The development of Peptide-Oligonucleotide Conjugates (POCs) depends on the careful integration of advanced chemistry and detailed analytical testing. POC Synthesis and Characterization plays a central role in helping drug discovery programs overcome the natural delivery barriers of nucleic acids. By linking peptides with oligonucleotides, scientists can guide genetic material directly to specific tissues with better precision and control. This combined strategy improves intracellular delivery while maintaining molecular stability in the bloodstream. As gene-based therapies continue to grow, reliable POC Synthesis and Characterization has become essential for successful translational research.
Executive Summary
- Peptide–Oligonucleotide Conjugates (POCs) combine peptides with nucleic acids to overcome delivery barriers, enabling targeted, stable, and efficient intracellular gene modulation.
- Strategic conjugation design—including optimized peptide carriers, linkers, and oligonucleotide chemistries—improves tissue specificity, pharmacokinetics, and therapeutic performance.
- Advanced synthesis approaches, such as solid-phase assembly and post-synthetic parallel conjugation, enable scalable and high-purity manufacturing for both discovery and clinical development.
- High-resolution analytical characterization using HRMS, NMR, and specialized chromatography ensures precise structural confirmation, impurity profiling, and regulatory compliance.
- Technical challenges like aggregation, stereochemical complexity, and solubility are addressed through optimized chemistries, purification strategies, and orthogonal analytical methods.
- Growing clinical success and regulatory alignment position POCs as a cornerstone technology for next-generation genomic medicines across rare diseases, oncology, neuromuscular, and neurodegenerative disorders.
The Strategic Importance of POC Synthesis and Characterization in Modern Medicine
POC Synthesis and Characterization involves chemically connecting peptides and oligonucleotides, followed by thorough analytical testing to confirm structure, purity, and biological function. This field has become increasingly important because it allows researchers to target genetic pathways that were previously considered difficult or impossible to treat. Many nucleic acid therapies struggle with cell entry, which limits their clinical success. Conjugation strategies directly address this challenge by improving delivery efficiency. With better tissue targeting and controlled release, POCs enhance both pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic performance.
The pharmaceutical industry has shifted strongly toward large-molecule therapeutics, especially peptides and oligonucleotides, often called TIDES. Oligonucleotides provide highly specific gene-level targeting, but their size and negative charge make it difficult for them to cross cell membranes. By attaching these molecules to peptides—such as Cell-Penetrating Peptides (CPPs) or receptor-targeting sequences—scientists can significantly improve intracellular uptake. This approach enables selective accumulation in specific tissues. As a result, peptide-assisted delivery is now a key driver of next-generation genomic medicine.
Explore our specialized solutions: Peptide Oligonucleotide Conjugates (POCs) Synthesis Services
ResolveMass Laboratories Inc., based in Montreal, Canada, supports biotechnology and pharmaceutical companies across North America, Europe, and Asia. The team brings deep industry experience in complex bioconjugation projects. Each POC Synthesis and Characterization program is conducted with strict quality systems, full analytical documentation, and regulatory awareness. From early discovery to regulatory submission, the laboratory ensures scientific accuracy and compliance. This structured workflow promotes reproducibility and transparency at every development stage.
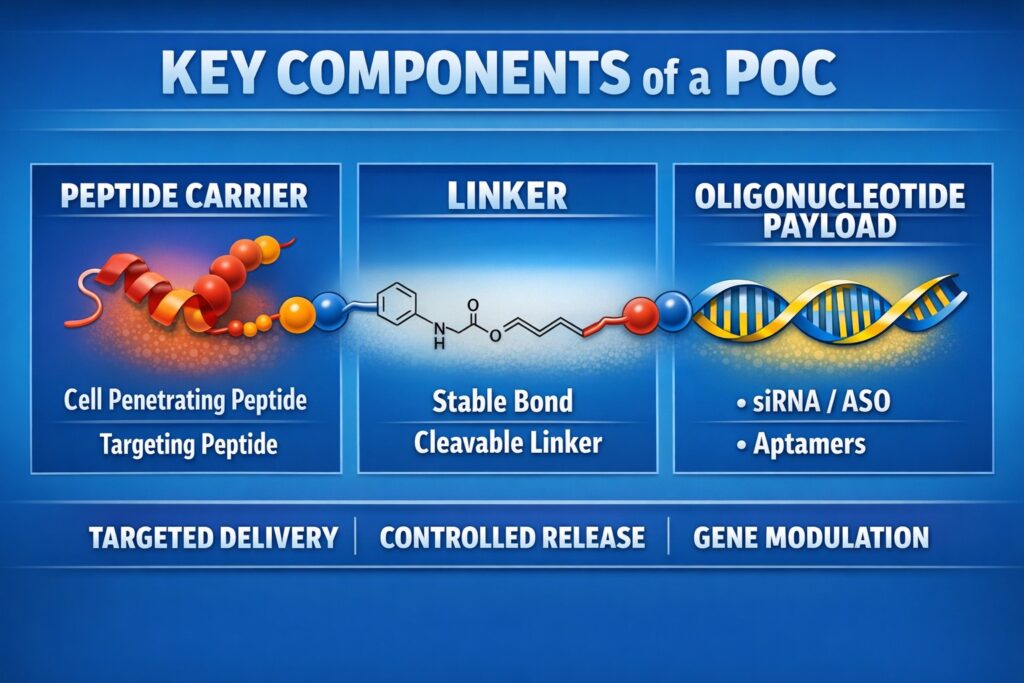
Foundational Components of POC Architecture
A therapeutic POC is built from three interconnected modules. Each module influences how the molecule behaves in the body, including distribution, stability, and biological effect. Even small changes in one section can alter therapeutic performance. Therefore, rational design and optimization are critical. A balanced structure supports effective delivery and predictable clinical results.
The Peptide Carrier
Peptide carriers usually contain 5 to 30 amino acids. Cationic Cell-Penetrating Peptides (CPPs), such as HIV-1 TAT or polyarginine ($R_8-R_{10}$), interact with negatively charged cell membranes to promote uptake. Receptor-Targeting Peptides (RTPs) bind specific surface receptors, such as insulin receptors or tumor-associated integrins. This allows selective delivery into defined cell populations. By adjusting sequence length and charge distribution, researchers can improve tissue specificity and reduce off-target effects. The peptide component strongly influences biodistribution.
The Linker System
The linker connects the peptide to the oligonucleotide and must remain stable in circulation. At the same time, it should allow controlled release once inside the target cell. Non-cleavable linkers formed through click chemistry offer high stability for antisense applications. Cleavable linkers, such as disulfide bonds or enzyme-sensitive sequences, release the payload in response to intracellular conditions. Proper linker choice affects half-life, safety, and therapeutic index. Careful optimization ensures controlled and predictable drug behavior.
The Oligonucleotide Payload
The oligonucleotide core may include siRNA, antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs), or aptamers. Chemical modifications such as phosphorothioate ($PS$) backbones or 2′-O-methyl groups improve resistance to enzymatic degradation. These changes also influence immune response and binding strength. Selecting the correct backbone chemistry maintains stability during systemic delivery. Together, all three modules determine the mechanism of action and clinical potential.
Advanced Methodologies in POC Synthesis and Characterization
The chemical synthesis of POCs requires careful handling because peptides and nucleic acids have different chemical properties. Successful POC Synthesis and Characterization programs at ResolveMass Laboratories Inc. rely on two primary strategies. The selected approach depends on molecular size and structural complexity. Each workflow is designed to maintain compatibility and maximize purity. Analytical feedback guides process improvements throughout development.
Partner with a leading Canadian CRO: Drug Discovery CRO in Canada
Stepwise Solid-Phase Assembly
In stepwise synthesis, the peptide and oligonucleotide are built sequentially on the same solid support. The peptide is first assembled using Fmoc-based Solid Phase Peptide Synthesis (SPPS). After completing the peptide chain, the oligonucleotide is extended using phosphoramidite chemistry. This method reduces intermediate handling and limits purification steps. It is especially useful during early research phases when rapid testing is required.
However, strong acids such as trifluoroacetic acid ($TFA$) can damage nucleic acids during deprotection. To reduce this risk, modified protecting group strategies are applied. Systems such as Boc/tBu chemistry with mild borate-buffer deprotection at $90^\circ\text{C}$ help preserve oligonucleotide integrity. Careful monitoring prevents degradation and ensures consistent results.
Post-Synthetic Parallel Conjugation
Parallel conjugation is commonly used for complex drug development projects. In this method, peptides and oligonucleotides are synthesized and purified separately. The purified components are then linked using selective bioorthogonal chemistry. This approach minimizes unwanted side reactions and improves overall stability. It also provides greater flexibility for longer sequences and protein conjugates.
| Feature | Stepwise Assembly | Post-Synthetic Parallel Conjugation |
| Workflow Efficiency | High (single purification) | Moderate (triple purification required) |
| Sequence Flexibility | Limited (short/simple sequences) | High (long peptides and full proteins) |
| Chemical Stability | High risk of depurination | Low risk (isolated chemistries) |
| Solubility Management | Managed on-resin | Challenging (requires aqueous-organic blends) |
| Scalability | Good for early discovery | Superior for GMP clinical batches |
Learn more about our conjugation capabilities: Peptide Oligonucleotide Conjugation Services
Precision Conjugation Chemistries in POC Synthesis and Characterization
Selecting the right conjugation chemistry is critical for maintaining biological activity. ResolveMass focuses on site-specific and bioorthogonal reactions to ensure uniform products. Reaction selectivity directly influences yield, safety, and regulatory acceptance. Conditions are validated using orthogonal analytical methods.
Copper(I)-Catalyzed Azide-Alkyne Cycloaddition (CuAAC):
This classic click reaction forms a stable triazole linkage with high selectivity. It provides strong yields and metabolic stability. CuAAC is widely used in early-stage development. Careful copper removal is required before biological use.
Strain-Promoted Azide-Alkyne Cycloaddition (SPAAC):
This copper-free method uses strained cyclooctynes such as DBCO or BCN. It avoids metal contamination, making it suitable for clinical-grade materials. SPAAC maintains high specificity and works well with sensitive biomolecules.
Amide Coupling:
Reagents such as EDC, Oxyma, or HBTU link carboxyl and amine groups. Strict pH control and side-chain protection are necessary to prevent unwanted reactions. Proper monitoring ensures complete coupling.
Thioether and Disulfide Linkages:
Cysteine residues allow formation of thioether or disulfide bonds. Disulfide bonds are useful in prodrug strategies because intracellular glutathione can cleave them. This mechanism enables controlled intracellular release.
Connect with our specialist CRO team: Peptide Oligonucleotide Conjugates CRO
High-Resolution Characterization of POC Bioconjugates
Due to their hybrid structure, POCs require extensive analytical validation. POC Synthesis and Characterization at ResolveMass integrates high-resolution mass spectrometry and multinuclear NMR. Multiple analytical techniques provide reliable confirmation of sequence, purity, and structural stability. This level of detail supports regulatory submissions and clinical progress.
High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry (HRMS) in POC Synthesis and Characterization
Mass spectrometry is central to confirming molecular identity. Platforms such as the Thermo Q Exactive Plus Orbitrap and SCIEX QTRAP 6500 provide accurate mass data and structural insights.
The Orbitrap system delivers resolving power up to 1,000,000 (FWHM) with mass accuracy below 1 ppm. This sensitivity allows detection of minor impurities such as truncated (n-1) or extended (n+1) sequences. MS/MS fragmentation techniques confirm peptide attachment sites. Quantitative analysis ensures purity levels above 95% for IND submissions.
Atomic-Level Verification: NMR in POC Synthesis and Characterization
NMR spectroscopy offers structural confirmation beyond mass analysis. Using a Bruker Avance III 500 MHz system, ResolveMass performs detailed solution-state studies.
Phosphorus-31 (31P) NMR differentiates between phosphodiester (PO) and phosphorothioate (PS) linkages. Quantitative NMR (qNMR) determines purity without a reference standard. Diffusion-Ordered Spectroscopy (DOSY) evaluates aggregation behavior. Together, these tools provide atomic-level validation.
Ensure the quality of your therapeutic leads: Peptide Characterization Service
Chromatographic Separation and Quality Control
Purification is essential to remove synthesis impurities. Because POCs often contain both positively and negatively charged regions, aggregation can complicate separation.
ResolveMass uses optimized Ion-Pairing Reversed-Phase HPLC (IP-RP-HPLC) with wide-pore C18 columns. Ion-pairing agents such as butylammonium acetate at 80°C improve peak resolution. Careful temperature and solvent control enhance sensitivity. These methods ensure consistent batch quality.
| Instrument | Specialized Role in POC Analysis | Key Advantage |
| Orbitrap HRMS | Impurity identification and sequence confirmation. | Ultra-high resolution and sub-ppm mass accuracy. |
| Triple Quad MS | Trace-level quantitation and bioanalysis. | Exceptional sensitivity for pharmacokinetic studies. |
| 500 MHz NMR | Structural elucidation and backbone verification. | Non-destructive atomic-level detail. |
| SEC-GPC | Molecular weight distribution and aggregation. | Detects large-scale physical instabilities. |
| FTIR | Secondary structure and functional group ID. | Rapid identification of bioconjugate components. |
Overcoming Technical Challenges in POC Synthesis and Characterization
Developing a POC from research to clinical stage requires solving challenges related to solubility, aggregation, and stereochemistry. Each development step involves repeated optimization and testing. Without proper control, impurities or instability may delay regulatory approval. A structured analytical approach reduces risk and improves reproducibility.
Managing Electrostatic Interactions and Aggregation
Positively charged peptides (e.g., R_9) can strongly interact with negatively charged nucleic acids. This may lead to insoluble complexes.
ResolveMass addresses this issue using optimized mobile phases and organic solvents such as acetonitrile or DMSO. Neutral backbone analogs like PMOs or PNAs can also reduce charge interactions. Buffer pH is carefully controlled to maintain solubility. These combined strategies improve handling and purification.
Addressing Diastereomers and Sequence Heterogeneity
Phosphorothioate-modified oligonucleotides create mixtures of stereoisomers. For example, a 20-mer $PS$ oligo may contain $2^{19}$ stereoisomers. This complexity can broaden chromatographic peaks and hide impurities.
Ion Mobility Spectrometry (IMS) combined with HRMS helps resolve these species. Automated peptide mapping identifies truncated sequences and residual protecting groups. Detailed impurity profiling strengthens regulatory documentation.
Regulatory Compliance and Impurity Profiling in POC Synthesis and Characterization
Recent FDA and EMA updates in 2024 and 2025 have introduced stricter requirements for conjugated oligonucleotide therapies. These guidelines emphasize full structural characterization, immunogenicity testing, and metabolic stability assessment.
ResolveMass aligns with ICH Q2/Q3 standards using LCMS-based impurity profiling. Stability-indicating methods and forced degradation studies support shelf-life evaluation. Risk-based immunogenicity testing assesses cytokine response potential. This proactive compliance strategy reduces regulatory uncertainty.
Data Integrity and Quality Systems
ResolveMass Laboratories Inc. is an FDA-registered facility (FEI No.: 3042696771) and ISO 9001:2015 certified. These certifications confirm adherence to recognized quality systems.
Each project includes validated analytical methods, complete spectral datasets, and full material traceability. Documentation packages are audit-ready and structured for regulatory review. Consistent quality practices ensure reproducible results.
Accelerate your chemistry programs: Drug Discovery Chemistry Services
Market Trends and Therapeutic Applications of POCs
The rapid growth of the TIDES pipeline highlights the expanding role of POC Synthesis and Characterization in modern medicine. Recent approvals confirm the clinical maturity of oligonucleotide platforms. Improved delivery technologies are expanding beyond rare liver diseases into broader therapeutic areas.
Landmark Clinical Approvals in 2024-2025
| Generic Name | Brand Name | Indication | Approval Year | Delivery Mechanism |
| Fitusiran | Qfitlia | Hemophilia A/B | 2025 | GalNAc Ligand |
| Donidalorsen | Dawnzera | Hereditary Angioedema | 2025 | GalNAc mediated |
| Plozasiran | Redemplo | Familial Chylomicronemia | 2025 | GalNAc mediated |
| Imetelstat | Rytelo | Myelodysplastic Syndromes | 2024 | 3′-Amino Modification |
| Elamipretide | Forzinity | Barth Syndrome | 2025 | Mitochondrial targeting |
These approvals demonstrate that advanced delivery systems can support scalable manufacturing and clinical success. Many therapies rely on improved targeting to reduce dosing frequency and side effects. Strong analytical foundations remain essential for regulatory approval.
Therapeutic Frontiers: Neuromuscular and Oncology
Neuromuscular Disease:
Peptide-PMO conjugates such as SRP-5051 are under investigation for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. Enhanced muscle uptake improves therapeutic effect compared to unconjugated oligonucleotides. Early clinical data show promising intracellular delivery improvements.
Oncology:
Peptide-targeted siRNA and ASO conjugates allow selective tumor cell delivery. This targeted approach reduces systemic toxicity. Precision gene silencing supports personalized cancer treatment strategies.
Neurodegenerative Disorders:
Research is ongoing to develop peptides capable of crossing the blood-brain barrier. This could enable central nervous system therapies for Alzheimer’s and Huntington’s diseases. Continued optimization may expand treatment options for complex neurological conditions.
Conclusion: The Future of POC Synthesis and Characterization
POC Synthesis and Characterization is a powerful platform in precision medicine. By combining peptide-based targeting with oligonucleotide gene regulation, researchers can design therapies beyond the reach of traditional small molecules. This modular approach supports flexible and scalable development.
ResolveMass Laboratories Inc. provides specialized expertise in high-resolution mass spectrometry, advanced NMR, and regulatory-aligned synthesis workflows. Each project is supported by strong quality systems and detailed analytical documentation. As delivery technologies and regulatory standards continue to evolve, POC Synthesis and Characterization will remain a cornerstone of genomic drug development.
Plan your next research milestone: Early Drug Discovery Chemistry Milestones
Frequently Asked Questions
POC Synthesis and Characterization refers to the controlled chemical attachment of a peptide to an oligonucleotide, forming a single conjugated molecule. After synthesis, advanced analytical tools such as HRMS, NMR, and HPLC are used to confirm its identity, purity, and structural stability. This process ensures that the final bioconjugate meets research and regulatory quality standards. It is a critical step in developing safe and effective gene-based therapies.
Peptides improve delivery by acting as molecular carriers that help oligonucleotides enter cells. Some peptides, known as Cell-Penetrating Peptides (CPPs), move directly across cell membranes. Others, called Receptor-Targeting Peptides (RTPs), bind to specific receptors on the cell surface to trigger uptake. This strategy overcomes the natural difficulty nucleic acids face when trying to cross lipid membranes.
There are two main approaches used to produce POCs. The first is stepwise solid-phase assembly, where both the peptide and oligonucleotide are built sequentially on the same resin. The second method is post-synthetic parallel conjugation, where each component is prepared and purified separately before being chemically linked. The choice depends on sequence complexity and production scale.
Orbitrap High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry is used because it offers exceptional mass accuracy and resolving power. It can detect very small differences in molecular weight, which helps identify impurities and confirm sequence integrity. This precision is especially important for complex bioconjugates like POCs. Accurate mass verification supports both research reliability and regulatory compliance.
Current drug development programs must follow the FDA’s 2024 and 2025 draft guidances related to clinical pharmacology and nonclinical safety for oligonucleotide therapies. These documents outline expectations for structural characterization, impurity profiling, and safety evaluation. Compliance with these guidelines helps ensure smooth regulatory review. Global standards from agencies such as the EMA are also important for international submissions.
NMR spectroscopy provides detailed information about the molecular structure at the atomic level. Techniques such as $^{31}P$ NMR confirm backbone modifications like phosphorothioate linkages. Quantitative NMR (qNMR) can also measure purity without needing a reference standard. This makes NMR an essential complementary tool to mass spectrometry.
Reference
- Klabenkova, K., Fokina, A., & Stetsenko, D. (2021). Chemistry of peptide-oligonucleotide conjugates: A review. Molecules, 26(17), 5420. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26175420
- AlShaer, D., Al Musaimi, O., Albericio, F., & de la Torre, B. G. (2026). 2025 FDA TIDES (Peptides and oligonucleotides) harvest. Pharmaceuticals, 19(2), 244. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph19020244
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. (2025). Novel drug approvals for 2025. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Retrieved February 13, 2026, from https://www.fda.gov/drugs/novel-drug-approvals-fda/novel-drug-approvals-2025
- Malinowska, A. L., Huynh, H. L., & Bose, S. (2024). Peptide-oligonucleotide conjugation: Chemistry and therapeutic applications. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 46(10), 11031–11047. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb46100655
- Malinowska, A. L., Huynh, H. L., & Bose, S. (2024). Peptide–Oligonucleotide Conjugation: Chemistry and Therapeutic Applications. Current Issues in Molecular Biology, 46(10), 11031–11047. https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb46100655
- Oprea, I., & Smith, T. K. (2025). Click chemistry methodology: The novel paintbrush of drug design. ACS Chemical Biology, 20(1), 19–32. https://doi.org/10.1021/acschembio.4c00608