Introduction
LC-MS bioanalysis for oligonucleotides has emerged as the cornerstone analytical technique supporting the rapid advancement of RNA-based therapeutics in modern medicine. The pharmaceutical landscape has witnessed unprecedented growth in oligonucleotide drug development, with multiple FDA-approved therapies targeting previously untreatable genetic disorders, rare diseases, and complex conditions including cancer and cardiovascular diseases.
The complexity of oligonucleotide molecules—ranging from 13 to over 5,000 nucleotides in length—demands sophisticated analytical approaches that can simultaneously assess purity, identity, potency, and stability. Traditional bioanalytical methods often fall short when characterizing these large, negatively charged biomolecules that exhibit unique pharmacokinetic properties and metabolic pathways. LC-MS technology bridges this gap by offering exceptional mass accuracy, resolving power, and sensitivity required for comprehensive oligonucleotide characterization throughout the drug development lifecycle.
At ResolveMass Laboratories Inc., a specialized bioanalytical CRO supporting global drug development programs, we provide end-to-end LC-MS bioanalytical services tailored for oligonucleotides and RNA-based therapeutics. Our expertise spans discovery, regulated bioanalysis, and IND/ANDA/NDA-enabling studies.
Summary
LC-MS bioanalysis for oligonucleotides represents the gold standard in analytical methodology for characterizing and quantifying nucleic acid-based therapeutics. This comprehensive guide explores how liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) enables precise analysis of oligonucleotide drugs, including antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs), small interfering RNAs (siRNAs), and messenger RNAs (mRNAs).
Key Takeaways:
- LC-MS bioanalysis provides unmatched sensitivity and specificity for oligonucleotide quantification in biological matrices
- Ion-pair reversed-phase chromatography coupled with high-resolution mass spectrometry enables comprehensive structural characterization
- Advanced bioanalytical method development overcomes matrix effects and instability Challenges in Bioanalytical Method Development
- Robust method validation ensures regulatory compliance
- PK, TK, and biodistribution studies rely on accurate LC-MS bioanalysis
- Experienced Bioanalytical Outsourcing CRO partners accelerate development timelines
- Quality bioanalytical services accelerate drug development timelines while ensuring regulatory compliance
1: Understanding Oligonucleotide Therapeutics and Their Analytical Challenges
1.1 What Are Oligonucleotide Therapeutics?
Oligonucleotide therapeutics are short sequences of nucleic acids designed to modulate gene expression at the RNA level. These therapeutics work by binding to specific RNA sequences through Watson-Crick base pairing, enabling precise control over protein production. The major classes include:
Types of Oligonucleotide Therapeutics:
| Therapeutic Class | Mechanism of Action | Typical Length | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Antisense Oligonucleotides (ASOs) | RNA degradation via RNase H | 13-25 nucleotides | Nusinersen, Inotersen |
| Small Interfering RNAs (siRNAs) | RNA interference pathway | 21-23 nucleotides (duplex) | Patisiran, Givosiran |
| MicroRNA Mimics/Inhibitors | Endogenous miRNA pathway modulation | 18-25 nucleotides | Cobomarsen |
| Messenger RNAs (mRNAs) | Protein translation template | 500-5000+ nucleotides | COVID-19 vaccines |
| Aptamers | Target protein binding | 20-100 nucleotides | Pegaptanib |
1.2 Unique Analytical Challenges in LC-MS Bioanalysis for Oligonucleotides
Oligonucleotides present distinct analytical challenges that differentiate them from small molecule drugs and protein therapeutics. The high molecular weight, extreme hydrophilicity, and polyanionic nature create significant obstacles for traditional chromatographic separation and mass spectrometric detection. Chemical modifications—including phosphorothioate backbones, 2′-O-methyl sugars, and conjugated lipids—further complicate analysis by introducing structural heterogeneity.
Matrix effects pose another substantial challenge, as biological samples contain endogenous nucleic acids, proteins, and salts that can suppress ionization and interfere with detection. Metabolic stability assessment requires distinguishing parent oligonucleotides from chain-shortened metabolites that differ by only a single nucleotide, demanding exceptional chromatographic resolution and mass accuracy.
2: LC-MS Methodologies for Oligonucleotide Bioanalysis
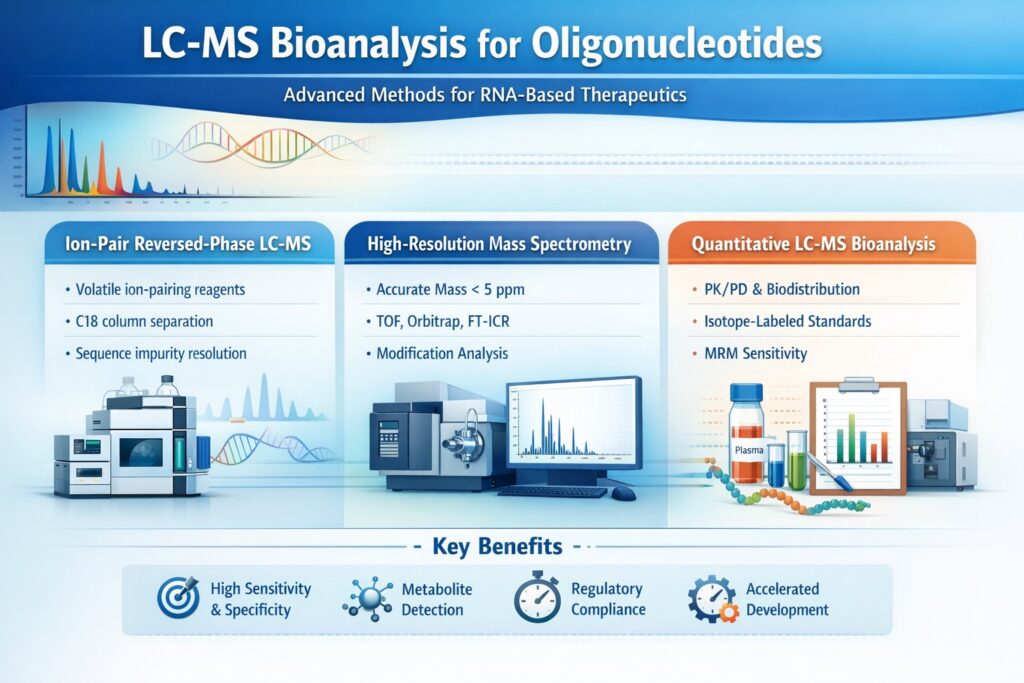
2.1 Ion-Pair Reversed-Phase LC-MS
Ion-pair reversed-phase LC-MS is widely used for oligonucleotide analysis across both discovery and regulated bioanalytical services.
Ion-pair reversed-phase chromatography represents the most widely adopted separation technique for LC-MS bioanalysis for oligonucleotides. This approach uses volatile ion-pairing reagents such as triethylamine, hexafluoroisopropanol (HFIP), or diisopropylethylamine to neutralize the negative charges on the phosphate backbone, enabling retention on conventional C18 or C8 columns.
This approach is frequently implemented within LC-MS/MS bioanalytical services, including advanced applications such as LC-MS/MS bioanalysis of xenobiotics.
Key Advantages:
- Excellent compatibility with electrospray ionization mass spectrometry
- Superior resolution of sequence-related impurities and metabolites
- Flexibility to optimize selectivity through ion-pair reagent selection
- Scalability from analytical to preparative applications
The typical mobile phase system employs HFIP and triethylamine in methanol or acetonitrile gradients, providing robust separations while maintaining MS-compatible volatile conditions. Method development focuses on optimizing ion-pairing reagent concentrations, organic modifier composition, and gradient profiles to achieve baseline resolution of target oligonucleotides from structurally similar species.
For highly complex RNA modalities, ion-pair LC-MS is often combined with LC-MS for large molecules to achieve sufficient resolution and mass accuracy.
2.2 High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry Platforms
High-resolution accurate mass (HRAM) spectrometry provides definitive structural characterization essential for oligonucleotide drug development. Time-of-flight (TOF), Orbitrap, and Fourier-transform ion cyclotron resonance (FT-ICR) instruments deliver mass accuracy below 5 ppm, enabling unambiguous molecular formula determination and confident identification of modifications, impurities, and degradation products.
Electrospray ionization (ESI) in negative mode generates multiply charged molecular ions, with the charge state distribution dependent on oligonucleotide length and sequence composition. Sophisticated deconvolution algorithms transform complex charge state envelopes into simplified neutral mass spectra, facilitating rapid data interpretation and structural confirmation.
2.3 Quantitative LC-MS Bioanalysis for Oligonucleotides
Quantitative bioanalysis supports pharmacokinetic studies, biodistribution assessments, and tissue accumulation investigations critical for regulatory submissions. LC-MS bioanalysis for oligonucleotides achieves lower limits of quantification (LLOQ) in the low ng/mL to pg/mL range in plasma, tissue homogenates, and other biological matrices through optimized sample preparation and sensitive detection.
Quantitative LC-MS bioanalysis for oligonucleotides supports pharmacokinetic, biodistribution, and toxicokinetic assessments critical for decision-making in drug development. These assays directly feed into PK/PD bioanalysis and toxicokinetic bioanalysis programs.
Quantification Strategies:
- Stable isotope-labeled internal standards compensate for matrix effects and recovery variability
- Solid-phase extraction or liquid-liquid extraction removes interfering matrix components
- Multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) on triple quadrupole instruments provides maximum sensitivity
- Careful validation following regulatory guidelines ensures data quality and reproducibility
Sample preparation typically involves protein precipitation, nuclease digestion, or solid-phase extraction to isolate oligonucleotides from complex biological matrices while minimizing losses and degradation. Isotope-labeled internal standards that exactly match the target sequence ensure accurate quantification by correcting for extraction efficiency, ionization variability, and instrument response fluctuations.
High-sensitivity LC-MS workflows are also applied in:
- Clinical bioanalytical services for first-in-human and late-phase trials
- High-throughput bioanalysis for discovery-stage screening
3: Method Development and Validation for Oligonucleotide LC-MS Bioanalysis
3.1 Strategic Approach to Method Development
Successful method development for LC-MS bioanalysis for oligonucleotides begins with thorough understanding of the molecule’s physicochemical properties, chemical modifications, and anticipated impurity profile. A systematic approach evaluates chromatographic conditions, mass spectrometer parameters, and sample preparation protocols to achieve optimal performance.
Method Development Workflow:
- Preliminary Screening – Evaluate column chemistries, ion-pairing reagents, and MS detection modes
- Optimization Phase – Fine-tune gradient profiles, temperatures, and flow rates for resolution
- Robustness Testing – Assess method stability to minor parameter variations
- Transfer and Validation – Establish performance characteristics per regulatory requirements
Column selection critically impacts separation quality, with modern oligonucleotide-specific stationary phases offering enhanced retention and peak shape compared to conventional reversed-phase materials. Temperature optimization balances resolution requirements against stability concerns, as elevated temperatures can accelerate degradation for certain chemically modified oligonucleotides.
3.2 Regulatory Validation Requirements
Bioanalytical method validation for oligonucleotide therapeutics follows guidelines established by FDA, EMA, and ICH, with specific considerations for the unique properties of nucleic acid drugs. LC-MS bioanalysis for oligonucleotides requires demonstration of selectivity, sensitivity, linearity, accuracy, precision, recovery, and stability under anticipated storage and handling conditions.
Critical Validation Parameters:
| Parameter | Acceptance Criteria | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Selectivity | No interference at LLOQ | Confirms matrix blank free of interferences |
| Sensitivity (LLOQ) | ±20% accuracy, ≤20% CV | Establishes lowest quantifiable concentration |
| Linearity | r² ≥ 0.99 | Validates calibration range |
| Accuracy | 85-115% of nominal | Ensures trueness of measurements |
| Precision | ≤15% CV (≤20% at LLOQ) | Confirms reproducibility |
| Recovery | Consistent across range | Assesses extraction efficiency |
| Stability | Maintains integrity | Validates sample handling |
Matrix effects assessment evaluates ion suppression or enhancement from biological components, typically through post-column infusion experiments or comparison of matrix-spiked versus neat standards. Incurred sample reanalysis provides additional confidence in method reliability by reanalyzing subject samples from actual studies and comparing results to original values.
Successful LC-MS bioanalysis for oligonucleotides begins with structured bioanalytical method development, followed by comprehensive validation to meet regulatory expectations.
Validated assays are essential for:
These workflows ensure compliance across both discovery and regulated phases.
4: Applications of LC-MS Bioanalysis for Oligonucleotides in Drug Development
4.1 Pharmacokinetic and Biodistribution Studies
LC-MS bioanalysis for oligonucleotides enables comprehensive pharmacokinetic characterization that guides dosing regimen selection and predicts clinical efficacy. Quantitative analysis in plasma, tissues, and excreta elucidates absorption, distribution, metabolism, and elimination (ADME) profiles essential for regulatory filings and clinical trial design.
Tissue distribution studies reveal preferential accumulation in liver, kidney, and other organs, informing potential toxicity concerns and therapeutic targeting strategies. Advanced LC-MS platforms simultaneously quantify parent drug and chain-shortened metabolites, providing complete pictures of oligonucleotide fate in vivo.
4.2 Impurity Profiling and Quality Control
Manufacturing process monitoring relies on sensitive LC-MS bioanalysis for oligonucleotides to detect and quantify synthesis-related impurities, including deletion sequences, addition products, and incompletely modified species. High-resolution mass spectrometry identifies unexpected impurities arising from synthesis chemistry or degradation pathways, supporting root cause investigations and process improvements.
Quality control laboratories implement validated LC-MS methods for batch release testing, stability studies, and comparability assessments following manufacturing changes. The specificity and sensitivity of LC-MS detection ensures product quality meets stringent pharmaceutical standards throughout the product lifecycle.
4.3 Metabolism and Biotransformation Studies
Oligonucleotide metabolism proceeds primarily through exonuclease-mediated chain shortening, producing N-1, N-2, and further truncated metabolites that retain portions of the original sequence. LC-MS bioanalysis for oligonucleotides resolves these closely related metabolites, enabling mechanistic understanding of metabolic pathways and identification of potential biomarkers.
Chemical modifications influence metabolic stability, with phosphorothioate linkages and 2′-sugar modifications conferring nuclease resistance. Comprehensive metabolite profiling using high-resolution LC-MS informs structure-activity relationships and guides medicinal chemistry optimization for enhanced in vivo performance.
LC-MS bioanalysis for oligonucleotides supports a broad range of therapeutic programs, including:
- Cell and gene therapy bioanalysis
- Biosimilar bioanalysis
- Biomarker bioanalytical services, enabling PK/PD correlations
5: Advanced Technologies and Future Directions in Oligonucleotide LC-MS Bioanalysis
Emerging LC-MS Technologies
Innovation continues advancing LC-MS bioanalysis for oligonucleotides capabilities through novel separation chemistries, ionization techniques, and mass analyzer architectures. Multidimensional chromatography combines orthogonal separation mechanisms for enhanced peak capacity, resolving complex mixtures that challenge one-dimensional approaches.
Cutting-Edge Developments:
- Ion mobility spectrometry adds gas-phase separation dimension, improving specificity
- Data-independent acquisition (DIA) captures comprehensive MS/MS fragmentation data
- Miniaturized LC systems reduce sample consumption and solvent waste
- Automated high-throughput platforms accelerate screening and development timelines
Native mass spectrometry preserves non-covalent interactions, enabling characterization of oligonucleotide-protein complexes and higher-order structures relevant to mechanism of action. These advanced approaches complement traditional bioanalytical methods, providing deeper insights into oligonucleotide behavior in biological systems.
Addressing Next-Generation Oligonucleotide Modalities
The therapeutic oligonucleotide pipeline increasingly features complex conjugated species incorporating lipids, peptides, antibodies, and N-acetylgalactosamine (GalNAc) targeting moieties. LC-MS bioanalysis for oligonucleotides adapts to these challenges through specialized sample preparation protocols and detection strategies tailored to conjugate physicochemical properties.
Large mRNA therapeutics, exemplified by COVID-19 vaccines, demand analytical workflows capable of characterizing molecules exceeding 5,000 nucleotides encapsulated in lipid nanoparticles. Middle-down and top-down mass spectrometry approaches provide sequence coverage and modification mapping essential for ensuring product quality and consistency.
6: Why Choose ResolveMass Laboratories for Your Oligonucleotide Bioanalysis Needs
Proven Expertise in Oligonucleotide Analytics
ResolveMass Laboratories Inc. brings extensive experience in LC-MS bioanalysis for oligonucleotides, supporting dozens of development programs across the full spectrum of nucleic acid therapeutic modalities. Our scientific team combines deep mass spectrometry expertise with specialized knowledge of oligonucleotide chemistry, metabolism, and regulatory requirements.
Our comprehensive service portfolio includes:
- Method development and validation for quantitative and qualitative analysis
- Pharmacokinetic sample analysis for preclinical and clinical studies
- Impurity profiling and structural characterization
- Stability studies and comparability assessments
- Metabolite identification and biotransformation investigations
- Regulatory submission support and consultation
State-of-the-Art Infrastructure
Our laboratories feature the latest high-resolution mass spectrometry platforms from industry-leading manufacturers, providing the sensitivity, selectivity, and mass accuracy demanded by oligonucleotide bioanalysis. Dedicated oligonucleotide workspaces minimize cross-contamination risks while specialized sample preparation equipment ensures optimal recovery and minimal degradation.
Quality management systems aligned with GLP and GMP standards ensure data integrity and regulatory compliance. Our commitment to scientific excellence, rapid turnaround times, and personalized client service has established ResolveMass Laboratories as a trusted partner for oligonucleotide developers worldwide.
Why Outsource LC-MS Bioanalysis for Oligonucleotides?
Outsourcing LC-MS bioanalysis allows sponsors to reduce infrastructure costs while accessing specialized expertise through bioanalytical outsourcing models for pharma and biotech.
ResolveMass supports:
- Virtual biotech companies
(https://resolvemass.ca/bioanalytical-cro-for-virtual-biotech/, https://resolvemass.ca/virtual-bioanalytical-strategy/) - Early-stage startups seeking affordability
(https://resolvemass.ca/affordable-bioanalytical-services-for-biotech-startups/, https://resolvemass.ca/cost-effective-bioanalytical-services/, https://resolvemass.ca/bioanalytical-testing-services-cost/) - Discovery-focused sponsors
(https://resolvemass.ca/bioanalytical-cro-for-drug-discovery/, https://resolvemass.ca/outsource-bioanalysis-for-biotech-startups/)
Outsourced bioanalysis continues to play a critical role in modern RNA drug development
(https://resolvemass.ca/outsourced-bioanalysis-for-drug-development/).
Conclusion
LC-MS bioanalysis for oligonucleotides has revolutionized the development of RNA-based therapeutics by providing the analytical precision necessary to characterize these complex molecules throughout discovery, development, and commercialization. The unique challenges posed by oligonucleotide size, charge, and chemical modifications require specialized expertise in chromatographic separation, mass spectrometric detection, and bioanalytical method development.
As the oligonucleotide therapeutic pipeline continues expanding with increasingly sophisticated modalities, the importance of robust LC-MS bioanalysis for oligonucleotides will only grow. Advanced technologies including high-resolution mass spectrometry, ion mobility, and automated platforms promise even greater capabilities for future applications.
ResolveMass Laboratories Inc. stands ready to support your oligonucleotide development programs with comprehensive bioanalytical services backed by scientific expertise, cutting-edge technology, and unwavering commitment to quality. Our specialized capabilities in LC-MS bioanalysis for oligonucleotides ensure your project receives the analytical rigor required for regulatory success and therapeutic impact.
Frequently Asked Questions:
LC-MS bioanalysis for oligonucleotides is an analytical approach used to quantitatively and qualitatively measure DNA, RNA, siRNA, ASOs, and other oligonucleotide therapeutics in biological matrices using liquid chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry.
LC-MS offers higher molecular specificity, the ability to distinguish metabolites, and reduced cross-reactivity compared to ligand-binding assays, making LC-MS bioanalysis for oligonucleotides ideal for complex RNA-based therapeutics.
Common matrices include plasma, serum, tissues, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), urine, and intracellular extracts, depending on the pharmacokinetic and biodistribution objectives.
Key challenges include poor ionization efficiency, matrix effects, adsorption losses, enzymatic degradation, and the need for specialized sample preparation techniques tailored to oligonucleotide chemistry.
Extraction methods typically involve solid-phase extraction (SPE), hybridization-based capture, ion-pairing techniques, or enzymatic digestion followed by LC-MS detection.
Yes, LC-MS bioanalysis for oligonucleotides can accurately differentiate parent compounds from chain-shortened or chemically modified metabolites based on mass-to-charge ratios.
Absolutely. LC-MS platforms are well-suited for analyzing chemically modified oligonucleotides, including LNA, PMO, and phosphorothioate backbones, with proper method optimization.
Reference
- Maotian Zhou, Xue Zhang, Huan Yan, Lili Xing, Yi Tao &Liang Shen.Review on the bioanalysis of non-virus-based gene therapeutics.https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/17576180.2024.2437418
- Laixin Wang & Chengjie Ji.Advances in Quantitative Bioanalysis of Oligonucleotide Biomarkers and Therapeutics.https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.4155/bio.15.234
- Ethan J. Sanford ,Jianzhong Chen, Julia Tran, Ilia Korboukh & Guangnong Zhang.Development of an LC-MS/MS assay to analyze a lipid-conjugated siRNA by solid phase extraction (SPE) in mouse plasma and tissue using a stable isotope labeled internal standard (SILIS).https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/17576180.2025.2535953
- Matthew Ewles,Aaron R Ledvina,Brendan Powers &C Eric Thomas.Observations from a decade of oligonucleotide bioanalysis by LC-MS.https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.4155/bio-2024-0007
- Shalini Andersson, Madeleine Antonsson , Marie Elebring , Rasmus Jansson-Löfmark , Lars Weidolf.Drug metabolism and pharmacokinetic strategies for oligonucleotide- and mRNA-based drug development.https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1359644617301691

