
Introduction
Custom polymer synthesis has become a cornerstone for various industries, including healthcare, electronics, energy, and sustainability. This evolving sector is fueled by growing demand for tailored materials that meet specific performance criteria, regulatory compliance, and environmental considerations.
In this article, we analyze the market dynamics, trends, challenges, and future projections of the global custom polymer synthesis
Key Takeaways
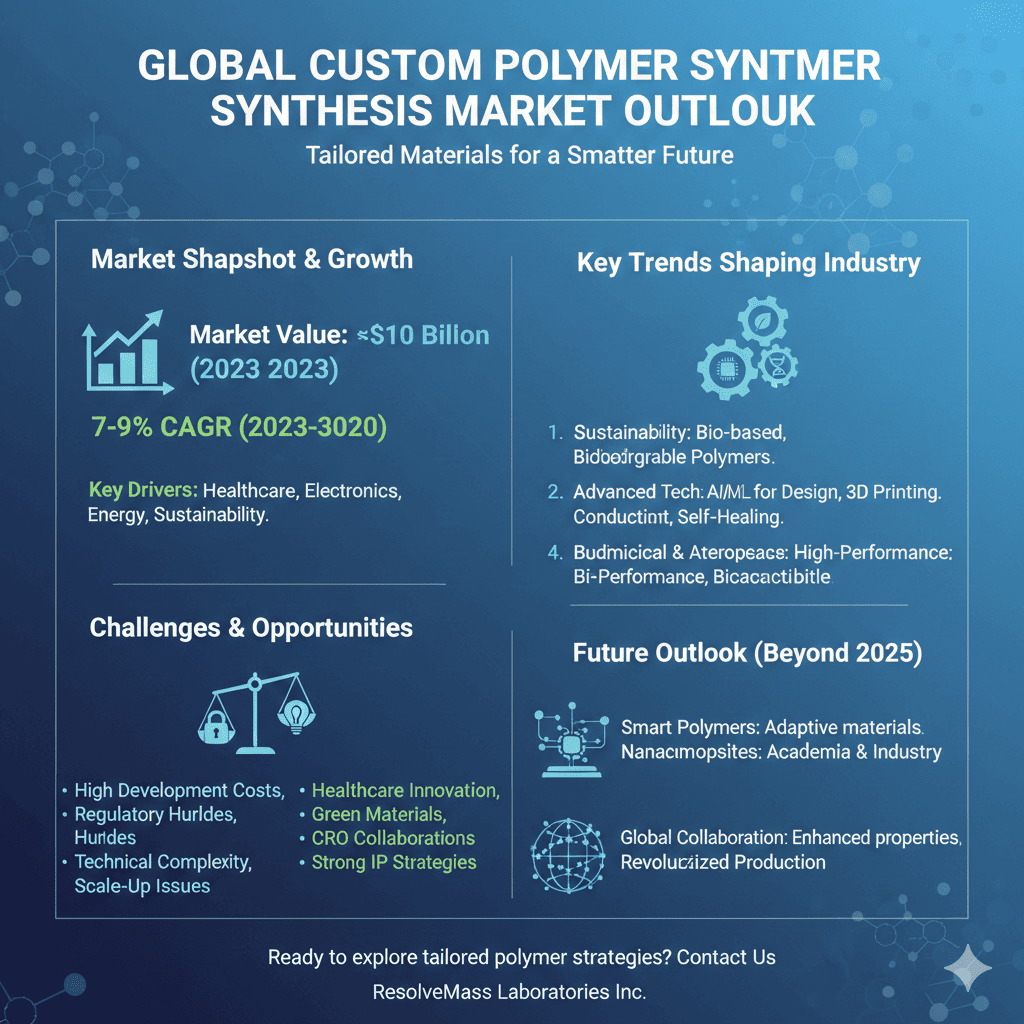
- Future growth beyond 2025 will be led by smart polymers, nanocomposites, and global industry collaborations.
- The global custom polymer synthesis market is valued at ~$10 billion (2023) and is expected to grow at a 7–9% CAGR through 2030, driven by healthcare, electronics, energy, and sustainability needs.
- Sustainability, regulatory compliance, and advanced technologies such as AI and 3D printing are reshaping polymer design and production.
- Demand for functional and high-performance polymers is rising across biomedical, aerospace, electronics, and renewable energy applications.
- Challenges include high development costs, regulatory hurdles, technical complexity, and scaling from lab to commercial production.
- Opportunities are expanding through healthcare innovation, green materials, CRO collaborations, and strong intellectual property strategies.
1. Market Size and Growth Potential
Current Market Overview
The global custom polymer synthesis market was valued at approximately $10 billion in 2023, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7-9% projected through 2030. Key factors driving growth include:
- Increasing applications in healthcare and drug delivery.
- Rising demand for sustainable materials.
- Advancements in polymer technology, including nanostructured and functional polymers.
Explore why polymer synthesis plays such a key role in making these advanced materials possible – The Importance of Polymer Synthesis in Modern Science and Technology
Regional Insights
- North America: Leads in innovation, driven by strong demand in pharmaceuticals and electronics.
- Europe: Focused on sustainable polymers due to stringent environmental regulations.
- Asia-Pacific: The fastest-growing region, fueled by manufacturing, automotive, and packaging industries.
- Middle East & Africa: Emerging markets with opportunities in construction and oil & gas.
1.1 Role of Custom Polymer Synthesis in Supply Chain Resilience
The global disruptions experienced in recent years have highlighted the importance of resilient and flexible supply chains. Custom polymer synthesis plays a critical role by enabling manufacturers to localize production, reduce dependency on single-source raw materials, and adapt formulations based on regional availability. This flexibility allows companies to maintain consistent product performance even when traditional feedstocks or suppliers face disruptions.
Additionally, customized polymers enable faster response times to market fluctuations. Manufacturers can rapidly adjust polymer compositions to meet changing regulatory standards, customer requirements, or logistics constraints. As a result, organizations that invest in in-house or outsourced custom polymer capabilities gain a strategic advantage in managing risk while maintaining continuity across global operations.
1.2 Impact of Regulatory Frameworks on Market Expansion
Regulatory policies significantly influence the pace and direction of custom polymer synthesis adoption. Governments across regions are implementing stricter controls on material safety, recyclability, and environmental impact. While compliance can initially increase development costs, it also drives innovation by encouraging safer, cleaner, and more efficient polymer formulations.
In the long term, harmonized international standards are expected to benefit market growth. Companies that proactively align their synthesis processes with regulatory expectations gain faster market access and improved customer trust. This regulatory-driven innovation is particularly evident in medical-grade polymers, food-contact materials, and environmentally certified products.
2. Key Trends Shaping the Industry
2.1 Sustainability as a Driving Force
The shift towards eco-friendly polymers is transforming the market. Companies are focusing on biodegradable polymers, bio-based alternatives, and circular economy solutions.
- Example: Bio-derived polyethylene (PE) and polylactic acid (PLA) are being adopted in packaging and agriculture.
- Market Impact: The biodegradable polymer segment is expected to grow at a CAGR of over 12% by 2030.
The foundation of eco-friendly polymers starts with the right monomers, the guide Monomer Selection Strategies for Custom Polymer Synthesis explains how.
2.2 Integration with Advanced Technologies
Emerging technologies such as AI, machine learning, and 3D printing are revolutionizing polymer design and production.
- AI enables rapid prototyping by predicting polymer properties based on molecular structure.
- Additive manufacturing requires polymers with precise flow and curing properties.
Here’s a closer look at how artificial intelligence is being used to create better, more efficient polymers 👉 How AI Is Revolutionizing Custom Polymer Synthesis
2.3 Functional Polymers for Specialized Applications
The demand for polymers with unique properties, such as conductivity, self-healing, or responsiveness to external stimuli, is growing.
- Example: Conductive polymers for flexible electronics.
- Application: These materials are pivotal in renewable energy, IoT devices, and medical diagnostics.
2.4 Custom Polymers in Biomedical Engineering and Implants
Biomedical engineering has emerged as a major growth avenue for custom polymer synthesis. Tailored polymers are being designed to match specific mechanical properties, degradation rates, and biocompatibility requirements for implants and prosthetics. These materials enable better integration with human tissue, reducing rejection risks and improving patient outcomes.
Furthermore, advances in polymer chemistry allow for surface modifications that promote cell adhesion and controlled biological responses. Custom polymers are now being used in orthopedic implants, cardiovascular devices, and wound healing matrices. This trend reflects a broader shift toward personalized medical solutions supported by precision material design.
2.5 High-Performance Polymers for Aerospace and Defense
The aerospace and defense sectors demand materials that can withstand extreme conditions, including high temperatures, mechanical stress, and chemical exposure. Custom polymer synthesis enables the development of lightweight yet durable materials that meet stringent performance and safety standards. These polymers contribute to fuel efficiency, extended service life, and enhanced structural integrity.
In defense applications, customized polymers are used in protective coatings, radar-absorbing materials, and advanced composites. Their ability to be engineered for specific functional properties makes them indispensable in next-generation aircraft, satellites, and military equipment. As global investment in aerospace technology grows, demand for specialized polymers is expected to rise steadily.
3. Challenges and Opportunities
Challenges
- Cost Constraints: Custom polymer synthesis can be expensive, particularly for small-scale production.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Stringent safety and environmental regulations, especially in the EU and US, increase development timelines.
- Technical Complexity: Developing polymers with specific molecular structures demands advanced expertise and equipment.
Opportunities
- Healthcare Applications: Innovations in drug delivery systems, biocompatible materials, and tissue engineering offer significant growth potential.
- Sustainability Initiatives: Governments and industries are investing heavily in green materials, opening avenues for biodegradable and recyclable polymers.
- Collaboration and Outsourcing: Custom polymer synthesis contract research organizations (CROs) are bridging the gap for startups and mid-sized firms by offering expertise and scalable solutions.
See how current challenges are actually creating new opportunities for innovation and growth 👉 Top Challenges and Opportunities in Custom Polymer Synthesis
3.1 Scaling from Laboratory to Commercial Production
One of the most critical challenges in custom polymer synthesis is transitioning from laboratory-scale development to commercial-scale manufacturing. Polymers that perform well in small batches often face consistency and quality issues when scaled up. Factors such as reaction kinetics, heat transfer, and impurity control become increasingly complex at larger volumes.
However, this challenge also presents opportunities for innovation in process engineering and automation. Continuous polymerization techniques, advanced reactors, and real-time monitoring systems are helping manufacturers achieve reproducibility at scale. Companies that successfully bridge this gap can significantly reduce time-to-market while maintaining high product quality.
3.2 Intellectual Property as a Competitive Advantage
Intellectual property (IP) plays a vital role in the custom polymer synthesis market. Proprietary polymer formulations, synthesis methods, and application-specific designs provide companies with long-term competitive differentiation. Strong IP portfolios not only protect innovations but also increase company valuation and partnership opportunities.
Moreover, collaborative research between CROs, academic institutions, and industrial partners is generating shared IP models. These collaborations accelerate innovation while distributing risk. As competition intensifies, strategic IP management is becoming just as important as technical expertise in sustaining market leadership.
4. Industry Applications Driving Growth
4.1 Pharmaceuticals and Biotechnology
Custom polymers are transforming drug delivery systems, enabling targeted therapies and controlled release mechanisms.
- Example: PEGylated polymers enhance drug stability and solubility.
- Market Impact: The pharmaceutical polymer market is expected to reach $5 billion by 2028.
Want to know how polymer science supports pharma and biotech? Start with this in – depth look at deuterated polymers
4.2 Electronics and Advanced Materials
The demand for lightweight, durable, and functional polymers is surging in the electronics sector.
- Example: Polymers used in flexible OLED screens and dielectric layers for microelectronics.
4.3 Packaging and Consumer Goods
Sustainable packaging solutions, such as bio-based polymers, are becoming mainstream in response to consumer demand and regulatory pressures.
4.4 Energy Sector
Custom polymers are critical in renewable energy technologies, such as fuel cells, solar panels, and energy storage systems.
- Example: Polymer membranes for hydrogen fuel cells.
4.5 Automotive and Mobility Applications
The automotive industry is increasingly adopting custom polymers to meet evolving performance, safety, and sustainability requirements. Lightweight polymer components help improve fuel efficiency and extend the range of electric vehicles. Customized materials are also used in battery housings, interior components, and advanced sealing systems.
Beyond weight reduction, polymers engineered for thermal stability and chemical resistance enhance vehicle durability. As mobility solutions shift toward electrification and autonomous technologies, demand for application-specific polymers will continue to grow, reinforcing the role of custom synthesis in future transportation systems.
4.6 Construction and Infrastructure Development
Custom polymers are gaining traction in construction and infrastructure due to their durability, corrosion resistance, and design flexibility. Tailored polymer materials are used in coatings, adhesives, insulation, and composite reinforcements, offering longer service life compared to traditional materials.
Infrastructure projects increasingly require materials that can withstand harsh environmental conditions while minimizing maintenance costs. Custom polymer synthesis enables the development of solutions optimized for specific climates and structural demands. This trend is particularly relevant in large-scale urban development and smart infrastructure initiatives worldwide.
5. Future Outlook: Trends Beyond 2025
- Smart Polymers: Materials that adapt to environmental conditions, including temperature-sensitive hydrogels for drug delivery.
- Nanocomposite Polymers: Enhanced mechanical, thermal, and electrical properties for advanced manufacturing.
- Global Collaboration: Cross-border partnerships between academia, industry, and CROs to accelerate innovation.
See how innovations in polymer design and development are likely to grow after 2025 👉 Emerging Trends in Custom Polymer Synthesis for 2025 and Beyond
Conclusion
The global market for custom polymer synthesis is poised for significant growth, driven by technological advancements, rising sustainability demands, and expanding applications across industries. However, realizing its full potential will require addressing challenges such as cost, regulatory compliance, and scalability.
For those interested in how his trend extends to the pharmaceutical world, here’s a quick informative read – Why Custom API Synthesis is Essential for Generic and Specialty Pharmaceuticals
For companies looking to capitalize on these opportunities, partnering with specialized service providers like ResolveMass Laboratories Inc. can be a game-changer.
How ResolveMass Can Help
At ResolveMass Laboratories Inc., we offer end-to-end solutions in custom polymer synthesis to help businesses achieve their goals. From sustainable materials to advanced healthcare applications, our expertise ensures you stay ahead of the curve.
- Explore our Custom Polymer Synthesis Services.
- Learn about our Material Characterization Expertise.
- For inquiries, visit our Contact Us page.
Frequently Asked Questions
Custom polymer synthesis focuses on creating bespoke macromolecules with precise architectural control, tailoring properties like molecular weight dispersity, end-group functionality, and tacticity to specific needs. Unlike commercial production, which prioritizes high-volume output of standardized grades (like commodity polyethylene), custom synthesis is typically low-volume and high-value, often used for R&D, medical devices, or specialized coatings. This approach allows researchers to fine-tune material performance for applications where standard commercial polymers would fail to meet rigorous specifications.
Scaling up a custom polymer from a milligram-scale lab reaction to a kilogram-scale pilot batch presents significant hurdles, particularly in managing heat transfer and viscosity changes. As reaction volumes increase, maintaining the precise temperature control required for living polymerization techniques becomes difficult, potentially broadening the molecular weight distribution. Additionally, removing impurities and catalysts to meet pharmaceutical or electronic grade standards becomes exponentially more complex and costly at larger scales.
The selection of a polymerization method dictates the level of control over the polymer’s architecture, including its block structure and chain uniformity. Techniques like Reversible Addition-Fragmentation Chain Transfer (RAFT) or Atom Transfer Radical Polymerization (ATRP) allow for the synthesis of complex block copolymers with narrow polydispersity indices, which is critical for self-assembling materials. In contrast, standard free-radical polymerization is less controlled but more robust, making it suitable for simpler materials where precise chain length is less critical than cost or speed.
Custom synthesis is indispensable in nanomedicine for creating “smart” polymers that can encapsulate drugs and release them in response to specific biological triggers like pH or temperature. By chemically engineering biodegradable backbones or attaching targeting ligands to the polymer chain, scientists can ensure that therapeutic agents are delivered directly to diseased tissue, minimizing systemic side effects. This level of bio-compatibility and functionalization is rarely achievable with generic, unmodified polymers.
The cost is primarily driven by the complexity of the synthetic route, the number of reaction steps, and the purity requirements of the final product. Specialized monomers that are not commercially available must be synthesized first, adding significant labor and material costs to the project before polymerization even begins. Furthermore, rigorous analytical characterization (such as NMR, GPC, or DSC) required to validate the structure and purity adds another layer of expense compared to buying bulk materials.
Custom synthesis enables the design of novel bioplastics and degradable polymers derived from renewable biomass feedstocks rather than fossil fuels. Researchers can specifically engineer polymer chains to have weak links that facilitate chemical recycling or biodegradation under industrial composting conditions, addressing the global plastic waste crisis. This proactive molecular design ensures that the end-of-life handling of the material is built into its chemical structure from the very beginning.
When choosing a partner, it is crucial to assess their specific technical expertise with the required polymerization class (e.g., condensation vs. addition) and their analytical capabilities. A reliable CRO should offer transparent communication regarding intellectual property (IP) ownership and have a proven track record of troubleshooting unexpected synthetic failures. Additionally, their ability to provide comprehensive documentation and certificates of analysis (CoA) is vital for ensuring the material can be used in regulated downstream applications.
References
- SelectScience. (n.d.). Custom Polymer Synthesis. SelectScience. https://www.selectscience.net/product/custom-polymer-synthesis
- Chatard, C. (2021, May). What is custom synthesis & why you should outsource your chemical syntheses? SPECIFIC POLYMERS. https://specificpolymers.com/what-is-custom-synthesis-and-why-you-should-outsource-your-chemical-syntheses/
- Rapp, J. L., Borden, M. A., Bhat, V., Sarabia, A., & Leibfarth, F. A. (2024). Continuous polymer synthesis and manufacturing of polyurethane elastomers enabled by automation. ACS Polymers Au, 4(2), 120–127. https://doi.org/10.1021/acspolymersau.3c00033
- Polysciences, Inc. (n.d.). Polymer synthesis | Tailored solutions for materials innovation. Polysciences. https://polysciences.com/pages/polymer-synthesis

