OVERVIEW
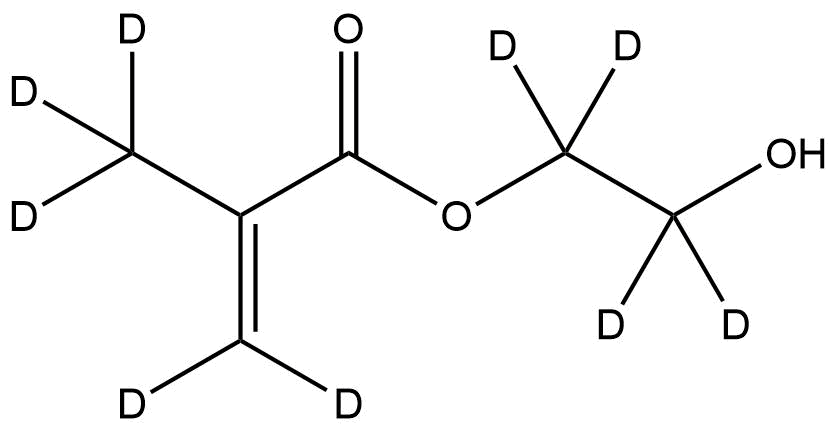
Deuterated 2-Hydroxyethyl methacrylate-d9 is a stable-isotope-labeled analogue of HEMA in which nine hydrogen atoms are replaced with deuterium. This isotopic substitution provides enhanced utility for analytical, mechanistic, and materials-science applications where precise molecular tracing, advanced characterization, or isotope-dependent kinetic evaluation is required. Owing to its well-defined structure, predictable reactivity, and compatibility with a wide range of polymerization systems, HEMA-d9 serves as a versatile building block for researchers developing polymer networks, biomedical surfaces, hydrogel systems, and analytical standards.
This high-purity monomer is particularly valued in pharmaceutical formulation research, polymer degradation studies, and LC–MS/NMR-based quantitation of polymeric systems. The addition of the hydroxyl group on the hydroxyethyl functionality allows for post-polymerization modifications, improved hydrophilicity, and enhanced compatibility with aqueous systems—while the deuterium incorporation enables precise differentiation from non-labeled analogues in complex matrices.
CHEMICAL INFORMATION
Chemical Name: 2-Hydroxyethyl Methacrylate-d9
Synonyms: HEMA-d9; Deuterated Hydroxyethyl Methacrylate
Isotopic Enrichment: ≥ 98% D
Functional Groups: Methacrylate ester; primary alcohol
Typical Purity: ≥ 98% (GC/NMR)
Physical State: Colorless to pale liquid
Deuteration introduces a mass shift while preserving electronic structure and chemical reactivity. This makes HEMA-d9 ideal for direct substitution in experiments that would otherwise use standard HEMA, ensuring minimal influence on polymerization kinetics, functional group reactivity, or hydrogel network formation—yet providing the mass/chemical shift needed for unambiguous identification.
KEY FEATURES
-
Stable-isotope labeled with nine deuterium atoms, enabling high-fidelity tracking in LC–MS, MS/MS, and NMR workflows.
-
Retains the polymerization characteristics of HEMA, supporting free-radical, UV-initiated, and controlled polymerization techniques.
-
Hydroxyl functionality enables post-polymerization modification, crosslinking, and improved hydrophilicity of copolymers.
-
Ideal internal standard for quantitation of HEMA-based materials and degradation products.
-
Suitable for biomedical and chemically demanding environments due to predictable degradation behavior and structural consistency.
APPLICATIONS of Deuterated 2-Hydroxyethyl methacrylate-d9
Isotopic Internal Standard for Analytical Methods
HEMA-d9 is widely used as an internal calibration standard in high-resolution mass spectrometry and quantitative NMR because the deuterium isotope pattern ensures strong signal separation from native HEMA. This makes it valuable for:
-
Monitoring hydrogel degradation pathways
-
Quantifying trace monomer residues in polymer matrices
-
Studying polymer leachables and extractables
-
Evaluating polymer–drug interactions in drug delivery systems
Its inclusion improves measurement accuracy and reduces matrix-related quantitation errors.
Polymer and Hydrogel Research
Due to its methacrylate functionality, HEMA-d9 readily participates in:
-
Free-radical polymerization
-
Controlled radical polymerization (RAFT, ATRP, NMP)
-
UV-crosslinked hydrogel formation
Researchers use HEMA-d9 to track polymer chain growth, evaluate monomer reactivity ratios, and monitor network formation. The ability to track labeled segments within complex copolymers is essential for understanding microstructure distribution, crosslinking efficiency, and swelling behavior.
Biomedical Material Studies
HEMA-based hydrogels have a long history in biocompatible materials such as contact lenses, biosensors, wound dressings, and drug-delivery matrices. The deuterated version supports:
-
Mechanistic studies of biomaterial degradation
-
Tracing monomer release in physiological fluids
-
Studying surface functionalization processes on medical device coatings
The stable incorporation of deuterium aids in understanding long-term stability without affecting polymer functionality.
Mechanistic and Kinetic Studies
Because HEMA-d9 mirrors the reactivity of its non-labeled counterpart, it enables precise mechanistic studies involving:
-
Free-radical chain propagation
-
Ester hydrolysis kinetics
-
Oxidative degradation pathways
-
Intermolecular dynamics within polymer networks
The isotope effect is minimal for methacrylate polymerization, ensuring that researchers can use HEMA-d9 without perturbing the underlying chemistry.
ANALYTICAL ADVANTAGES
HEMA-d9 offers unique analytical benefits:
-
LC–MS/MS: Distinct mass signature provides superior accuracy for quantitation.
-
NMR Spectroscopy: Deuterium incorporation reduces proton background, improving clarity in proton NMR experiments.
-
GPC/SEC Studies: Enables differentiation between labeled and unlabeled polymer segments.
-
Surface Characterization: Useful in ToF-SIMS, FTIR mapping, and Raman spectroscopy for tracing chemical distribution.
These advantages support high-precision studies where sensitivity, selectivity, and molecular traceability are critical.
Learn more through,
Deuterated Polymers: A Cornerstone Guide to Synthesis, Applications, and Future Trends
Availability of All the Deuterated Chemicals at ResolveMass Laboratories Inc.
ResolveMass Laboratories: Leading Deuterated Chemical Synthesis Company in the United States.
Deuterated Internal Standards for LC-MS: Selection & Custom Synthesis
How to Choose the Right Deuterated Labelled Chemical Synthesis Company in Canada
How to Choose the Right Deuterium Labelled Compounds Supplier for Your Lab
Deuterium-Labelled Compounds — Synthesis, Applications & Ordering
Custom Synthesis of Deuterated Chemicals
Reviews
There are no reviews yet.