Introduction: Nitrosamine Testing in Ranitidine
Nitrosamine Testing in Ranitidine is a key concern for drug safety after major recalls revealed harmful levels of cancer-causing compounds like NDMA. At ResolveMass Laboratories Inc., we use high-level testing methods to detect nitrosamine impurities from the early stages of API synthesis to the final drug product. The presence of NDMA and nitrosamine drug substance-related impurities (NDSRIs) has made detailed analysis more important than ever. In this article, we’ll explain how these impurities form, how Ranitidine’s structure plays a role, and what global regulators are saying. This information will help manufacturers stay compliant and protect patient health.
How Ranitidine is Made: Understanding the Synthesis
Ranitidine hydrochloride is made using several chemical steps, including compounds like thiosemicarbazide and furan derivatives. These reactions produce structural elements such as dimethylaminomethyl and nitroethene groups. These groups are highly reactive and can break down or interact with other chemicals to form nitrosamines.
This makes the drug especially prone to forming impurities like NDMA and NDSRIs. Looking closely at each step of the synthesis process helps us understand exactly where these harmful compounds can appear.
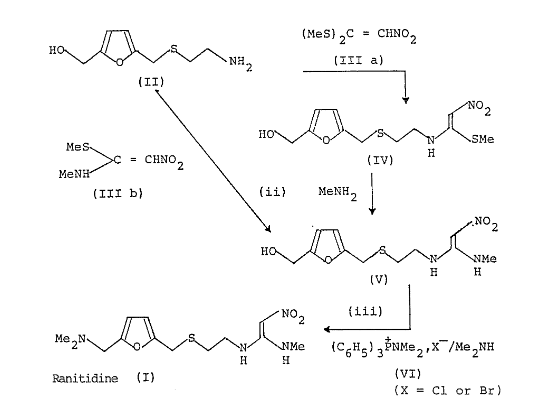
Alhede, B., & Clausen, F. P. (1987). Process for the preparation of ranitidine or acid addition salts thereof, and intermediates for this preparation (EP0219225A1). European Patent Office. https://worldwide.espacenet.com/patent/search/family/011400070/publication/EP0219225A1
Nitrosamine Risk Points in Ranitidine API Manufacturing
The production of the Ranitidine API involves steps that can easily lead to the formation of nitrosamines. Here are a few important risk factors:
- Solvents like dimethylformamide (DMF) and dimethylacetamide (DMA) may release dimethylamine (DMA), which reacts with nitrites to form NDMA.
- Chemical reactions involving furan-2-carboxaldehyde and thiosemicarbazide can lead to the formation of secondary amines, which can later become nitrosamines.
- N-methylpyrrolidone (NMP) and methylamine hydrochloride used during amidation increase the chance of forming N-nitrosomethylamine.
- Reused solvents may still have nitrites or amines, adding to the risk of forming nitrosamines during further processing.
- Cleaning agents like bleach or oxidizers can change some ingredients into nitrosamine-generating compounds.
- The use of quaternary ammonium salts and certain catalysts in acidic environments can also trigger NDSRI formation.
All these risks should be handled with strict controls and validated testing methods.
Nitrosamine Formation Risks in Ranitidine Finished Product
Even after the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) is made, nitrosamine testing in Ranitidine is still necessary at the product level. Here’s why:
- The Ranitidine API includes dimethylamine, which can become NDMA if nitrites are present.
- Common excipients such as sodium starch glycolate and microcrystalline cellulose might have hidden nitrite contaminants.
- Ranitidine can break down in heat or moisture, releasing amines that interact with nitrites.
- Some packaging materials may release acids or nitrites, which worsen the problem and lead to the formation of complex NDSRIs, like:
- N-nitroso-N-methyl-4-aminobutanal
- N-nitroso-N-methyl-2-butanamine
Proper formulation, packaging, and storage are essential to minimize these risks.
List of Known Nitrosamines in Ranitidine
Scientific data and regulatory findings have identified several nitrosamine compounds in Ranitidine. These include:
- N-nitrosodimethylamine (NDMA)
- N-nitroso-N-methyl-2-butanamine (NMBA)
- N-nitrosomethylfurfurylamine
- N-nitroso-N-methyl-4-aminobutanal
- N-nitroso-N-methyl-N-phenylamine
- Nitrosomethylamine derivatives related to Ranitidine
- N-nitrosohydrazines
- N-nitrosoaminopropylamines
- Other NDSRIs listed by the European Medicines Agency (EMA) in 2023
Each of these must be carefully monitored according to international toxicology guidelines.
Related Studies on Nitrosamine Testing in Ranitidine and Other Drugs
To expand your understanding, check out our additional reports on nitrosamine risks:
- Nitrosamine Testing in Orphenadrine
- Nitrosamine Testing in Nizatidine
- Nitrosamine Testing in Metformin
- NDSRIs in Nitrosamine Testing
- Acceptable Intake of Nitrosamines
- Nitrosamine CRO Support Services
- Nitrosamine Risk Assessment Guide
- Nitrosamine Analysis Laboratory
- Nitrosamine Testing in Quetiapine
These studies help manufacturers meet both pre-market and post-market regulatory expectations.
Conclusion: Why Nitrosamine Testing in Ranitidine is Essential
Nitrosamine testing in Ranitidine is not optional—it is a must for ensuring drug safety. The risks come from both how the drug is made and how it is stored. Dimethylamine content, contaminated excipients, and packaging issues can all lead to dangerous impurities like NDMA and NDSRIs.
At ResolveMass Laboratories Inc., we provide complete lab testing and risk evaluations that meet the highest standards. Our goal is to help pharmaceutical companies stay compliant while protecting public health. Contact our experts for testing solutions, regulatory support, or customized consultation.
For personalized consultation or regulatory support, reach us via the Contact Page
FAQs on Nitrosamine Testing in Ranitidine
The main nitrosamine impurities found in Ranitidine include NDMA (N-nitrosodimethylamine), NMBA, and other nitrosamine drug substance-related impurities (NDSRIs). These impurities can form during manufacturing, storage, or from degradation of the drug. They are considered harmful and must be carefully monitored.
Nitrosation of Ranitidine is a chemical reaction where parts of the drug react with nitrites to form nitrosamines like NDMA. This can happen under heat, acidic conditions, or in the presence of certain chemicals. The structure of Ranitidine makes it especially prone to this type of reaction.
The amount of NDMA in Ranitidine can vary depending on how the drug is made and stored. Some tests have shown levels higher than the FDA’s daily limit of 96 nanograms. Because of these high levels, many Ranitidine products were recalled from the market.
The nitroso impurity in Ranitidine refers mostly to NDMA, which is formed when the drug breaks down or reacts with nitrites. Other related impurities like NMBA and NDSRIs can also be present. These nitroso compounds are harmful and possibly cancer-causing.
NDMA was found in Ranitidine because the drug can degrade over time, especially when exposed to heat or moisture. It can also form during manufacturing or when exposed to nitrites. The chemical structure of Ranitidine makes it easy for NDMA to be created under certain conditions.
Impurity C in Ranitidine is a known by-product that appears during its chemical synthesis. It is officially listed in pharmacopeia references and is regularly monitored during quality control. While it is not a nitrosamine, it still needs to stay within safe limits.
Impurity B is another identified compound that can form as a result of incomplete reactions or degradation of Ranitidine. It is a standard impurity tracked during testing. Its levels must be controlled to meet regulatory quality standards.
The main carcinogenic compound in Ranitidine is NDMA (N-nitrosodimethylamine). It is classified as a probable human carcinogen. NDMA can form naturally from the drug over time or when stored under certain conditions like high temperatures.
References
- Alhede, B., & Clausen, F. P. (1987). Process for the preparation of ranitidine or acid addition salts thereof, and intermediates for this preparation (EP0219225A1). European Patent Office. https://worldwide.espacenet.com/patent/search/family/011400070/publication/EP0219225A1
- Control of Nitrosamine Impurities in Human Drugs
- Information about Nitrosamine Impurities in Medications


