| Molecular Packing Density | $1.114$ g/$cm^3$ | $1.139$ g/$cm^3$ |
| Reorganization Energy ($\lambda$) | $0.775$ eV | $0.655$ eV |
Global Logistics and Safety Protocols for Bulk Deuterated Benzene-d6 for OLED Application Supply
Bulk Deuterated Benzene-d6 for OLED Application is regulated under international transport rules. It is classified as a Category 2 Flammable Liquid and Group 1A Carcinogen. Safe transport requires UN-approved stainless steel containers and nitrogen blanketing. Grounding and bonding procedures are used to prevent static discharge. These steps protect both people and product quality during shipping.
Small research quantities are supplied in sealed glass ampoules under inert atmosphere. Industrial volumes are shipped in certified drums with full documentation, including SDS and dangerous goods declarations. Strict compliance ensures smooth global logistics and uninterrupted OLED production.
Source your materials from a trusted global distributor: Find a reliable supplier of deuterated reagents
| Logistics Factor | Protocol/Specification | Regulatory Body |
|---|---|---|
| Hazard Classification | Flammable Liquid (Cat 2), Carcinogen (Cat 1A) | GHS/OSHA |
| UN Number | UN 1114 (Packing Group II) | DOT/IATA/IMDG |
| Packaging Requirements | UN-certified Stainless Steel Drums/IBCs | UN/PHMSA |
| Inerting Method | Nitrogen/Argon Blanketing | NFPA/API |
| Static Protection | Grounding and Bonding | NFPA 77 |
| Documentation | SDS, CoA, CoQ, Dangerous Goods Dec | IATA/IMO |
Synthesis Pathways and Catalytic H/D Exchange Mechanisms
High-enrichment benzene-d6 ($>99.9$ atom % D) is mainly produced through catalytic hydrogen–deuterium exchange. Modern methods use platinum, iridium, or nickel catalysts with $D_2O$ or $D_2$ gas as the deuterium source. The catalyst activates the C–H bond and replaces hydrogen with deuterium. Careful process control ensures full $M+6$ isotopic substitution.
The reaction typically involves a metal-aryl intermediate. After bond activation, deuterium replaces hydrogen, and the catalyst is regenerated. Preventing back-exchange with moisture is important to maintain enrichment levels. Proper storage and inert handling protect isotopic integrity.
Access tailored chemical solutions for your specific needs: Request a quote for custom deuterated compounds
| Catalyst System | Mechanism | Chemical Purity | Enrichment Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| Platinum Black | Heterogeneous H/D Exchange | $\ge 99%$ | $99.2$ atom % D |
| Iridium (III) Complexes | C-H Bond Activation | $99.7%$ | $98 – 99.9$ atom % D |
| Nickel Catalyst | Vapor Phase Exchange | Not specified | Moderate |
| Pt/Alumina (Microwave) | Rapid Flow Exchange | $\ge 99.5%$ | $91 – 99.96$ atom % D |
Circular Economy: Recovery and Re-enrichment Programs for Deuterated Benzene-d6 for OLED Application
Recovery programs for Deuterated Benzene-d6 for OLED Application help manufacturers reduce cost and waste. During OLED synthesis, partially exchanged material may accumulate. Instead of discarding it, the material can be purified and re-enriched to $99.96$ atom % D. This restores it to electronic-grade quality.
Recycling lowers procurement expenses and reduces environmental impact. It also conserves global deuterium resources used in medical and semiconductor industries. This circular approach supports both sustainability and supply chain stability.
Cost Reduction: Re-enriched material costs less than newly synthesized benzene-d6.
Environmental Sustainability: Recycling reduces hazardous waste and emissions.
Resource Conservation: Preserves valuable deuterium supplies for critical industries.
Conclusion
High-purity Deuterated Benzene-d6 for OLED Application is a critical material for achieving long lifetime and high efficiency in modern OLED displays. Through the Kinetic Isotope Effect, stronger C–D bonds reduce degradation and improve charge transport. Meeting strict electronic-grade purity standards ensures consistent device performance. Advanced flow synthesis and recovery programs further enhance scalability and sustainability.
Ready to upgrade your OLED production materials?Buy high-purity deuterated compounds today
ResolveMass Laboratories Inc. remains committed to supplying high-quality deuterated materials with reliable global logistics and technical support. For technical consultations, custom synthesis, or bulk supply inquiries, please visit:
Contact Us
FAQs on High-Purity Deuterated Benzene-d6 for OLED Applications
Electronic-grade Deuterated Benzene-d6 for OLED Application is manufactured with much tighter specifications than common lab-grade solvent. It requires very high isotopic enrichment (≥ 99.96 atom % D) and extremely low impurity levels. Trace metals, halogens, and moisture must be controlled at ppm to ppb levels. These strict standards are necessary to protect OLED devices from quenching and early degradation.
Deuteration replaces weaker C–H bonds with stronger C–D bonds. Because C–D bonds have lower vibrational energy and are harder to break, they are more stable under high electrical stress. In blue OLEDs, where excitation energy is higher, this added bond strength reduces molecular damage. As a result, the T90 lifetime can increase significantly.
Deuterated host materials often show tighter molecular packing and lower reorganization energy. These properties help charges move more efficiently through the emitting layer. Improved charge transport means the device can reach the same brightness at a slightly lower voltage. In many cases, the operating voltage can drop by around 0.3 V.
Moisture can damage sensitive metal catalysts used during OLED material synthesis. Even small amounts of water may reduce reaction efficiency or introduce unwanted side reactions. In finished devices, trapped moisture can speed up film degradation. Therefore, strict moisture limits are essential for both synthesis and device reliability.
Yes, it is fully compatible with vacuum deposition workflows. Although C6D6 itself is a precursor, it is used to produce highly pure host and dopant materials. High isotopic and chemical purity ensures that no volatile contaminants enter the evaporation chamber. This helps maintain clean equipment and uniform thin-film formation.
Benzene-d6 is classified as a flammable liquid and a carcinogenic substance. It must be stored in approved containers with proper grounding and bonding to prevent static discharge. Handling should be done in well-ventilated areas using suitable personal protective equipment (PPE). Inert gas blanketing is often applied during transfer to reduce fire risk.
Reference
- Yao, J., Dong, S.-C., Tam, B. S. T., & Tang, C. W. (2023). Lifetime enhancement and degradation study of blue OLEDs using deuterated materials. **ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 15(5), 7255–7262. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.2c22882
- Kopf, S., Bourriquen, F., & Li, W. (2022). Recent developments for the deuterium and tritium labeling of organic molecules. Chemical Reviews, 122(6), 6634–6718. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.1c00795
- Yuan, W., Huang, T., Zhou, J., Tang, M.-C., Zhang, D., & Duan, L. (2024). High-efficiency and long-lifetime deep-blue phosphorescent OLEDs using deuterated exciplex-forming host [Preprint]. ChemRxiv. https://doi.org/10.26434/chemrxiv-2024-8bn7g


