Introduction:
Complex matrix interference is one of the most common and underestimated obstacles in proteomics, especially in regulated and translational studies. In Proteomics Bioanalytical Services, biological matrices such as plasma, serum, tissue lysates, and cell culture media contain thousands of endogenous components that can suppress ionization, distort chromatographic separation, and compromise data integrity. These challenges are closely aligned with broader bioanalytical matrix effects commonly observed across advanced LC–MS workflows.
For organizations relying on high-quality proteomics data to support drug discovery, biomarker validation, or clinical research, overcoming matrix interference is not optional—it is mission-critical. This is particularly true across modern bioanalytical services in drug development, where proteomics increasingly supports translational and clinical decisions.
At ResolveMass Laboratories Inc., extensive hands-on experience with real biological samples has shaped proteomics workflows designed to minimize matrix effects while maximizing sensitivity, robustness, and reproducibility—core principles across the company’s broader bioanalytical services portfolio.
Summary:
- Complex biological matrices are one of the biggest challenges in proteomics-based bioanalysis, similar to challenges seen in large-molecule LC–MS bioanalysis
- Matrix interference can significantly impact sensitivity, accuracy, and reproducibility of protein quantification, especially in regulated workflows governed by bioanalytical method development and validation requirements
- Advanced Proteomics Bioanalytical Services leverage optimized sample preparation, LC–MS/MS strategies, and data processing workflows to overcome these challenges, often integrating rapid bioanalytical method development approaches
- This case study demonstrates how ResolveMass Laboratories Inc. successfully addressed matrix effects in a real-world proteomics application aligned with biomarker bioanalytical services
- Robust proteomics workflows improve confidence in biomarker discovery, translational research, and regulated bioanalytical services
1: What Is Complex Matrix Interference in Proteomics?
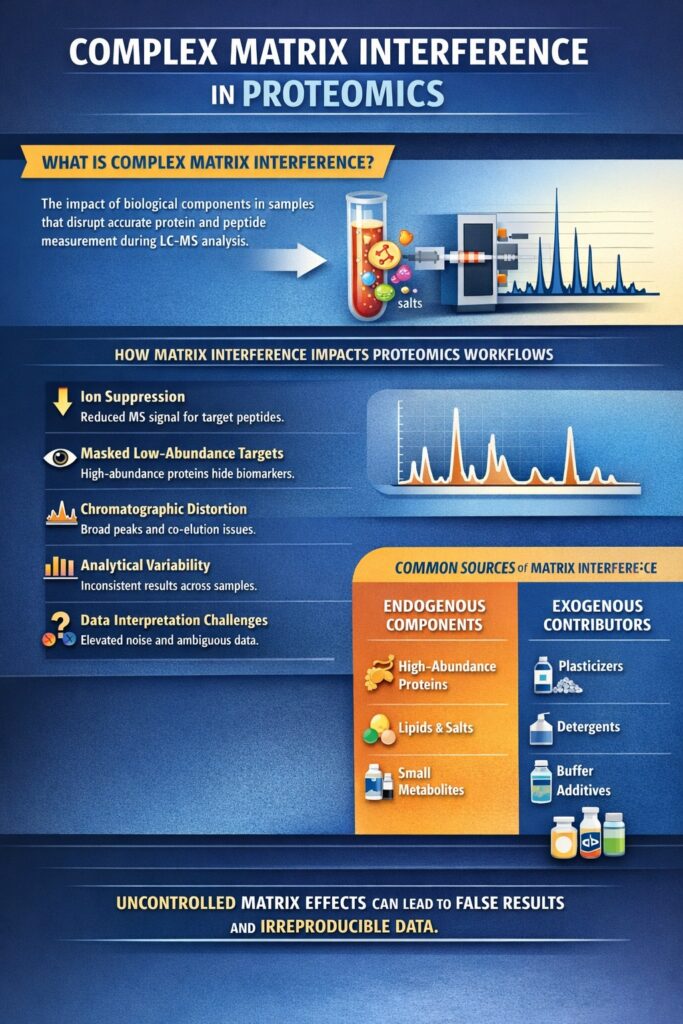
Complex matrix interference refers to the collective impact of endogenous biological components that disrupt accurate protein and peptide measurement during LC–MS-based proteomics. In Proteomics Bioanalytical Services, this interference affects every stage of the analytical workflow—from sample preparation and chromatographic separation to ionization efficiency and data interpretation, similar to challenges encountered in LC–MS/MS bioanalysis of xenobiotics.
Proteomics is uniquely susceptible to matrix effects because biological samples contain thousands of proteins spanning concentration ranges of more than 10 orders of magnitude—an issue also discussed when comparing small-molecule vs large-molecule bioanalysis.
How Matrix Interference Impacts Proteomics Workflows
Matrix interference does not present as a single failure point; instead, it introduces cumulative effects that degrade analytical performance.
Key impacts include:
- Ion suppression and enhancement
Co-eluting matrix components alter ionization efficiency in the MS source, leading to under- or overestimation of peptide abundance. - Reduced sensitivity for low-abundance targets
High-abundance proteins dominate MS response, masking clinically or biologically relevant biomarkers. - Chromatographic distortion
Matrix components can broaden peaks, shift retention times, and increase co-elution, complicating peptide identification. - Increased analytical variability
Differences in matrix composition across samples introduce run-to-run and batch-to-batch variability. - Data interpretation challenges
Elevated background noise and ambiguous spectra reduce confidence in peptide assignments and quantitative accuracy.
Common Sources of Complex Matrix Interference
Endogenous biological components:
- High-abundance proteins (e.g., albumin, immunoglobulins)
- Lipids and phospholipids that co-elute and suppress ionization
- Salts and small metabolites that destabilize electrospray efficiency
Exogenous contributors:
- Plasticizers and contaminants from sample handling materials
- Detergents and chaotropes used during protein extraction
- Buffer components and additives introduced during digestion and cleanup
2: Why Matrix Interference Is a Major Challenge in Proteomics Bioanalytical Services
Matrix interference is a critical challenge in Proteomics Bioanalytical Services because proteomics workflows must analyze extremely complex biological samples while preserving sensitivity for low-abundance protein targets. The simultaneous presence of thousands of endogenous components directly impacts analytical performance at multiple levels.
Key challenges include:
- Ion suppression – Co-eluting matrix components reduce ionization efficiency, leading to diminished MS signal for target peptides
- Poor reproducibility – Variability in biological matrix composition across samples introduces inconsistent analytical response
- Limited dynamic range – High-abundance proteins mask low-abundance biomarkers, restricting detection capability
- Data complexity – Increased spectral noise results in ambiguous peptide identifications and reduced confidence in quantitation
These challenges are further amplified in regulated and decision-critical environments, including GLP bioanalytical services and clinical bioanalytical services, where data integrity, reproducibility, and audit readiness are mandatory.
They also influence outsourcing decisions when selecting a bioanalytical CRO or evaluating bioanalytical CRO vs in-house strategies.
3: Case Study Overview: Proteomics Matrix Interference in Plasma Samples
Plasma-based proteomics presents one of the most challenging analytical environments due to its extreme complexity and dynamic protein range. In this case, a client required quantitative proteomics analysis of low-abundance biomarkers in human plasma to support translational research. Initial LC–MS/MS analyses revealed inconsistent peptide responses and pronounced ion suppression, indicating significant matrix interference.
Study parameters:
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Matrix | Human plasma |
| Objective | Quantitative proteomics of low-abundance biomarkers |
| Analytical Platform | LC–MS/MS |
| Key Issue | Severe matrix interference and ion suppression |
This case study reflects a common challenge in advanced Proteomics Bioanalytical Services, particularly for plasma-based biomarker programs where unmanaged matrix effects can compromise sensitivity, reproducibility, and data reliability.
This scenario reflects challenges frequently encountered in biomarker bioanalytical services and PK/PD bioanalysis, where plasma-based matrices dominate study design.
4: How ResolveMass Approaches Matrix Interference in Proteomics Bioanalytical Services
Matrix interference is best addressed by controlling the biological matrix itself rather than compensating at the instrument level. In Proteomics Bioanalytical Services, ResolveMass Laboratories Inc. applies a multi-layered, experience-driven strategy designed to reduce interference at every stage of the analytical workflow.
1. Optimized Sample Preparation Strategy
Effective sample preparation is the single most critical step in minimizing matrix interference in proteomics workflows. By selectively removing interfering components before analysis, downstream chromatographic and mass spectrometric performance is significantly improved.
Key sample preparation optimizations included:
- Depletion of high-abundance plasma proteins to improve detection of low-abundance targets
- Selective protein precipitation to remove non-protein matrix components
- Improved digestion efficiency through optimized enzyme-to-protein ratios, ensuring consistent peptide generation
- Cleanup using solid-phase extraction (SPE) to reduce salts, lipids, and co-eluting contaminants
Together, these measures substantially reduced matrix complexity and co-eluting interferences prior to LC–MS analysis, forming a robust foundation for high-quality Proteomics Bioanalytical Services.
ResolveMass’s approach aligns closely with best practices in bioanalytical method development and addresses well-documented challenges in bioanalytical method development.
These strategies are especially relevant for complex modalities such as antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) and advanced bioanalytical strategies for complex drug modalities.
5: Role of Chromatographic Optimization in Proteomics Bioanalytical Services
Chromatographic optimization plays a critical role in minimizing matrix interference in Proteomics Bioanalytical Services by reducing peptide co-elution and improving separation efficiency. Well-designed LC methods directly enhance detection sensitivity and quantitative reliability in complex biological matrices.
Chromatographic optimization principles used here parallel those applied in LC–MS/MS bioanalytical services and high-throughput bioanalysis, where separation efficiency directly affects data quality.
ResolveMass Laboratories Inc. implemented targeted chromatographic strategies, including:
- Extended gradient methods to improve peptide resolution and reduce co-eluting matrix components
- Carefully selected column chemistries optimized for complex proteomic samples and broad peptide coverage
- Controlled flow rates to enhance chromatographic resolution while maintaining analytical sensitivity
This chromatographic approach is a cornerstone of high-quality Proteomics Bioanalytical Services, particularly for quantitative proteomics workflows where consistency, sensitivity, and reproducibility are essential.
6: Advanced Mass Spectrometry Strategies to Reduce Matrix Effects
Data processing and quality control are where matrix interference is either revealed or effectively controlled in Proteomics Bioanalytical Services. Robust analytical workflows ensure that matrix-related issues are identified early and do not compromise downstream interpretation or decision-making.
ResolveMass Laboratories Inc. applies a structured, quality-driven approach that includes:
- Rigorous QC sample placement throughout analytical batches to monitor system performance and detect drift
- Monitoring of system suitability markers to confirm chromatographic and mass spectrometric stability
- Statistical evaluation of matrix effects to quantify variability and identify interference-driven trends
- Consistent review of peptide-level performance to ensure reliability across runs, analysts, and sample sets
This systematic data processing and quality control framework strengthens confidence in proteomics results, supports reproducibility across studies, and delivers regulatory-ready outcomes suitable for both research and development environments.
7: Data Processing and Quality Control in Proteomics Bioanalytical Services
Data analysis is where matrix interference either gets exposed—or controlled.
ResolveMass applied:
- Rigorous QC sample placement
- Monitoring of system suitability markers
- Statistical evaluation of matrix effects
- Consistent review of peptide-level performance
This quality framework aligns with ResolveMass’s emphasis on bioanalytical data integrity, bioanalytical stability testing, and emerging AI in bioanalysis strategies.
8: Results: Impact of Matrix Control on Proteomics Performance
Effective matrix control delivers immediate and measurable improvements in proteomics workflows. After implementing targeted optimization strategies, the performance gains were clear across all critical analytical parameters within the Proteomics Bioanalytical Services workflow.
Key outcomes observed:
- Improved signal-to-noise ratios, enabling clearer peptide detection
- Reduced variability across plasma samples, improving data consistency
- Enhanced detection of low-abundance biomarkers, critical for translational studies
- Reproducible quantitative performance, suitable for large-scale and longitudinal studies
Performance comparison before and after matrix optimization:
| Metric | Before Optimization | After Optimization |
|---|---|---|
| Signal Stability | Poor | Excellent |
| Ion Suppression | High | Minimal |
| Reproducibility | Inconsistent | Robust |
These results demonstrate that expertly designed Proteomics Bioanalytical Services do not merely improve analytical performance—they fundamentally strengthen data quality, confidence, and usability for high-impact scientific and regulatory decision-making.
9: Why Experience Matters in Proteomics Bioanalytical Services
Experience is the defining factor in successful Proteomics Bioanalytical Services because complex matrix interference cannot be resolved using generic, textbook workflows. It requires practical knowledge gained from working with real biological samples, navigating real-world analytical constraints, and meeting stringent regulatory and data-quality expectations.
ResolveMass Laboratories Inc. brings deep, hands-on proteomics experience across drug discovery, biomarker research, and translational studies. This practical expertise enables the design of matrix-aware proteomics workflows that are not only scientifically sound but also reliable, scalable, and fit for purpose.
This experience directly translates into:
- Faster troubleshooting, driven by early identification of matrix-related failure points
- Fewer re-runs, reducing cost, timelines, and sample consumption
- Higher confidence in reported data, supported by consistent peptide performance and controlled variability
- Long-term method robustness, ensuring reproducibility across studies, analysts, and sample batches
In proteomics, success is not defined by instrumentation alone—it is defined by the experience behind every analytical decision. That experience is what allows Proteomics Bioanalytical Services to deliver data that teams can trust for critical scientific and regulatory decisions.
This experience is especially valuable for organizations leveraging bioanalytical outsourcing, virtual biotech strategies, or cost-effective bioanalytical services for startups.
10: Applications Benefiting from Matrix-Optimized Proteomics
Matrix-optimized Proteomics Bioanalytical Services are essential for applications where biological complexity directly impacts data reliability. By minimizing matrix interference, these workflows enable accurate protein identification, quantification, and interpretation across diverse research and development programs.
Key applications include:
- Biomarker discovery and validation
Matrix-controlled proteomics improves detection of low-abundance biomarkers and ensures consistent performance across sample cohorts, supporting confident biomarker selection and validation. - Mechanism-of-action studies
High-quality proteomics data enables precise mapping of protein expression changes and pathway modulation, helping researchers understand how therapeutic candidates exert their biological effects. - IND/ANDA and NDA-enabling bioanalytical service
- Translational and clinical proteomics
Robust, matrix-aware methods ensure reproducible protein measurements across preclinical and clinical samples, supporting data continuity from early research through clinical development. - Toxicokinetic bioanalysis
- PK/PD-related protein analysis
Optimized Proteomics Bioanalytical Services enable reliable quantification of drug targets, receptors, and downstream signaling proteins in complex matrices, strengthening exposure–response interpretation. - Biosimilar bioanalysis
- Comparative expression profiling
Controlled matrix effects allow accurate comparison of protein expression across treatment groups, disease states, or time points, reducing analytical variability and improving statistical confidence. - Cell and gene therapy bioanalysis
In each of these applications, matrix optimization is not a refinement—it is a prerequisite for generating proteomics data that is reproducible, interpretable, and decision-ready.
Conclusion:
Matrix interference is one of the defining challenges in proteomics—but it is also one of the clearest indicators of analytical expertise. This case study highlights how thoughtful method design, grounded in experience and scientific rigor, enables Proteomics Bioanalytical Services to deliver reliable, high-quality data even in the most complex biological matrices.
At ResolveMass Laboratories Inc., proteomics workflows are built not just to generate data—but to generate trustworthy, reproducible, and decision-ready insights. This philosophy is embedded across the company’s full bioanalytical services overview and CRO capabilities.
Frequently Asked Questions :
Matrix effects are overcome by controlling or removing interfering components before and during analysis, rather than compensating after data generation.
Effective strategies include:
-Optimized sample preparation (protein depletion, precipitation, SPE cleanup)
-Matrix-matched calibration or use of isotopically labeled internal standards
-Chromatographic optimization to reduce co-elution
-Dilution of samples to reduce matrix concentration
-Instrument parameter optimization (ion source conditions in LC–MS)
-Rigorous QC and system suitability monitoring
In proteomics and bioanalysis, early matrix control is the most reliable way to ensure reproducible and accurate results.
Proteomic technologies face both technical and biological challenges in clinical and diagnostic applications.
Key difficulties include:
-High biological variability between patients
-Wide dynamic range of protein concentrations
-Low abundance of disease-specific biomarkers
-Matrix interference from complex biological samples
-Reproducibility issues across platforms and laboratories
-Complex data analysis and interpretation
-Regulatory validation challenges for clinical use
These factors make robust method development and standardization essential for diagnostic proteomics.
Matrix interference is caused by non-target components in the sample that affect analyte measurement.
Common causes include:
-High-abundance endogenous compounds (proteins, salts, lipids)
-Co-eluting substances during chromatography
-Chemical interactions between matrix components and analytes
-Ionization competition in mass spectrometry
-Physical effects such as viscosity and surface tension differences
Matrix interference occurs when these factors alter analyte signal intensity, stability, or accuracy.
Recent advancements in proteomics focus on sensitivity, throughput, and biological relevance.
Key advancements include:
-Data-independent acquisition (DIA) and advanced hybrid MS methods
-Single-cell proteomics for ultra-low sample analysis
-High-resolution mass spectrometry with improved speed and accuracy
-AI- and machine-learning–driven data analysis
-Targeted proteomics (PRM, SRM) for clinical applications
-Improved sample preparation automation
-Multi-omics integration (proteomics with genomics and metabolomics)
These innovations are expanding proteomics into clinical and translational applications.
In Flame Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy (FAAS), matrix interferences arise primarily from chemical and physical effects.
Main sources include:
-High concentrations of salts
-Organic compounds that alter flame characteristics
-Viscosity differences affecting nebulization
-Ionization of analytes in the flame
-Formation of refractory compounds that reduce atomization
These interferences affect atom formation and absorption efficiency.
Interference occurs because analytical techniques are sensitive not only to the analyte but also to the surrounding sample environment.
Underlying reasons include:
-Competition between analyte and matrix components for excitation or ionization
-Changes in physical properties of the sample
-Chemical reactions that alter analyte availability
-Instrumental limitations in separating target signals from background noise
Interference is fundamentally a result of complex sample composition interacting with measurement physics and chemistry.
Reference
- Kondethimmanahalli Chandramouli, Pei-Yuan Qian. Proteomics: Challenges, Techniques and Possibilities to Overcome Biological Sample Complexity.https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC2950283/
- AnnSofi Sandberg , Rui M.M. Branca, Janne Lehtiö, Jenny Forshed.Quantitative accuracy in mass spectrometry based proteomics of complex samples: The impact of labeling and precursor interference.https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1874391913005502
- Bernd O. Keller , Jie Sui , Alex B. Young , Randy M. Whittal. Interferences and contaminants encountered in modern mass spectrometry.https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0003267008007605
- Péter Horvatovich, Berend Hoekman, Natalia Govorukhina, Rainer Bischoff. Multidimensional chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry in analysing complex proteomics samples.https://analyticalsciencejournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/jssc.201000050
- Spyros Garbis , Gert Lubec , Michael Fountoulakis.Limitations of current proteomics technologies.https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0021967305008496

