Summary
- Deep technical insight into PLGA Characterization for RLD using the USP Lupron Depot study
- Detailed evaluation of analytical techniques: NMR, GPC/SEC, DSC, XRD, IR
- Insights on block length, monomer ratio, polymer architecture, and end-group analysis
- Comparison between extracted polymer and in-house standards (L:G 75:25)
- How ResolveMass Laboratories Inc. delivers advanced polymer analytics and Q1/Q2/Q3 equivalence for complex generics
- Regulatory alignment with USP–FDA initiatives on PLGA reference standards and monographs
Introduction:
Developing a long-acting injectable generic that truly matches the Reference Listed Drug requires deep and detailed PLGA Characterization for RLD. The USP Lupron Depot® case study remains one of the best examples of how a complete analytical approach helps developers understand polymer identity and performance. Lessons from this study continue to guide both innovators and generic manufacturers working with PLGA platforms today.
At ResolveMass Laboratories Inc., our polymer scientists apply these standardized USP methods to bridge the gap between RLD polymers and generic formulations. We use validated workflows to understand polymer variability, evaluate structural differences, and help developers build analytical packages that regulators expect. With this support, teams can move more smoothly from early development to final product approval.
➡️ Looking for high-purity PLGA that meets regulatory expectations? Explore our pharmaceutical-grade options: https://resolvemass.ca/pharmaceutical-grade-plga-supplier/
Why PLGA Characterization Defines Generic Success
The approval of Vivitrol®, the first PLGA-based generic in 2023, showed the industry how important clear and precise polymer analysis truly is. Strong PLGA Characterization for RLD helps developers demonstrate Q1/Q2 sameness and Q3 equivalence, which are essential for reducing formulation risk and building a solid ANDA submission.
Lupron Depot®, approved in 1989, remains the model for PLGA depot systems. Its long history provides valuable insight into how very small changes in polymer microstructure can influence release rate, stability, and overall product behavior. Because the challenges in these formulations usually come from the polymer—not the drug—developers must fully decode the PLGA fingerprint, including monomer ratio, molecular weight, architecture, and end-group chemistry. Understanding these aspects ensures the generic performs like the RLD throughout the entire release period.
➡️ If you need PLGA customized for specific release kinetics or microstructure, explore our custom synthesis services: https://resolvemass.ca/custom-plga-synthesis/
Analytical Framework for PLGA Characterization for RLDs
The USP Lupron Depot study demonstrates that matching an RLD polymer to an in-house PLGA sample requires an orthogonal set of analytical tools. Each tool provides a different layer of information about polymer structure and behavior. When combined, these techniques create a full molecular picture that helps confirm polymer sameness.
ResolveMass Laboratories follows this same blueprint in its workflows to deliver highly reproducible data. By using multiple complementary techniques, developers gain confidence in batch-to-batch consistency and can establish equivalence before moving into larger-scale manufacturing.
➡️ For developers scaling to clinical or commercial levels, ResolveMass also provides PLGA contract manufacturing
1. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) – Core of PLGA Characterization for RLD
Answer upfront: NMR determines monomer ratio, block length, polymer architecture, and end-group identity of the PLGA used in the RLD.
In the USP study, both ¹H NMR and ¹³C NMR provided essential information. The ¹H NMR confirmed the lactide:glycolide ratio of 75:25, while ¹³C NMR helped determine block length and identify the acid end-group. These measurements form the foundation for all other analytical work and ensure developers understand the polymer’s core structure.
ResolveMass enhances this approach using quantitative NMR with T₁/T₂ relaxation mapping. This helps verify polymer architecture and supports predictive modeling of degradation behavior. Such clarity is valuable during regulatory review, where detailed understanding of polymer performance is expected.
➡️ To learn more about monomer-ratio determination using NMR, visit: https://resolvemass.ca/nmr-spectroscopy-for-accurate-monomer-ratio/
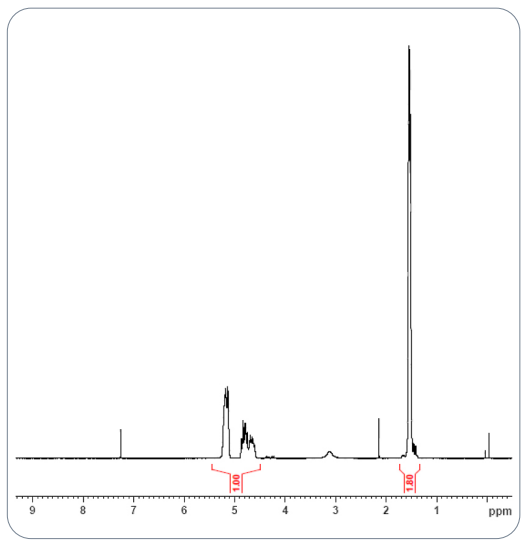
Fig.1 NMR spectra of extracted PLGA polymer from RLD
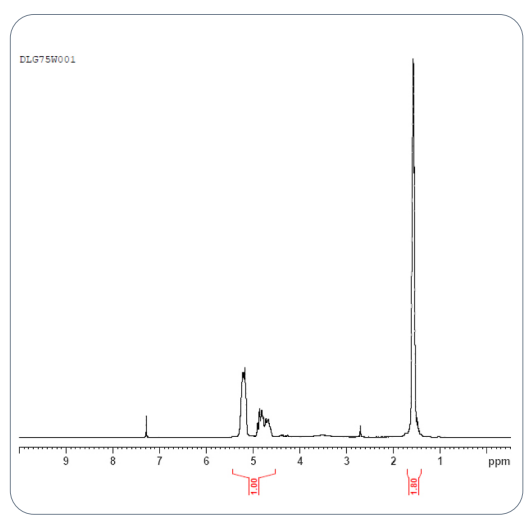
Fig.2 NMR spectra of PLGA polymer standard
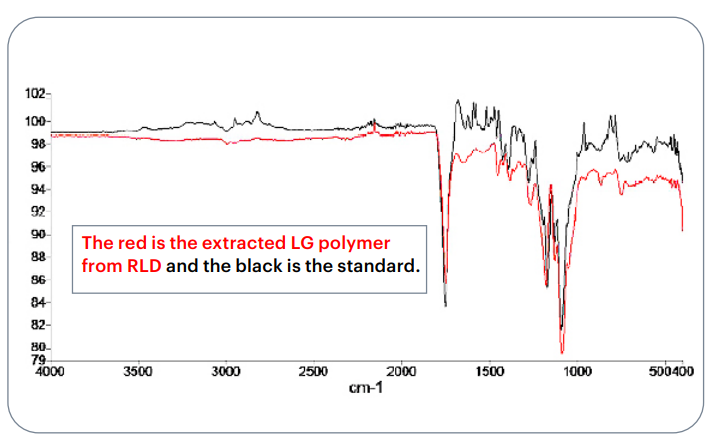
Fig.3 IR spectral comparison of the extracted PLGA polymer
from the RLD
2. Gel Permeation Chromatography (GPC/SEC) – Molecular Weight and Distribution for PLGA Characterization for RLD
Answer upfront: GPC determines molecular weight, distribution, and inherent viscosity—key parameters needed to assess polymer sameness and support PLGA Characterization for RLD.
In the USP Lupron Depot® study, the extracted PLGA showed an Mw of 13,583 Da with a polydispersity index of 1.68. These values closely matched the in-house 75:25 LG polymer standard, which measured an Mw of 12,118 Da and a PD of 1.70. Such close alignment shows well-controlled polymer manufacturing and reliable polymer synthesis, both of which directly impact drug release rate and depot performance.
At ResolveMass Laboratories Inc., we strengthen GPC analysis by using 4D GPC coupled with multi-angle light scattering. This advanced system provides deeper insights into molecular size, branching, and polymer topology. For developers working on PLGA Characterization for RLD, this level of detail helps link molecular weight distribution to microsphere behavior, degradation patterns, and long-term stability. These insights support better process optimization and help confirm that a generic product mirrors the RLD throughout its lifecycle.
➡️ For guidance on PLGA molecular weight and PDI evaluation, check: https://resolvemass.ca/plga-polymer-molecular-weight-and-pdi/
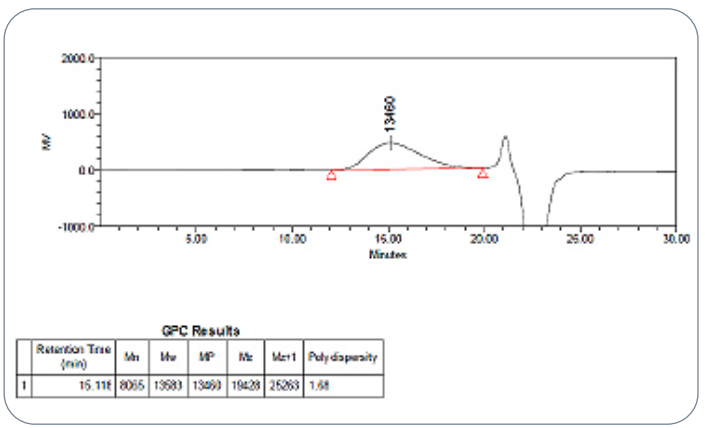
Fig.4 GPC chromatogram for the extracted PLGA polymer
from the RLD
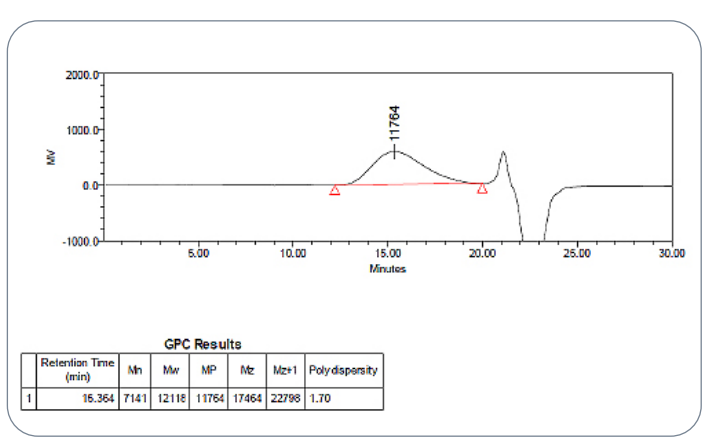
Fig.5 GPC chromatogram for the in-house PLGA polymer
standard
3. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) – Thermal Behavior Insight in PLGA Characterization for RLD
Answer upfront: DSC determines the glass transition temperature (Tg), which reflects thermal stability, polymer mobility, and overall structural behavior—key factors in PLGA Characterization for RLD.
In the USP Lupron Depot® case study, the extracted polymer exhibited a Tg of 40.54 °C, while the in-house PLGA standard showed a Tg of 43.84 °C. These values are closely aligned, indicating that both polymers share similar amorphous characteristics and thermal responses. This similarity is essential because Tg affects microsphere stability during manufacturing steps such as mixing, extrusion, and drying, as well as during storage.
At ResolveMass Laboratories Inc., we combine traditional DSC with modulated DSC and thermogravimetric analysis to provide a deeper thermal profile. This approach captures minor thermal transitions or early degradation events that may not be visible in standard tests. Such detailed assessment ensures developers understand the polymer’s thermal limits and can design processes that maintain polymer integrity—an important step when matching an RLD’s performance.
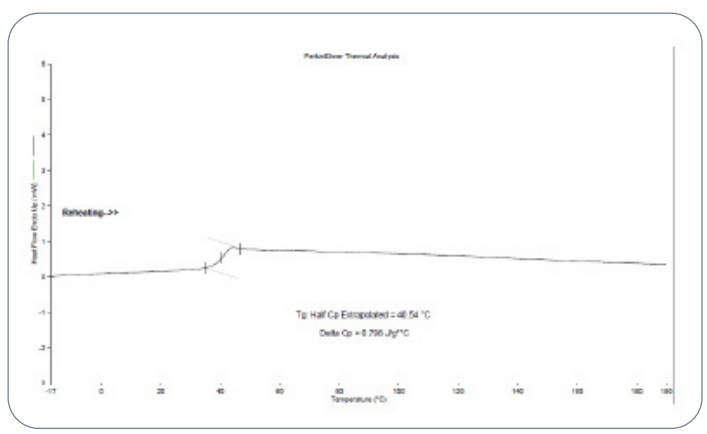
Fig.6 Glass transition temperature by DSC for the
extracted PLGA polymer from the RLD
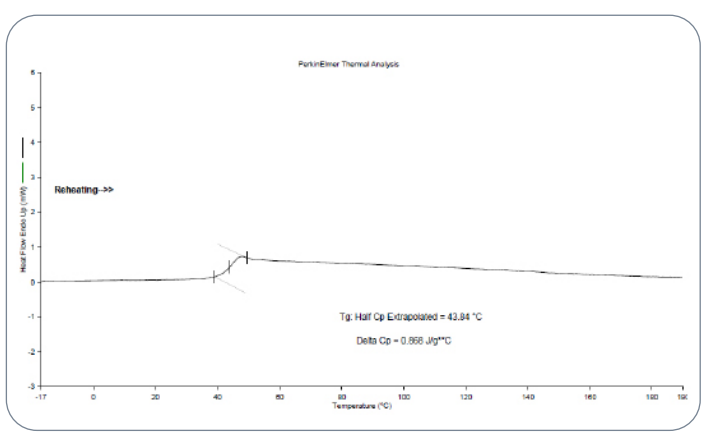
Fig.7 Glass transition temperature by DSC for the
PLGA polymer standard
4. X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) – Crystallinity and Structural Form for PLGA Characterization for RLD
Answer upfront: XRD identifies whether the polymer is amorphous or crystalline, helping confirm structural equivalence—an important part of PLGA Characterization for RLD.
In the USP Lupron Depot® study, both the extracted polymer and the in-house PLGA standard displayed amorphous diffraction patterns. This is typical for DL-lactide:glycolide copolymers with a 75:25 ratio. Matching amorphous profiles is critical because structural form affects polymer solubility, water uptake, and drug-release behavior over the full dosing interval.
At ResolveMass Laboratories Inc., XRD is paired with polarized optical microscopy to examine polymer uniformity and detect subtle variations in molecular packing. This combined approach helps identify early signs of instability or unwanted structural shifts during storage or processing. By ensuring that the polymer maintains its expected amorphous nature, developers gain confidence that the generic product will behave consistently with the RLD throughout manufacturing and long-term use.
5. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR) – Functional Group Equivalence in PLGA Characterization for RLD
Answer upfront: FT-IR identifies key functional groups—especially ester and carbonyl peaks—to confirm chemical identity, making it a valuable tool in PLGA Characterization for RLD.
In the USP Lupron Depot® case study, the IR spectra of the extracted polymer and the in-house PLGA standard showed nearly identical patterns. Clear overlaps in ester carbonyl stretching and aliphatic C–H bands confirmed that both materials shared the same chemical structure. This quick and reliable test helps verify polymer identity early in development before running more advanced analytical techniques.
At ResolveMass Laboratories Inc., FT-IR is routinely used as an initial screening tool during formulation work. Once the polymer’s basic chemical identity is confirmed, teams proceed with deeper structural analyses such as NMR, GPC, and DSC. This layered approach shortens development timelines and ensures that downstream testing is carried out on a verified and consistent polymer source.
6. End Group and Acid Number Analysis – Essential for PLGA Characterization for RLD
Answer upfront: Acid number measurement helps determine end-group functionality, which directly affects degradation rate and is vital for PLGA Characterization for RLD.
In the USP Lupron Depot® study, the extracted polymer showed an acid value of 10.2 mg KOH/g, while the in-house PLGA standard measured 11.8 mg KOH/g. These closely matched values indicate that both polymers are acid-terminated, which is important because end-group chemistry strongly influences hydrolysis, erosion rate, and release behavior. Matching acid numbers therefore supports confidence in achieving similar in vivo performance.
ResolveMass Laboratories Inc. combines potentiometric titration with confirmatory ¹³C NMR analysis to create a reliable end-group profile. This dual approach improves accuracy and ensures consistent interpretation across batches. With clearer insight into end-group behavior, developers can better predict polymer breakdown and align their generic formulation with the RLD’s release characteristics.
7. Polymer Architecture Assessment – Structural Accuracy in PLGA Characterization for RLD
Answer upfront: Determining whether a polymer is linear or branched is crucial, because polymer architecture has a direct effect on degradation and release performance in PLGA Characterization for RLD.
The USP Lupron Depot® study confirmed that the extracted polymer was linear, based on NMR peak alignment and block-length distribution. A linear structure typically produces predictable erosion and steady release kinetics, making architectural sameness an important marker of equivalence between the RLD and a generic product.
ResolveMass Laboratories Inc. enhances this assessment using diffusion-ordered spectroscopy (DOSY NMR) and 4D GPC topology mapping. These advanced tools evaluate subtle structural features such as branching, chain connectivity, and molecular organization. By matching polymer architecture at this detailed level, developers can ensure that their formulation behaves similarly to the RLD during processing, storage, and clinical use.
USP Lupron Depot Case Study – Key Comparative Results for PLGA Characterization for RLD
The USP Lupron Depot® case study provides one of the most complete comparisons between an RLD polymer and an in-house PLGA standard. These results show how closely matched polymers can demonstrate strong equivalence when each critical parameter is evaluated through a full PLGA Characterization for RLD workflow. The table below summarizes the major findings and highlights how both polymers align across appearance, composition, molecular weight, and structural attributes.
Such close alignment across orthogonal methods confirms that the extracted polymer from the RLD and the in-house PLGA standard share nearly identical physicochemical properties. This type of matching supports confidence that the generic formulation will perform similarly to the RLD throughout its release period, storage, and clinical use. For developers, these results reinforce the importance of combining multiple analytical tools to establish a comprehensive polymer fingerprint before moving toward regulatory submission.
Key Comparative Table
| Parameter | In House LG Polymer | Extracted from Lupron Depot (RLD) | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| Appearance | White powder | White powder | Equivalent |
| L:G Ratio | 75:25 | 75:25 | Match |
| Inherent Viscosity | 0.17 dL/g | 0.18 dL/g | Match |
| Molecular Weight | 12,118 Da | 13,583 Da | Match |
| Polydispersity | 1.70 | 1.68 | Match |
| Block Length | 1.37 | 1.39 | Match |
| Tg | 43.84 °C | 40.54 °C | Match |
| Acid Number | 11.8 | 10.2 | Match |
| Polymer Type | Acid-terminated linear | Acid-terminated linear | Match |
Interpretation:
Both polymers displayed nearly identical profiles across all critical parameters, demonstrating the value of thorough PLGA Characterization for RLD using orthogonal tools. Matching these attributes is a strong indicator that a generic formulation is likely to exhibit similar release behavior, stability, and overall clinical performance as the RLD. These results also show how proper analytical strategy can reduce uncertainty during generic development and strengthen the foundation of an ANDA submission.
Regulatory and USP Advancements in PLGA Standards – Supporting PLGA Characterization for RLD
USP, in partnership with the FDA, has developed general chapters <315> and <316> to guide analytical testing of lactide–glycolide polymers. These chapters define best practices for NMR and GPC analysis, offering a unified approach for laboratories worldwide. For developers working on complex generics, these standards simplify communication with regulators and ensure polymer testing is consistent, reliable, and scientifically defensible.
At ResolveMass Laboratories Inc., all polymer testing is fully aligned with these USP methods. This alignment ensures each dataset supports Q1/Q2 sameness and Q3 equivalence, which are key expectations for PLGA Characterization for RLD. Using USP-compliant workflows also helps reduce potential regulatory gaps, improves the strength of the analytical narrative, and shortens the time needed to prepare submission-ready data.
By following these established guidelines, developers gain a smoother regulatory pathway and can demonstrate that their analytical approach meets the same standards used in the USP Lupron Depot® case study. This consistency gives reviewers greater confidence in the data and supports faster, more predictable approvals for complex generic products.
ResolveMass Laboratories Inc. – Leadership in PLGA Analytics and PLGA Characterization for RLD
ResolveMass Laboratories Inc. provides a complete and scientifically advanced framework for evaluating PLGA polymers, especially for developers seeking strong PLGA Characterization for RLD. Our team uses a fully orthogonal analytical platform that includes NMR, GPC/SEC, DSC, XRD, and FT-IR to build a detailed understanding of polymer identity, structure, and behavior. This holistic approach ensures that every critical element influencing drug release and stability is thoroughly examined.
Our capabilities extend to full monomer and end-group profiling, detailed architectural mapping through 4D GPC and DOSY NMR, and customized method transfer for both ANDA and 505(j) pathways. We also incorporate polymer simulation and degradation modeling to help clients predict real-world performance more accurately. These scientific tools strengthen formulation robustness and help developers maintain tight control over polymer variability across batches.
By combining deep analytical knowledge with regulatory expectations, ResolveMass Laboratories ensures that all data generated is clear, reproducible, and submission-ready. Our goal is to support partners through every step of the characterization process—helping them reduce risk, accelerate development, and meet all requirements for PLGA-based complex generics.
➡️ If your generic development requires PLGA designed for sustained-release injectables, explore: https://resolvemass.ca/plga-for-controlled-release/
Conclusion – The Importance of PLGA Characterization for RLD
The USP Lupron Depot® case study clearly shows that strong and detailed PLGA Characterization for RLD is the foundation of successful complex generic development. By using orthogonal analytical tools, developers can build a full picture of polymer identity, quality, and performance. This approach reduces uncertainty, supports better decision-making, and strengthens the scientific basis of every formulation step.
Combining NMR, GPC/SEC, DSC, XRD, and FT-IR allows researchers to decode the complete polymer fingerprint, including monomer ratio, end groups, molecular weight distribution, and architecture. These insights help ensure that the generic product behaves like the RLD throughout manufacturing, storage, and clinical use. ResolveMass Laboratories Inc. applies these validated strategies to help clients achieve analytical equivalence, reduce development risks, and accelerate regulatory approval timelines.
With advanced testing capabilities, regulatory alignment, and expert interpretation, ResolveMass stands as a trusted partner for developers navigating PLGA-based drug products. From early polymer assessment to final submission, our scientific support helps bring high-quality generics to market with confidence.
🔗 Contact ResolveMass Laboratories
FAQs on PLGA Characterization for RLD
PLGA is a biodegradable and biocompatible polymer made from lactic and glycolic acids. Its key characteristics include adjustable molecular weight, variable monomer ratios, and controlled mechanical strength. PLGA also offers predictable thermal behavior and tunable degradation, making it widely used in drug delivery and medical implants.
PLGA degradation is mainly influenced by monomer ratio, molecular weight, end-group chemistry, and polymer crystallinity. Environmental factors such as pH, moisture, and temperature can also change the breakdown rate. Device design, size, and manufacturing conditions further shape how quickly the polymer erodes.
PLGA shows strong FT-IR absorbance peaks around ~1750 cm⁻¹ for ester carbonyl stretching and ~1180 cm⁻¹ for C–O–C stretching. Additional peaks appear near ~1450 cm⁻¹ for CH₃ bending and around ~2940–2990 cm⁻¹ for C–H stretching. This spectrum helps verify polymer identity and confirms the presence of key functional groups.
PLGA types are defined mainly by their lactide:glycolide ratios, such as 50:50, 65:35, 75:25, and 85:15. These ratios affect degradation speed, mechanical properties, and final polymer behavior. Variants may also differ in end-group chemistry, such as acid-terminated or ester-terminated PLGA.
The degradation time of PLGA can range from a few weeks to several months depending on polymer composition. Faster-degrading forms like 50:50 PLGA may break down in 1–2 months, while higher lactide grades degrade more slowly. Molecular weight and processing conditions also influence total erosion time.
To prevent early degradation, PLGA should be stored in cool, dry, and low-humidity conditions. Avoiding high temperatures, strong light exposure, and reactive chemicals helps maintain stability. Using protective packaging and controlling the manufacturing environment further reduces unwanted hydrolysis.
PLGA degrades mainly by hydrolysis of its ester bonds, where water slowly breaks the polymer chains into shorter segments. This process begins internally and progresses outward, creating a gradual loss of strength and mass. Final degradation products are lactic and glycolic acids, which the body naturally processes.
Most medical-grade PLGA is amorphous due to the irregular arrangement of lactide and glycolide units. This non-crystalline structure allows water to penetrate easily, leading to predictable and uniform degradation. Only PLGA with very high lactide content may exhibit slight crystallinity.
Reference
- Kuehster, L., Bingham, P. A., Lundberg, D. J., Kilgallon, L. J., Cooper, J. C., et al. (2025). Characterization of the repeat unit sequence of poly(lactide‑co‑glycolide). Macromolecules, 58(8), 3886–3897. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.macromol.4c02895
- Makadia, H. K., & Siegel, S. J. (2011). Poly lactic‑co‑glycolic acid (PLGA) as biodegradable controlled drug delivery carrier. Polymers, 3(3), 1377–1397. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym3031377
- United States Pharmacopeia. (n.d.). Lactide–glycolide polymers (LG polymers). Retrieved November 28, 2025, from https://www.usp.org/excipients/lg-polymers
- United States Pharmacopeia. (2023). Robust LG polymer characterization: A case study of a reference listed drug, Lupron Depot 3ef3bd1e-44ca-41bc-a348-05f8d61…. United States Pharmacopeial Convention.