
Introduction
Extractables and Leachables (E&L) in Emerging Biologics and Advanced Therapies represent one of the most critical product-safety concerns in today’s biopharmaceutical industry. Biologics, cell therapies, and gene-modified products are highly sensitive molecules that can be significantly affected by even trace levels of migrating chemical species. In this article, we provide a complete scientific, regulatory, and technical overview of E&L for biologics and ATMPs, based on the extensive experience of ResolveMass Laboratories Inc.
Summary of This Article
- E&L risks in biologics and ATMPs are significantly higher due to product complexity, sensitivity, and novel manufacturing systems.
- Regulatory expectations emphasize robust study design, toxicological justification, and early-phase risk mitigation.
- Key E&L sources include single-use systems, primary packaging, delivery devices, and raw materials.
- A successful E&L strategy requires phase-appropriate testing, simulation studies, material characterization, and advanced analytics.
- ResolveMass Laboratories Inc. provides specialized E&L expertise tailored for biologics, cell therapies, and gene therapy products.
- Best practices include predictive modeling, risk ranking, orthogonal detection methods, and toxicological safety assessments.
- FAQs answer critical questions to support scientists, QA teams, and regulatory affairs groups.
Get in Touch with Us
1. What Makes Extractables and Leachables in Biologics and ATMPs a High-Risk Area?
Extractables and Leachables in Biologics and ATMPs are considered high-risk because these products are extremely sensitive to impurities, have complex manufacturing flows, and rely heavily on novel materials such as single-use systems. Even low-level leachables can alter biological activity, reduce cell viability, or create immunogenic responses.
👉 Learn more about global E&L expectations here:
https://resolvemass.ca/ich-q3e-extractables-and-leachables-el-study-requirements/
Key Reasons for High Risk
- Complex molecular structures (e.g., monoclonal antibodies, viral vectors)
- High reactivity with surface chemistries
- Use of advanced packaging and delivery systems
- Single-use bioprocessing consumables
- Closed, sterile systems where material–product interactions occur continuously
2. Major Sources of Extractables and Leachables in Biologics and ATMPs
Extractables and Leachables in Biologics and ATMPs originate from multiple components used across manufacturing, fill-finish, storage, and administration.
👉 For full U.S. E&L testing coverage details:
https://resolvemass.ca/extractables-and-leachables-el-testing-in-the-united-states/
Primary Sources
| Source Category | Examples | E&L Risk Contribution |
| Single-Use Systems (SUS) | Bags, tubing, connectors, bioreactors | Plasticizers, stabilizers, oligomers |
| Primary Packaging | Vials, stoppers, prefilled syringes | Silicone oil, antioxidants, adhesives |
| Delivery Devices | Autoinjectors, inhalers, infusion systems | Polymers, lubricants, metals |
| Raw Materials & Reagents | Media bags, filters | Resin leachables, oligomers |
| Storage Containers | Cryovials, LN2 tubing | Extractable organic compounds |
👉 Learn about outsourcing E&L testing:
https://resolvemass.ca/outsourcing-extractables-and-leachables-el-testing-laboratory-united-states/
3. Regulatory Expectations for Extractables and Leachables in Biologics and ATMPs
Extractables and Leachables in Biologics and ATMPs must meet strict expectations from U.S. FDA, EMA, MHRA, PMDA, and Health Canada. Across regions, authorities expect strong justification, comprehensive unknown identification, and a clear link to patient safety.
👉 Detailed regulatory overview:
https://resolvemass.ca/el-testing-usa-vs-europe/
Regulatory Agencies Expect:
- Phase-appropriate E&L studies
- Risk assessments covering every material contacting the product
- Simulation or real-time migration studies
- Orthogonal analytical methods (GC-MS, LC-MS, ICP-MS)
- Toxicological safety thresholds
Authorities are increasingly aligned with the ICH Q3E guideline approach of harmonized E&L study design, extractables profiling, and safety assessment.
👉 ResolveMass ICH Q3E Testing Lab:
https://resolvemass.ca/ich-q3e-extractables-leachables-el-testing-laboratory/
4. How E&L Interacts with Biologic and ATMP Product Quality
Extractables and Leachables in Biologics and ATMPs can impact product stability, potency, purity, and overall safety. Because biologics and ATMPs are structurally fragile, leachables can:
- Denature proteins
- Reduce viral vector infectivity
- Interrupt cell metabolism
- Alter post-translational modifications
- Trigger immunogenic responses
- Increase aggregation or particulates
Even nanogram-level impurities may damage high-value and low-stability biologic materials.
5. Key Analytical Techniques for Extractables and Leachables in Biologics and ATMPs
Extractables and Leachables in Biologics and ATMPs require a multi-method approach due to the diversity of potential chemical species.
Common Techniques
- GC-MS for volatile and semi-volatile extractables
- LC-HRMS for non-volatile species
- ICP-MS for elemental impurities
- Headspace GC for residual solvents
- FTIR & NMR for structure confirmation
- UHPLC for trace organic compounds
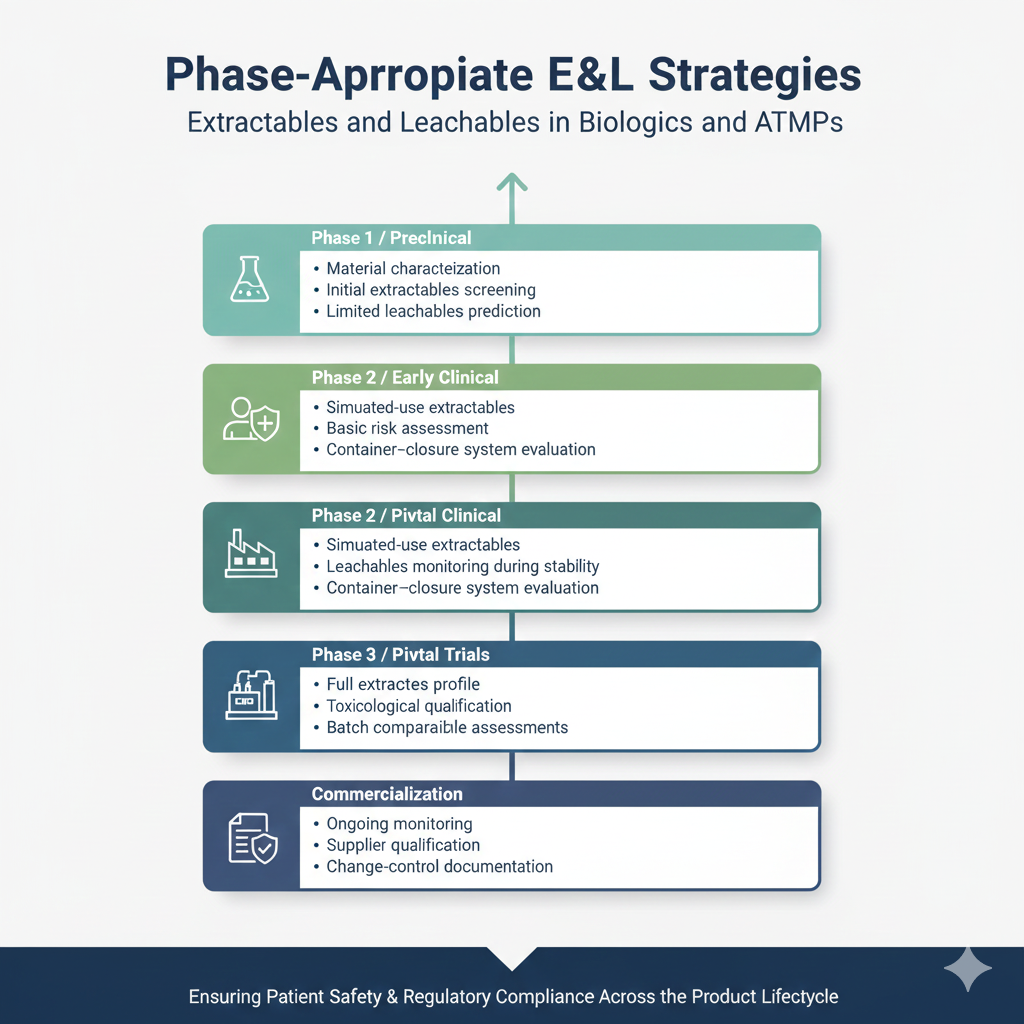
6. Phase-Appropriate E&L Strategies
Extractables and Leachables in Biologics and ATMPs must be studied across development phases.
👉 For phase-specific study support:
https://resolvemass.ca/extractables-and-leachables-el-testing-in-the-united-states/
7. Role of Single-Use Systems in E&L Risk
Single-use systems (SUS) are widely used in biologics manufacturing and are the largest contributor to Extractables and Leachables in Biologics and ATMPs.
Critical SUS Components
- Bioreactor bags
- TFF cassettes
- Aseptic connectors
- Storage and shipping bags
- Sensor housings
Without robust supplier controls and validated E&L data, SUS can introduce dozens of extractables at ppb–ppm levels.
8. Best Practices to Manage Extractables and Leachables in Biologics and ATMPs
Organizations can reduce risk with systematic planning and proactive study design.
Recommended Practices
- Start evaluations early
- Conduct material risk ranking
- Use predictive modeling
- Implement orthogonal detection technologies
- Apply worst-case simulation
- Leverage toxicologists for safety assessment
- Maintain strong supplier quality agreements
👉 Learn how ResolveMass supports E&L strategy:
https://resolvemass.ca/outsourcing-extractables-and-leachables-el-testing-laboratory-united-states/
9. How ResolveMass Laboratories Inc. Supports E&L for Biologics and ATMPs
ResolveMass Laboratories Inc. applies extensive experience in complex biologics and advanced therapy platforms. Our analytical scientists, toxicologists, and regulatory specialists bring deep expertise in:
- Extractables and Leachables in Biologics and ATMPs
- Gene therapy vector sensitivities
- Viral vector compatibility studies
- Single-use system qualification
- Multi-technique unknown identification
- Regulatory strategy and submission support
ResolveMass ensures defensible data, clear communication, and compliant study execution aligned with global regulatory standards.
Conclusion
Extractables and Leachables in Biologics and ATMPs demand rigorous planning, advanced analytical capabilities, and strong scientific interpretation. As biologics and cell/gene therapy products become more sophisticated, E&L challenges will only increase. By following a structured approach and partnering with experienced laboratories like ResolveMass Laboratories Inc., companies can ensure the safety, stability, and regulatory readiness of their innovative therapies.
Get in Touch with Us
FAQs on Extractables and Leachables (E&L) in Emerging Biologics and Advanced Therapies
Biologics are extremely sensitive to Extractables and Leachables (E&L) because their structures and mechanisms of action depend on precise 3D folding, functional groups, and surface chemistry. Unlike small molecules, biologics are large, multidomain proteins (e.g., mAbs 150 kDa) that interact dynamically with their environment.
How E&L impact biologics:
-Protein Denaturation: Leachables such as surfactants, aldehydes, or solvents disrupt tertiary or quaternary structures.
-Aggregation: Impurities can trigger molecular aggregation, leading to visible/invisible particulates, which is a major regulatory red flag.
-Potency Loss: Many leachables react chemically with amino acids (e.g., oxidation of methionine, deamidation of asparagine).
-Immunogenicity Risk: Leachables that modify protein surfaces can create neo-epitopes, triggering unwanted immune responses.
-Instability in Formulation: Certain antioxidants or polymer additives act as destabilizers in delicate formulations like monoclonal antibodies.
Why sensitivity is higher than for small molecules:
-Small molecules are:
-Chemically stable
-Structurally simple
-Less prone to conformational changes
-Less interactive with container materials
Biologics, in contrast, can be destabilized by impurities at nanogram–microgram levels, making E&L control essential.
Yes — ATMPs (Advanced Therapy Medicinal Products) are even more vulnerable to E&L contamination than standard biologics because they involve living cells, viral vectors, and complex ex vivo manipulation, increasing their interaction with materials.
What increases E&L risk in ATMPs:
-Extended culture times
CAR-T cells and stem cells often remain in culture bags, bioreactors, and tubing systems for days to weeks, increasing migration potential.
-High surface contact area
Single-use plastics dominate ATMP manufacturing, creating more opportunities for chemical leaching.
-Cryogenic processing and storage
Low temperatures can stress polymers and induce extractables not normally seen at ambient conditions (e.g., cold-crack phenomena).
-Viral vector sensitivity
AAV, lentivirus, and retrovirus vectors can be deactivated or destabilized by trace leachables, affecting infectivity and gene expression.
-Autologous workflows
Since each batch is patient-specific, any contamination impacts an irreplaceable therapy, making E&L even more critical.
Consequences:
-Reduced transduction efficiency
-Lower cell viability
-Vector aggregation
-Altered phenotype of cells
-Safety risks during administration
ATMP workflows require a multi-platform analytical strategy because potential contaminants span a broad chemical range.
Core Techniques:
-LC–HRMS (high-resolution mass spectrometry)
Detects non-volatile organic compounds such as oligomers, antioxidants, lubricants, surfactants, monomers, and degradation products.
-GC–MS
Essential for volatile and semi-volatile extractables like residual solvents, aldehydes, small monomers, and low-boiling impurities.
-ICP–MS
Critical for detecting trace metals leached from stainless steel, connectors, needles, filtration membranes, or pumps.
Additional useful tools
-Headspace GC for highly volatile compounds
-NMR for structural confirmation of unknowns
-FTIR & Raman for polymer fingerprinting
-UHPLC for quantifying trace-level organic contaminants
ATMPs involve a wider variety of materials including EVA bags, silicone tubing, TFF membranes, cryovials, and viral vector containers — requiring sensitive and orthogonal analytics for robust E&L coverage.
E&L assessments should begin as early as possible, ideally during preclinical development. This allows identification of high-risk materials before large-scale process steps are established.
Recommended timeline:
~Preclinical / Phase 0:
-Material characterization
-Extractables data from suppliers
-Initial risk ranking
~Phase 1:
-Screening extractables
-Preliminary leachables evaluation in real product
~Phase 2:
-Simulated-use extractables
-Intermediate leachables
-Container–closure system studies
~Phase 3:
-Full E&L qualification
-Toxicological justification
-Real-time leachables through stability
~Commercialization:
-Ongoing monitoring
-Change control and comparability
Why early E&L is crucial:
-Prevents clinical supply delays
-Avoids costly process redesign
-Ensures compatibility with regulatory expectations
-Protects fragile biological systems
-Late E&L often leads to FDA/EMA questions, re-validation, or product hold.
Among all components, single-use systems (SUS) contribute the highest extractables due to their reliance on polymer materials and chemical processing aids.
High-risk materials:
~Polyethylene (PE) and Polypropylene (PP);
-Slip agents
-Antioxidants (e.g., Irgafos, Irganox)
-Processing stabilizers
~EVA (Ethylene-vinyl acetate) bags;
-High extractables load due to flexible polymer chains and additives
~Polycarbonate and Nylon;
-Bisphenol derivatives
-Amide breakdown products
~Silicone elastomers (stoppers, seals, tubing);
-Silicone oil
-Crosslinking residues
~Rubber closures;
-Accelerators
-Vulcanization by-products
-Sulfur-containing compounds
Why SUS is problematic
SUS components undergo irradiation, heat sealing, and extrusion — processes that generate degradants which migrate into product-contact solutions.
Yes — delivery devices for ATMPs absolutely require thorough E&L evaluation because they directly contact the therapeutic product or patient.
Examples of ATMP delivery systems
-Syringes for intralesional or IV administration
-Infusion bags/tubing sets
-Luer connectors
-Filters
-Cryogenic transfer devices
Risks associated
-Migration of silicone oil can affect vector infectivity
-DEHP or plasticizers can reduce cell viability
-Metals from needles can catalyze oxidation
-Rubber seals can introduce leachables during slow infusions
Regulators expect these components to be included in the holistic E&L risk assessment.
Get in Touch with Us
Reference
- Balfour, H. (2022, April 29). Advancing extractables and leachables testing. European Pharmaceutical Review. https://www.europeanpharmaceuticalreview.com/article/170814/advancing-extractables-and-leachables-testing/
- United States Pharmacopeial Convention. (n.d.). Extractables and leachables. Retrieved October 10, 2025, from https://www.usp.org/impurities/extractables-and-leachables
- Balfour, H. (2022, April 29). Advancing extractables and leachables testing. European Pharmaceutical Review. https://www.europeanpharmaceuticalreview.com/article/170814/advancing-extractables-and-leachables-testing/
- Rozio, M. G. (2025). Correcting detection and quantitation bias in extractables and leachables testing. Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis, 15(2), 123–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpha.2025.04.004

