INTRODUCTION:
PLGA Microsphere Formulation is the most reliable strategy for delivering highly potent APIs (HPAPIs) because it reduces systemic toxicity, protects the drug, and ensures controlled release. Right from the first phase of formulation, PLGA enables predictable degradation and safe handling of potent molecules.
Highly potent APIs—including oncology agents, peptide therapeutics, hormones, and immunomodulators—demand specialized encapsulation systems that minimize exposure risk and maximize therapeutic control. PLGA Poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) microspheres have become the gold standard due to their biocompatibility, tunable degradation profile, and long market history of FDA-approved products.
ResolveMass Laboratories Inc. supports global R&D teams with high-grade PLGA, custom particle engineering, and technical expertise to accelerate safe microsphere development.
To help researchers deepen PLGA understanding, ResolveMass provides resources such as:
- PLGA Degradation Profile → https://resolvemass.ca/plga-degradation-profile/
- PLGA Depot Formulation → https://resolvemass.ca/plga-depot-formulation/
- PLGA Characterization for RLD → https://resolvemass.ca/plga-characterization-for-rld/
SUMMARY
- PLGA microsphere formulation enables safe, sustained, and controlled delivery of highly potent APIs by encapsulating them inside a biodegradable polymer matrix.
- Formulation success depends on polymer selection, drug–polymer interaction, particle size control, encapsulation efficiency, solvent choice, and process parameters.
- Highly potent APIs require enhanced operator safety, controlled exposure, containment systems, and optimized microencapsulation workflows.
- Stability, release kinetics, and sterilization are critical to ensure product performance and regulatory compliance.
- ResolveMass Laboratories Inc. specializes in providing high-purity PLGA polymers and expert guidance for complex PLGA microsphere formulation programs worldwide.
1: What Makes PLGA Microsphere Formulation Ideal for Highly Potent APIs?
PLGA microsphere formulation is ideal for highly potent APIs because it provides controlled release, reduces peak-related toxicities, and ensures safe handling through encapsulation. This combination makes PLGA a preferred system for sensitive and powerful drug substances.
Key reasons include:
- Biodegradability: PLGA breaks down into lactic and glycolic acid naturally.
- Long-acting delivery: Release profiles can range from days to months.
- Reduced dosing frequency: Improves compliance and therapeutic adherence.
- Stabilization: Protects fragile actives (peptides, proteins, hormones).
- Safety: Encapsulation reduces occupational exposure risk.
Researchers working on specific release timelines can explore:
- Custom PLGA Release Control → https://resolvemass.ca/custom-plga-release-control/
2: Critical Considerations When Initiating PLGA Microsphere Formulation for HPAPIs
The success of PLGA microsphere formulation starts with understanding API attributes, polymer characteristics, and process risks. HPAPIs require stricter control of powder handling, airborne exposure, and process validation.
Key considerations include:
- API potency class (OEL / OEB requirements)
- Solubility in organic solvents
- Sensitivity to pH, temperature, or shear stress
- Drug loading limits and encapsulation efficiency
- Regulatory guidelines for potent compounds
Operator Safety Requirements
- Negative-pressure containment
- Isolators or RABS systems
- Enclosed mixers and homogenizers
- Respiratory PPE based on OEL class
- Solvent vapor control
For in-depth polymer equivalence and regulatory support:
- Q1/Q2 Polymer Equivalence Assessment → https://resolvemass.ca/q1-q2-polymer-equivalence-assessment/
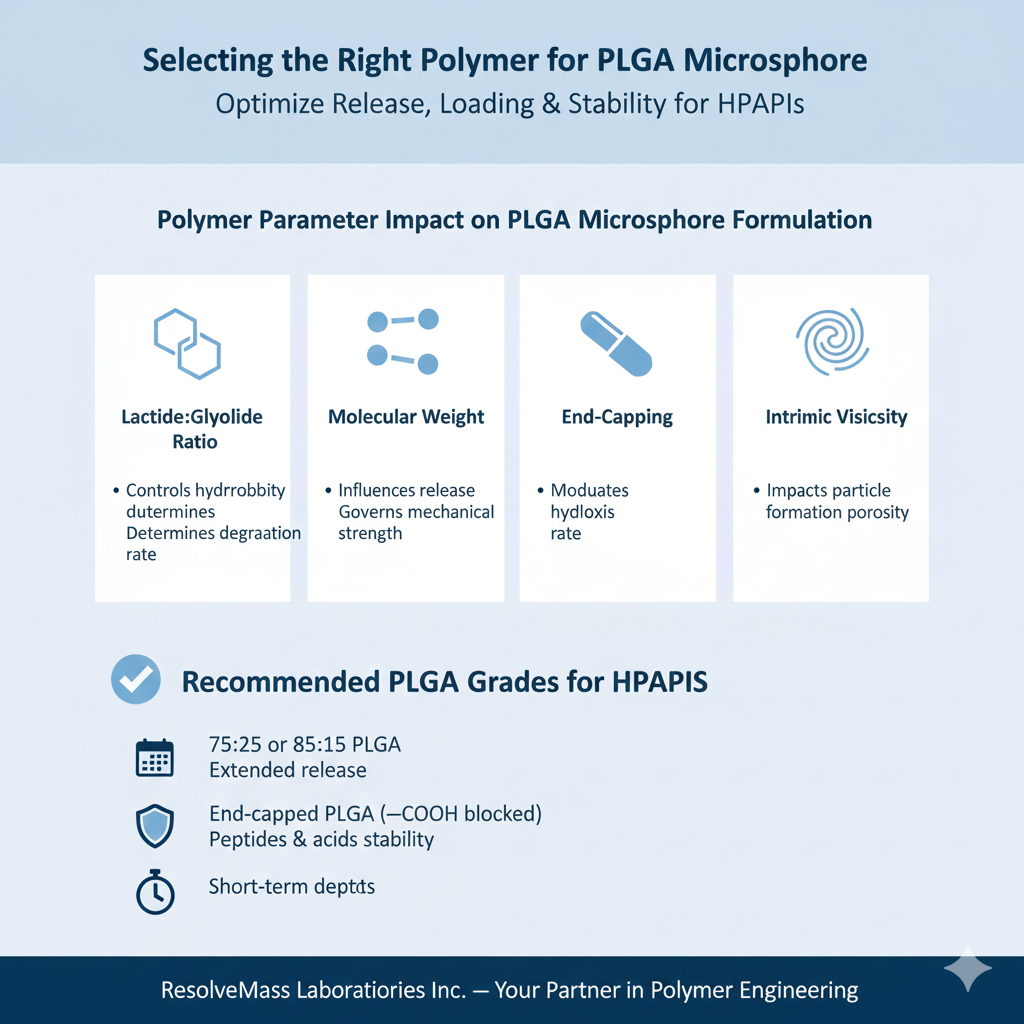
3: Selecting the Right Polymer for PLGA Microsphere Formulation
Choosing the right PLGA polymer determines release rate, drug loading, and microsphere stability for HPAPIs. The polymer’s lactide:glycolide ratio, molecular weight, and end-group chemistry should match both the target release profile and drug–polymer compatibility.
| Polymer Parameter | Impact on PLGA Microsphere Formulation |
|---|---|
| Lactide:Glycolide Ratio | Controls hydrophobicity and degradation rate |
| Molecular Weight | Influences release duration and mechanical strength |
| End-Capping | Affects initial burst and hydrolysis rate |
| Intrinsic Viscosity | Impacts particle formation and porosity |
Detailed PLGA resources:
- PLGA 50:50 Supplier → https://resolvemass.ca/plga-5050-supplier/
- End-Capped PLGA → https://resolvemass.ca/end-capped-plga/
Recommended PLGA Grades for HPAPIs
- 75:25 or 85:15 PLGA for extended release
- End-capped PLGA (–COOH blocked) for peptides and acids
- Low Mw PLGA for short-term depots
ResolveMass Laboratories Inc. provides pharmaceutical-grade PLGA with precise molecular weight control for reproducible performance.
For scale-up strategies:
- PLGA Scale-Up Case Study → https://resolvemass.ca/plga-scale-up-case-study/
4: Drug–Polymer Compatibility Studies in PLGA Microsphere Formulation
Drug–polymer compatibility is assessed upfront to prevent instability, poor encapsulation, or burst release in PLGA microsphere formulation.
Key compatibility evaluation methods:
- Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
- FTIR spectroscopy
- Solubility analysis in organic solvents
- pKa matching and ionization behavior
- Accelerated degradation studies
For detailed solvent insights:
- Dissolving PLGA in Solvents — Complete Guide → https://resolvemass.ca/dissolving-plga-in-solvents/
Drug Properties That Influence Encapsulation Efficiency:
- Partition coefficient
- Hydrophilicity/hydrophobicity
- Acid/base nature
- Molecular weight and charge
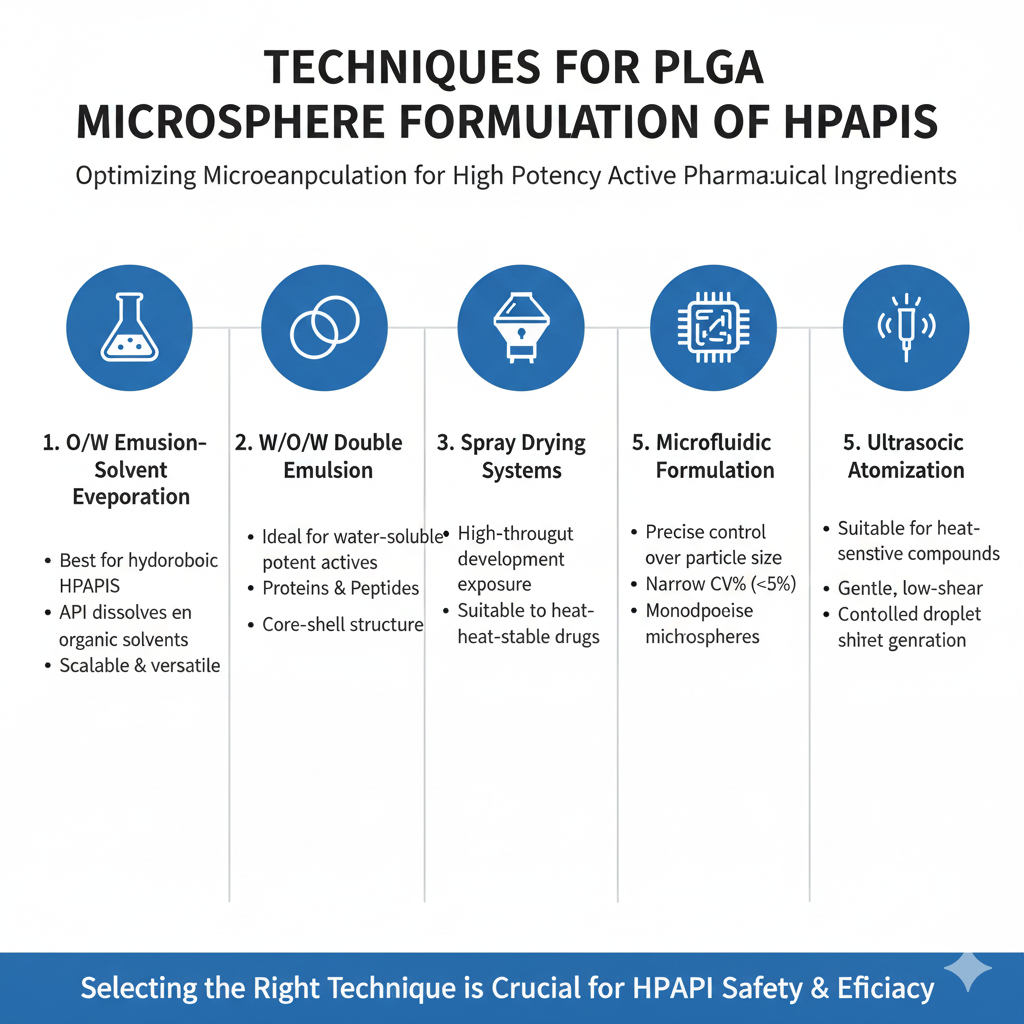
5: Common Techniques Used in PLGA Microsphere Formulation for HPAPIs
PLGA microsphere formulation uses multiple microencapsulation techniques, each suited to API solubility and potency considerations.
1. Oil-in-Water (O/W) Emulsion–Solvent Evaporation
Best for hydrophobic HPAPIs that dissolve in organic solvents.
2. Water-in-Oil-in-Water (W/O/W) Double Emulsion
Ideal for peptides, proteins, and water-soluble potent actives.
3. Spray Drying Systems
Used for high-throughput development with minimized operator exposure.
4. Microfluidic PLGA Microsphere Formulation
Delivers precise control over particle size distribution (narrow CV%).
5. Ultrasonic Atomization
Suitable for heat-sensitive potent compounds.
For peptide-specific microencapsulation methods:
- PLGA Peptide Delivery → https://resolvemass.ca/plga-peptide-delivery/
6: Process Parameters That Control PLGA Microsphere Formulation Quality
Critical process parameters directly determine particle size, release rate, and encapsulation efficiency in PLGA microsphere formulation.
Most Influential Parameters:
- Polymer concentration
- API loading percentage
- Emulsifier concentration (PVA)
- Homogenization speed
- Organic solvent type (DCM, EA, acetone)
- Temperature and mixing conditions
- Solvent evaporation rate
Desired Quality Attributes (QbD Approach):
- Particle size (20–100 µm for injectables)
- PDI < 0.2
- High encapsulation efficiency (>70% typical)
- Predictable release kinetics
- Low residual solvents (ICH Q3C compliance)
For optimized, stable process methods:
- PLGA Formulation Stability → https://resolvemass.ca/plga-formulation-stability/
7: Encapsulation Efficiency Optimization in PLGA Microsphere Formulation
High encapsulation efficiency is essential for costly HPAPIs to reduce manufacturing losses and ensure dosage accuracy.
Strategies to Improve Entrapment:
- Adjust polymer:drug ratio
- Optimize internal aqueous phase volume
- Use stabilizers or pH modifiers
- Reduce drug leakage during emulsification
- Apply low-solubility solvents for HPAPIs
- Increase viscosity of organic phase
Common Challenges:
- Drug burst release
- Low loading capacity
- Peptide instability
- Hydrolysis during emulsification
Properly selected PLGA grades from ResolveMass significantly mitigate these issues.
8: Particle Size and Morphology Requirements for HPAPI PLGA Microsphere Formulation
Particle size determines injectability, depot formation, and release kinetics in PLGA microsphere formulation. Uniform spheres ensure predictable therapeutic outcomes, especially for potent molecules.
Control Strategies:
- Homogenization speed tuning
- PVA concentration optimization
- Solvent evaporation rate control
- Microfluidics for ultra-uniformity
Ideal Morphological Features:
- Smooth surface
- Minimal porosity (controlled release)
- No aggregation or coalescence
- Consistent spherical shape
9: Sterilization and Aseptic Processing for PLGA Microsphere Formulation
HPAPI formulations must be sterile because most PLGA depots are parenterally administered.
Viable Sterilization Approaches:
- Aseptic processing (preferred for PLGA)
- Sterile filtration of polymer solutions
- Gamma irradiation (limited use due to polymer degradation)
- Ethylene oxide (rarely favored due to residual concerns)
Aseptic microsphere production under cGMP conditions remains the industry gold standard.
10: Stability Testing Requirements for HPAPI PLGA Microsphere Formulation
Stability testing ensures long-term performance and safety of PLGA microsphere formulations.
Key Stability Indicators:
- Degradation rate of PLGA polymer
- Residual solvent levels
- API potency and purity
- Microsphere morphology over time
- Release rate consistency
- Moisture absorption levels
Recommended Testing Conditions:
- 25°C/60% RH (long-term)
- 40°C/75% RH (accelerated)
- Light exposure testing
- Freeze–thaw cycles (for peptide depots)
Learn stability principles in detail:
- PLGA Formulation Stability Guide → https://resolvemass.ca/plga-formulation-stability/
11: Regulatory Considerations for Highly Potent PLGA Microsphere Formulation
HPAPI microsphere products must meet stringent global regulatory standards, especially concerning potency handling, GMP, and residual solvents.
Key Regulatory Frameworks:
- ICH Q3C (Residual Solvents)
- ICH Q8–Q10 (QbD, risk management)
- FDA Guidance on Long-Acting Injectables
- Occupational Exposure Limit (OEL) compliance
- EU Annex 3 for sterile products
ResolveMass products support DMF referencing and are suitable for GMP microencapsulation workflows.
For polymer comparability and regulatory alignment:
- Q1/Q2 Polymer Equivalence Assessment → https://resolvemass.ca/q1-q2-polymer-equivalence-assessment/
12: Case Applications of PLGA Microsphere Formulation for HPAPIs
Several therapeutic areas rely on PLGA microsphere formulation to manage potent drugs safely and effectively.
Major Use Cases:
- Oncology sustained-release depots
- Peptide hormone delivery (e.g., LH-RH analogs)
- CNS and pain-management depots
- Immunomodulatory potent APIs
- Novel biologic fragments and therapeutic peptides
Scientifically validated methods are outlined in:
- PLGA Peptide Delivery → https://resolvemass.ca/plga-peptide-delivery/
- PLGA Depot Formulation → https://resolvemass.ca/plga-depot-formulation/
13: Why Partner with ResolveMass Laboratories Inc. for PLGA Microsphere Formulation?
ResolveMass Laboratories Inc. provides high-purity PLGA polymers, technical guidance, and reliable global support for PLGA microsphere formulation programs involving highly potent APIs.
What Makes ResolveMass a Trusted Partner:
- Consistent, high-purity PLGA with DMF support
- Deep experience in polymer science and microencapsulation
- Reliable global supply chain
- Technical advisory for formulation scientists
- Fast response and scientific support
You may also explore:
- Custom PLGA Release Control → https://resolvemass.ca/custom-plga-release-control/
- PLGA Scale-Up Case Study → https://resolvemass.ca/plga-scale-up-case-study/
CONCLUSION:
PLGA microsphere formulation remains the cornerstone technology for safely and effectively delivering highly potent APIs. By offering controlled release, improved safety, and tunable pharmacokinetics, PLGA enables the next generation of long-acting injectables. With the right polymer grade, optimized microencapsulation strategy, and scientific support from ResolveMass Laboratories Inc., development timelines become faster, safer, and more predictable.
FAQs on Highly Potent APIs Using PLGA Microspheres
PLGA microspheres are suitable for HPAPIs because they encapsulate the drug inside a biodegradable polymer matrix, minimizing peak plasma concentrations and systemic toxicity. For HPAPIs, PLGA’s controlled degradation ensures sustained release, reducing dosing frequency and improving patient safety. Its biocompatibility, FDA acceptance, and predictable hydrolysis make it a preferred system for potent and sensitive molecules.
Polymer composition directly controls degradation rate. Higher glycolic content (e.g., PLGA 50:50) degrades faster due to increased hydrophilicity, providing shorter release durations. Higher lactide ratios (e.g., PLGA 75:25, 85:15) degrade more slowly, enabling long-term depots. Polymer end-capping, molecular weight, and intrinsic viscosity further fine-tune the release kinetics for HPAPIs.
Key challenges include maintaining API stability during solvent exposure, preventing dose dumping, achieving high encapsulation efficiency, and ensuring minimal operator exposure due to potency hazards. Additional difficulties involve controlling particle size, preventing acid-induced degradation inside PLGA, and selecting the right emulsification or spray-drying technique for each API class.
The most used methods are single emulsion (O/W) for hydrophobic APIs, double emulsion (W/O/W) for peptides and hydrophilic APIs, spray drying for heat-stable molecules, and microfluidics for precision-controlled microspheres. Each method affects encapsulation efficiency, stability, and final release profile—critical for HPAPI safety and consistency.
Terminal sterilization is generally avoided because heat, radiation, and steam degrade PLGA chains and destabilize potent APIs. Therefore, manufacturers rely on aseptic processing, sterile filtration of components, low-temperature solvent evaporation, and final aseptic drying. This approach preserves polymer integrity and ensures HPAPI safety.
Reference
- Han, F. Y., Thurecht, K. J., Whittaker, A. K., & Smith, M. T. (2016). Bioerodable PLGA-based microparticles for producing sustained-release drug formulations and strategies for improving drug loading. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 7, 185.https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2016.00185
- Makadia, H. K., & Siegel, S. J. (2011). Poly lactic-co-glycolic acid (PLGA) as biodegradable controlled drug delivery carrier. Polymers, 3(3), 1377–1397.https://doi.org/10.3390/polym3031377
- Danhier, F., Ansorena, E., Silva, J. M., Coco, R., Le Breton, A., & Préat, V. (2012). PLGA-based nanoparticles: An overview of biomedical applications. Journal of Controlled Release, 161(2), 505–522.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2012.01.043

