OVERVIEW
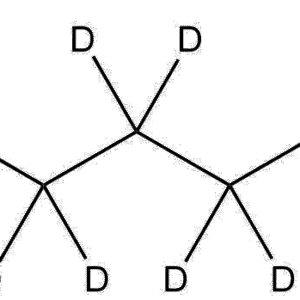
Deuterated 1,3-Butadiene-d6 | CAS 1441-56-1 is a fully deuterated analogue of 1,3-butadiene, widely valued in polymer research, reaction mechanism studies, and advanced spectroscopic applications. With six deuterium atoms replacing the hydrogen atoms in the parent molecule, this isotopically labeled compound offers enhanced utility in tracking molecular interactions, studying polymerization pathways, and developing next-generation materials. Its stable isotopic substitution allows chemists and material scientists to precisely monitor reactions using NMR, mass spectrometry, and kinetic studies where non-deuterated analogues would not provide sufficient contrast or clarity.
The compound retains the core structural features and reactivity profile of conventional butadiene but provides measurable isotopic shifts that make it indispensable for analytical, mechanistic, and material-property investigations. As a gaseous hydrocarbon at room temperature, it requires controlled handling conditions, but its versatility and research value make it a critical reagent across polymer chemistry, catalysis research, and isotopic tracing studies.
CHEMICAL INFORMATION
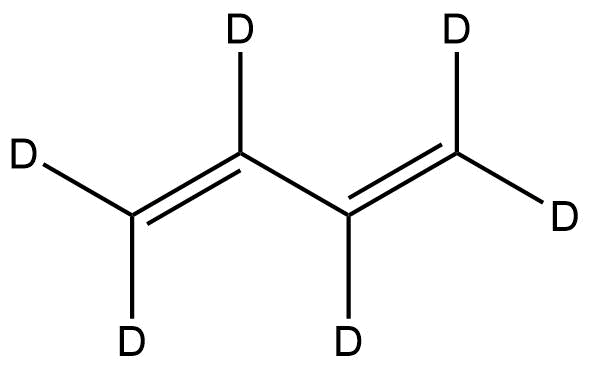
Chemical Name: Deuterated 1,3-Butadiene-d6
CAS Number: 1441-56-1
Molecular Formula: C4D6
Molecular Weight: ~58.1 g/mol
Synonyms: Butadiene-d6, 1,3-Butadiene-d6, Fully deuterated butadiene
Deuterated 1,3-butadiene is structurally identical to standard 1,3-butadiene except for the replacement of all six hydrogens with deuterium. This isotopic substitution causes predictable modifications in vibrational modes, NMR profiles, and kinetic isotope effects, making it particularly useful for controlled studies in mechanistic and materials research.
The compound exists as a colorless, highly flammable gas with a conjugated diene system. The double-bond conjugation remains intact in the deuterated form, preserving reactivity toward polymerization, Diels–Alder reactions, and radical processes.
KEY PROPERTIES
-
Fully deuterated (six deuterium atoms) for enhanced isotopic labeling
-
Conjugated 1,3-diene structure
-
Highly reactive toward polymerization and cycloaddition reactions
-
Exhibits kinetic isotope effects useful for mechanistic differentiation
-
Ideal tracer molecule for reaction pathway elucidation
-
Suitable for NMR (¹H suppression), IR, Raman, and MS studies
-
Gas-phase reagent requiring proper material handling and inert conditions
APPLICATIONS of Deuterated 1,3-Butadiene-d6 | CAS 1441-56-1
Polymer Chemistry & Material Science
Deuterated 1,3-Butadiene-d6 plays a significant role in polymer science, especially in studies focused on synthetic rubbers, elastomers, and block copolymer materials. Because of its isotopic labeling, it allows researchers to track monomer incorporation, investigate polymer chain growth, and evaluate microstructural distributions with exceptional clarity.
Its use in the polymerization of butadiene-based materials helps scientists understand stereochemistry (cis/trans configurations), branching behavior, and the influence of catalysts on molecular weight distribution. Deuterium labeling also enables direct observation of polymer segments in NMR and neutron scattering experiments, which is not feasible with non-labeled monomers.
Reaction Mechanism Studies
The compound is widely used in mechanistic and kinetic studies due to its strong kinetic isotope effects. Replacing hydrogen with deuterium slows certain reaction steps, allowing scientists to isolate rate-determining processes and clarify catalytic pathways. This makes the reagent vital for studying:
-
Diels–Alder reaction pathways
-
Metal-catalyzed polymerizations
-
Radical and anionic addition reactions
-
Chain transfer mechanisms
-
Mechanistic differentiation between competing reactive species
By evaluating the variations in rate constants and structural evolution during reactions, chemists gain deep insight into molecular transformations that would otherwise be challenging to monitor.
Spectroscopy & Analytical Applications
Deuterated 1,3-Butadiene-d6 is highly valued for spectroscopic techniques because of its reduced proton background and shifted vibrational frequencies. In NMR spectroscopy, the absence of hydrogen allows for clean spectra with minimal interference, facilitating advanced structural analyses in polymer mixtures and reaction intermediates.
In infrared and Raman spectroscopy, isotopic substitution generates distinct vibrational shifts that help differentiate overlapping peaks or track specific functional group behaviors. Mass spectrometrists use the compound as an internal standard or tracer for fragmentation pathway elucidation.
Isotopic Tracing & Environmental Research
Because deuterium is a stable non-radioactive isotope, it can be used safely in tracing experiments. Deuterated 1,3-Butadiene-d6 enables monitoring of gas-phase reactions, atmospheric degradation pathways, and photochemical transformations. Its isotopic signature can be detected even at low concentrations, making it suitable for environmental modeling and combustion research.
STABILITY & HANDLING
As a conjugated diene, 1,3-butadiene-d6 is highly reactive and must be handled with care. It is a flammable gas that can undergo spontaneous polymerization under improper storage conditions. To maintain stability, it should be stored under refrigeration, away from oxygen, heat sources, and direct sunlight. Use of inhibitors, inert gas blankets, and compatible pressure vessels is common practice for safe handling.
Proper personal protective equipment, gas-rated regulators, and well-ventilated laboratory conditions are essential. Researchers should follow institutional safety protocols when working with pressurized deuterated gases.
Learn more through,
Deuterated Polymers: A Cornerstone Guide to Synthesis, Applications, and Future Trends
Availability of All the Deuterated Chemicals at ResolveMass Laboratories Inc.
ResolveMass Laboratories: Leading Deuterated Chemical Synthesis Company in the United States.
Deuterated Internal Standards for LC-MS: Selection & Custom Synthesis
How to Choose the Right Deuterated Labelled Chemical Synthesis Company in Canada
How to Choose the Right Deuterium Labelled Compounds Supplier for Your Lab
Deuterium-Labelled Compounds — Synthesis, Applications & Ordering
Custom Synthesis of Deuterated Chemicals
Reviews
There are no reviews yet.