Introduction: Understanding the Impact of ICH M7(R2) Updates on Nitrosamine Risk Assessment
The Impact of ICH M7(R2) Updates on Nitrosamine Risk Assessment is reshaping how pharmaceutical manufacturers manage genotoxic impurities. Unlike earlier guidance, ICH M7(R2) places clear and direct focus on nitrosamines rather than applying broad impurity limits across different compounds.
The revision expands acceptable intake limits using the latest toxicological and carcinogenicity data. This allows for compound-specific risk management that is based on science rather than overly conservative default thresholds. For a deeper understanding of how acceptable intake limits are determined and applied, explore this guide on acceptable intake for nitrosamines. As a result, decision-making is more accurate and transparent.
Manufacturers are now expected to understand how nitrosamines can form during manufacturing. This includes evaluating raw materials, solvents, reagents, processing conditions, degradation pathways, and potential cross-contamination risks. To learn more about where nitrosamines originate across pharmaceutical processes, review this overview of nitrosamine impurities in pharmaceuticals.
Because of these expectations, impurity control strategies for both APIs and finished drug products must be carefully designed wherever nitrosamine formation is possible.
Quick Summary
- Pharmaceutical manufacturers must update their control strategies and analytical protocols immediately to remain compliant.
- The ICH M7(R2) revision has transformed how nitrosamine risks are assessed, setting stricter impurity control expectations.
- It introduces updated safety limits, new mutagenicity data, and enhanced categorization for nitrosamine impurities.
- The guidance requires integrated impurity risk assessments combining process knowledge, analytical data, and toxicological evaluation.
- ResolveMass Laboratories Inc. enables compliance by providing advanced impurity profiling, risk quantification, and analytical validation aligned with ICH M7(R2).
- The update also encourages global harmonization of risk evaluation frameworks between regulatory agencies.
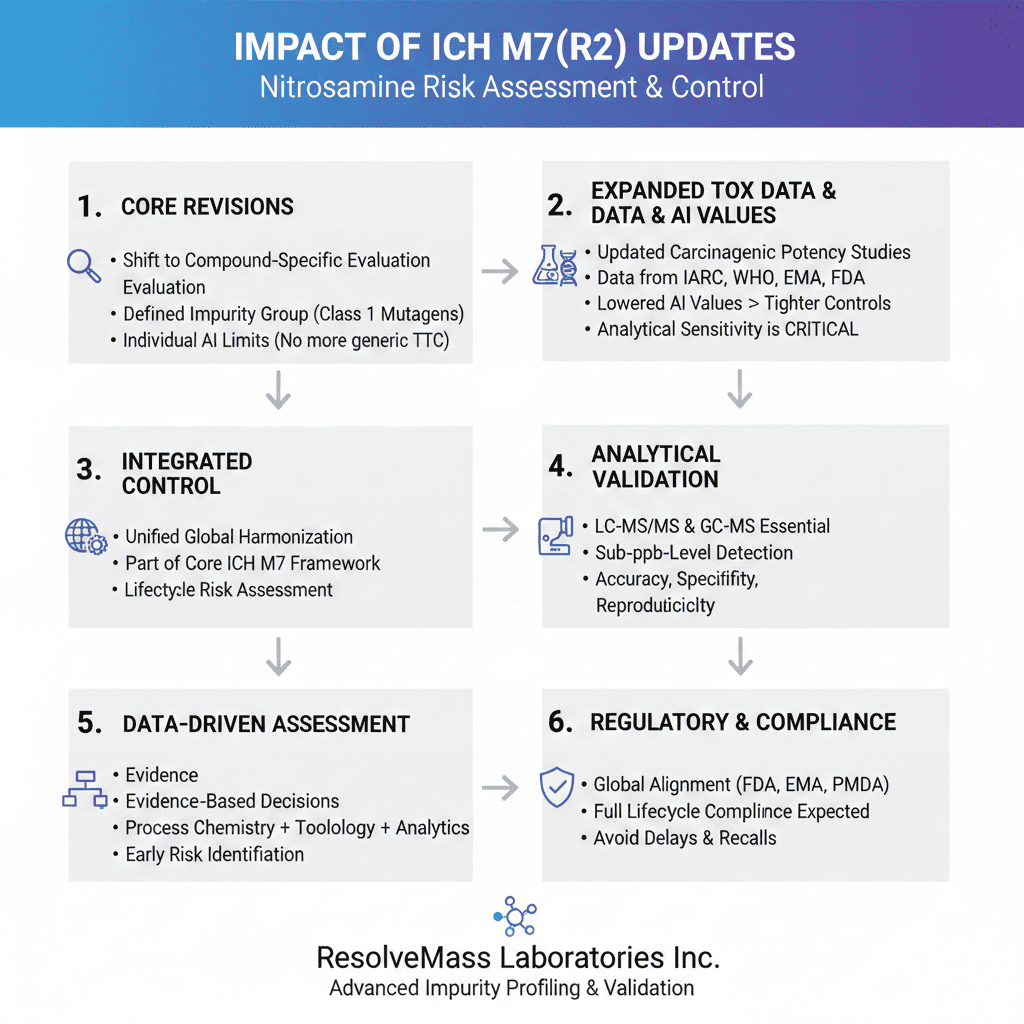
1. Core Revisions in ICH M7(R2): A Shift in Risk Paradigm
ICH M7(R2) builds on the earlier M7(R1) framework by adding newly available nitrosamine data and refining safety thresholds based on scientific evidence. This marks a shift from generalized categorization to compound-specific evaluation.
One major change is the clear classification of nitrosamines as a defined impurity group supported by validated carcinogenic data. This removes uncertainty about how these impurities should be handled during regulatory review and aligns closely with global regulatory expectations, as outlined in this summary of global guidelines for nitrosamine testing.
The guideline also moves away from a single Threshold of Toxicological Concern (TTC). Instead, it introduces individual acceptable intake limits for many nitrosamines, reflecting their true potency and risk.
Additionally, ICH M7(R2) uses data from multiple global scientific and regulatory sources. This improves consistency and reliability in risk assessment across different regions.
ICH M7(R2) requires compound-specific nitrosamine evaluation using real toxicological data instead of generic TTC values
2. Expanded Toxicological Data and Acceptable Intake (AI) Values under the Impact of ICH M7(R2) Updates on Nitrosamine Risk Assessment
ICH M7(R2) uses updated carcinogenic potency studies to establish individual AI limits for several nitrosamines. This represents a clear departure from the earlier one-size-fits-all TTC approach.
The guideline draws on data from trusted organizations such as IARC, WHO, EMA, and FDA. These sources help define lifetime exposure limits that better reflect actual cancer risk.
In many cases, the revised AI values are lower than previous generic limits. This increases the need for highly sensitive analytical methods and tighter process controls. To ensure compliance with these stricter limits, manufacturers should review nitrosamine impurity limits for Health Canada submissions and align their strategies accordingly.
Manufacturers must now support their impurity limits with strong analytical data and toxicological justification, ensuring their strategies are robust during inspections and submissions.
3. Integration of Nitrosamine Control into the ICH M7 Framework
Before ICH M7(R2), nitrosamines were often managed using separate regional guidance documents. The revised guideline fully integrates nitrosamine control into the core ICH M7 framework.
This integration creates a single, harmonized approach for global regulatory submissions. It reduces confusion and eliminates inconsistencies between regional expectations.
By default, nitrosamines are treated as Class 1 mutagens unless strong scientific data support reclassification. This reinforces a conservative approach to patient safety.
Risk assessments must also consider formation mechanisms, degradation during storage, and potential carryover throughout the product lifecycle. Understanding nitrosamine degradation pathways is critical, and this resource on nitrosamine degradation pathways provides practical insights for lifecycle risk evaluation.
ICH M7(R2) establishes a unified, globally accepted approach for nitrosamine risk assessment and control.
4. Analytical Methodology Alignment and Validation Standards
ICH M7(R2) places strong emphasis on analytical capability, especially for detecting nitrosamines at extremely low levels. Methods must match the sensitivity required by updated AI limits.
Validated techniques such as LC-MS/MS and GC-MS are now essential rather than optional. To understand why LC-MS/MS is the gold standard for ultra-trace detection, explore this detailed guide on LC-MS/MS nitrosamine testing. Method validation must clearly demonstrate accuracy, specificity, and reproducibility.
The guideline also highlights the importance of understanding matrix effects, sample stability, and analytical interferences. To understand why LC-MS/MS is the gold standard for ultra-trace detection, explore this detailed guide on LC-MS/MS nitrosamine testing. These factors can greatly impact trace-level measurements if not addressed properly.
ResolveMass Laboratories Inc. supports these needs through validated LC-MS/MS methods designed to meet ICH M7(R2) requirements, even at ultra-trace concentrations.
Manufacturers must use sub-ppb-level analytical methods validated according to ICH Q2(R2).
5. Data-Driven Nitrosamine Risk Assessment under ICH M7(R2)
ICH M7(R2) formally shifts impurity risk assessment toward a data-driven model. Decisions must now be supported by real analytical and toxicological evidence rather than theoretical assumptions.
Risk assessments should combine process chemistry knowledge, historical impurity data, toxicological reference values, and confirmatory testing results. For a structured approach, manufacturers can refer to this nitrosamine risk assessment guide for drug products. Each element strengthens the overall justification.
This approach improves transparency and reduces uncertainty during regulatory review. It also encourages early risk identification during development.
ResolveMass Laboratories helps manufacturers prepare comprehensive impurity risk dossiers that integrate chemistry, toxicology, and analytical data.
ICH M7(R2) replaces assumption-based assessments with validated, evidence-based evaluations.
6. Regulatory and Compliance Implications of the Impact of ICH M7(R2) Updates on Nitrosamine Risk Assessment
The Impact of ICH M7(R2) Updates on Nitrosamine Risk Assessment directly affects regulatory strategy. Authorities now expect clear and complete compliance before approval or renewal.
Agencies including the FDA, EMA, PMDA, and Health Canada are aligning with M7(R2). Submissions without strong justification face increased scrutiny.
Manufacturers must maintain updated risk assessments, scientifically justified AI limits, and validated analytical data. Failure to comply can lead to delays, requests for additional data, or even recalls. The potential regulatory and commercial impact is detailed in this overview of the consequences of nitrosamine detection. Ongoing monitoring for nitrosamine formation is also expected.
Failure to comply can lead to delays, requests for additional data, or even product recalls.
Regulators now expect full, lifecycle-based compliance with ICH M7(R2).
7. Practical Steps for Implementing ICH M7(R2) Compliance
ICH M7(R2) compliance requires a structured and proactive impurity management strategy.
Manufacturers should reassess APIs, excipients, and packaging materials for nitrosamine precursors. Supplier qualification and traceability play a critical role, as outlined in this guide on nitrosamine control during supplier qualification.
Process routes should be reviewed to identify potential formation pathways, including stressed and worst-case conditions. Degradation risks must also be evaluated.
Analytical methods should be updated to meet new detection limits, and documentation should clearly link chemistry, analytics, and toxicology. ResolveMass Laboratories Inc. provides full support across these activities.
8. Global Harmonization and Industry Impact
ICH M7(R2) strengthens global alignment in nitrosamine control standards.
By harmonizing expectations across regions, the guideline reduces regulatory uncertainty for multinational submissions. This improves efficiency and predictability.
Shared use of globally accepted toxicological data also reduces duplicate testing and resource burden.
Overall, companies benefit from smoother submissions, better lifecycle management, and faster access to global markets.
9. Future Outlook: Beyond Compliance
ICH M7(R2) supports a move toward predictive and preventive impurity control.
Advanced tools such as AI-based impurity modeling can help identify nitrosamine risks early in development. This reduces late-stage remediation.
Integration of global toxicology databases will further improve consistency and decision-making speed.
ResolveMass Laboratories continues to invest in advanced impurity assessment technologies to help clients stay ahead of evolving regulations.
Conclusion
The Impact of ICH M7(R2) Updates on Nitrosamine Risk Assessment and Control represents a major step forward in pharmaceutical impurity management. With compound-specific AI limits, integrated nitrosamine control, and stronger analytical expectations, the guideline sets a higher and more consistent global standard.
For manufacturers, aligning with ICH M7(R2) is essential not only for regulatory compliance but also for patient safety and product quality.
To ensure full compliance with ICH M7(R2) and maintain regulatory confidence, connect with our experts:
👉 Contact ResolveMass Laboratories Inc.
FAQs on ICH M7(R2) and Nitrosamine Risk Assessment
The main goal of ICH M7(R2) is to strengthen how nitrosamine and other mutagenic impurities are assessed and controlled. It aims to protect patient safety by using updated scientific data and consistent risk evaluation methods. The guideline also supports global regulatory alignment.
ICH M7(R2) goes beyond the earlier version by introducing compound-specific acceptable intake limits for nitrosamines. It formally brings nitrosamine control into the ICH M7 framework. This reduces reliance on generic limits and improves scientific accuracy.
The guideline recommends highly sensitive analytical techniques such as LC-MS/MS and GC-MS. These methods must be validated to detect nitrosamines at very low levels. Proper validation ensures accuracy, reliability, and regulatory acceptance.
Yes, wherever sufficient data is available, AI limits are set individually for each nitrosamine. These limits are based on carcinogenicity and toxicological studies. This approach provides more realistic and protective exposure thresholds.
ICH M7(R2) applies to all drug substances and drug products where nitrosamine risk may exist. This includes risks from synthesis, degradation, packaging, or storage. Manufacturers must assess the entire product lifecycle.
If AI limits cannot be met, manufacturers must provide a strong scientific justification. This includes toxicological rationale, analytical data, and risk mitigation strategies. Regulators review these justifications carefully before acceptance.
Legacy products should undergo retrospective risk assessments aligned with the updated guideline. This often includes reviewing manufacturing processes and performing confirmatory analytical testing. The goal is to ensure continued patient safety and compliance.
Major agencies such as the FDA, EMA, PMDA, and Health Canada are aligning their expectations with ICH M7(R2). This alignment supports consistent review standards across regions. It also simplifies global regulatory submissions.
Generic manufacturers must demonstrate that their products meet the updated impurity control expectations. This includes revised risk assessments and validated nitrosamine testing. Compliance is essential to avoid approval delays.
Reference
- Zhang, Y., Widart, J., Ziemons, E., Hubert, P., & Hubert, C. (2025). N-nitrosamine risk assessment in pharmaceuticals: Where are we from a regulatory point of view in 2025? Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis Open, 6, Article 100084. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpbao.2025.100084
- European Medicines Agency. (2020). Nitrosamine impurities in human medicinal products: Assessment report (Procedure EMEA/H/A5(3)/1490). Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/opinion-any-scientific-matter/nitrosamines-emea-h-a53-1490-assessment-report_en.pdf
- Cioc, R. C., Joyce, C., Akehurst, H., Urquhart, M. W., Burns, M. J., & Dobo, K. L. (2025). Drug substance and drug product workflows for quality risk management for the presence of nitrosamines in medicines. Organic Process Research & Development, 29(6), 1538–1553. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.oprd.5c00097
- Heads of Medicines Agencies (HMA). (n.d.). Nitrosamine impurities: Information on nitrosamines for marketing authorisation holders. CMDh, Heads of Medicines Agencies. https://www.hma.eu/human-medicines/cmdh/nitrosamine-impurities.html


