
Introduction
PLGA drug loading represents a critical parameter in developing controlled-release pharmaceutical formulations using poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) microspheres and implants. The efficiency of PLGA drug loading determines not only the therapeutic payload delivered to patients but also influences release kinetics, stability, and overall treatment efficacy. At ResolveMass Laboratories Inc., we understand that optimizing drug loading efficiency requires systematic evaluation of polymer properties, drug characteristics, fabrication techniques, and process parameters to achieve reproducible, high-quality formulations for clinical applications.
The biodegradable and biocompatible nature of PLGA polymers has established them as the gold standard for sustained-release drug delivery systems approved by regulatory agencies worldwide. However, achieving optimal PLGA drug loading while maintaining drug stability and desired release profiles presents significant formulation challenges that require specialized expertise and analytical capabilities.
For foundational concepts, see our detailed guide on PLGA microsphere formulation:
👉 https://resolvemass.ca/plga-microsphere-formulation/
Summary
Key Takeaways:
- PLGA drug efficiency directly impacts therapeutic efficacy, with optimization techniques achieving 70-95% encapsulation rates
- Critical factors include polymer composition (50:50 vs 75:25 ratios), drug solubility characteristics, and fabrication method selection
- Double emulsion (W/O/W) and single emulsion (O/W) techniques offer distinct advantages for hydrophilic versus hydrophobic compounds
- Process parameters such as polymer concentration, organic solvent type, emulsifier selection, and homogenization speed significantly influence loading outcomes
- Advanced characterization methods enable precise measurement of drug distribution, release kinetics, and formulation stability
- ResolveMass Laboratories provides comprehensive PLGA drug loading optimization services with validated analytical protocols
- Explore formulation stability principles here:
👉 https://resolvemass.ca/plga-formulation-stability/ - ResolveMass Laboratories provides comprehensive PLGA drug loading optimization services with validated analytical protocols.
- Learn more about PLGA microspheres, implants, and controlled-release formulation strategies:
👉 https://resolvemass.ca/plga-depot-formulation/
1: Understanding PLGA Polymer Characteristics for Drug Loading
PLGA Composition and Its Impact on Drug Loading
The lactide-to-glycolide ratio in PLGA copolymers fundamentally affects PLGA drug loading capacity and release behavior. Common ratios of 50:50, 65:35, and 75:25 offer different hydrophobicity levels, degradation rates, and drug compatibility profiles. The 50:50 PLGA composition provides faster degradation (1-2 months) and is ideal for water-soluble drugs requiring rapid release, while 75:25 formulations offer extended release over 4-6 months, making them suitable for highly potent compounds requiring sustained therapeutic levels.
Molecular weight selection equally influences drug loading efficiency. Higher molecular weight PLGA (>50 kDa) creates more viscous polymer solutions that can encapsulate larger drug quantities but may slow drug release. Lower molecular weight variants (<20 kDa) facilitate faster degradation and drug release but may compromise initial PLGA drug loading efficiency.
- For PLGA 50:50 sourcing and properties, see:
👉 https://resolvemass.ca/plga-5050-supplier/ - For detailed solvent compatibility:
👉 https://resolvemass.ca/dissolving-plga-in-solvents/
Drug-Polymer Compatibility Considerations
Successful PLGA drug depends critically on physicochemical compatibility between the therapeutic agent and polymer matrix. Key compatibility factors include:
- Hydrophobicity: Lipophilic drugs naturally achieve higher loading in hydrophobic PLGA matrices
- Solubility parameters: Drugs with similar Hansen solubility parameters to PLGA exhibit superior loading efficiency
- Ionization state: pH-dependent ionization affects drug-polymer interactions and distribution
- Molecular size: Small molecules (<500 Da) may exhibit burst release, while larger biologics (>5 kDa) require specialized encapsulation strategies
Learn about PLGA solubility enhancement strategies here:
👉 https://resolvemass.ca/plga-solubility-enhancement/
2: PLGA Drug Loading Fabrication Techniques
1.Single Emulsion (Oil-in-Water) Method
The O/W single emulsion technique suits hydrophobic drugs requiring incorporation into PLGA microspheres. This method achieves PLGA drug by dissolving both polymer and drug in an organic solvent (typically dichloromethane or ethyl acetate), then emulsifying this phase into an aqueous solution containing stabilizers like polyvinyl alcohol (PVA). Drug loading efficiency through this method typically ranges from 60-85% for lipophilic compounds, with particle sizes between 1-100 micrometers depending on homogenization parameters.
See real-world application in this PLGA microsphere case study:
👉 https://resolvemass.ca/plga-microsphere-case-study/
2.Double Emulsion (Water-in-Oil-in-Water) Method
For hydrophilic drugs, proteins, and peptides, the W/O/W double emulsion method provides superior PLGA drug loading capabilities. This technique first creates a primary water-in-oil emulsion containing the aqueous drug solution dispersed in PLGA-organic solvent, followed by secondary emulsification into an external aqueous phase. While more complex, this method enables loading of water-soluble therapeutics with efficiencies reaching 70-90% when properly optimized.
Learn more about formulating complex or highly potent APIs with PLGA:
👉 https://resolvemass.ca/formulating-highly-potent-apis-using-plga-polylactic-co-glycolic-acid-microspheres/
3.Spray Drying for PLGA Drug Loading
Spray drying offers rapid, scalable production of PLGA drug microspheres by atomizing polymer-drug solutions into heated chambers. This technique achieves excellent batch-to-batch reproducibility and enables continuous manufacturing, though PLGA drug loading efficiency may be slightly lower (50-75%) compared to emulsion methods due to potential drug loss during the drying process.
4.Electrospraying and Advanced Techniques
Electrospraying technology enables precise control over particle size distribution and PLGA drug loading uniformity. By applying high voltage to polymer-drug solutions, this method produces microspheres with narrow size distributions (1-10 micrometers) and drug loading efficiencies approaching 85-95%, particularly valuable for expensive therapeutic compounds requiring maximum utilization.
3: Critical Process Parameters Affecting PLGA Drug Loading
Polymer Concentration Optimization
| Polymer Concentration | Drug Loading Impact | Particle Size | Release Profile |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5-10% w/v | Lower encapsulation (50-65%) | 1-20 μm | Faster release |
| 15-25% w/v | Optimal loading (70-85%) | 20-80 μm | Controlled release |
| >30% w/v | Variable loading (60-80%) | 80-150 μm | Extended release |
Higher PLGA concentrations in organic solvents create more viscous emulsions that resist drug partitioning into the external aqueous phase, thereby improving PLGA drug. However, excessive viscosity may hinder homogenization and create larger particles with heterogeneous drug distribution.
1.Organic Solvent Selection
The choice of organic solvent profoundly impacts PLGA drug efficiency through multiple mechanisms:
- Dichloromethane (DCM): High volatility enables rapid solidification, minimizing drug loss but potentially causing drug crystallization
- Ethyl acetate: Lower toxicity and moderate evaporation rate improve drug distribution within PLGA matrix
- Chloroform: Enhanced PLGA solubility but regulatory concerns limit pharmaceutical applications
- Acetone: Water miscibility reduces drug loading for hydrophilic compounds
Learn about solvent choice and dissolution behavior:
👉 https://resolvemass.ca/dissolving-plga-in-solvents/
2.Homogenization and Emulsification Parameters
Controlled homogenization speed and duration directly influence PLGA drug outcomes. Higher speeds (10,000-20,000 rpm) create smaller particles with larger surface areas, potentially increasing drug loss to external phases and reducing loading efficiency. Moderate speeds (5,000-10,000 rpm) with optimized emulsification times (2-5 minutes) typically maximize drug retention while producing clinically relevant particle sizes.
3.Drug-to-Polymer Ratio
Theoretical PLGA drug increases proportionally with drug-to-polymer ratio, but practical encapsulation efficiency often decreases at higher ratios due to:
- Saturation of polymer matrix exceeding solubility limits
- Increased drug presence at particle surfaces leading to burst release
- Altered particle morphology affecting stability
Optimal ratios typically range from 1:5 to 1:20 (drug:polymer) depending on specific formulation requirements and drug properties.
4: Analytical Characterization of PLGA Drug Loading
1.Quantifying Drug Loading and Encapsulation Efficiency
At ResolveMass Laboratories Inc., we employ validated analytical methods to precisely measure PLGA drug loading parameters:
Drug Loading (DL%) = (Mass of drug in microspheres / Total mass of microspheres) × 100
Encapsulation Efficiency (EE%) = (Actual drug loading / Theoretical drug loading) × 100
High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), ultra-performance liquid chromatography (UPLC), and UV-visible spectroscopy provide accurate quantification of encapsulated drug content. These methods enable determination of both surface-associated and matrix-incorporated drug fractions, critical for predicting release kinetics.
For polymer equivalence frameworks:
👉 https://resolvemass.ca/q1-q2-polymer-equivalence-assessment/
2.Morphological and Structural Analysis
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) reveals surface morphology, particle size distribution, and surface-associated drug crystals that impact PLGA drug quality. Smooth, spherical particles indicate optimal formulation conditions, while porous or irregular surfaces suggest processing issues affecting drug retention and release.
Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) identifies drug crystalline states within PLGA matrices. Amorphous drug dispersion typically indicates molecular-level incorporation with enhanced stability, while crystalline peaks suggest potential storage and release challenges.
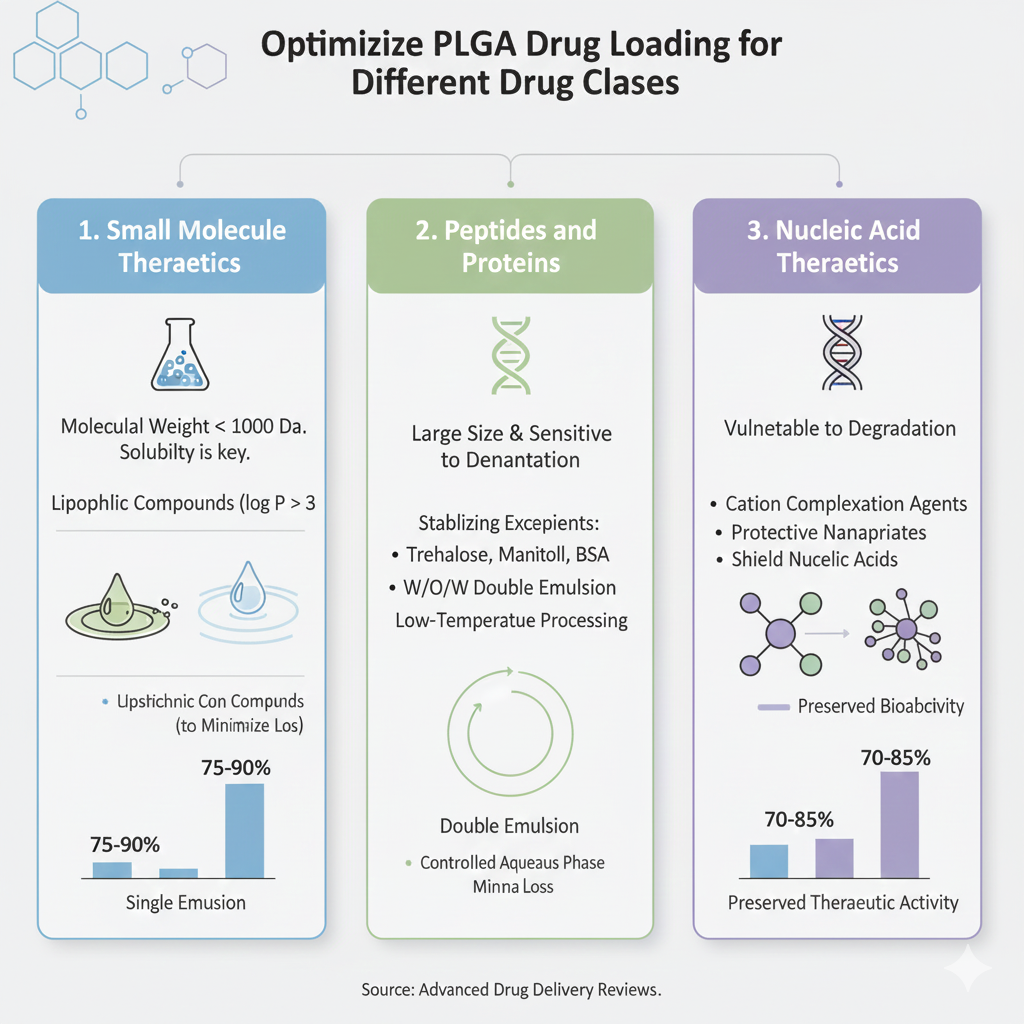
5: Optimizing PLGA Drug Loading for Different Drug Classes
1.Small Molecule Therapeutics
Small molecule drugs with molecular weights below 1000 Da require careful consideration of solubility and partition coefficients. For lipophilic compounds (log P > 3), single emulsion methods with optimized PLGA drug loading achieve 75-90% efficiency. Hydrophilic molecules (log P < 0) benefit from double emulsion techniques with carefully controlled aqueous phase compositions to minimize drug loss.
2.Peptides and Proteins
Protein therapeutics present unique challenges for PLGA drug due to their aqueous solubility, large molecular size, and susceptibility to denaturation. Stabilizing excipients such as trehalose, mannitol, or bovine serum albumin protect protein structure during encapsulation. W/O/W double emulsion with low-temperature processing preserves bioactivity while achieving drug loading efficiencies of 60-80%.
3.Nucleic Acid Therapeutics
DNA and RNA molecules require specialized PLGA drug strategies incorporating cationic complexation agents or protective nanoparticles. These approaches shield nucleic acids from degradation while enabling loading efficiencies approaching 70-85% with preserved therapeutic activity upon release.
Learn more about enhancing solubility and compatibility here:
👉 https://resolvemass.ca/plga-solubility-enhancement/
6: Advanced Strategies for Enhanced PLGA Drug Loading
1.Co-Encapsulation Approaches
Simultaneous loading of multiple therapeutic agents within PLGA microspheres enables combination therapies with synchronized release kinetics. This strategy requires careful optimization of drug-drug and drug-polymer interactions to maintain individual PLGA drug loading efficiencies while avoiding incompatibilities.
2.Surface Modification Techniques
Post-fabrication surface modifications enhance targeting capabilities without compromising PLGA drug loading. Conjugation of targeting ligands, antibodies, or cell-penetrating peptides to microsphere surfaces improves cellular uptake and therapeutic efficacy while maintaining the controlled-release properties of the drug-loaded core.
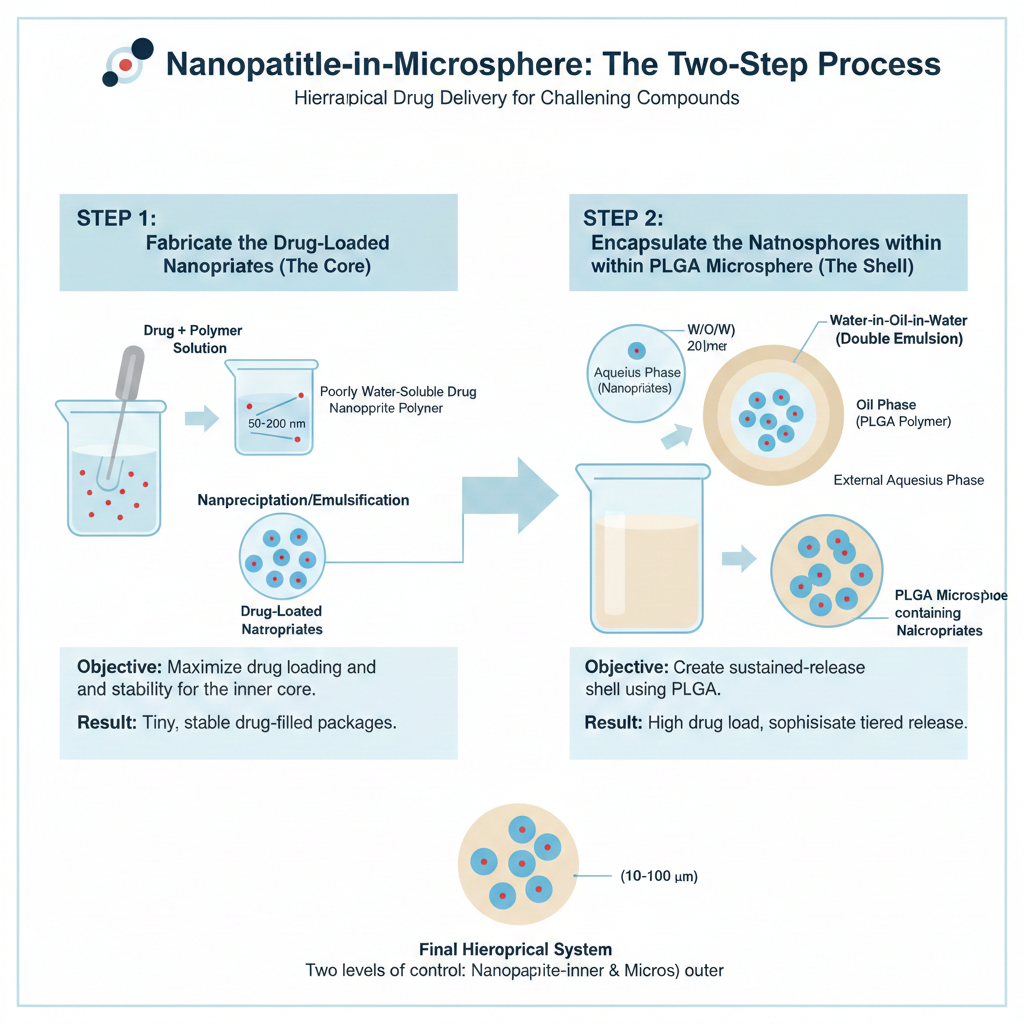
3.Nanoparticle-in-Microsphere Systems
Incorporating drug-loaded nanoparticles within PLGA microspheres creates hierarchical delivery systems with improved drug loading capacity and sophisticated release profiles. This approach proves particularly valuable for poorly water-soluble compounds requiring solubilization strategies combined with sustained release.
7: Quality Control and Regulatory Considerations
Establishing Drug Loading Specifications
Regulatory submissions require well-defined PLGA drug specifications with acceptance criteria based on clinical dose requirements and therapeutic windows. Typical specifications include:
- Drug loading content: Target ± 10%
- Encapsulation efficiency: >70%
- Particle size distribution: D50 within specified range ± 15%
- Release profile: Compliance with dissolution specifications
Stability Studies for Drug-Loaded PLGA Formulations
Long-term stability testing under ICH conditions evaluates PLGA drug loading retention, drug degradation, and release profile consistency. Accelerated studies (40°C/75% RH) predict shelf life and identify potential degradation pathways requiring formulation adjustments.
Dive deeper into PLGA stability fundamentals:
👉 https://resolvemass.ca/plga-formulation-stability/
8: ResolveMass Laboratories: Your PLGA Drug Loading Partner
ResolveMass Laboratories Inc. offers comprehensive services for optimizing PLGA drug across diverse therapeutic applications. Our state-of-the-art facilities and experienced scientists provide:
- Formulation development and PLGA drug loading optimization
- Analytical method development and validation
- Physicochemical characterization
- Stability testing programs
- Regulatory support documentation
- Scale-up and technology transfer services
Our proven track record includes successful optimization of PLGA drug for small molecules, peptides, proteins, and nucleic acids across preclinical and clinical development stages.
- See our scale-up success story:
👉 https://resolvemass.ca/plga-scale-up-case-study/ - Explore alternative biodegradable excipients like PCL:
👉 https://resolvemass.ca/pcl-excipient-supplier/
9: Troubleshooting Common PLGA Drug Loading Challenges
Low Encapsulation Efficiency
When PLGA drug falls below target specifications, systematic evaluation of these factors typically identifies root causes:
- Excessive drug partitioning to external aqueous phase (solution: increase polymer concentration or modify aqueous phase composition)
- Incomplete drug solubilization in organic phase (solution: evaluate alternative solvents or co-solvents)
- Rapid drug diffusion during solvent evaporation (solution: optimize evaporation rate and temperature)
Learn core depot formulation strategies here:
👉 https://resolvemass.ca/plga-depot-formulation/
Burst Release Phenomena
Excessive initial drug release (>30% within 24 hours) indicates surface-associated drug accumulation rather than matrix incorporation. Optimization strategies include adjusting homogenization parameters, polymer concentration, and drug-to-polymer ratios to improve drug distribution within PLGA particles.
Particle Aggregation
Aggregated microspheres exhibit variable PLGA drug and release characteristics. Prevention strategies include optimizing stabilizer concentrations, ionic strength of aqueous phases, and implementing post-fabrication washing protocols to remove excess surfactants.
10: Future Perspectives in PLGA Drug Loading Technology
Emerging technologies continue advancing PLGA drug capabilities. Microfluidic fabrication enables precise control over particle formation with superior batch-to-batch consistency. Computational modeling predicts optimal formulation parameters, reducing experimental iterations. Advanced characterization techniques including confocal Raman microscopy provide three-dimensional drug distribution mapping within individual microspheres, enabling unprecedented understanding of PLGA drug loading mechanisms.
Conclusion
Optimizing PLGA drug loading efficiency in microspheres and implants requires comprehensive understanding of polymer chemistry, drug properties, fabrication techniques, and process parameters. The systematic approach to PLGA drug loading optimization presented here enables development of robust, reproducible formulations meeting clinical and regulatory requirements. Success in PLGA drug loading depends on careful characterization, methodical optimization, and rigorous quality control throughout development.
ResolveMass Laboratories Inc. combines scientific expertise with advanced analytical capabilities to solve complex PLGA drug loading challenges. Our commitment to quality and innovation ensures that your controlled-release formulations achieve optimal therapeutic performance. Whether developing novel sustained-release products or optimizing existing PLGA formulations, proper attention to drug loading efficiency establishes the foundation for successful clinical outcomes.
For expert assistance with your PLGA drug optimization projects, we invite you to explore how ResolveMass Laboratories can accelerate your formulation development. Our team of specialists is ready to discuss your specific requirements and design customized solutions for your therapeutic applications.
FAQs on Optimizing Drug Loading Efficiency in PLGA
Drug loading efficiency depends on several interacting parameters such as polymer molecular weight, lactide:glycolide ratio, polymer hydrophobicity, solvent selection, drug solubility in the organic phase, drug–polymer affinity, emulsifier concentration, and process conditions. Hydrophobic drugs typically show higher loading due to better compatibility with PLGA, while hydrophilic drugs often require additional strategies like complexation, double-emulsion methods, or solid-in-oil techniques to improve incorporation.
Compatibility between the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) and PLGA determines how well the drug partitions into the polymer phase during microsphere or implant formation. If compatibility is poor, the drug tends to escape into the external aqueous phase or crystallize out, reducing loading efficiency. Techniques like Hansen solubility parameter matching, differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), and miscibility prediction models help assess and improve drug–polymer affinity.
Solvents with high solubility for both PLGA and the drug (e.g., DCM, EA, acetone blends) generally enhance drug entrapment. Solvent evaporation rate also impacts encapsulation: fast-evaporating solvents may prematurely harden microspheres, pushing the drug out, while slow-evaporating solvents allow better distribution but may increase drug diffusion into the aqueous phase. Mixed solvent systems often offer optimal balance.
Higher molecular weight PLGA has greater viscosity, which slows diffusion of the drug during particle formation—often increasing entrapment. However, it also results in slower degradation and reduced release rates. Lower molecular weight PLGA may reduce loading efficiency for hydrophilic drugs due to faster diffusion during emulsification but speeds up release. A balance must be optimized based on the target product profile.
Reference
- Kadriye Kızılbey.Optimization of Rutin-Loaded PLGA Nanoparticles Synthesized by Single-Emulsion Solvent Evaporation Method.https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsomega.8b02767
- Maria del Moral,Maximilian Loeck, Eameema Muntimadugu 3, Guillem Vives 1,4, Vy Pham 3,5, Peter Pfeifer 1, Giuseppe Battaglia,Silvia Muro.Role of the Lactide:Glycolide Ratio in PLGA Nanoparticle Stability and Release under Lysosomal Conditions for Enzyme Replacement Therapy of Lysosomal Storage Disorders.https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10531859/
- Hirenkumar K Makadia , Steven J Siegel.Poly Lactic-co-Glycolic Acid (PLGA) as Biodegradable Controlled Drug Delivery Carrier.https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3347861/

