Executive Summary
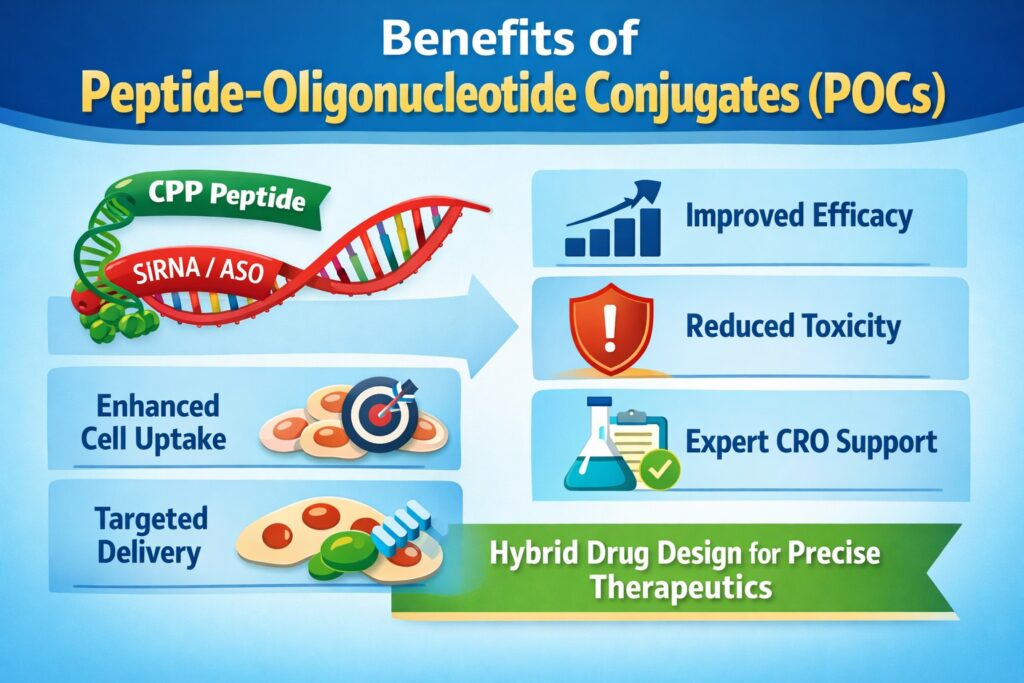
- Peptide-Oligonucleotide Conjugates (POCs) combine targeting peptides with antisense or siRNA to improve delivery, cellular uptake, and tissue specificity.
- Specialized CRO partners ensure precise conjugation, optimized workflows, and faster development with fewer synthesis failures.
- Advanced linker and bio-orthogonal chemistries enable controlled release, greater stability, and tailored biodistribution.
- Robust analytical validation (HRMS, LC-MS/MS, qNMR, chromatography) confirms purity, identity, and regulatory readiness.
- Scalable, sustainable manufacturing methods increase yield, lower waste, and support clinical and commercial supply.
- Integrated quality and regulatory systems help move complex POC therapeutics efficiently from research to the clinic.
Strategic Engineering of Peptide-Oligonucleotide Conjugates for Precision Medicine
Peptide-Oligonucleotide Conjugates are specially designed hybrid drugs created to solve delivery problems seen with naked nucleic acids. These molecules combine a peptide, often a cell-penetrating peptide (CPP), with an antisense or siRNA sequence. This design improves cellular uptake and directs the therapy to specific tissues. By working with a specialized Peptide Oligonucleotide Conjugates CRO, companies can ensure proper conjugation and analytical validation. The result is stronger biological activity with lower systemic exposure.
The conjugation process must protect both the peptide and the oligonucleotide during multiple chemical steps. Small mistakes in protecting groups or reaction timing can damage the molecule. Expert CRO teams carefully manage these risks using optimized workflows. This approach shortens development timelines and reduces batch failure.
Learn more about our specialized synthesis capabilities: Explore Peptide-Oligonucleotide Conjugates (POCs) Synthesis Services
POCs are now being explored for neuromuscular disorders, CNS diseases, and oncology. Their modular structure allows peptide swapping for targeted delivery. However, this flexibility increases manufacturing complexity. Strict quality control systems are required to maintain consistency.
Technical Advantages of Partnering with a Peptide Oligonucleotide Conjugates CRO
Collaborating with a dedicated Peptide Oligonucleotide Conjugates CRO provides access to specialized infrastructure that bridges peptide synthesis and phosphoramidite oligonucleotide chemistry under one controlled environment. These CROs design orthogonal protection strategies that prevent cross-reactivity between acid-sensitive and base-sensitive components. This level of precision significantly reduces synthesis failure rates and improves overall yield. Integrated workflows also enable smoother transitions from research-scale production to preclinical batches. The result is a more predictable and efficient development timeline.
Beyond synthesis, specialized CRO partners strengthen pharmacokinetic and formulation strategies. POC molecules often require careful balance between hydrophilicity and membrane permeability to optimize biodistribution. Advanced chromatography and high-resolution mass spectrometry platforms detect low-level impurities that may affect safety or potency. Early impurity profiling reduces the likelihood of regulatory queries during IND review. A strong analytical foundation ultimately supports long-term clinical success.
Accelerate your drug discovery timeline: Discover Custom Synthesis for Drug Discovery
In addition, regulatory-aligned documentation practices streamline submission processes. Dedicated project management teams coordinate chemistry, manufacturing, and controls (CMC) documentation in real time. Transparent communication ensures that sponsors maintain visibility into every stage of development. This collaborative structure reduces delays and strengthens confidence during agency inspections.
Comparison of Internal vs. CRO-Managed POC Development
| Development Parameter | Internal R&D Limitations | Peptide Oligonucleotide Conjugates CRO Advantage |
| Synthesis Infrastructure | Limited to standard solid-phase units | Advanced LPOS, SPOS, and parallel synthesis |
| Analytical Resolution | Basic HPLC and low-res MS | HRMS (Orbitrap/TOF), qNMR, and 2D-LC |
| Regulatory Readiness | General knowledge of ICH guidelines | Specialized FDA-registered facilities (ID: 3042696771) |
| Scaling Potential | Bench-scale only; high waste | Pilot-scale to commercial; low PMI processes |
| Turnaround Time | 3-6 months for new methods | 7-14 days for validated protocols |
| Quality Systems | Often non-GMP in research labs | ISO 9001:2015 and GMP-aligned QMS |
Advanced Synthesis Strategies in a Peptide Oligonucleotide Conjugates CRO
Successful POC synthesis requires a deep understanding of chemical compatibility between peptide and oligonucleotide chemistries. A Peptide Oligonucleotide Conjugates CRO typically employs either linear solid-phase assembly or convergent post-synthetic ligation strategies. Linear assembly demands carefully chosen protecting groups that tolerate both acidic and basic deprotection cycles. Convergent synthesis allows independent optimization of peptide and oligonucleotide fragments before final coupling. This method often improves purity when working with complex or cyclic constructs.
ResolveMass Laboratories Inc. integrates automated DNA/RNA synthesizers with advanced peptide synthesis platforms to achieve high-purity products. Oligonucleotides are produced using phosphoramidite chemistry under tightly controlled moisture conditions. Peptides are assembled using solid-phase peptide synthesis (SPPS) with optimized coupling reagents to ensure complete amino acid incorporation. Strict solvent management prevents cross-contamination and degradation. This coordinated workflow supports milligram-to-gram scale production without compromising structural integrity.
Process optimization also includes temperature control and reaction monitoring to prevent side-product formation. Acidic cleavage steps used in peptide synthesis can damage sensitive nucleic acid backbones if not properly managed. Similarly, strong bases used during oligonucleotide deprotection may affect peptide stability. Careful scheduling and orthogonal design minimize these incompatibilities. This technical depth defines the value of a specialized CRO partner.
Linker Engineering and Conjugation Chemistry in a Peptide Oligonucleotide Conjugates CRO
Linker selection determines how a POC behaves in circulation and within target cells. Cleavable linkers allow controlled release of the oligonucleotide payload once specific biological triggers are encountered. Non-cleavable linkers maintain structural stability when the intact conjugate is required for activity. The right design depends on disease indication, target tissue, and therapeutic mechanism. A knowledgeable Peptide Oligonucleotide Conjugates CRO evaluates these parameters during early development.
Cleavable vs. Non-Cleavable Linker Mechanisms
Cleavable linkers act as molecular switches that respond to enzymes, acidic environments, or intracellular reducing conditions. For example, the Valine-Citrulline (Val-Cit) linker remains stable in plasma but is cleaved by Cathepsin B inside lysosomes. This targeted release improves therapeutic specificity and reduces systemic toxicity. pH-sensitive and disulfide linkers offer alternative release triggers based on cellular environment.
Non-cleavable linkers such as thioether or triazole bonds maintain structural integrity until the molecule is degraded through natural biological processes. These linkers are useful when the full conjugate is required for receptor engagement or cellular transport. Selection between cleavable and stable linkers depends on pharmacodynamic goals. Even small structural changes can significantly affect biodistribution and immune response.
| Linker Category | Representative Chemistry | Cleavage Trigger | Therapeutic Application |
| Enzyme-Cleavable | Val-Cit (Peptide) | Cathepsin B (Lysosome) | Targeted siRNA delivery in solid tumors |
| pH-Sensitive | Hydrazone / Acetal | Low pH (Endosome) | ASO delivery to acidic tumor microenvironments |
| Reducible | Disulfide (-S-S-) | Glutathione (Cytosol) | High-concentration release in target cells |
| Non-Cleavable | Thioether / Triazole | Proteolytic degradation | Neuromuscular ASO delivery (e.g., PMOs) |
| Stable-PEG | Amide-PEG-Ether | None (Systemic) | Half-life extension and immunogenicity reduction |
Bio-orthogonal Chemistry in a Peptide Oligonucleotide Conjugates CRO
Bio-orthogonal chemistry enables conjugation under mild, aqueous conditions without interfering with biological functionality. The Inverse-Electron Demand Diels-Alder (IEDDA) reaction between tetrazine and trans-cyclooctene demonstrates extremely rapid kinetics, making it ideal for sensitive biomolecules. This reaction supports efficient coupling at low concentrations, preserving expensive targeting peptides. Its high selectivity reduces purification challenges and improves manufacturing yield.
The Strain-Promoted Azide-Alkyne Cycloaddition (SPAAC) eliminates the need for copper catalysts, which can be cytotoxic. This makes SPAAC suitable for therapeutic-grade production. Although slower, the Staudinger ligation remains useful for forming native amide bonds under specific conditions. Reaction choice is based on substrate compatibility, scalability, and cost considerations. Efficient ligation directly impacts throughput and process economics.
Analytical Validation Protocols for a Peptide Oligonucleotide Conjugates CRO
Comprehensive characterization of POCs requires multi-layered analytical strategies capable of confirming both peptide and oligonucleotide integrity. Sequence-related impurities such as truncated strands or amino acid deletions must be accurately quantified. These impurities can affect potency, immunogenicity, and safety. A qualified Peptide Oligonucleotide Conjugates CRO employs cross-validated analytical platforms to ensure complete structural confirmation.
High-resolution mass spectrometry (HRMS) provides precise mass accuracy, often below 5 ppm, confirming molecular formula and detecting minor modifications. LC-MS/MS mapping strengthens sequence verification and impurity identification. MALDI-TOF analysis supports molecular weight distribution profiling for larger constructs. Combined techniques offer robust analytical confidence suitable for regulatory submission.
Ensure the highest quality for your peptide constructs: View our Peptide Characterization Services
Optimized Chromatographic Parameters for POCs
| Parameter | Optimized Condition | Technical Rationale |
| Column Type | Wide-pore C18 (e.g., 300Å) | Accommodates large biopolymers; reduces steric hindrance |
| Column Temperature | $60 ^\circ C$ to $80 ^\circ C$ | Minimizes secondary structure and aggregation |
| Mobile Phase A | 0.1 M TEAA or Butylammonium Acetate | Ion-pairing for improved nucleic acid retention |
| Mobile Phase B | Acetonitrile (ACN) | Efficient elution of hydrophobic peptide regions |
| Detection Method | PDA ($260/280\text{ nm}$) and ESI-MS | Simultaneous monitoring of oligo and peptide signals |
| Flow Rate | $0.5 – 1.0\text{ mL/min}$ | Balanced resolution and analysis time |
Quantitative NMR (qNMR) further establishes absolute purity without reliance on reference standards. This technique is particularly valuable for regulatory documentation. Integrated analytical validation ensures product consistency across development stages. Strong analytical foundations support long-term commercial viability.
Scaling Challenges and Manufacturing Innovation
Scaling POC production from research batches to clinical supply introduces new technical challenges. Solid-Phase Oligonucleotide Synthesis (SPOS) often faces solvent consumption and linear scale limitations. Forward-looking CROs invest in Liquid-Phase Oligonucleotide Synthesis (LPOS) to improve atom economy and reduce waste. These improvements directly impact cost of goods and environmental sustainability.
Enzymatic synthesis methods, such as those using Terminal deoxynucleotidyl Transferase (TdT), offer emerging alternatives for specific constructs. While still evolving, these approaches reduce reliance on organic solvents. Sustainable process development is becoming a regulatory and commercial priority. Innovation in manufacturing strengthens long-term competitiveness.
Comparative Metrics of Manufacturing Paradigms
| Manufacturing Metric | Solid-Phase (SPOS) | Liquid-Phase (LPOS/AJIPHASE) | Enzymatic (TdT) |
| Scalability | Linear; limited to <10 kg batches | High; standard industrial reactors | Theoretical; “green” path to long oligos |
| Solvent Use | Massive excess; high PMI | Reduced (up to 60% less) | Aqueous; zero organic solvents |
| Purity Potential | High for short/medium chains | High; allows intermediate precipitation | Very high; fewer truncation products |
| Cost Profile | High due to reagent excess | Lowered through atom economy | High (current enzyme costs) |
| Modality Fit | Standard ASO/siRNA | High-volume commercial drugs | Research-stage for long constructs |
Regulatory Compliance Frameworks within a Peptide Oligonucleotide Conjugates CRO
POCs fall under both peptide and oligonucleotide regulatory frameworks, which increases compliance complexity. Detailed CMC documentation must address sequence confirmation, impurity profiling, residual solvents, and elemental impurities. ICH Q3A/B guidelines define impurity thresholds that must be justified and controlled. Early compliance planning reduces risk during IND and NDA review.
The 2025 nitrosamine (NDSRI) compliance deadline adds further urgency to risk assessments. CRO partners must evaluate potential nitrosation pathways and document mitigation strategies. Stability testing under ICH Q1A conditions ensures product integrity under stress. Proactive regulatory alignment strengthens submission confidence.
Request a quote for your specific project needs: Get a Project Quote from ResolveMass
Regulatory Checklist for POC IND/NDA Filings
- Identity and Sequence Verification: LC-MS/MS mapping confirmation.
- Purity Profiling: Validated RP-HPLC or HILIC quantification.
- Stability Testing: Stress studies under ICH Q1A conditions.
- Nitrosamine Risk Assessment: Compliance with 2025 FDA requirements.
- Method Validation: ICH Q2(R1/R2) adherence.
- Bioanalytical Support: Sensitive PK/PD assays in low ng/mL range.
Strategic Scaling Solutions for a Peptide Oligonucleotide Conjugates CRO
Scaling purification workflows requires advanced technologies beyond simple column enlargement. Multicolumn Countercurrent Solvent Gradient Purification (MCSGP) enables continuous separation with improved yield and solvent efficiency. This approach reduces waste while maintaining high resolution. Advanced purification supports consistent batch quality.
Phosphorothioate-modified oligonucleotides introduce stereochemical complexity that can affect potency. Modern platforms apply P-chirality control to generate stereopure constructs with predictable biological behavior. Improved stereochemical control enhances safety and regulatory confidence. These innovations reflect the evolving capabilities of specialized CRO providers.
CRO Procurement and Technical Due Diligence
Selecting the right Peptide Oligonucleotide Conjugates CRO directly influences development speed and regulatory outcomes. Sponsors should evaluate facility certifications, FDA registration history, and analytical infrastructure. Experience with complex sequences, including arginine-rich CPPs and PMOs, is essential. Transparent communication and real-time data access improve collaboration quality.
Technical Due Diligence Checklist for Bioconjugate Projects
- Facilities with ISO 9001:2015 and FDA registration (e.g., ID: 3042696771)
- In-house HRMS, qNMR, and ICP-MS
- Experience with CPPs and PMOs
- Digital data tracking and deviation control
- Dedicated PhD-level project leadership
- Proven audit readiness
Market Trends and the Future of Peptide Oligonucleotide Conjugates CRO Services
The TIDES market continues to expand as new oligonucleotide therapies receive regulatory approval. Delivery innovations, including peptide-mediated targeting, are central to this growth. CNS, skeletal muscle, and cardiac applications represent key focus areas. Pharmaceutical companies increasingly outsource complex conjugation chemistry to specialized providers.
As pipelines mature for rare genetic disorders and cardiovascular diseases, demand for advanced Peptide Oligonucleotide Conjugates CRO services will continue to increase. Companies offering integrated synthesis, analytical validation, and scalable manufacturing will maintain competitive advantage. Innovation in linker design and bio-orthogonal chemistry will shape the next generation of POC therapeutics.
Conclusion
Peptide-Oligonucleotide Conjugates represent a transformative advancement in nucleic acid therapeutics. Their successful development requires expertise in orthogonal chemistry, advanced analytics, scalable manufacturing, and regulatory compliance. Partnering with an experienced Peptide Oligonucleotide Conjugates CRO ensures that complex hybrid constructs move efficiently from research to clinical-grade production.
ResolveMass Laboratories Inc. provides PhD-led scientific oversight, FDA-registered facilities, and validated analytical systems tailored to bioconjugate development. With integrated expertise in synthesis, linker engineering, and purification innovation, ResolveMass supports precision-driven therapeutic programs. Strategic collaboration with a specialized CRO accelerates timelines while maintaining the highest standards of quality and compliance.
Contact ResolveMass Laboratories Inc. for Your Next Bioconjugate Project:
Contact us
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
The principal difficulty in preparing POCs arises from the differing chemical conditions required for peptide and oligonucleotide synthesis. Peptides are typically deprotected under acidic environments, whereas oligonucleotides often require basic conditions. These opposing requirements can compromise one component while processing the other. Specialized development teams overcome this issue by applying orthogonal protection strategies or by synthesizing each component separately and coupling them later using mild, bioorthogonal reactions that proceed under near-physiological conditions.
The linker determines how and where the oligonucleotide is released from the conjugate. For instance, enzyme-sensitive linkers such as Val–Cit are designed to be cleaved within lysosomes, ensuring intracellular release and limiting systemic exposure. Conversely, stable linkers that do not undergo cleavage maintain the conjugate as a single functional unit, which can be advantageous when the intact structure is responsible for biological activity. Thus, linker chemistry directly affects both efficacy and safety.
Accurate characterization of POCs relies on multiple complementary techniques. High-resolution mass spectrometry (HRMS) verifies molecular mass, while specialized high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), often using wide-pore columns, separates closely related impurities. Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy evaluates structural integrity. When absolute purity quantification is necessary—particularly for reference standards—quantitative NMR (qNMR) is widely regarded as the most precise approach.
POCs containing highly positively charged or arginine-rich peptides may interact strongly with negatively charged oligonucleotides, forming aggregates that compromise chromatographic resolution. Running HPLC at higher temperatures, such as 80°C, helps disrupt these electrostatic interactions and secondary structures. As a result, clearer separation between the conjugate and any unconjugated components can be achieved.
Regulatory authorities now require comprehensive assessment of potential nitrosamine impurities in drug substances. Following the 2025 implementation timeline, manufacturers must conduct formal risk evaluations and apply validated LC–MS/MS analytical methods capable of detecting trace levels of compounds such as NDMA and NDEA, often at parts-per-billion concentrations. Compliance depends on demonstrating that impurity levels remain within established acceptable intake limits.
The inverse electron-demand Diels–Alder reaction between tetrazines and trans-cyclooctenes is recognized for its exceptionally rapid reaction kinetics. Because of its high rate constant, conjugation can occur efficiently even at very low reactant concentrations. This is particularly valuable when working with costly therapeutic materials and in applications such as live-cell imaging, where fast reaction times are essential.
Traditional solid-phase synthesis can become inefficient and resource-intensive at larger scales. To improve scalability, contract research organizations are implementing liquid-phase oligonucleotide synthesis (LPOS) and advanced continuous purification systems such as multicolumn chromatography. These approaches enhance material efficiency, reduce solvent consumption, and make large-scale manufacturing more economically and environmentally viable.
Polyethylene glycol (PEG) segments increase the hydrophilicity of conjugates, which can slow renal filtration and decrease nonspecific protein binding. This often leads to prolonged circulation time in the bloodstream. Additionally, PEGylation may mask immunogenic regions of the molecule, potentially reducing immune responses and improving tolerability.
References
- Soliman, W. (2026, January 9). Oligonucleotide therapeutics at scale: Bottlenecks, breakthroughs, and what comes next. Advancing RNA. https://www.advancingrna.com/doc/oligonucleotide-therapeutics-at-scale-bottlenecks-breakthroughs-and-what-comes-next-0001
- Henderson, T. J. (2025, December 2). The scale-up singularity: Manufacturing innovations in oligonucleotide synthesis. Drug Discovery News. https://www.drugdiscoverynews.com/the-scale-up-singularity-manufacturing-innovations-in-oligonucleotide-synthesis-16856
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. (2024, June 14). Clinical pharmacology considerations for the development of oligonucleotide therapeutics: Guidance for industry. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents/clinical-pharmacology-considerations-development-oligonucleotide-therapeutics


