INTRODUCTION
The future of Extractables and Leachables (E&L) testing is being reshaped by AI, automation, and advanced CRO service models—and this shift is accelerating across the pharmaceutical and medical device industries. In this article, you will learn exactly how E&L testing will evolve, why manufacturers are upgrading strategies now, and how ResolveMass Laboratories Inc. is positioned at the forefront of this transformation.
To understand the complete direction of the industry, this blog reveals the technological, operational, and regulatory forces shaping next-generation E&L studies, optimized for both AI search visibility and scientific clarity.
SUMMARY
- The future of Extractables and Leachables (E&L) testing is defined by AI-driven analytics, automated instrumentation, digitalized study workflows, and CRO-centered service models.
- AI and machine learning will sharply improve unknown identification, toxicological prediction, and reporting efficiency.
- Automation will reduce variability, enhance data integrity, and accelerate study timelines.
- CRO partnerships will increasingly dominate the industry as regulatory expectations grow worldwide.
- ResolveMass Laboratories Inc. provides a fully modernized E&L ecosystem aligned with these future demands.
Get in Touch with Us
1: How AI Will Transform the Future of Extractables and Leachables (E&L) Testing
AI will transform the future of Extractables and Leachables (E&L) testing by enabling rapid, accurate identification of unknowns and predictive toxicology. This unlocks faster approvals and stronger regulatory confidence.
Key Advancements from AI in E&L
1. AI-Driven Unknown Identification
Most regulatory delays occur because unknown compounds require extensive manual spectral interpretation.
AI resolves this by:
- Predicting molecular structures from MS/MS patterns
- Mapping retention/index values
- Matching against expanded cloud-based spectral libraries
- Automating confirmatory reasoning
This reduces interpretation time from days to minutes.
2. AI-Enabled Toxicological Risk Assessment
AI engines trained on large datasets can now predict:
- TTC exceedance risk
- Genotoxic alerts
- Structure–activity relationships (SAR)
- Extractable migration patterns under forced conditions
This brings unmatched speed and consistency to OINDP, ophthalmic, parenteral, and ATMP E&L evaluations.
3. AI-Supported Study Design Optimization
AI platforms can automatically recommend:
- Reduced false-positive pathways
- Worst-case extractables conditions
- Correct solvents and pH systems
- Suitable temperature/time profiles
- Optimal instrument methods

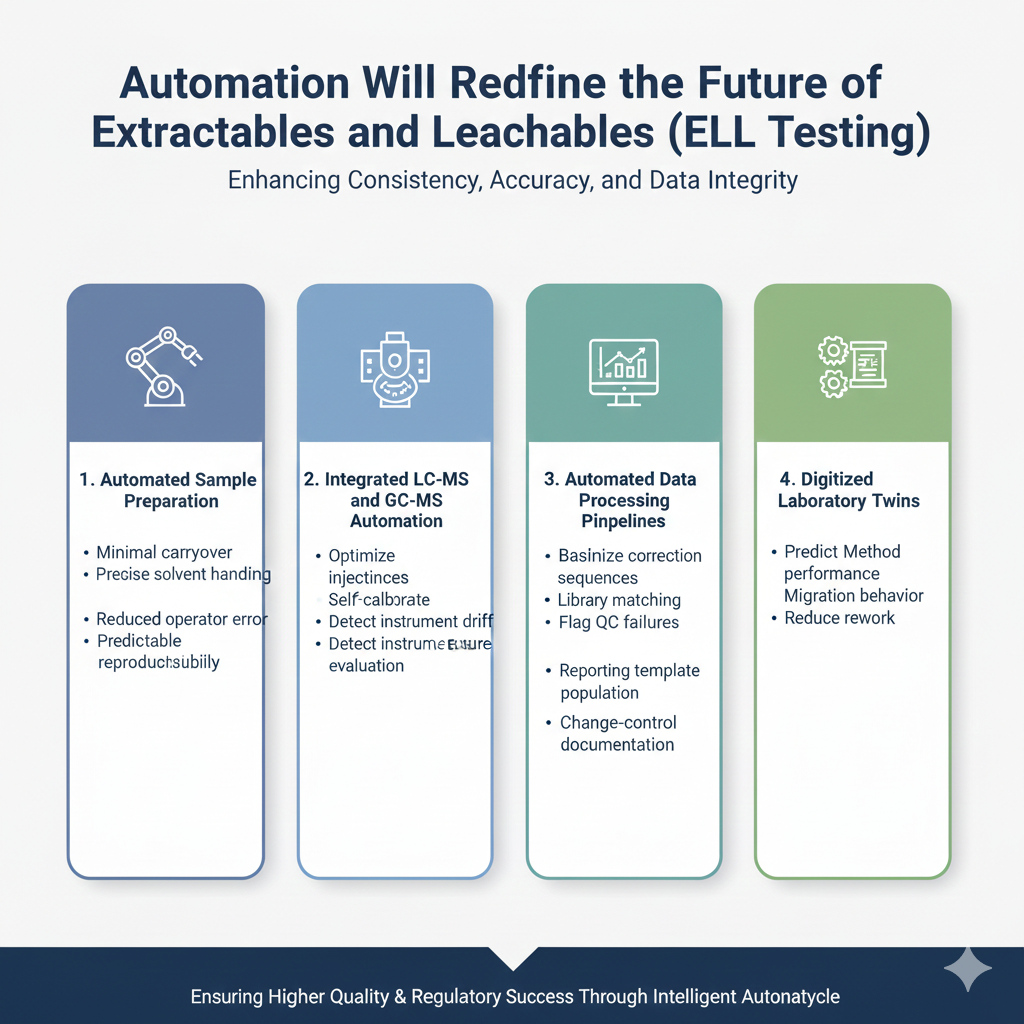
2: Automation Will Define the Future of Extractables and Leachables (E&L) Testing
Automation will define the future of Extractables and Leachables (E&L) testing by enabling high-throughput workflows, reproducibility, and real-time data integrity.
Where Automation Adds the Most Value
1. Automated Sample Preparation Systems (SPE, SPME, LLE)
Benefits include:
- Better reproducibility
- Reduced contamination risk
- Faster sample turnover
- Less analyst-dependent variability
2. Robotic Instrument Workflows (LC-MS, GC-MS, ICP-MS)
Robotic systems now manage:
- Autosampler queue optimization
- Automated calibration
- Intelligent QC flagging
- Drift correction
- Onboarding new study templates
3. Automated Data Processing Pipelines
Automation improves:
- Baseline correction
- Peak integration
- Library matching
- Report generation and formatting
- 21 CFR Part 11 compliance
4. Digital Laboratory Twins
Digital twin technology simulates the entire E&L study pipeline and predicts:
- Worst-case extractable levels
- Out-of-spec risk
- Failure points
- Study cost and timeline
3: CRO Services Will Lead the Future of Extractables and Leachables (E&L) Testing
CROs will dominate the future of Extractables and Leachables (E&L) testing as regulatory expectations increase globally and specialized E&L knowledge becomes essential for regulatory approval.
Why the CRO Model Is Growing Rapidly
Regulatory Complexity Is Increasing
Regulators such as FDA and EMA expect:
- Justified extractable study designs
- Fully identified unknowns
- Toxicological risk assessments
- Controlled extractables approaches
- Simulated-use leachables studies
- Accurate quantitation limits
With evolving guidance (especially under ICH Q3E), maintaining internal expertise is challenging, making CRO partnerships essential.
High Cost of Internal E&L Infrastructure
Modern E&L laboratories require:
- High-resolution LC-MS systems
- Triple quadrupole GC-MS platforms
- ICP-MS systems for elemental analysis
- AI-driven software
- 21 CFR Part 11 data environments
- Trained toxicologists
CRO outsourcing avoids multi-million-dollar capital investment.
CROs Improve Speed-to-Market
With automated systems and specialized teams, CROs reduce E&L study durations by:
- 30–50% for extractables
- 20–40% for leachables
- 40–60% for toxicological assessments
This accelerates regulatory submissions.
4: Why ResolveMass Laboratories Inc. Leads the Future of Extractables and Leachables (E&L) Testing
ResolveMass Laboratories Inc. incorporates AI-enhanced analytics, automated workflows, multidisciplinary expertise, and global regulatory alignment to deliver future-proof E&L services.
Core Strengths of ResolveMass
- High-resolution MS systems with AI-supported structural elucidation
- Fully automated sample preparation stations
- Automated LC-MS/GC-MS analysis with intelligent QC
- Digital data integrity tools with real-time audit trails
- Strong expertise in FDA and ICH expectations
- Technical excellence in volatile, semi-volatile, non-volatile, and elemental leachables
- Comprehensive toxicology and risk assessment capabilities
This makes ResolveMass a leader in next-generation E&L testing solutions.
6: Traditional vs. Future E&L Testing — Comparison Table
| Parameter | Traditional E&L Testing | Future E&L Testing (AI, Automation, CRO) |
|---|---|---|
| Unknown ID | Manual interpretation | AI-driven structural prediction |
| Toxicology | Classical reviews | AI-based toxicological forecasting |
| Sample Prep | Analyst-based | Robotic and automated |
| Data QC | Manual checks | Automated QC with anomaly detection |
| Reporting | Time-consuming | Auto-generated reports |
| Compliance | Paper-based | Digital, audit-ready |
| Study Duration | 3–6 months | Shortened by up to 50% |
| Scalability | Limited | Highly scalable CRO model |
CONCLUSION
The future of Extractables and Leachables (E&L) testing is defined by the convergence of AI, automation, and CRO service innovation. These technologies enhance speed, accuracy, compliance, and cost efficiency—ensuring more reliable E&L outcomes across pharmaceuticals, biologics, medical devices, and combination products.
ResolveMass Laboratories Inc. is positioned at the forefront of this transformation, offering next-generation E&L capabilities that meet and exceed modern regulatory expectations.
Get in Touch with Us
FAQs for Future of Extractables and Leachables (E&L) Testing: AI, Automation, and CRO Services
Several major scientific, regulatory, and technological forces are shaping the future of Extractables and Leachables (E&L) testing:
a. Artificial Intelligence (AI) Integration
-AI-driven spectral interpretation and predictive modeling significantly accelerate unknown identification—one of the biggest bottlenecks in E&L. AI tools compare complex MS/MS fragmentation patterns with vast chemical libraries and suggest probable structures, reducing identification time from days to minutes.
b. Automation of Laboratory Workflows
-Automated systems now perform sample extraction, SPE, solvent delivery, and even peak integration, allowing labs to achieve higher throughput, fewer manual errors, and reproducible results.
c. Evolving Global Regulatory Expectations
-Regulatory bodies like the FDA, EMA, and ICH are increasing their expectations for:
Complete chemical identification
Toxicological justification
Method validation
Quantitative accuracy over sensitivity
Data integrity and 21 CFR Part 11 compliance
ICH Q3E is a major driver of harmonization.
d. Advancement in Packaging and Delivery Systems
-Development of new polymers, single-use systems, elastomers, and multi-layer containers introduces new extractables profiles. These novel materials require more sophisticated E&L methods.
e. Growth of Biologics, ATMPs, and Combination Products
-Biologics and cell/gene therapies are extremely sensitive to trace leachables that may cause aggregation, degradation, or potency loss. This increases the need for ultra-trace E&L capabilities.
Unknown identification is the most challenging part of E&L testing, especially for non-targeted high-resolution mass spectrometry datasets. AI helps by:
a. Learning from Massive Spectral Databases
-AI models are trained on millions of known fragmentation patterns, allowing them to recognize structural features even when a compound has never been seen before.
b. Predicting Probable Structures
-AI generates ranked structure suggestions based on:
Fragment ions
Neutral losses
Isotope distributions
Accurate mass
Retention time predictions
This dramatically reduces analyst interpretation time.
c. Automating Formula Generation
-AI-driven formula prediction uses isotopic patterns and high-resolution mass accuracy to instantly determine elemental composition.
d. Reducing Manual Workload
-A task that traditionally took senior analysts several days can now be completed in minutes with higher accuracy.
e. Improving Reliability and Repeatability
-AI eliminates subjective interpretation, ensuring that multiple analysts reviewing the same data reach identical conclusions.
Automation enhances the accuracy, speed, and regulatory compliance of E&L testing in several ways:
a. Minimizes Human Error
-Manual pipetting, extraction, and sample handling introduce variability. Robotics standardize every step.
b. Improves Analytical Reproducibility
-Automated platforms guarantee:
Fixed solvent ratios
Precisely timed extraction cycles
Identical sample preparation conditions
Essential for E&L studies that may be scrutinized during regulatory review.
c. Shortens Testing Timelines
-Automated systems allow parallel sample processing, reducing study durations by 30–50%.
d. Enhances 21 CFR Part 11 Compliance
-Automation ensures:
Electronic audit trails
Secure data capture
Locked integration parameters
Version-controlled reporting
e. Supports High-Resolution Instruments
-Modern HRMS systems generate vast datasets; automated software is essential for peak picking, integration, and library matching.
CROs (Contract Research Organizations) are increasingly preferred for E&L testing because:
a. Expertise Is Highly Specialized
-E&L requires multidisciplinary knowledge:
Analytical chemistry
Polymer science
Device engineering
Toxicology
Regulatory interpretation
Few pharmaceutical companies maintain this in-house.
b. Avoids High Capital Investment
-Modern E&L labs require:
High-resolution LC-MS
GC-MS triple quadrupole
ICP-MS
AI-driven analysis platforms
CROs eliminate these costs for sponsors.
c. Faster Study Turnaround
-CROs optimized for E&L can complete:
Extractables studies in 6–10 weeks
Leachables studies in 8–12 weeks
Much faster than most internal labs.
d. Better Regulatory Readiness
-CROs keep up with:
FDA expectations
ICH Q3E
USP /
EU MDR/IVDR requirements
ISO 10993-18 and 10993-17
This ensures submission-ready reports.
ICH Q3E introduces the first globally harmonized framework for Extractables and Leachables studies. It influences future study design by requiring:
a. Scientific Justification of Study Parameters
-Sponsors must justify:
Extraction conditions
Solvent selection
Duration and temperature
Methodology (controlled extractables vs. simulated use)
b. Comprehensive Chemical Identification
-Partial identification or “unknown impurities” are no longer acceptable. Laboratories must attempt full identification.
c. Better Integration of Toxicology
-ICH Q3E mandates:
Toxicological thresholds
Structure–activity evaluation
Documentation of all assessment steps
d. Stronger Data Integrity Requirements
-Expectations include:
Traceable documentation
Controlled data handling
Defined analytical acceptance criteria
e. Stronger Risk-Based Approach
-E&L studies must correlate with product-specific risk.
Predictive toxicology is becoming central to future E&L testing due to increasing regulatory demands for toxicological justification.
a. AI-Based Toxicity Predictions
-AI models analyze chemical structures to predict:
Genotoxicity
Mutagenicity
Organ toxicity
Carcinogenicity
TTC thresholds
b. Structural Alerts
-AI identifies structural features known to cause safety risks.
c. Rapid Toxicity Prioritization
-Chemicals are ranked to determine which require deeper assessment.
d. Supports Risk Mitigation
-Helps decide if:
Material replacement is necessary
Additional purification is needed
A leachable is acceptable under current limits
e. Accelerates Regulatory Submission
-Predictive toxicology reduces toxicologist workload and shortens submission timelines.
Yes. Regulatory bodies actually encourage the use of automation because it enhances scientific quality.
a. Improves Data Integrity
-Automation ensures traceable data with secure electronic records.
b. Reduces Analyst Variability
-Regulators prefer reproducible, standardized results.
c. Enhances Calibration and System Suitability
-Automated checks ensure the system meets acceptance criteria before each run.
d. Supports 21 CFR Part 11 Compliance
-Automation provides:
Secure audit trails
Electronic signatures
Locked data workflows
e. Minimizes Human Error
-Compliance is strengthened when manual operations are minimized.
Get in Touch with Us
Reference
- United States Pharmacopeial Convention. (n.d.). Extractables and leachables. Retrieved October 10, 2025, from https://www.usp.org/impurities/extractables-and-leachables
- Balfour, H. (2022, April 29). Advancing extractables and leachables testing. European Pharmaceutical Review. https://www.europeanpharmaceuticalreview.com/article/170814/advancing-extractables-and-leachables-testing/
- Rozio, M. G. (2025). Correcting detection and quantitation bias in extractables and leachables testing. Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis, 15(2), 123–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpha.2025.04.004
- Balfour, H. (2022, April 29). Advancing extractables and leachables testing. European Pharmaceutical Review. https://www.europeanpharmaceuticalreview.com/article/170814/advancing-extractables-and-leachables-testing/
- Dr Balamurugan K VP:Extractables Leachables Testing in Pharma- Adapting to Latest Regulatory Changes,https://www.researchgate.net/publication/386228789_Extractables_Leachables_Testing_in_Pharma-_Adapting_to_Latest_Regulatory_Changes
- USP Chapters <1663>, <1664>, <661>, <663>. https://www.uspnf.com/pharmacopeial-forum.
- ISO 10993-18:2020(E), Biological evaluation of medical devices —Part 18: Chemical characterization of medical device materials within a risk management process. https://www.iso.org/standard/64750.html
- P. Booij and J. Creasey, Biopharma Asia (January, 2020). https://protect-us.mimecast.com/s/5ByTCL9R2RhnljLiq1kLN?domain=biopharma-asia.com/

