Introduction: The Challenge of Poorly Soluble APIs
The pharmaceutical industry faces a critical challenge: approximately 70-90% of drug candidates in development pipelines exhibit poor aqueous solubility. PLGA solubility enhancement has emerged as a validated solution for formulating these challenging compounds. At ResolveMass Laboratories Inc., we’ve witnessed firsthand how PLGA poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) transforms poorly soluble drugs into clinically viable therapeutic options through sophisticated encapsulation technologies and release modulation strategies.
👉 https://resolvemass.ca/standard-plga-grades/
Poor solubility directly impacts oral bioavailability, therapeutic efficacy, and patient compliance. Traditional approaches like salt formation, co-solvents, and surfactants often fall short when dealing with highly lipophilic or crystalline APIs. PLGA-based formulations address these limitations by creating a biocompatible, biodegradable matrix that enhances dissolution rates while providing controlled release characteristics.
Summary
PLGA solubility enhancement represents a breakthrough approach for improving the bioavailability of poorly soluble active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). This comprehensive guide explores how PLGA poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) transforms drug delivery systems through advanced encapsulation and controlled release mechanisms.
Key Takeaways:
- PLGA solubility enhancement improves bioavailability for BCS Class II and IV drugs by 3-10 fold
- The polymer’s tunable lactide-to-glycolide ratio (50:50 to 85:15) controls degradation rates from weeks to months👉 https://resolvemass.ca/plga-5050-supplier/
- PLGA nanoparticles and microparticles create sustained release profiles reducing dosing frequency
- FDA-approved biodegradable polymer eliminates safety concerns associated with non-degradable carriers
- Solubility enhancement occurs through particle size reduction, amorphous state stabilization, and surface area maximization
- Clinical applications span oncology, vaccines, hormonal therapies, and chronic disease management
- Advanced case studies available here:
👉 https://resolvemass.ca/plga-scale-up-case-study/
1: Understanding PLGA: The Gold Standard Biodegradable Polymer
PLGA is an FDA-approved copolymer synthesized from lactic acid and glycolic acid monomers. PLGA poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) degrades via hydrolytic cleavage of ester bonds into naturally occurring metabolites—lactic acid and glycolic acid—which are eliminated through normal metabolic pathways.
Learn more about end-capped and acid-terminated PLGA grades:
👉 https://resolvemass.ca/end-capped-plga/
Key Properties of PLGA for Solubility Enhancement
Physical and Chemical Characteristics:
- Biocompatible and biodegradable with established safety profiles
- Tunable degradation rates based on lactide:glycolide ratios
- Glass transition temperature (Tg) ranging from 40-60°C depending on composition
- Molecular weight variations from 10,000 to 200,000 Da
- Amphiphilic nature facilitating encapsulation of both hydrophobic and hydrophilic drugs
| PLGA Ratio | Degradation Time | Typical Applications | Solubility Enhancement Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|
| 50:50 | 1–2 months | Rapid release formulations | Maximum initial burst for acute conditions |
| 65:35 | 3–4 months | Intermediate release | Balanced release for subacute therapies |
| 75:25 | 5–6 months | Extended release | Sustained therapeutic levels |
| 85:15 | 6–12+ months | Long-acting injectables | Minimal burst with prolonged action |
Full degradation profile guide:
👉 https://resolvemass.ca/plga-degradation-profile/
2: Mechanisms of PLGA Solubility Enhancement
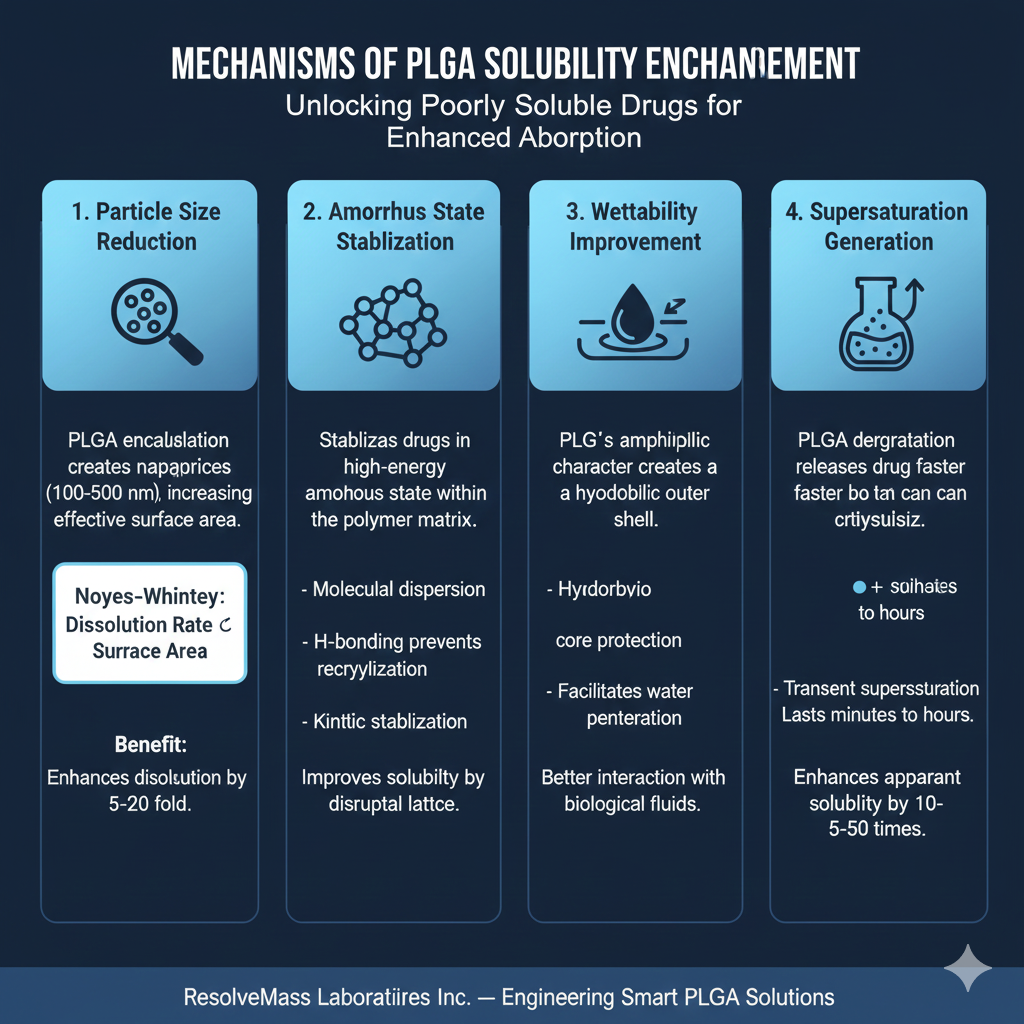
PLGA solubility enhancement operates through multiple synergistic mechanisms that address the fundamental barriers to poor drug dissolution and absorption.
1. Particle Size Reduction and Surface Area Maximization
PLGA encapsulation creates nanoparticles (100-500 nm) or microparticles (1-100 μm) that dramatically increase the effective surface area of poorly soluble APIs. According to the Noyes-Whitney equation, dissolution rate is directly proportional to surface area. By reducing crystalline drug particles from microns to nanoscale dimensions within PLGA matrices, ResolveMass Laboratories achieves dissolution rate enhancements of 5-20 fold compared to bulk drug powder.
Learn about PLGA nanoparticle characterization:
👉 https://resolvemass.ca/plga-characterization-for-rld/
2. Amorphous State Stabilization
Crystalline drugs exhibit lower solubility due to strong lattice energy requiring disruption before dissolution. PLGA solubility enhancement stabilizes APIs in their higher-energy amorphous state within the polymer matrix. The PLGA poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) acts as a molecular dispersion medium, preventing recrystallization through:
- Molecular-level drug distribution within polymer chains
- Hydrogen bonding interactions between drug and polymer
- Physical barrier preventing crystal nuclei formation
- Kinetic stabilization through high viscosity microenvironments
3. Wettability Improvement
Hydrophobic drugs exhibit poor wetting by aqueous gastrointestinal fluids, creating a fundamental barrier to dissolution. PLGA’s amphiphilic character improves interfacial properties between the drug-loaded particles and biological fluids. The polymer creates a hydrophilic outer shell that facilitates water penetration while protecting the encapsulated API.
4. Supersaturation Generation
As PLGA undergoes hydrolytic degradation, it releases drug molecules faster than they can crystallize, creating a supersaturated state in the surrounding microenvironment. This transient supersaturation—lasting minutes to hours—significantly enhances absorption before equilibrium solubility is reached. PLGA solubility enhancement through supersaturation can improve apparent solubility by 10-50 times during critical absorption windows.
Guidance on dissolving PLGA in different solvents:
👉 https://resolvemass.ca/dissolving-plga-in-solvents/
3: PLGA Formulation Strategies for Solubility Enhancement
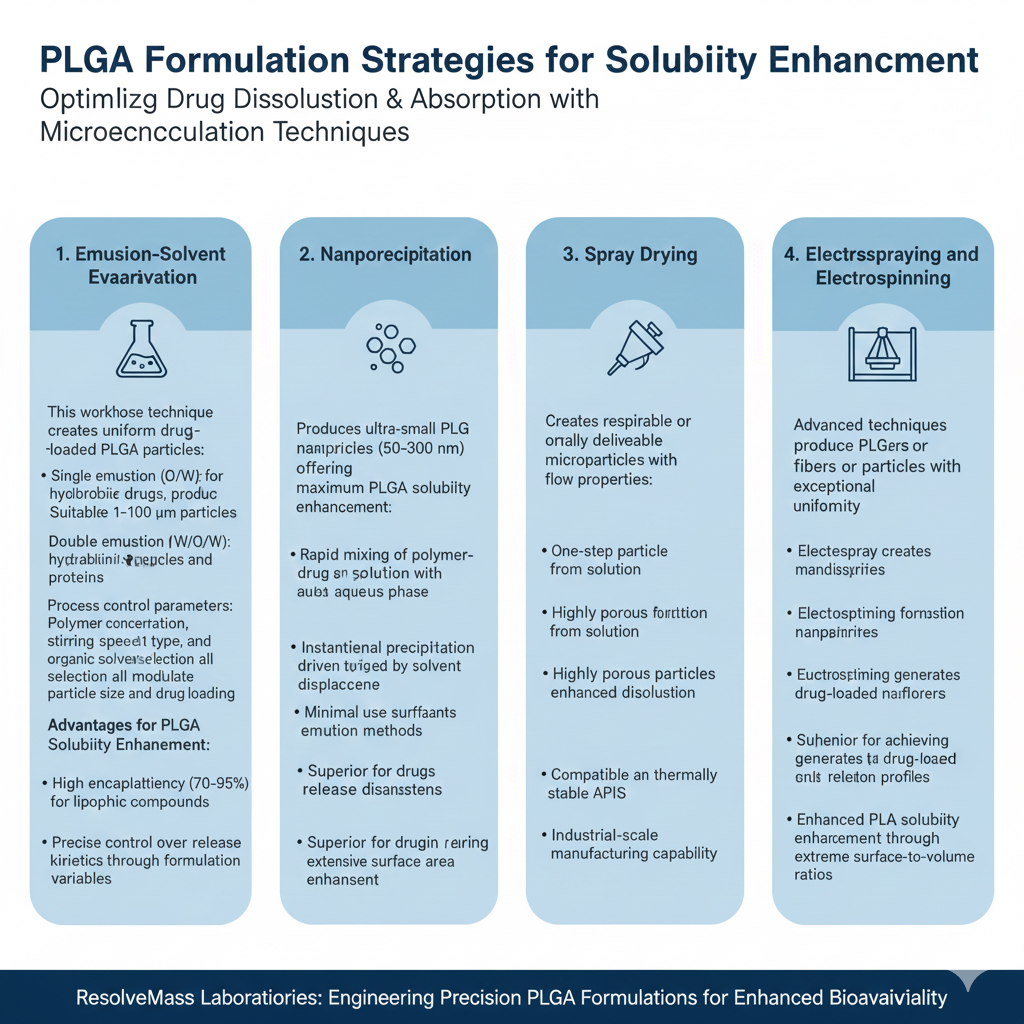
ResolveMass Laboratories employs several sophisticated fabrication techniques to optimize PLGA poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) solubility enhancement for specific APIs and therapeutic objectives.
Emulsion-Solvent Evaporation
This workhorse technique creates uniform drug-loaded PLGA particles:
- Single emulsion (O/W): Ideal for hydrophobic drugs, producing 1-100 μm particles
- Double emulsion (W/O/W): Suitable for hydrophilic peptides and proteins
- Process control parameters: Polymer concentration, stirring speed, surfactant type, and organic solvent selection all modulate particle size and drug loading
Advantages for PLGA Solubility Enhancement:
- High encapsulation efficiency (70-95%) for lipophilic compounds
- Scalable from laboratory to commercial production
- Precise control over release kinetics through formulation variables
Nanoprecipitation
Nanoprecipitation produces ultra-small PLGA nanoparticles (50-300 nm) offering maximum PLGA solubility enhancement:
- Rapid mixing of polymer-drug organic solution with aqueous phase
- Instantaneous precipitation driven by solvent displacement
- Minimal use of surfactants compared to emulsion methods
- Superior for drugs requiring extensive surface area enhancement
Spray Drying
Spray drying creates respirable or orally deliverable PLGA microparticles with excellent flow properties:
- One-step particle formation from solution
- Highly porous particles with enhanced dissolution
- Compatible with thermally stable APIs
- Industrial-scale manufacturing capability
Electrospraying and Electrospinning
These advanced techniques produce PLGA fibers or particles with exceptional uniformity:
- Electrospray creates monodisperse nanoparticles
- Electrospinning generates drug-loaded nanofibers
- Superior for achieving ultra-fast release profiles
- Enhanced PLGA solubility enhancement through extreme surface-to-volume ratios
4: Controlled Release Mechanisms in PLGA Systems
Beyond immediate solubility enhancement, PLGA poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) provides sophisticated release control mechanisms critical for optimizing therapeutic outcomes.
See custom release control systems:
👉 https://resolvemass.ca/custom-plga-release-control/
Triphasic Release Profile
PLGA formulations typically exhibit three distinct release phases:
- Initial Burst Phase (0-24 hours): Surface-associated drug rapidly dissolves, providing loading dose effects
- Lag Phase (Days to Weeks): Minimal release as polymer undergoes bulk erosion without significant mass loss
- Secondary Release Phase (Weeks to Months): Accelerated release as polymer degradation creates porous channels and complete matrix disintegration occurs
Factors Modulating PLGA Release Kinetics
Polymer Properties:
- Lactide:glycolide ratio (primary determinant of degradation rate)
- Molecular weight (higher MW = slower degradation)
- End-group chemistry (acid vs. ester termination affects hydrolysis rate)
Formulation Variables:
- Drug loading percentage (higher loading = greater burst)
- Particle size (smaller particles = faster complete release)
- Porosity and internal morphology
- Additives and excipients modulating hydration
Environmental Factors:
- pH of dissolution medium (acid-catalyzed ester hydrolysis)
- Temperature (hydrolysis rate increases with temperature)
- Enzyme presence (though PLGA degrades primarily via hydrolysis)
5: Clinical Applications of PLGA Solubility Enhancement
ResolveMass Laboratories has contributed to advancing PLGA solubility enhancement applications across diverse therapeutic areas where poorly soluble drugs present formulation challenges.
Oncology: Improving Chemotherapy Delivery
Many cancer drugs exhibit poor aqueous solubility, limiting dosing options and efficacy. PLGA poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) solubility enhancement addresses these limitations:
Explore PLGA Oncology:
👉 https://resolvemass.ca/plga-oncology-formulation/
- Paclitaxel PLGA formulations achieving sustained release over 30 days
- Docetaxel microparticles reducing systemic toxicity through localized delivery
- Curcumin nanoparticles overcoming rapid metabolism through protection and solubility enhancement
- 5-10 fold bioavailability improvements documented in preclinical studies
Vaccines and Immunotherapies
PLGA’s ability to enhance both solubility and immunogenicity makes it ideal for vaccine development:
- Single-injection depot vaccines providing months of antigen presentation
- Protection of protein antigens from degradation
- Enhanced uptake by antigen-presenting cells
- FDA-approved PLGA vaccines already in clinical use
Explore PLGA depot formulation:
👉 https://resolvemass.ca/plga-depot-formulation/
Hormonal and Peptide Therapies
Long-acting PLGA formulations transform treatment regimens:
- Leuprolide acetate depot (Lupron Depot®) providing 1-4 month release
- Risperidone long-acting injection improving psychiatric medication adherence
- GLP-1 agonist formulations extending therapeutic action
- PLGA solubility enhancement enabling subcutaneous delivery of previously intravenous-only peptides
More:
👉 https://resolvemass.ca/plga-peptide-delivery/
Anti-inflammatory and Pain Management
NSAIDs and other pain medications benefit from sustained release:
- Reduced gastrointestinal side effects through controlled release
- Decreased dosing frequency improving patient compliance
- Localized delivery to inflammation sites
- Enhanced solubility of poorly water-soluble analgesics
6: Analytical Characterization of PLGA Solubility Enhancement
At ResolveMass Laboratories Inc., comprehensive characterization ensures PLGA solubility enhancement formulations meet regulatory and performance standards.
Full stability guidelines here:
👉 https://resolvemass.ca/plga-formulation-stability/
Critical Quality Attributes
Particle Characterization:
- Dynamic light scattering (DLS) for size distribution
- Zeta potential measurement for stability prediction
- Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) for morphology
- Confocal microscopy for drug distribution mapping
Drug-Polymer Interactions:
- Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) confirming amorphous state
- X-ray powder diffraction (XRPD) verifying crystallinity reduction
- Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) identifying molecular interactions
- Solid-state NMR for detailed structural analysis
Release Performance:
- In vitro dissolution testing in biorelevant media
- HPLC/UPLC quantification of released drug
- Stability studies under ICH conditions
- Accelerated degradation studies predicting in vivo behavior
7: Advantages of PLGA Over Alternative Solubility Enhancement Technologies
PLGA solubility enhancement offers unique benefits compared to other approaches:
| Technology | Limitations | PLGA Advantages |
|---|---|---|
| Lipid-based systems | Stability issues, food effects | Robust stability, food-independent absorption |
| Cyclodextrins | Limited drug loading, renal safety concerns | High loading capacity, complete biodegradation |
| Solid dispersions | Recrystallization risk | Long-term amorphous stabilization |
| Nanosuspensions | Physical instability (aggregation, settling) | Matrix protection preventing aggregation |
| Salt formation | Limited to ionizable drugs | Applicable to all drug classes |
The PLGA poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) platform combines immediate solubility enhancement with controlled release, offering dual benefits unmatched by single-mechanism approaches.
8: Regulatory Considerations and Commercialization
PLGA’s established regulatory status accelerates development timelines:
- Multiple FDA-approved PLGA products establish precedent
- Well-characterized safety profile spanning decades
- Extensive toxicology data available in literature
- Quality-by-design (QbD) approaches applicable to PLGA formulations
Manufacturing Scalability:
- Robust processes transferable from lab to commercial scale
- GMP manufacturing facilities worldwide with PLGA expertise
- Process analytical technology (PAT) enabling real-time quality control
- Established supply chains for pharmaceutical-grade PLGA polymers
See Q1/Q2 polymer equivalence:
👉 https://resolvemass.ca/q1-q2-polymer-equivalence-assessment/
9: Future Directions in PLGA Solubility Enhancement
ResolveMass Laboratories continues advancing PLGA solubility enhancement technologies through:
Surface Modification Strategies:
- PEGylation for extended circulation time
- Targeting ligands for tissue-specific delivery
- Stimuli-responsive polymers for triggered release
Hybrid Systems:
- PLGA-lipid hybrid nanoparticles combining benefits of both platforms
- PLGA-cyclodextrin conjugates for synergistic solubility enhancement
- Theranostic PLGA systems incorporating imaging agents
Personalized Medicine Applications:
- 3D-printed PLGA implants with patient-specific release profiles
- Pharmacokinetic modeling optimizing individual dosing regimens
- Companion diagnostics guiding formulation selection
Conclusion
PLGA solubility enhancement represents a mature yet continually evolving technology addressing the pharmaceutical industry’s most persistent formulation challenges. PLGA poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) provides a validated, versatile platform for transforming poorly soluble drug candidates into commercially viable products with superior bioavailability, controlled release, and patient-friendly dosing regimens.
At ResolveMass Laboratories Inc., our expertise in PLGA solubility enhancement spans formulation development, analytical characterization, and regulatory support. We’ve helped numerous pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies overcome solubility barriers, advancing promising compounds from laboratory concepts to clinical applications.
The combination of immediate PLGA solubility enhancement through particle engineering and long-term controlled release through biodegradable matrices positions PLGA as the gold standard for poorly soluble API formulation. As drug discovery continues producing increasingly lipophilic candidates, PLGA poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) technologies will remain essential tools in the formulation scientist’s arsenal.
FAQs on How PLGA Modulates API Solubility and Release
PLGA enhances solubility primarily by converting crystalline APIs into an amorphous or molecularly dispersed state within the polymer matrix. This reduces lattice energy barriers and improves wettability. The polymeric encapsulation also prevents drug recrystallization during storage and release, ensuring sustained supersaturation at the absorption site. Together, these mechanisms significantly improve apparent solubility and bioavailability.
PLGA undergoes predictable hydrolytic degradation into lactic and glycolic acids, enabling precise control over the release rate. By adjusting polymer composition, molecular weight, and end-capping, scientists can tune release profiles from days to months. Its biocompatibility, FDA approval, and flexibility for microparticles, implants, and injectable depots make PLGA a gold-standard polymer for sustained release systems.
The lactide:glycolide ratio directly controls hydrophilicity and degradation rate. For example, PLGA 50:50 degrades fastest (1–2 months), resulting in rapid release, while PLGA 85:15 degrades over 6–12+ months for long-acting injectables. Higher glycolide content → faster water uptake → faster erosion. This enables precise tailoring of API release kinetics based on therapeutic needs.
Yes. Poorly soluble APIs often exhibit high burst release due to surface deposition. PLGA’s controlled matrix entrapment and slow hydration reduce initial diffusion. Higher lactide ratios (75:25, 85:15) and ester end-capping further minimize burst release by delaying polymer erosion and stabilizing the drug within the core.
Absolutely. PLGA enhances bioavailability through solubility improvement, prolonged residence time, and localized supersaturation. For drugs with low permeability (BCS Class IV), PLGA particles can also improve mucosal retention or enable injectable depot delivery, bypassing absorption barriers entirely.
Reference
- Ling-Yuan Guoa, Shu-Zhen Yana, Qiang Lia, Qiao Xua, Xi Lina, Shan-Shan Qia, Shu-Qin Yu*b and Shuang-Lin Chen.Poly(lactic-co-glycolic) acid nanoparticles improve oral bioavailability of hypocrellin A in rat.https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlehtml/2017/ra/c7ra04748g
- FDA’s Regulatory Science Program for Generic PLA/PLGA-Based Drug Products.https://www.americanpharmaceuticalreview.com/Featured-Articles/188841-FDA-s-Regulatory-Science-Program-for-Generic-PLA-PLGA-Based-Drug-Products/

