
INTRODUCTION
Selecting PLGA for peptide, protein, and nucleic acid delivery requires choosing the right polymer chemistry, molecular weight, and end-group to achieve predictable release and preserve biomolecule stability. This article explains how to systematically select the right PLGA properties for PLGA Peptide Delivery, protein stabilization, and mRNA/siRNA encapsulation.
As demand for controlled-release biologics grows, PLGA remains the most trusted biodegradable polymer, backed by decades of regulatory acceptance. But effective PLGA Peptide Delivery depends on understanding how polymer characteristics influence encapsulation efficiency, degradation behavior, and biological performance.
ResolveMass Laboratories Inc. provides pharmaceutical-grade PLGA and deep scientific expertise supported by resources such as:
- PLGA 50:50 Supplier: https://resolvemass.ca/plga-5050-supplier/
- PLGA Scale-Up Case Study: https://resolvemass.ca/plga-scale-up-case-study/
- End-Capped PLGA: https://resolvemass.ca/end-capped-plga/
SUMMARY
- Selecting the right PLGA for peptide, protein, and nucleic acid delivery is essential because polymer composition, molecular weight, end groups, and morphology directly control release kinetics, stability, and bioactivity.
- PLGA Peptide Delivery performance depends on polymer chemistry (50:50 vs 75:25), MW, inherent viscosity, end-capping, and microsphere/nanoparticle architecture.
- High hydrophilicity of peptides/proteins and instability of mRNA/siRNA require customized PLGA grades with controlled degradation, minimized burst release, and optimized encapsulation conditions.
- Acidic microclimate suppression, steric stabilization, and particle engineering are key success factors for advanced PLGA Peptide Delivery systems.
- ResolveMass Laboratories Inc. supports scientists with high-purity PLGA, analytical expertise, and formulation guidance for peptide, protein, and mRNA/siRNA delivery.
1:WHY PLGA IS THE GOLD STANDARD FOR PEPTIDE, PROTEIN, AND NUCLEIC ACID DELIVERY
PLGA works for peptides, proteins, and mRNA/siRNA because its degradation rate is tunable, biocompatible, and predictable. This tunability is essential for PLGA Delivery systems that require controlled release.
Key advantages:
- FDA-approved and widely published
- Adjustable degradation (weeks to months)
- Compatible with hydrophilic and hydrophobic payloads
- Safe metabolic by-products (lactic & glycolic acid)
- Processable into microspheres, nanoparticles, implants, and gels
Its flexibility makes it the top choice across biologics delivery — especially PLGA Delivery formulations.
ResolveMass ensures polymer identity and ratio accuracy through NMR verification:
🔗 https://resolvemass.ca/nmr-spectroscopy-for-accurate-monomer-ratio/
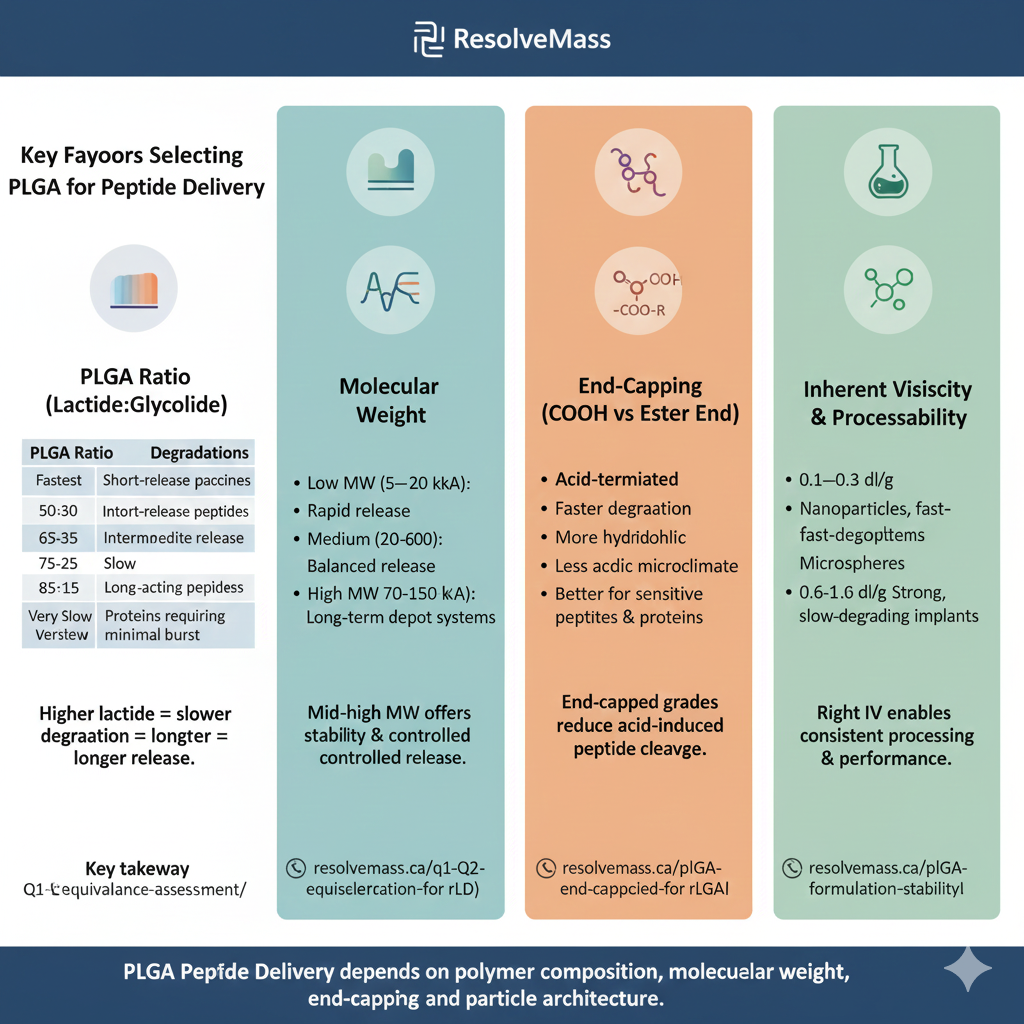
2: KEY FACTORS FOR SELECTING PLGA FOR PEPTIDE DELIVERY
PLGA Peptide Delivery depends on polymer composition, molecular weight, end-capping, and particle architecture. Each factor changes release kinetics, encapsulation efficiency, and peptide stability.
Below is a structured guide.
PLGA RATIO (LACTIDE : GLYCOLIDE)
The L:G ratio determines degradation time — the foundational parameter for PLGA Peptide Delivery systems.
| PLGA Ratio | Hydrophobicity | Degradation | Suitable Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| 50:50 | Medium | Fastest | Short-release peptides, vaccines |
| 65:35 | Higher | Medium | Intermediate peptide release |
| 75:25 | High | Slow | Long-acting peptides |
| 85:15 | Highest | Very slow | Proteins requiring minimal burst |
Rule: Higher lactide = slower degradation = longer PLGA Peptide Delivery release.
- Learn more about PLGA ratio selection and equivalence methods here:
🔗 https://resolvemass.ca/q1-q2-polymer-equivalence-assessment/ - For the most widely used grade (50:50), refer to:
🔗 https://resolvemass.ca/plga-5050-supplier/
MOLECULAR WEIGHT
More molecular weight = stronger matrix = slower diffusion and degradation.
- Low MW (5–20 kDa): Rapid release
- Medium MW (20–60 kDa): Balanced release
- High MW (70–150 kDa): Long-term depot systems
For PLGA Peptide Delivery, mid–high MW offers both stability and controlled release.
ResolveMass offers pharmaceutical-grade MW characterization for regulatory submissions:
🔗 https://resolvemass.ca/plga-characterization-for-rld/
END-CAPPING (COOH VS ESTER END)
End groups dramatically affect peptide release behavior.
- Acid-terminated (COOH):
- Faster degradation
- More hydrophilic
- Suitable for hydrophobic peptides
- Ester-terminated (End-Capped PLGA):
- Slower degradation
- Less acidic microclimate
- Better for sensitive peptides & proteins
End-capped grades are essential in advanced PLGA Peptide Delivery to reduce acid-induced peptide cleavage.
Detailed technical resource:
🔗 https://resolvemass.ca/end-capped-plga/
INHERENT VISCOSITY & PROCESSABILITY
Inherent viscosity correlates with molecular weight and mechanical strength.
- 0.1–0.3 dL/g: Nanoparticles, fast-degrading systems
- 0.3–0.6 dL/g: Microspheres
- 0.6–1.0+ dL/g: Strong, slow-degrading implants
Choosing the right IV enables consistent PLGA Delivery processing and performance.
See practical formulation insights here:
🔗 https://resolvemass.ca/plga-formulation-stability/
3:CHALLENGES IN PLGA PEPTIDE DELIVERY AND HOW TO SOLVE THEM
1. Burst Release
Peptides diffuse quickly from the surface.
Solutions:
- Higher lactide
- End-capped PLGA
- Double emulsion optimization
- Surface modification
Reduce by using end-capped PLGA or lactide-rich grades:
🔗 https://resolvemass.ca/custom-plga-release-control/
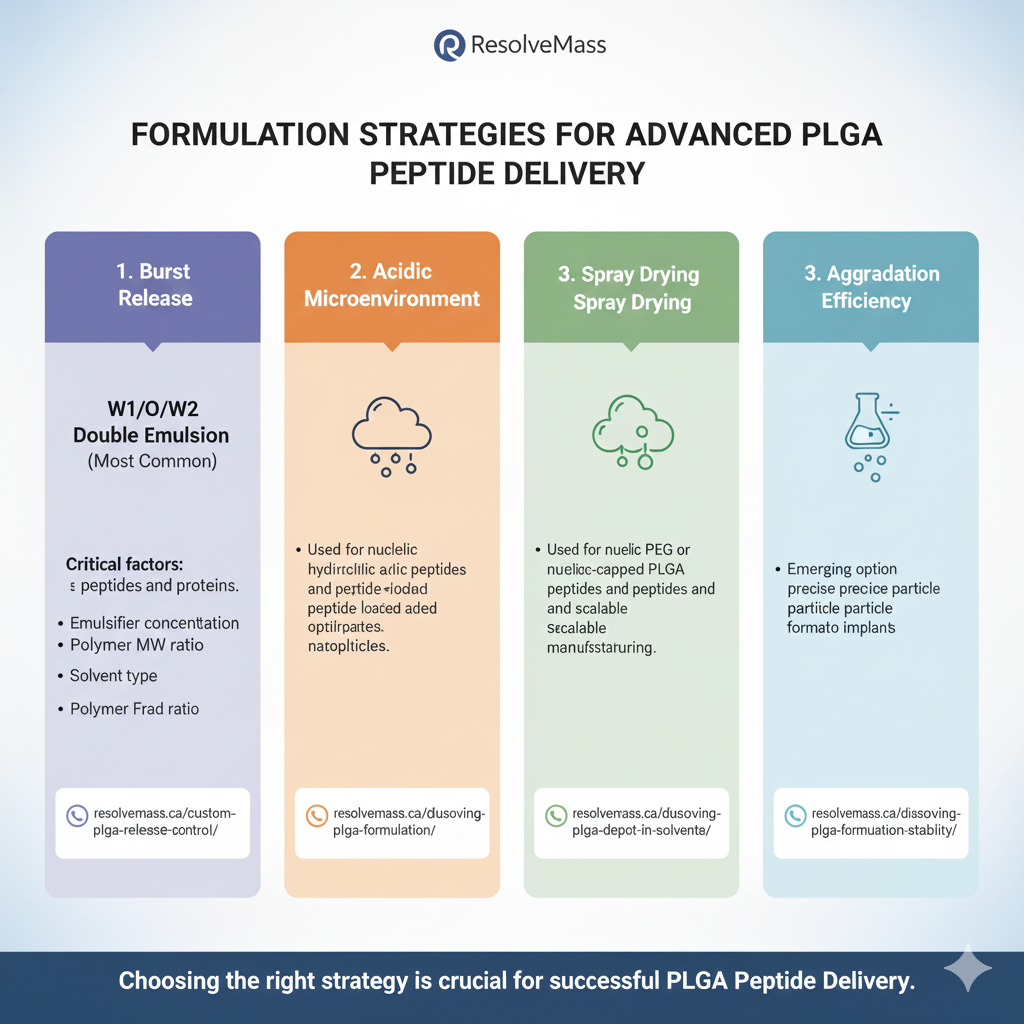
2. Acidic Microenvironment
Degradation generates acidic by-products that destabilize peptides.
Solutions:
- Blending with PEG or PVP
- Using ester-capped PLGA
- Incorporating buffering agents
- Selecting higher lactide ratios
Improve stability with ester-end PLGA (link above) and optimized depot design:
🔗 https://resolvemass.ca/plga-depot-formulation/
3. Low Encapsulation Efficiency
Peptides are hydrophilic and leak during emulsification.
Solutions:
- W1/O/W2 double emulsion
- Adjust pH to reduce peptide solubility
- Add stabilizing excipients
4. Aggregation or Denaturation
Proteins are sensitive to organic solvents and pH shifts.
Solutions:
- Use mild solvent systems
- Stabilize with sugars, albumin
- Optimize lyophilization parameters
High-quality PLGA Delivery requires solving all four challenges.
Understanding solvent interactions is essential for double emulsions and nanoprecipitation.
Reference guide:
🔗 https://resolvemass.ca/dissolving-plga-in-solvents/

4:SELECTING PLGA FOR PROTEIN DELIVERY
PLGA selection for protein delivery requires minimizing denaturation risk, reducing acidic stress, and controlling moisture exposure. Proteins degrade easily, so their stabilization is a core concern.
Recommended PLGA characteristics:
- End-capped PLGA to minimize acid buildup
- Higher lactide ratios (65:35, 75:25)
- Medium–high MW for structural integrity
- Low residual solvents < 100 ppm
Formulation scientists prefer these PLGA types because proteins exhibit better structural stability and sustained release.
For formulation case studies:
🔗 https://resolvemass.ca/plga-microsphere-case-study/
5: SELECTING PLGA FOR NUCLEIC ACID (mRNA/siRNA) DELIVERY
Delivering nucleic acids using PLGA requires optimizing charge balance, encapsulation efficiency, and protection against nucleases.
PLGA Peptide Delivery principles apply, but nucleic acids require extra stabilization.
Ideal characteristics for mRNA/siRNA delivery:
- 50:50 PLGA for faster release profiles
- Surface-modified PLGA nanoparticles
- Cationic coatings (PEI, chitosan) to bind RNA
- Low MW for rapid release to cytoplasm
Why PLGA works for nucleic acids:
- Protects mRNA/siRNA from enzymatic degradation
- Enables targeted delivery with ligand modification
- Provides stable nanoparticle architecture
PLGA nanoparticles are now widely explored as LNP alternatives for non-lipid RNA delivery applications.
Scale-up and manufacturing guidance:
🔗 https://resolvemass.ca/plga-microencapsulation-scale-up/
6: PARTICLE ARCHITECTURE: MICROSPHERES VS NANOPARTICLES
Microspheres
Best for long-acting PLGA Peptide Delivery.
- 20–100 µm
- Depot systems
- Injectable suspensions
Nanoparticles
Best for mRNA/siRNA or rapid-release peptides.
- <300 nm
- Ideal for cellular uptake
- Surface functionalization possible
The choice depends on therapeutic target and required release duration.
- Microspheres = long-acting peptide depots (case study link):
🔗 https://resolvemass.ca/plga-microsphere-case-study/ - Nanoparticles = ideal for mRNA/siRNA
Retention, encapsulation, and release can be tuned with custom PLGA modifications:
🔗 https://resolvemass.ca/custom-plga-release-control/
7: FORMULATION STRATEGIES FOR ADVANCED PLGA PEPTIDE DELIVERY
1. W1/O/W2 Double Emulsion (Most Common)
Ideal for hydrophilic peptides and proteins.
Critical factors:
- Emulsifier concentration
- Solvent type
- Polymer MW and ratio
Scale-up challenges and solutions:
🔗 https://resolvemass.ca/plga-microencapsulation-scale-up/
2. Nanoprecipitation
Used for nucleic acids and peptide-loaded nanoparticles.
3. Spray Drying
Useful for heat-stable peptides and scalable manufacturing.
4. Microfluidics
Emerging option for precise, reproducible particle formation.
8:QUALITY PARAMETERS FOR SELECTING THE RIGHT PLGA
High-end Peptide Delivery systems require pharmaceutical-grade PLGA with tight specifications.
Key parameters:
- Residual solvents (DCM, acetone, EA)
- End-group purity
- Monomer ratio consistency
- Inherent viscosity accuracy
- Heavy metal limits
- Bioburden and endotoxin control
ResolveMass Laboratories Inc. follows strict quality controls to ensure every PLGA batch is consistent and reproducible.
Related technical resources:
- NMR Monomer Ratio: https://resolvemass.ca/nmr-spectroscopy-for-accurate-monomer-ratio/
- Stability Considerations: https://resolvemass.ca/plga-formulation-stability/
- Regulatory Characterization (RLD): https://resolvemass.ca/plga-characterization-for-rld/
9: HOW RESOLVEMASS LABORATORIES SUPPORTS PLGA PEPTIDE DELIVERY PROGRAMS
Scientists rely on ResolveMass because:
- We supply premium pharmaceutical-grade PLGA
- Full analytical support: GPC, NMR, GC, KF
- Expert consultation for PLGA Peptide Delivery formulation
- Regulatory documentation support
- Fast global delivery
Our experience allows us to guide researchers in selecting the exact PLGA grade for peptides, proteins, and mRNA/siRNA.
All relevant resources:
- https://resolvemass.ca/plga-scale-up-case-study/
- https://resolvemass.ca/custom-plga-release-control/
- https://resolvemass.ca/plga-microencapsulation-scale-up/
CONCLUSION
Selecting the right PLGA for peptide, protein, and nucleic acid delivery is crucial because polymer composition, MW, and end-group control release, stability, and biological performance. Effective PLGA Peptide Delivery requires optimized polymer chemistry and formulation strategies.
By understanding PLGA ratios, molecular weight, end-capping, and particle architecture, scientists can build safer, more stable, and more efficient controlled-release drug systems.
ResolveMass Laboratories Inc. is committed to supplying high-quality PLGA and scientific expertise to support your advanced delivery programs.
FAQs on PLGA for Peptide, Protein, and Nucleic Acid Delivery
The PLGA ratio determines degradation rate, which directly controls peptide release.
-50:50 PLGA degrades fastest (weeks) and is ideal for short-acting peptides.
-65:35 or 75:25 provides mid-range degradation suitable for multi-week sustained release.
-85:15 offers very slow degradation for long-acting depot formulations.
The rule is: higher lactide = slower degradation = longer release, making it the most important parameter in PLGA Peptide Delivery.
Molecular weight controls matrix density, mechanical strength, and erosion behavior.
-Low MW (5–20 kDa): fast degradation and rapid diffusion
-Medium MW (20–60 kDa): balanced release, commonly used for peptides
-High MW (70–150 kDa): strongest and slowest degrading for long-term depots
Higher MW generally improves encapsulation efficiency and reduces burst release, which is critical for proteins and peptides.
PLGA protects biomolecules by forming a barrier against enzymatic and environmental stress. However, its acidic degradation products can destabilize actives.
Stabilization requires:
-Ester-capped PLGA to reduce acidity
-Higher lactide ratios
-Addition of buffering agents
-Lyophilization or sugar stabilization for proteins
With proper design, PLGA enables predictable, stable, long-acting formulations.
Nucleic acids require faster release and enhanced stabilization. Ideal PLGA properties include:
-50:50 composition for faster erosion
-Low MW for rapid cytoplasmic release
-Surface functionalization (PEI, chitosan, ligands) to improve RNA binding
-Nanoparticle size < 200–300 nm for cellular uptake
PLGA nanoparticles offer strong protection against nuclease degradation and can act as a non-lipid alternative to LNPs.
Reference
- Su, Y., Zhang, B., Sun, R., Liu, W., Zhu, Q., Zhang, X., Wang, R., & Chen, C. (2021). PLGA-based biodegradable microspheres in drug delivery: recent advances in research and application. Drug Delivery, 28(1), 1397–1418. https://doi.org/10.1080/10717544.2021.1938756 PMC+1
- Omidian, H., Wilson, R. L., & Castejon, A. M. (2025). Recent Advances in Peptide-Loaded PLGA Nanocarriers for Drug Delivery and Regenerative Medicine. Pharmaceuticals, 18(1), 127. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18010127 MDPI+1
- Siepmann, J., & Siepmann, F. (2025). Release mechanisms of PLGA-based drug delivery systems: A review. International Journal of Pharmaceutics: X, 10, 100440. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpx.2025.100440 PMC
- Mohajgani Allahyari, M., & Mohit, E. (2015). Peptide/protein vaccine delivery system based on PLGA particles. Human Vaccines & Immunotherapeutics, 12(3), 806–828. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4964737/

