Introduction
PLGA Characterization Methods are essential to ensure the performance, purity, safety, and reproducibility of Poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid)—one of the most widely used biodegradable polymers in drug delivery. The analytical testing approaches described below form the foundation of quality assurance for PLGA manufacturing and formulation development.
ResolveMass Laboratories Inc. performs specialized analytical evaluation of PLGA using advanced instrumentation, validated methods, and deep domain expertise to help pharmaceutical innovators achieve consistent, high-quality results.
Summary
- PLGA characterization methods such as NMR, GPC, DSC, and residual monomer analysis provide the essential data needed to ensure polymer quality, batch consistency, and regulatory compliance.
- NMR quickly determines lactide:glycolide ratio and confirms polymer identity.
- GPC measures molecular weight and polydispersity, which directly control degradation rate and drug release profile.(see: PLGA depot formulation: https://resolvemass.ca/plga-depot-formulation/).
- DSC reveals thermal transitions, crystallinity, and polymer stability—critical for formulation design.
- Residual monomer testing confirms PLGA purity, ensures safety, and aligns with cGMP and ICH regulatory expectations.(related article: https://resolvemass.ca/q1-q2-polymer-equivalence-assessment/).
- Together, these methods provide a complete analytical framework required for pharmaceutical-grade PLGA.
1: Why Analytical Testing of PLGA Is Critical
Analytical testing ensures that PLGA meets the required composition, purity, and performance specifications. Upfront, the key reasons PLGA must be rigorously characterized include:
- Drug release control (molecular weight, end-groups)
- Degradation predictability (composition, crystallinity)
- Safety (low residual monomers/solvents)
- Regulatory approval readiness (GMP/ICH compliance)
- Batch-to-batch consistency
The PLGA characterization methods below define the scientific backbone for PLGA quality assessment.
2: NMR Analysis of PLGA (¹H & ¹³C NMR)
NMR is used to accurately determine the lactide:glycolide ratio, end-group chemistry, and polymer identity. These parameters directly influence degradation rate and drug release behavior.
For a detailed resource dedicated to monomer ratio accuracy, see:
👉 https://resolvemass.ca/nmr-spectroscopy-for-accurate-monomer-ratio/
How NMR Supports PLGA Characterization Methods
NMR provides rapid and molecular-level insights into:
- Copolymer composition (LA:GA molar ratio)
- End-capping status (acid vs ester)
- Polymer backbone integrity
- Residual monomer levels (if applicable)
- Confirmation of polymer identity for regulatory compliance
NMR results are essential for high-performance end-capped PLGA selection (https://resolvemass.ca/end-capped-plga/).
Key NMR Outputs
| Parameter | What It Tells You | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| LA:GA ratio | Copolymer composition | Controls degradation rate |
| End-group chemistry | Ester-capped vs acid-terminated | Affects hydrophobicity & stability |
| Signal purity | Chemical uniformity | Ensures quality & authenticity |
| Back-bone signals | Chain integrity | Detects unwanted reactions |
Why NMR Matters for Drug Delivery
Since PLGA degradation is governed by hydrolysis of ester linkages, knowing the exact chemistry via NMR is crucial for:
- Microencapsulation formulations
- Long-acting injectable design
- Implant stability modeling
NMR is one of the most important PLGA characterization methods, helping ensure scientific and regulatory confidence.
3: GPC (Gel Permeation Chromatography) for PLGA Molecular Weight
GPC is used to determine the molecular weight (Mn, Mw) and polydispersity index (PDI) of PLGA. These metrics dictate release kinetics and degradation behavior.
For real-world examples, see how GPC analysis informed:
- PLGA microencapsulation scale-up: https://resolvemass.ca/plga-microencapsulation-scale-up/
- PLGA scale-up case study: https://resolvemass.ca/plga-scale-up-case-study/
What GPC Measures
- Number average MW (Mn)
- Weight average MW (Mw)
- Polydispersity (PDI = Mw/Mn)
- Detection of degraded or low-MW fractions
Importance of Molecular Weight
| Molecular Weight Feature | Effect on Drug Delivery |
|---|---|
| High MW | Slower degradation, longer release |
| Low MW | Faster degradation, shorter release |
| Narrow PDI | Predictable controlled-release behavior |
| Broad PDI | Inconsistent drug release |
Since molecular weight directly controls performance, GPC is one of the core PLGA characterization methods used in regulated industries.
4: DSC (Differential Scanning Calorimetry) of PLGA
DSC evaluates thermal transitions, melting behavior, and glass transition temperature (Tg), which help predict polymer processing and storage stability.
This is especially relevant for:
- Custom release control projects: https://resolvemass.ca/custom-plga-release-control/
- PLGA formulation stability assessments: https://resolvemass.ca/plga-formulation-stability/
Key DSC Outputs
- Tg (glass transition temperature)
- Crystallinity
- Thermal degradation onset
- Polymer purity indicators
- Compatibility with excipients
Why Tg Matters
For PLGA:
- Tg typically ranges 40–60°C
- Tg defines polymer rigidity
- Tg predict stability during:
- Sterilization
- Microencapsulation
- Spray drying
- Storage
DSC is a crucial part of PLGA characterization methods, ensuring the polymer remains stable during formulation and handling.
5: Residual Monomer Analysis (Lactic Acid & Glycolic Acid)
Residual monomer testing measures unreacted lactic acid and glycolic acid, ensuring polymer purity and safety. High levels can accelerate degradation and cause batch variability.
Residual monomer control is a key factor in all Q1/Q2 polymer equivalence assessments:
👉 https://resolvemass.ca/q1-q2-polymer-equivalence-assessment/
Analytical Techniques Used
- ¹H NMR / ¹³C NMR
- GC-MS
- HPLC / Ion Chromatography
Why Residual Monomers Matter
| Issue | Impact |
|---|---|
| Accelerated hydrolysis | Faster-than-expected degradation |
| Acidic microenvironment | Drug instability (especially peptides/proteins) |
| Reduced shelf life | Poor storage stability |
| Regulatory failures | Non-compliant purity levels |
Keeping residual monomers low is essential for GMP-grade PLGA. Therefore, this remains one of the most important PLGA characterization methods.
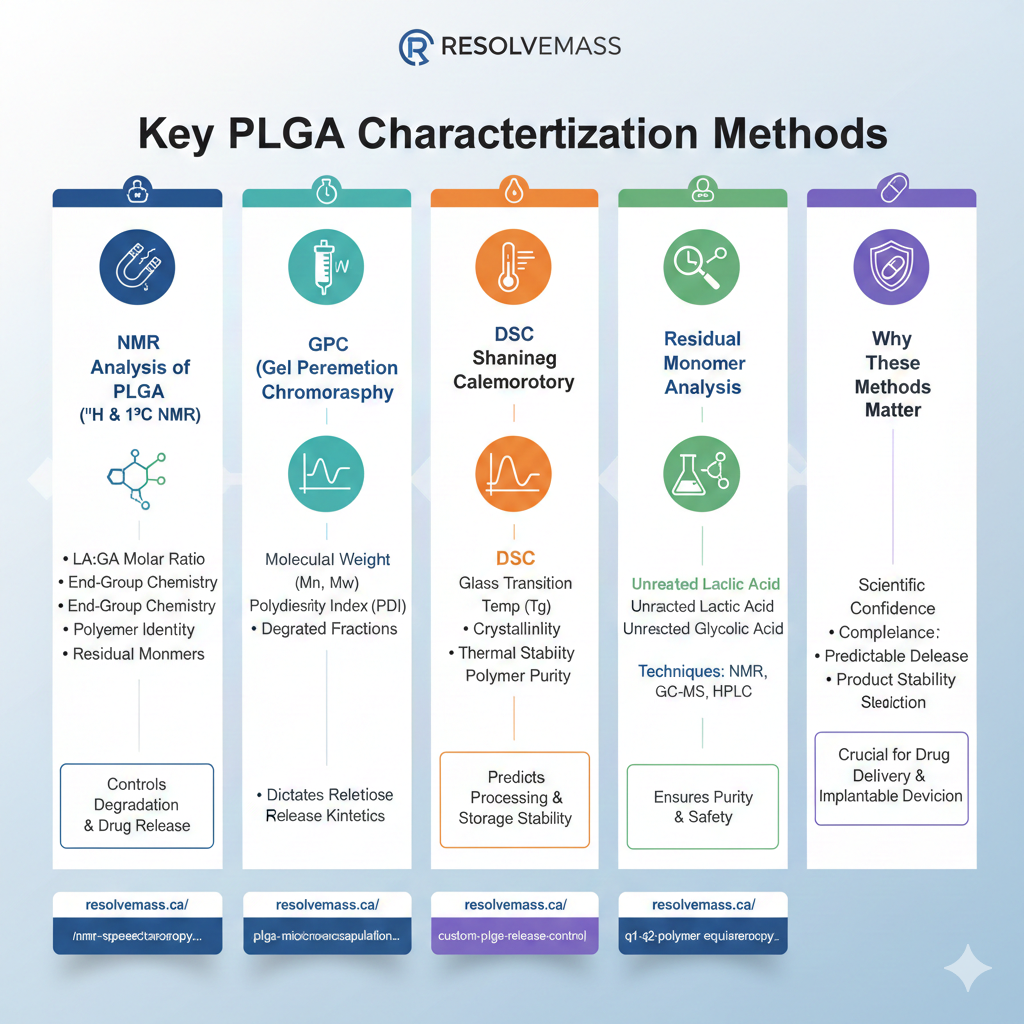
6: Integrating All PLGA Characterization Methods for Complete Quality Control
A comprehensive analytical profile is essential to meet regulatory requirements (ICH, USP, FDA). A summary of required techniques:
Comprehensive analysis requires combining NMR, GPC, DSC, and monomer testing to match RLD references (https://resolvemass.ca/plga-characterization-for-rld/) and maintain consistency during scale-up (https://resolvemass.ca/plga-scale-up-case-study/).
Table: Complete PLGA Characterization Methods Overview
| Method | Purpose | Key Output |
|---|---|---|
| NMR | Composition, end groups, identity | LA:GA ratio, purity |
| GPC | Molecular weight profile | Mn, Mw, PDI |
| DSC | Thermal behavior | Tg, crystallinity |
| Residual Monomer Testing | Purity & safety | Lactic/Glycolic acid % |
This integrated approach ensures:
- Batch reproducibility
- Predictable degradation
- cGMP-compliant manufacturing
- Drug stability and safety
7: Application Areas Requiring Rigorous PLGA Characterization
PLGA characterization methods are essential for:
- Long-acting injectable formulations
- Depot microspheres and nanoparticles
- Implants and scaffolds
- Gene delivery systems
- Vaccine delivery platforms
These methods support advanced applications including:
- Oncology formulations (https://resolvemass.ca/plga-oncology-formulation/)
- Microsphere design (https://resolvemass.ca/plga-microsphere-case-study/)
- Solvent processing optimization (https://resolvemass.ca/dissolving-plga-in-solvents/)
- Shelf-life and stability modeling (https://resolvemass.ca/plga-formulation-stability/)
- Depot injectable systems (https://resolvemass.ca/plga-depot-formulation/)
For all these applications, analytical precision ensures consistent therapeutic outcomes.
8: How ResolveMass Laboratories Inc. Establishes EEAT in PLGA Analytical Testing
ResolveMass Laboratories demonstrates deep expertise in:
- Polymer chemistry
- GMP analytical method development
- Regulatory-aligned characterization
- Advanced mass spectrometry & NMR
- Customized PLGA testing protocols
Our team works with global pharmaceutical innovators, supporting R&D, scale-up, and commercialization—reinforcing trust, reliability, and scientific authority.
Explore our PLGA release control expertise:
👉 https://resolvemass.ca/custom-plga-release-control/
Conclusion
In summary, PLGA Characterization Methods—including NMR, GPC, DSC, and residual monomer analysis—are essential to understanding the composition, purity, molecular weight, and stability of PLGA. These analytical tools guarantee consistent quality, predictable degradation, and regulatory-ready documentation. By applying these methods together, pharmaceutical formulators can ensure safe, reproducible, and high-performing PLGA-based drug delivery systems.
FAQs on Analytical Testing of PLGA
The essential PLGA characterization methods include NMR, GPC, DSC, and residual monomer analysis, which together provide a complete chemical, thermal, and molecular profile of the polymer.
NMR determines the LA:GA ratio and end-group chemistry, GPC measures molecular weight and polydispersity, DSC evaluates thermal transitions (Tg, crystallinity), and monomer analysis confirms polymer purity and regulatory compliance. These methods are mandatory for Q1/Q2 equivalence, RLD matching, and long-acting injectable development.
NMR provides direct molecular-level confirmation of the copolymer composition, identifying the lactide:glycolide ratio and ensuring the polymer aligns with the intended degradation profile.
It also detects end-capping, residual monomers, and structural abnormalities. These factors influence polymer hydrophobicity, degradation rate, and compatibility with APIs. For regulatory submissions, NMR is considered one of the most authoritative identity-confirmation test
GPC determines molecular weight distribution (Mn, Mw, PDI), which directly governs the degradation rate and drug release behavior of PLGA.
High molecular weight PLGA degrades slowly, while low molecular weight grades degrade rapidly. A narrow PDI ensures reproducible release kinetics, essential for FDA/EMA-approved depot formulations. GPC is also used to confirm polymer stability during scale-up, sterilization, and storage.
Residual monomers (lactic acid and glycolic acid) can trigger accelerated hydrolysis, pH drops, and API instability—especially in peptide and protein formulations.
Regulatory agencies require low monomer levels to ensure safety, stability, and batch consistency. Residual monomer analysis supports Q1/Q2 polymer equivalence, impurity assessment, and controlled degradation modeling.
End-capped PLGA contains esterified terminal groups, making the polymer more hydrophobic and slower to degrade. Acid-terminated PLGA degrades faster and creates a more acidic microenvironment.
NMR and titration methods identify end-group chemistry, while GPC confirms changes in molecular weight. End-capping selection is one of the key design decisions for microspheres, depots, and implants.
Reference
- Anderson, J.M., & Shive, M.S. (2012). Biodegradation and biocompatibility of PLA and PLGA. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 64, 72–82.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2012.09.004
- Makadia, H.K., & Siegel, S.J. (2011). Poly lactic-co-glycolic acid (PLGA) as biodegradable controlled drug delivery carrier. Polymers, 3(3), 1377–1397.https://doi.org/10.3390/polym3031377
- Fredenberg, S. et al. (2011). The mechanisms of drug release from PLGA-based formulations. International Journal of Pharmaceutics, 415(1–2), 34–52.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2011.05.014
- Danhier, F., Ansorena, E., Silva, J.M. et al. (2012). PLGA-based nanoparticles: An overview of biomedical applications. Journal of Controlled Release, 161(2), 505–522.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2012.01.043
- EMA – ICH Q3C Guidelines for Residual Solvents. European Medicines Agency.https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/ich-q3c-r8-residual-solvents
- US Pharmacopeia (USP) <467> Residual Solvents.https://www.usp.org

