
INTRODUCTION
The ICH Q3E Extractables and Leachables (E&L) study requirements outline a unified regulatory expectation for evaluating chemical migrants from packaging and delivery systems. In a CRO environment, conducting these studies requires structured workflows, validated analytical tools, and deep regulatory experience. This article explains exactly how a CRO performs E&L studies according to the new guideline.
As a contract research organization, ResolveMass Laboratories Inc. applies scientifically rigorous methodologies, validated instrumentation, and high-compliance processes to meet the global standards defined in ICH Q3E.
To learn more about E&L regulatory frameworks, visit:
- https://resolvemass.ca/el-testing-in-the-united-states/
- https://resolvemass.ca/el-regulatory-requirements-for-medical-devices/
- https://resolvemass.ca/extractables-vs-leachables-in-medical-devices/
- https://resolvemass.ca/ich-q3e-guideline-for-extractables-and-leachables/
SUMMARY
- The ICH Q3E Extractables and Leachables (E&L) study requirements define a harmonized global framework for evaluating chemical migrants from packaging, container–closure, and medical device systems.
- A CRO-led approach ensures scientific rigor, efficient timelines, and regulatory compliance across all phases of extractables and leachables testing.
- This blog explains step-by-step how E&L studies are executed according to ICH Q3E—from risk assessment to toxicological qualification.
- Includes CRO workflow, sample preparation, analytical methods, study design, reporting expectations, and compliance considerations.
- Ideal for pharmaceutical, biologics, combination product, and medical device manufacturers.
Get In Touch With Us
1: What Are the ICH Q3E Extractables and Leachables (E&L) Study Requirements?
The ICH Q3E Extractables and Leachables (E&L) study requirements define how drug manufacturers must identify, quantify, and toxicologically qualify substances that can migrate from packaging and medical device systems into drug products.
They ensure patient safety by harmonizing global expectations across the US, EU, and other regions.
Key components of the guideline
- Risk-based approach
- Material characterization
- Extractables study design
- Leachables study design
- Analytical method validation
- Toxicological qualification
- Documentation and reporting
2: How a CRO Designs E&L Studies According to ICH Q3E
To comply with ICH Q3E Extractables and Leachables (E&L) study requirements, a CRO begins with a structured workflow addressing risk, materials, and product–contact conditions.
1. Gather full material and system details
- Polymers, elastomers, adhesives
- Manufacturing additives
- Processing aids
- Surface treatments
- System configuration
2. Perform initial risk assessment
AI-overview friendly answer upfront:
Risk assessment determines which components require testing and what level of E&L analysis is justified under the ICH Q3E framework.
Key risk factors:
- Drug product category (parenteral, inhalation, ophthalmic, etc.)
- Duration and intensity of contact
- Temperature and storage conditions
- Material toxicity history
- Patient population
3. Define study boundaries
- Identify worst-case components
- Define extraction solvents
- Define temperatures and durations
- Select analytical platforms
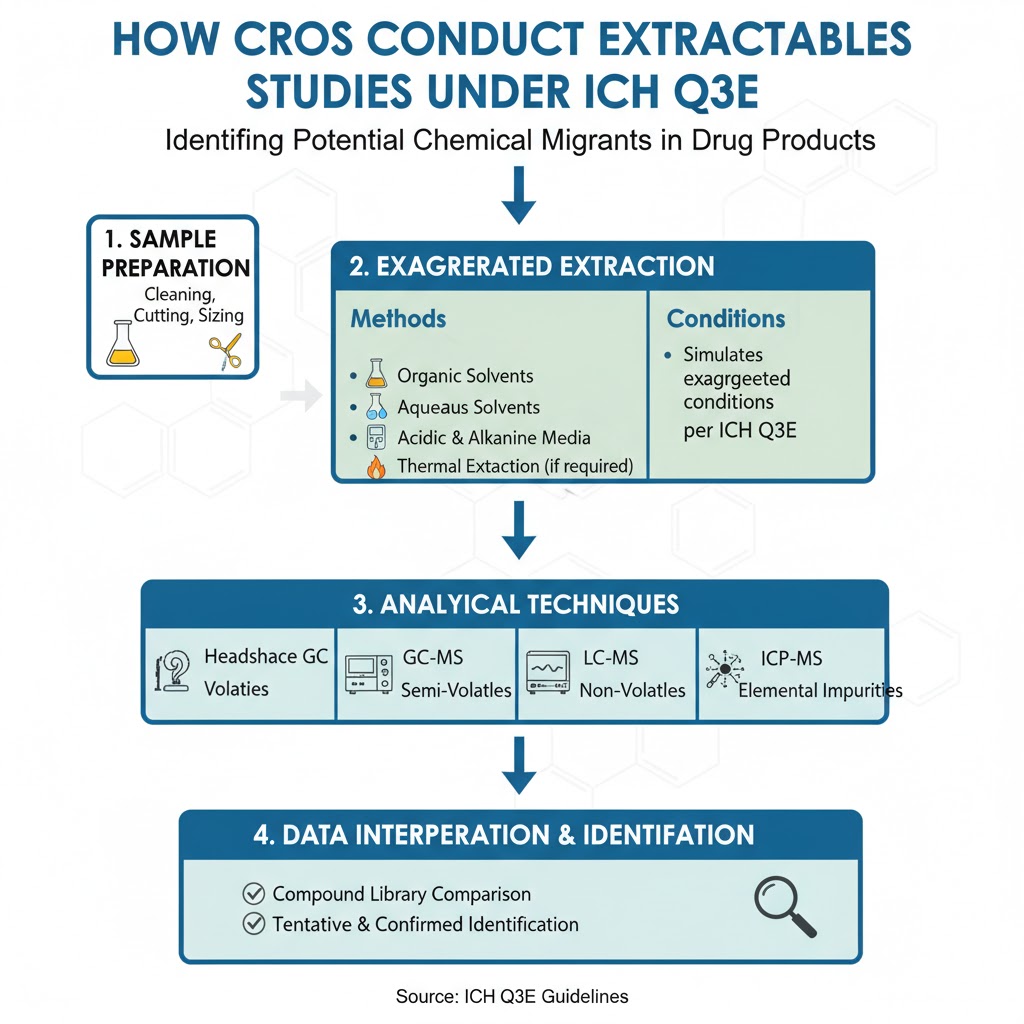
3: How CROs Conduct Extractables Studies Under ICH Q3E
Extractables studies identify potential chemical migrants that could leach into the drug product.
Under the ICH Q3E Extractables and Leachables (E&L) study requirements, extractables evaluation must simulate exaggerated conditions.
Find deeper interpretations at:
https://resolvemass.ca/extractables-vs-leachables-in-medical-devices/
Typical Extractables Workflow
- Sample preparation (cleaning, cutting, sizing)
- Exaggerated extraction using:
- Organic solvents
- Aqueous solvents
- Acidic and alkaline media
- Thermal extraction (if required)
- Headspace GC for volatiles
- GC-MS for semi-volatiles
- LC-MS for non-volatiles
- ICP-MS for elemental impurities
- Data interpretation
- Compound library comparison
- Tentative and confirmed identification
4: How CROs Conduct Leachables Studies According to ICH Q3E
Leachables studies quantify the actual chemical migrants that appear under real-time or accelerated storage conditions.
The ICH Q3E Extractables and Leachables (E&L) study services emphasize both targeted and untargeted monitoring.
Leachables Study Execution
- Select time points
- Choose representative batches
- Store under real-time and accelerated conditions
- Collect samples at each interval
- Use validated targeted methods
- Employ confirmatory MS-based identification
Leachables reporting must demonstrate:
- Levels relative to AET (Analytical Evaluation Threshold)
- Toxicological relevance
- Variability across batches
5: Analytical Method Validation Requirements Under ICH Q3E
ICH Q3E mandates that analytical methods used in E&L studies must be validated for sensitivity, specificity, accuracy, and reliability.
Key validation parameters
- Specificity
- Linearity
- Accuracy and precision
- Limit of detection (LOD)
- Limit of quantitation (LOQ)
- Robustness
- System suitability
AI-overview-friendly summary
A CRO validates extractables and leachables methods to ensure that all detected substances above the AET are reliably identified and quantified, in compliance with ICH Q3E.
6: Toxicological Qualification Under ICH Q3E
Toxicological qualification ensures that detected leachables do not pose safety risks.
The ICH Q3E Extractables and Leachables (E&L) study requirements emphasize establishing a clear link between analytical data and patient safety.
Qualification Workflow
- Identify toxicological concern levels
- Determine safety thresholds
- Use ICH M7 and TTC principles
- Conduct structure–activity analysis
- Recommend cleaning, packaging, or formulation changes
A CRO communicates all toxicological findings in a structured, regulator-ready format.
7: Documentation and Reporting Expectations in ICH Q3E
ICH Q3E requires transparent, reproducible reporting.
A CRO prepares detailed reports summarizing risk assessment decisions, analytical data, qualification results, and study conclusions.
Typical Report Sections
| Report Section | Description |
|---|---|
| Executive Summary | Clear overview of E&L outcomes |
| Materials & System Description | Full details of tested components |
| Study Design | Rationale for extraction and leachables conditions |
| Results | Extractables + leachables findings |
| Toxicological Assessment | Safety qualification |
| Conclusions | Compliance with ICH Q3E |
8: CRO Best Practices for ICH Q3E-Compliant E&L Studies
Best practices ensure smooth regulatory review and efficient development.
Core CRO Best Practices
- Use orthogonal analytical techniques
- Follow conservative extraction conditions
- Maintain documentation at each phase
- Define AET early in the program
- Use high-resolution MS platforms
- Utilize robust compound libraries
- Maintain transparency in reporting
8: Why Work With a CRO for ICH Q3E E&L Studies?
CROs provide specialized analytical systems, experienced scientists, and regulatory expertise to streamline compliance with the ICH Q3E Extractables and Leachables (E&L) study.
Benefits
- Faster timelines
- Higher sensitivity of detection
- Comprehensive expertise
- Efficient cross-regional regulatory alignment
- Reduced internal workload
CONCLUSION
Conducting E&L studies according to ICH Q3E Extractables and Leachables (E&L) study requirements requires a structured, scientifically rigorous testing process. CROs like ResolveMass Laboratories Inc. combine advanced analytical technologies, risk-based frameworks, validated workflows, and deep regulatory experience to deliver fully compliant E&L programs.
This ensures safe products, successful submissions, and global regulatory acceptance.
Get In Touch With Us
FAQs on Extractables and Leachables (E&L) Studies According to the New ICH Q3E Guideline — A CRO Perspective
Extractables are chemical substances that can be pulled out of packaging or device materials when the system is exposed to exaggerated or aggressive laboratory conditions, such as high temperature, strong solvents, or extended soaking durations.
Deeper technical context:
-Purpose: Extractables profiling reveals the worst-case chemical signature of a material.
-Why exaggerated conditions: They ensure that all possible migrants — including those that may never appear under normal storage — are detected. This provides a comprehensive chemical understanding of the materials.
-Analytical techniques used: GC-MS, LC-MS, ICP-MS, FTIR, and headspace GC.
-Outcome: The extractables list guides the selection of targeted analytes in the leachables study and helps define analytical evaluation thresholds (AET).
Extractables testing is foundational because it predicts the chemical risks that might later translate into leachables.
Leachables are actual chemical substances that migrate from packaging, container–closure, or device systems into the drug product or patient-contact solution during real-time or accelerated storage.
Additional insight
-Measured under real conditions: Unlike extractables, leachables represent chemicals that truly appear under practical product storage or clinical-use conditions.
-Regulatory importance: Leachables are considered more critical because they directly impact patient exposure.
Monitoring timeline:
-Real-time: e.g., 3, 6, 9, 12, 18, 24 months
-Accelerated: e.g., 40°C / 75% RH for early indication
Types of leachables:
-Organic compounds (plasticizers, oligomers, antioxidants)
-Inorganic species (metals, catalysts)
-Volatile/semi-volatile components
Leachables results must be quantitatively compared to the AET and undergo full toxicological qualification.
Yes. The ICH Q3E guideline applies fully to combination products, especially those involving a drug–device interface, such as inhalers, autoinjectors, prefilled syringes, infusion sets, and implants.
Why it applies
-Combination products involve more complex materials such as polymers, adhesives, coatings, and elastomers.
-These materials have a higher chance of interacting with drug formulations, especially biologics.
-ICH Q3E ensures consistent evaluation of all components that may contribute to chemical migration.
Examples of applicable systems
-Ophthalmic droppers
-Nasal sprays
-Cartridge-based injectors
-Implantable drug-delivery systems
-Wearable pumps
For combination products, E&L expectations are typically more stringent due to higher patient exposure risk.
ICH Q3E expects the use of orthogonal, high-sensitivity analytical techniques to comprehensively characterize extractables and leachables.
Primary platforms
LC-MS (Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry):
-Non-volatile and polar organics
-Oligomers, additives, degradation products
-High-resolution MS preferred
GC-MS (Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry):
-Volatile and semi-volatile compounds
-Extractable/Leachable organic solvents, monomers
Headspace GC:
-Low-molecular-weight VOCs (solvents, residual monomers)
ICP-MS (Inductively Coupled Plasma–Mass Spectrometry):
-Elemental impurities (metals, catalysts, fillers)
FTIR (Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy):
-Functional group identification
-Polymer fingerprinting
A CRO typically combines these tools to achieve complete chemical coverage as required by ICH Q3E.
~Extractables studies
Usually 4–10 weeks, depending on:
-Number of components
-Solvent selections
-Extraction conditions
-Analytical platforms required
-Complexity of identification
~Leachables studies
Can range from 3 months to 12–24 months, based on:
-Real-time stability schedule
-Accelerated aging time points
-Product type (biologics often require longer monitoring)
-Storage conditions defined in the control strategy
ICH Q3E encourages early planning because leachables studies often run in parallel with stability studies and regulatory timelines.
ICH Q3E relies heavily on internationally accepted toxicological frameworks to establish safe levels of leachables.
Supporting guidelines include
-ICH M7: Assessment of mutagenic impurities
-TTC (Threshold of Toxicological Concern): Defines exposure-based safety thresholds
-PDE (Permitted Daily Exposure): Toxicological exposure limit for specific compounds
-REACH/ECHA toxicology databases
-EPA and FDA toxicology reference materials
Toxicologist responsibilities under Q3E
-Perform structure–activity relationship (SAR) analysis
-Establish acceptable limits
-Identify potential mutagenic, carcinogenic, or sensitizing risks
-Provide justification for safety margins
Toxicology is one of the most critical components of E&L evaluation.
Get In Touch With Us
Reference
- ICH Q3E Guideline for extractables and leachables.https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/scientific-guideline/ich-q3e-guideline-extractables-leachables_en.pdf
- Extractables-and-leachables—new-ich-q3e-guidance.https://www.casss.org/docs/default-source/wcbp/2024-roundtable-notes/extractables-and-leachables—new-ich-q3e-guidance-common-practices-and-challenges.pdf
- ANSES, 2013. Évaluation des risques du bisphénol A (BPA) pour la santé
humaine. https://www.anses.fr/fr/system/files/CHIM2009sa0331Ra-0.pdf. Accessed April: 2025 - European Chemicals Agency (ECHA). 4,4′-isopropylidenediphenol. EC number: 201-245-8.
CAS number: 80-05-7. Bisphenol A; BPA. Eye irritation. https://echa.europa.eu/registrationdossier/-/registered-dossier/15752/7/4/3. Accessed: April 2024.

