Introduction
GPC analysis of polymers is a critical analytical technique used to determine molecular weight averages and molecular weight distribution, which directly influence polymer properties such as strength, viscosity, solubility, and processability. In polymer research, manufacturing, and regulatory environments, accurate molecular weight characterization is essential for ensuring product performance and batch-to-batch consistency.
At ResolveMass Laboratories Inc., our extensive experience in polymer characterization allows us to deliver reliable, regulatory-ready GPC analysis of polymers tailored to diverse material classes including synthetic polymers, biopolymers, and specialty materials.
Summary
- GPC analysis of polymers is the gold-standard technique for determining molecular weight distribution and polymer architecture
- Molecular weight parameters such as Mn, Mw, Mz, and PDI directly influence polymer performance, processing, and regulatory acceptance
- GPC (also called SEC) separates polymers based on hydrodynamic volume, not chemical interaction
- Proper method development, column selection, calibration strategy, and detector choice are critical for accurate results
- ResolveMass Laboratories Inc. provides expert-driven, application-specific GPC analysis of polymers for R&D, quality control, and regulatory studies
1: What Is GPC Analysis of Polymers?
GPC analysis is a chromatographic technique used to separate and analyze polymers based on their molecular size in solution. The process involves passing a polymer sample through a column packed with porous beads. Larger molecules elute faster because they cannot enter the pores, while smaller molecules take longer as they travel through the pores.
GPC analysis of polymers is a chromatographic technique that separates polymer molecules based on their size in solution to determine molecular weight distribution.
GPC separates polymer chains according to hydrodynamic volume, enabling precise molecular weight characterization without chemical interaction with the stationary phase.
Key Components of GPC Analysis
- Column: Contains porous beads of specific sizes to separate molecules.
- Mobile Phase: A solvent that carries the sample through the column.
- Detector: Measures the concentration of eluted molecules (e.g., refractive index, UV, or light scattering detectors).
- Data System: Analyzes and interprets the results to determine molecular weight distribution.
- Also known as Size Exclusion Chromatography (SEC)
- Separation is purely entropic, not based on polarity or charge
- Larger molecules elute first; smaller molecules elute later
- Applicable to soluble polymers across multiple industries
2: Principle of GPC Analysis of Polymers
The principle of GPC analysis of polymers is based on size-based separation using porous columns.
How GPC Works (Answered Upfront)
GPC columns contain porous beads that allow smaller polymer chains to penetrate deeper, delaying elution, while larger chains bypass pores and elute earlier.
GPC Workflow
- Polymer dissolution in a suitable solvent
- Injection into GPC column system
- Size-based separation in columns
- Detection and molecular weight calculation
3: Key Molecular Weight Parameters Obtained from GPC Analysis of Polymers
GPC analysis of polymers provides multiple molecular weight averages critical for material characterization.
| Parameter | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Mn | Number average molecular weight | Influences osmotic properties |
| Mw | Weight average molecular weight | Correlates with mechanical strength |
| Mz | Z-average molecular weight | Sensitive to high MW tail |
| PDI (Mw/Mn) | Polydispersity index | Indicates molecular uniformity |
Understanding these parameters helps predict polymer behavior in real-world applications.
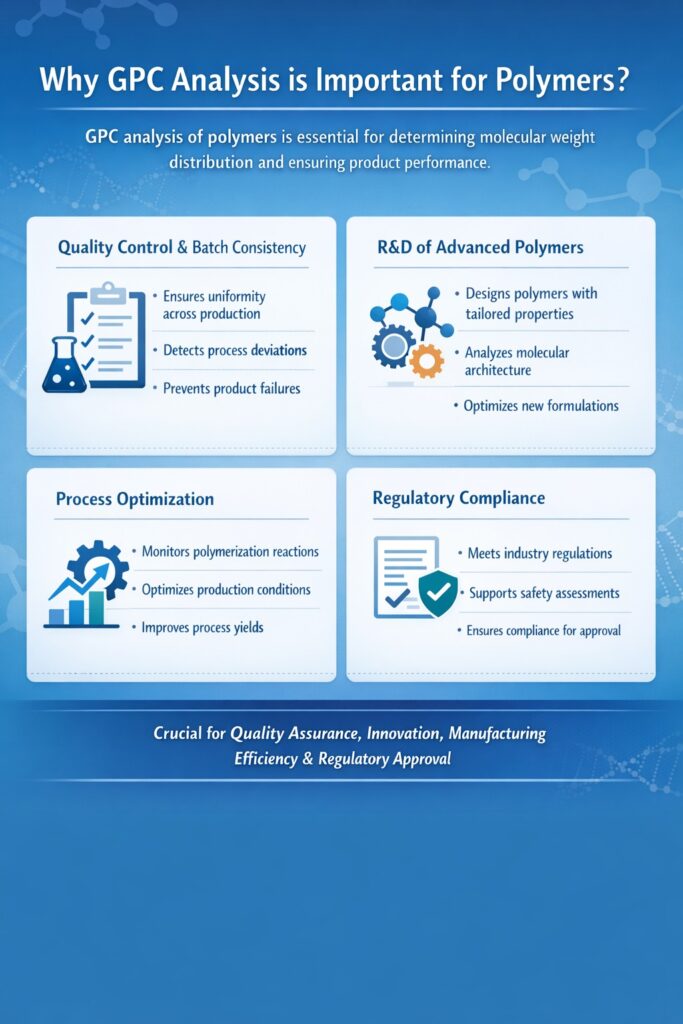
4: Why Is GPC Analysis Important for Polymers?
GPC analysis is important for polymers because molecular weight distribution directly determines their physical performance, processing behavior, and regulatory acceptability. Even polymers with identical chemical composition can behave very differently if their molecular weight profiles vary, making accurate characterization essential.
Gel Permeation Chromatography (GPC) provides quantitative insight into number-average molecular weight (Mn), weight-average molecular weight (Mw), and polydispersity index (PDI), which together define how a polymer will perform in real-world applications.
Key Reasons GPC Analysis Is Critical for Polymers
1. Quality Control and Batch Consistency
GPC analysis ensures polymers consistently meet predefined quality specifications by verifying molecular weight distribution across production batches.
- Confirms batch-to-batch uniformity
- Detects process deviations early
- Prevents performance failures in end-use applications
This is especially critical in industries such as plastics, coatings, elastomers, and pharmaceutical excipients, where even small molecular weight variations can impact product reliability.
2. Research and Development of Advanced Polymers
In polymer R&D, GPC analysis enables structure–property correlation, helping scientists design materials with targeted performance characteristics.
- Supports development of polymers with controlled viscosity, strength, and flexibility
- Assists in evaluating polymer architecture such as branching and chain length
- Enables comparison of formulation or synthesis strategies
By understanding molecular weight distribution, researchers can rationally tailor polymers rather than relying on trial-and-error approaches.
3. Polymerization Monitoring and Process Optimization
GPC analysis plays a vital role in monitoring polymerization reactions and optimizing manufacturing processes.
- Tracks molecular weight growth during polymerization
- Confirms reaction completion and reproducibility
- Helps optimize reaction conditions for yield and performance
This makes GPC an essential tool for scale-up, manufacturing control, and process validation.
4. Regulatory Compliance and Product Approval
Many regulated industries require documented molecular weight characterization as part of compliance and safety assessments.
- Supports regulatory submissions in pharmaceuticals and medical materials
- Ensures compliance for food-contact and packaging polymers
- Provides traceable, auditable data for quality and safety reviews
GPC analysis helps demonstrate that polymers meet regulatory, safety, and performance requirements, reducing approval risks and delays.
5: Techniques Used in GPC Analysis of Polymers
GPC analysis involves several advanced techniques to achieve accurate and reliable results. Below are the key techniques used in polymer characterization:
1. Conventional GPC
Conventional GPC uses a single detector, typically a refractive index (RI) detector, to measure the concentration of eluted molecules. This technique is suitable for routine analysis of polymers.
2. Multi-Detector GPC
Multi-detector GPC combines multiple detectors, such as RI, UV, and light scattering detectors, to provide more comprehensive data. This technique is ideal for complex polymer samples and advanced research.
3. High-Temperature GPC
High-temperature GPC is used for analyzing polymers that require elevated temperatures to dissolve, such as polyethylene and polypropylene. This technique ensures accurate results for high-performance materials.
4. Aqueous GPC
Aqueous GPC uses water as the mobile phase and is specifically designed for analyzing water-soluble polymers, such as polysaccharides and proteins.
5. GPC-MALDI-TOF
GPC coupled with Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Time-of-Flight (MALDI-TOF) mass spectrometry provides detailed information about the molecular weight and structure of polymers.
6: Applications of GPC Analysis in Polymer Science
GPC analysis has a wide range of applications across various industries. Below are some of the key applications:
1. Plastics and Polymers
- Polymer Synthesis: GPC monitors the polymerization process and ensures the desired molecular weight distribution.
- Quality Control: GPC verifies the consistency and performance of plastic materials.
2. Coatings and Adhesives
- Resin Analysis: GPC characterizes the molecular weight of resins used in coatings and adhesives.
- Performance Optimization: GPC helps optimize the properties of coatings and adhesives for specific applications.
3. Pharmaceuticals
- Polymer Excipients: GPC evaluates the molecular weight distribution of polymer excipients used in drug formulations.
- Drug Delivery Systems: GPC analyzes polymeric carriers used in controlled drug delivery systems.
4. Biotechnology
- Biopolymer Analysis: GPC evaluates the molecular weight and structure of biopolymers, such as polysaccharides and proteins.
- Protein Characterization: GPC analyzes the molecular weight and aggregation of proteins, ensuring drug safety and efficacy.
5. Environmental Science
- Polymer Degradation: GPC studies the degradation of polymers in environmental samples.
- Water Treatment: GPC analyzes flocculants and coagulants used in water treatment processes.

7: Advantages of GPC Analysis for Polymers
GPC analysis offers several advantages for polymer characterization:
- High Precision: Provides accurate molecular weight distribution data.
- Versatility: Suitable for a wide range of polymers and applications.
- Speed: Delivers results quickly, enabling efficient decision-making.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensures polymers meet industry standards and regulations.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Helps optimize processes and reduce material waste.
8: Challenges in GPC Analysis
Even though GPC is powerful, expert execution is critical.
Common Challenges
- Polymer-column interactions
- Incomplete dissolution
- Incorrect calibration standards
- Detector sensitivity limitations
Our team mitigates these challenges through method development, orthogonal detection, and scientific review, reinforcing the trustworthiness of results.
9: Why Choose ResolveMass Laboratories for GPC Analysis?
At ResolveMass Laboratories, we specialize in GPC analysis of polymers. Our state-of-the-art facilities and experienced team ensure accurate and reliable results. Here’s why clients choose us:
- Advanced Techniques: We use multi-detector GPC, high-temperature GPC, and GPC-MALDI-TOF for comprehensive analysis.
- Industry Expertise: Our team has extensive experience in polymer science and related industries.
- Regulatory Compliance: We adhere to ISO, FDA, and other regulatory standards.
- Customized Solutions: We tailor our services to meet your specific needs.
- Fast Turnaround: We deliver results quickly without compromising accuracy.
Conclusion
GPC analysis of polymers remains the cornerstone technique for molecular weight characterization, enabling informed material design, regulatory confidence, and product reliability. From early-stage R&D to commercial quality control, accurate GPC data drives better polymer decisions.
At ResolveMass Laboratories Inc., our scientifically grounded, experience-driven approach ensures your GPC analysis of polymers meets the highest standards of accuracy, reproducibility, and trust.
Reference
- Izunobi JU, Higginbotham CL. Polymer molecular weight analysis by 1H NMR spectroscopy. Journal of Chemical Education. 2011 Aug 1;88(8):1098-104.
- Wiley. Characterization and analysis of polymers. John Wiley & Sons; 2008 Feb 8.
- Neira‐Velázquez MG, Rodríguez‐Hernández MT, Hernández‐Hernández E, Ruiz‐Martínez AR. Polymer molecular weight measurement. Handbook of polymer synthesis, characterization, and processing. 2013 Feb 25:355-66.
- Podzimek S. The use of GPC coupled with a multiangle laser light scattering photometer for the characterization of polymers. On the determination of molecular weight, size and branching. Journal of applied polymer science. 1994 Oct 3;54(1):91-103.
PK and TK Bioanalysis: What Regulators Expect from CRO Data
Introduction: In modern drug development, PK TK bioanalysis is one of the most scrutinized scientific…
How Bioanalytical Data Supports IND-Enabling Studies
Introduction: IND enabling Bioanalytical Studies are the scientific proof that a drug can be safely…
Where to Buy Deuterated Benzene-d6 for OLED Material Research?
Introduction: If you are planning to Buy Deuterated Benzene-d6 for OLED material research, it is…
High-Purity Deuterated Benzene-d6 for OLED Applications: Specifications, Purity & Bulk Supply
Introduction: High-purity Deuterated Benzene-d6 for OLED Application plays a key role in the development of…
Case Study: Identifying Unknown Impurities using High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry
Introduction: Identifying Unknown Impurities by HRMS is one of the most powerful analytical approaches in…
Advanced Technical Strategies in the Contract Manufacturing of Peptide-Oligonucleotide Conjugates
Introduction: Peptide Oligonucleotide Conjugate Manufacturing is a highly specialized process that combines peptide chemistry with…