OVERVIEW
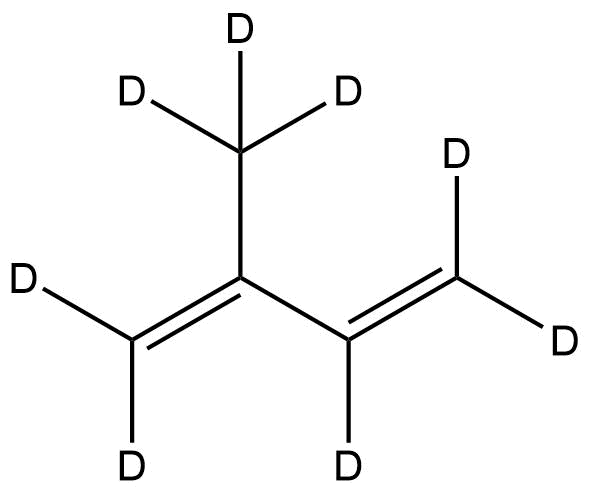
Deuterated Isoprene-d8 is a selectively deuterated analog of isoprene in which eight hydrogen atoms are replaced with deuterium. This isotopic substitution makes the molecule an indispensable tool across polymer research, mechanistic studies, and advanced spectroscopic analysis. Thanks to its structural alignment with native isoprene and its enhanced analytical visibility, Isoprene-d8 enables researchers to investigate polymerization kinetics, degradation mechanisms, diffusion pathways, and molecular interactions with exceptional clarity.
In many research environments—particularly those involving PLGA, elastomeric systems, or advanced analytical chemistry—deuterated compounds offer benefits that simply cannot be achieved with non-labeled molecules. Isoprene-d8 represents one such high-value reagent, designed to support sophisticated investigations in both industrial and academic laboratories.
CHEMICAL INFORMATION
Chemical Name: Isoprene-d8
Synonyms: 2-Methyl-1,3-butadiene-d8
Molecular Formula: C₅D₈
Isotopic Enrichment: ≥98% D
Molecular Weight: 76.15 g/mol
The eight deuterium substitutions do not significantly alter the overall physicochemical behavior of the parent hydrocarbon, but they provide measurable differences in vibrational frequencies, NMR signatures, and certain kinetic isotope effects (KIE), which are extremely useful in mechanistic studies.
KEY FEATURES & BENEFITS
• Ideal for NMR tracking and quantification: Deuterium substitution minimizes background proton signals, allowing precise monitoring of polymerization, degradation, and reaction intermediates.
• Enhanced mass spectrometric resolution: The added mass from deuterium improves MS identification, enabling clear distinction between labeled and unlabeled species.
• Useful in kinetic isotope effect studies: The presence of multiple deuterium atoms allows researchers to explore reaction pathways and rate-determining steps with higher precision.
• Compatible with polymer and elastomer research: Particularly valuable in studying polyisoprene formation, degradation, and crosslinking mechanisms.
• Stable, well-characterized isotopic label: Ensures reproducibility in analytical and synthetic workflows.
APPLICATIONS
Deuterated Isoprene-d8 is used broadly across chemistry, materials science, polymer science, and pharmaceutical formulation research. Major application categories include:
1. Polymerization Mechanism Studies
Isoprene-d8 plays a central role in elucidating anionic, cationic, and radical polymerization pathways. Its isotopic distinction allows researchers to:
• Track monomer incorporation during early propagation steps
• Determine chain-transfer and termination events
• Understand microstructure development in polyisoprene (cis/trans ratio effects)
• Evaluate catalyst efficiency and selectivity
These insights support the development of elastomers with improved strength, elasticity, and aging resistance.
2. Spectroscopic and Structural Analysis
Because deuterium exhibits drastically different NMR and vibrational behavior compared to protium, Isoprene-d8 provides added resolution in techniques such as:
• ¹H/²H NMR – Reduced proton background enhances clarity in complex spectra
• IR/Raman spectroscopy – Deuterium shifts provide insight into bond environments
• Advanced mass spectrometry – Improved isotopic separation facilitates fragmentation analysis
3. Tracking Degradation Pathways
Isoprene-containing materials, including polyisoprene rubber, undergo oxidative, thermal, and mechanical degradation. Deuterated Isoprene-d8 enables clearer identification of:
• Oxidation intermediates
• Backbone-cleavage routes
• Crosslinking or chain-scission patterns
• Volatile off-gassing or residual monomer release
This makes it an essential reagent for product stability assessments and material lifetime predictions.
4. Diffusion and Transport Studies
In complex composite or multilayer systems, the mobility of small isoprenoid molecules is often difficult to quantify. Isoprene-d8 acts as a molecular tracer that can be monitored through NMR or MS to determine:
• Diffusion coefficients
• Partitioning behavior
• Interaction with polymer matrices
• Migration profiles into or out of elastomers
5. Research in Specialty Elastomers and Biomedical Polymers
Although primarily associated with rubber chemistry, Isoprene-d8 is increasingly used in biomedical research—particularly in understanding how unsaturated monomers interact with hydrophobic polymer phases or degrade under physiological conditions.
Learn more through,
Deuterated Polymers: A Cornerstone Guide to Synthesis, Applications, and Future Trends
Availability of All the Deuterated Chemicals at ResolveMass Laboratories Inc.
ResolveMass Laboratories: Leading Deuterated Chemical Synthesis Company in the United States.
Deuterated Internal Standards for LC-MS: Selection & Custom Synthesis
How to Choose the Right Deuterated Labelled Chemical Synthesis Company in Canada
How to Choose the Right Deuterium Labelled Compounds Supplier for Your Lab
Deuterium-Labelled Compounds — Synthesis, Applications & Ordering
Custom Synthesis of Deuterated Chemicals

Reviews
There are no reviews yet.