OVERVIEW
Deuterated N-isopropyl methacrylamide-d7 | CAS 1219803-32-3 is a highly specialized, isotopically enriched monomer engineered for advanced polymer science, analytical chemistry, and mechanistic studies involving stimuli-responsive hydrogels. Structurally identical to conventional N-isopropyl methacrylamide (NIPAM) except for selective deuterium substitution, NIPAM-d7 provides powerful advantages in NMR tracing, polymerization mechanism elucidation, and material characterization under both aqueous and organic conditions. The presence of seven deuterium atoms dramatically reduces background proton signals, enabling precise integration, quantitative isotopic profiling, and accurate monitoring of copolymerization kinetics.
As a premium deuterated monomer, NIPAM-d7 is widely used in the study of thermoresponsive polymers, especially poly(N-isopropyl methacrylamide) (PNIPAM) and related smart materials that exhibit tunable lower critical solution temperature (LCST) behavior. Because isotopic labeling does not significantly alter the physicochemical nature of the parent monomer, researchers can directly compare deuterated and non-deuterated analogs to understand solvent interactions, polymer relaxation dynamics, and chain mobility with minimal perturbation to the system.
ResolveMass Laboratories Inc. supplies research-grade NIPAM-d7 for demanding academic, industrial, and pharmaceutical applications where polymer traceability, high isotopic purity, and reproducible performance are essential.
CHEMICAL INFORMATION
Chemical Name: Deuterated N-isopropyl methacrylamide-d7
CAS Number: 1219803-32-3
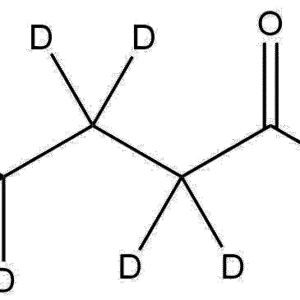
Molecular Formula: C7H2D7NO
Isotopic Labeling: d7 (seven deuterium atoms incorporated into the isopropyl substituent)
Chemical Class: Deuterated methacrylamide monomer
Functional Groups: Amide, methacrylate, isotopically substituted alkyl
The structural similarity to native N-isopropyl methacrylamide ensures compatibility with standard polymerization workflows, while the deuterium labeling enriches its performance in spectroscopic and analytical methods.
KEY FEATURES
-
High Deuterium Incorporation (d7): Provides strong signal suppression for ¹H NMR, enhancing spectral clarity and quantification accuracy.
-
Ideal for Smart Polymer Research: Supports synthesis of thermo-responsive PNIPAM-based materials used in drug delivery and bioconjugates.
-
Compatible with Controlled Radical Polymerization: Suitable for RAFT, ATRP, and free-radical polymerization mechanisms.
-
Minimal Structural Perturbation: Deuteration maintains the physicochemical and polymerization behavior of the non-labeled monomer.
-
Excellent Traceability: Enables kinetic studies, copolymer composition mapping, and mechanistic polymer research.
APPLICATIONS of Deuterated N-isopropyl methacrylamide-d7 | CAS 1219803-32-3
1. Polymerization Mechanism and Kinetic Studies
NIPAM-d7 is frequently used to study free-radical polymerization and RAFT-mediated processes. Because the deuterated monomer is spectrally distinct, researchers can directly monitor monomer consumption, chain propagation, and end-group functionality with high precision. This is essential for polymer chemists designing low-PDI smart materials or investigating structure–property relationships.
2. Synthesis of Thermoresponsive and Smart Hydrogels
PNIPAM-based hydrogels are famous for their LCST-driven phase transition—a property preserved in materials synthesized from NIPAM-d7. Deuteration helps researchers study hydration layers, chain mobility, polymer collapse behavior, and microenvironmental changes using techniques such as NMR, neutron scattering, and vibrational spectroscopy.
3. Advanced NMR and Mass Spectrometry Applications
With reduced proton background interference, NIPAM-d7 significantly improves resolution in:
-
¹H NMR and ²H NMR tracking
-
Diffusion-ordered spectroscopy (DOSY) analysis
-
Quantitative NMR (qNMR)
-
LC-MS validation of polymer composition
The isotopic signature assists in differentiating polymer blocks, modular sequences, and grafted segments in complex macromolecular structures.
4. Deuterium-Labeled Model Systems in Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Research
Thermoresponsive polymers based on PNIPAM are widely explored for:
-
Injectable hydrogels
-
Temperature-dependent drug release systems
-
Tissue engineering scaffolds
-
Cell encapsulation matrices
Using NIPAM-d7, researchers can trace polymer behavior, confirm degradation pathways, and monitor molecular interactions during formulation development.
5. Neutron Scattering and Contrast Variation Experiments
Deuteration dramatically enhances contrast in small-angle neutron scattering (SANS) and neutron reflectometry. This is especially useful for studying polymer brush formation, micelle assembly, nanoparticle coatings, and responsive soft-matter interfaces.
TECHNICAL BENEFITS FOR FORMULATION SCIENTISTS
-
Enhanced Data Accuracy: Ideal for high-fidelity structure–property correlation studies.
-
Improved Mechanistic Understanding: Enables direct monitoring of polymer collapse, solvation effects, and LCST transitions.
-
Superior Analytical Performance: Delivers clean spectra with minimal overlapping proton signals.
-
Support for Multi-Modal Characterization: Useful across NMR, MS, neutron scattering, FTIR, Raman spectroscopy, and thermal analysis.
RELATED PRODUCTS (SUGGESTED PAIRINGS)
-
Deuterated methacrylic monomers for block copolymer contrast
-
RAFT chain transfer agents optimized for NIPAM polymerization
-
PNIPAM-d isotopically enriched polymers
-
Deuterated solvents (D2O, CDCl₃) for advanced NMR workflows
Learn more,
Deuterated Polymers: A Cornerstone Guide to Synthesis, Applications, and Future Trends
Availability of All the Deuterated Chemicals at ResolveMass Laboratories Inc.
ResolveMass Laboratories: Leading Deuterated Chemical Synthesis Company in the United States.
Deuterated Internal Standards for LC-MS: Selection & Custom Synthesis
How to Choose the Right Deuterated Labelled Chemical Synthesis Company in Canada
How to Choose the Right Deuterium Labelled Compounds Supplier for Your Lab
Deuterium-Labelled Compounds — Synthesis, Applications & Ordering
Custom Synthesis of Deuterated Chemicals

Reviews
There are no reviews yet.