Poly DL-lactide | Mw = 18,000‑24,000 | End Group : Ester | CAS 26680-10-4
OVERVIEW
Poly DL-lactide | Mw = 18,000‑24,000 | End Group : Ester | CAS 26680-10-4 is an amorphous, biodegradable, and biocompatible aliphatic polyester synthesized from racemic D- and L-lactic acid. Derived from renewable feedstocks such as corn starch and sugarcane, PDLLA is widely used in biomedical engineering, drug delivery, and environmentally friendly materials.
Unlike the semicrystalline PLLA, PDLLA is fully amorphous, offering faster degradation, enhanced flexibility, and easier processability. These characteristics make PDLLA ideal for applications requiring rapid resorption, low modulus, and homogeneous drug release.
Its breakdown into metabolizable lactic acid ensures both physiological compatibility and environmental sustainability, reinforcing its status as a core polymer in medical and green-material innovation.
CHEMICAL STRUCTURE AND COMPOSITION
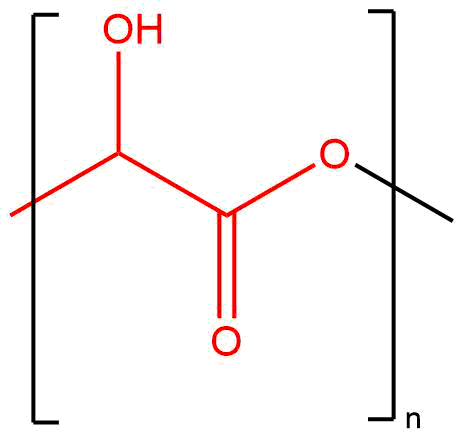
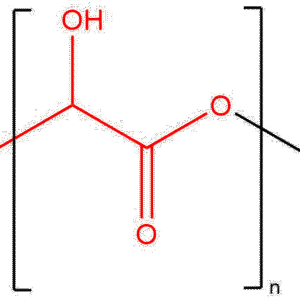
Poly(DL-lactide) is a random copolymer of D- and L-lactic acid isomers, produced via ring-opening polymerization of racemic DL-lactide. Its repeating structure is:
[–O–CH(CH₃)–CO–]ₙ
Key structural attributes include:
-
Racemic Composition: Random distribution of D- and L-units prevents crystallization.
-
Amorphous Nature: 0% crystallinity → predictable, uniform hydrolysis.
-
Glass Transition Temperature (Tg): ~50–60°C
-
No Distinct Melting Temperature (Tm): PDLLA is fully amorphous.
The absence of stereoregularity results in greater flexibility, lower stiffness, and faster degradation compared to highly crystalline PLLA.
SYNTHESIS of Poly DL-lactide | Mw = 18,000‑24,000 | End Group : Ester | CAS 26680-10-4
PDLLA is synthesized through catalytic ring-opening polymerization (ROP) of DL-lactide, typically under controlled anhydrous and inert conditions.
Typical Synthesis Parameters
-
Monomer: DL-lactide (racemic)
-
Catalyst: Sn(Oct)₂, zinc lactate, or other metal catalysts
-
Temperature: 120–180°C
-
Reaction Time: 6–24 hours
-
Atmosphere: Nitrogen or argon
-
Mechanism: Coordination–insertion ROP
Post-polymerization purification through precipitation and solvent washing ensures removal of unreacted monomer and catalyst residues, producing medical-grade material suitable for drug and device applications.
PHYSICOCHEMICAL PROPERTIES
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Chemical Name | Poly(DL-lactide) |
| CAS Number | 26680-10-4 |
| Molecular Formula | (C₃H₄O₂)ₙ |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid/granules |
| Molecular Weight (Mw) | 18,000‑24,000 g/mol |
| Biodegradability | Complete hydrolytic degradation via ester cleavage |
DEGRADATION BEHAVIOR
PDLLA undergoes bulk hydrolytic degradation, making it a preferred polymer in fast-resorbing biomedical systems.
Stages of degradation:
1. Molecular Weight Reduction
Random cleavage of ester bonds reduces Mw, softening the polymer.
2. Solubilization and Resorption
Low-Mw oligomers dissolve and are metabolized to lactic acid, entering the Krebs cycle and ultimately converting to CO₂ and water.
Factors influencing degradation rate:
-
Amorphous structure: Faster water diffusion → rapid degradation.
-
Molecular weight: Lower Mw → faster breakdown.
-
Environmental conditions: Higher temperature, lower pH, and moisture accelerate hydrolysis.
Typical degradation time:
Weeks to months (significantly faster than PLLA’s months-to-years).
APPLICATIONS of Poly DL-lactide | Mw = 18,000‑24,000 | End Group : Ester | CAS 26680-10-4
1. Biomedical and Pharmaceutical Applications
Fast-Resorbing Implants
Ideal for temporary scaffolds, wound closure systems, and resorbable fixation devices where rapid mass loss is needed.
Drug Delivery Systems
-
Microspheres
-
Nanoparticles
-
Long-acting injectable depots
-
Implantable drug-release matrices
The amorphous nature allows uniform drug dispersion and predictable release kinetics.
Tissue Engineering
Used for:
-
Soft-tissue scaffolds
-
Cartilage regeneration
-
Cell-laden hydrogels (when blended with PEG or PLGA)
Medical Device Coatings
Provides controlled degradation coatings for bioresorbable devices.
2. Sustainable Packaging and Materials
PDLLA is used in:
-
Compostable packaging films
-
Eco-friendly disposable items
-
Bioplastic compounds requiring higher flexibility than PLLA
Its amorphous structure provides good clarity and low processing temperatures.
3. Custom Polymer Development
At ResolveMass Laboratories Inc., PDLLA can be customized through:
-
Tuned molecular weights (low, medium, or high Mw)
-
End-group functionalization (acid, hydroxyl, custom groups)
-
Copolymer blends (with PEG, PLA stereocopolymers, PGA, or PCL)
This enables precise adjustment of:
-
Mechanical properties
-
Degradation rate
-
Hydrophilicity
-
Drug-release behavior
QUALITY ASSURANCE AND CHARACTERIZATION
Every batch of PDLLA is characterized using:
-
¹H and ¹³C NMR – monomer purity and racemic distribution
-
GPC – molecular weight and dispersity
-
DSC – Tg, absence of crystallinity
-
TGA – thermal stability
-
FTIR / HPLC – functional group verification and impurity analysis
Manufactured under ISO 9001:2015–compliant workflows, with full documentation including CoA, MSDS, and analytical reports.
ADVANTAGES
-
Fully amorphous → predictable, fast degradation
-
Biodegradable and biocompatible
-
Renewable origin
-
Excellent processability and flexibility
-
Ideal for drug delivery and fast-resorbing implants
-
Tailorable molecular weight and properties
-
Environmentally sustainable polymer
CONCLUSION
Poly(DL-lactide) (PDLLA, CAS 26680-10-4) is an essential biodegradable polymer valued for its amorphous structure, rapid degradation, and outstanding biocompatibility. These attributes make PDLLA indispensable in drug delivery, resorbable medical devices, and sustainable materials.
ResolveMass Laboratories Inc. provides research-grade and GMP-grade PDLLA with customizable properties for applications across biomedical engineering, pharmaceutical formulation, packaging, and advanced polymer research.
Read below Learn with Us Articles:
PLGA Nanoparticles Synthesis: A Step-by-Step Guide for Beginners
PLGA 50:50 Poly(D L-lactide-co-glycolide) Supplier Guide: What to Look for in a Reliable Provider
The Science Behind GPC: A Deep Dive into Analyzing PLA, PLGA, and PCL for Research
Reviews
There are no reviews yet.