Share With Your Network:
Introduction: Why QC Release Testing Service Is the Final Gatekeeper in Pharmaceutical Quality
Every pharmaceutical product must pass through a QC Release Testing Service before it can be supplied to patients or healthcare markets. This service acts as the last and most important quality checkpoint, ensuring that each manufactured batch meets approved standards for safety, identity, strength, and purity. Without proper QC release testing, there is no scientific proof that a product is suitable for human use.
More than a routine laboratory task, QC release testing is a strict regulatory requirement across global markets. Pharmaceutical manufacturers rely on qualified analytical laboratories to meet Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP), ICH guidelines, and pharmacopoeial standards such as USP, EP, and JP. A reliable QC Release Testing Service provides confidence that products are manufactured, tested, and released in a controlled and compliant way, often supported by advanced analytical platforms such as high-resolution mass spectrometry (HRMS) analysis to ensure precise impurity profiling and regulatory acceptance.
Summary — What You’ll Learn
- How outsourcing QC Release Testing Service accelerates time-to-market
- Full end-to-end process of QC Release Testing Service for pharmaceuticals
- How sample preparation, analytical validation, and batch certification are managed
- Integration of GMP, ICH, and pharmacopoeial compliance in QC release
- How analytical data integrity ensures patient safety and regulatory trust
- Modern automation and digital systems in QC release workflows
- Common pitfalls in QC testing and how advanced labs overcome them
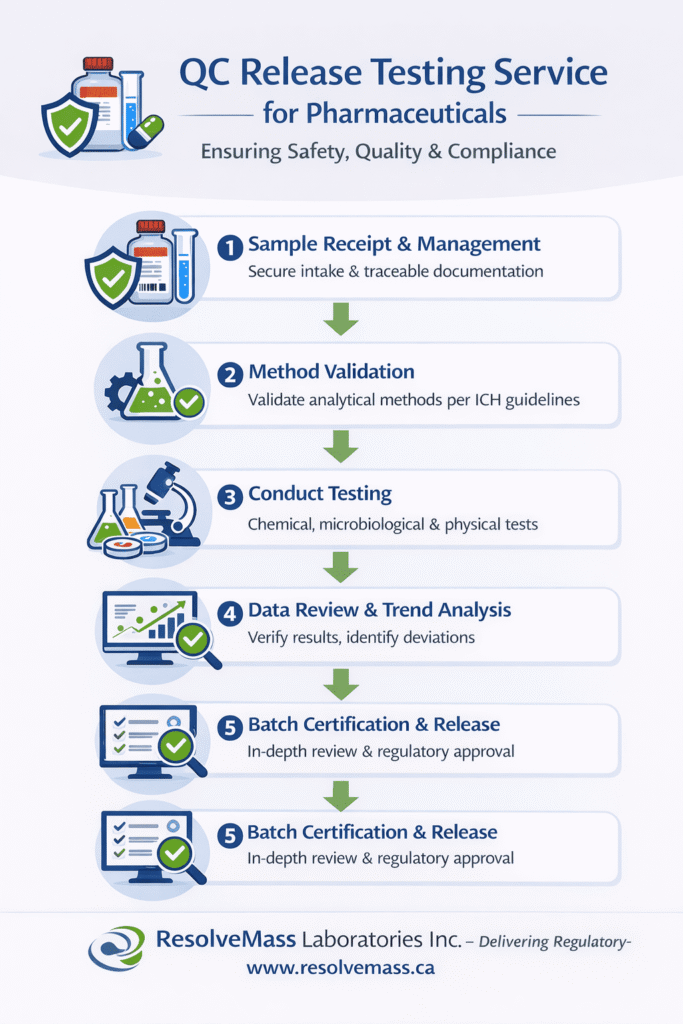
1. Understanding the End-to-End QC Release Workflow
The QC release workflow begins immediately after a manufacturing batch is completed and continues until the batch is formally approved for distribution. This structured and well-documented process ensures that all analytical, quality, and regulatory requirements are fully met before market release. Each step is designed to reduce risk and maintain full traceability.
The workflow usually includes controlled sample receipt, analytical method validation or verification, execution of testing, detailed data review, and final batch certification. Throughout the process, laboratories use secure electronic systems, audit trails, and controlled environments. These measures protect data integrity, support regulatory inspections, and ensure consistent quality across batches, especially when complex workflows integrate techniques such as LC-MS analysis for sensitive quantitative and qualitative evaluations.
| Stage | Key Activities | Primary Objective |
|---|---|---|
| Sample Receipt | Secure collection, chain-of-custody documentation | Ensure sample traceability |
| Method Validation / Verification | Ensure analytical methods are fit-for-purpose | Regulatory compliance |
| Testing Execution | Perform chemical, microbiological, and physical testing | Data accuracy |
| Data Review & Trend Analysis | Evaluate results, identify deviations | Ensure consistency |
| Batch Certification & Release | QP approval or final report issuance | Market authorization |
2. Sample Management: The Foundation of Reliable QC Release Testing Service
In a professional QC Release Testing Service, reliable results depend heavily on how samples are managed from the very beginning. Any mistake during receipt or handling can affect test accuracy and cause regulatory delays. For this reason, laboratories follow strict and documented procedures.
Samples are logged using barcode-based systems to maintain complete traceability from receipt to final disposal. Storage conditions such as ambient, refrigerated, or frozen environments are validated based on product stability requirements. Clear labeling and controlled access further reduce the risk of mix-ups or contamination, which is particularly critical for studies involving extractables and leachables (E&L) testing where sample integrity directly impacts patient safety assessments.
Most advanced laboratories use Laboratory Information Management Systems (LIMS) to automate sample tracking and documentation. This digital control improves audit readiness and strengthens laboratory credibility, supporting Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness (E-E-A-T).
3. Analytical Method Validation and Verification in QC Release Testing Service
Before routine testing can start, laboratories must prove that analytical methods are suitable for their intended use. Method validation is performed according to ICH Q2 (R2) guidelines and is a core requirement of any QC Release Testing Service. This step confirms that test results are accurate, reliable, and reproducible.
Validation studies assess parameters such as accuracy, precision, specificity, linearity, range, and robustness. These checks ensure consistent performance across different analysts, instruments, and days. When a client provides their own method, method verification confirms that the testing laboratory can achieve equivalent results, including those used for nitrosamine testing and analysis, where ultra-low detection limits and regulatory scrutiny are critical.
This phase demonstrates the technical strength of the laboratory and ensures that generated data can stand up to regulatory review. Proper validation also reduces the risk of Out-of-Specification results during batch release.
4. Core Testing Activities in QC Release Testing Service
The heart of a QC Release Testing Service is the execution of laboratory testing across different scientific areas. Each testing category focuses on specific quality attributes defined in regulatory filings and pharmacopoeial standards. Together, these tests confirm that the product meets all approved specifications.
4.1 Chemical Testing in QC Release Testing Service
Chemical testing confirms the identity, assay, purity, and performance of pharmaceutical products. Techniques such as HPLC, GC, LC-MS/MS, and ICP-MS are commonly used to evaluate assay values, impurity profiles, and elemental content. For routine and stability testing, validated HPLC analysis plays a central role in ensuring batch consistency and compliance with compendial limits. Additional tests such as dissolution, disintegration, pH, moisture, and osmolality help confirm dosage form quality.
Residual solvent analysis is another critical requirement, particularly for API and finished dosage forms. Laboratories often apply residual solvent testing using gas chromatography to confirm compliance with ICH Q3C guidelines before batch release.
4.2 Microbiological Testing in QC Release Testing Service
Microbiological testing ensures that products are safe from microbial contamination. This includes sterility testing as per USP <71>, microbial limit testing, bacterial endotoxin testing, and antimicrobial effectiveness testing. These studies are essential for both sterile and non-sterile products.
4.3 Physical Testing
Physical testing evaluates appearance, hardness, friability, particle size, viscosity, and density. For polymer-based formulations and excipients, gel permeation chromatography (GPC) analysis may be applied to assess molecular weight distribution and ensure formulation consistency. All test data is captured using 21 CFR Part 11-compliant systems to maintain data integrity. Container closure integrity testing ensures that packaging protects the product throughout its shelf life.
5. Data Review, Trend Analysis, and OOS Management
After testing is complete, all analytical data undergoes a detailed review process. This step ensures calculations, raw data, and reports are complete, accurate, and scientifically justified. Any unusual results are carefully examined.
Supervisory reviewers check audit trails and confirm compliance with approved procedures. Trend analysis across multiple batches helps detect early signs of variability or risk. If Out-of-Specification or Out-of-Trend results occur, formal investigations and CAPA actions are initiated.
Many laboratories now use digital dashboards to monitor trends in real time. This approach allows QC teams to move from reactive issue management to proactive quality control.
6. Batch Certification and Final Release
Batch certification is the final step in a QC Release Testing Service. At this stage, all test results must meet specifications, deviations must be resolved, and documentation must be complete and accurate. Only then can a batch be approved for market release.
A Qualified Person (QP) or authorized quality representative reviews the full data package and signs the Certificate of Analysis (CoA). This document confirms regulatory compliance and product quality. Batch certification reflects accountability, regulatory confidence, and laboratory authority.
7. Regulatory Integration in QC Release Testing Service
A strong QC release process is fully aligned with global regulatory expectations. Compliance with GMP, ICH, and pharmacopoeial standards ensures acceptance of test results across regions. This alignment supports global submissions and regulatory inspections.
| Guideline | Relevance to QC Release |
|---|---|
| ICH Q7 | GMP principles for API manufacturing |
| ICH Q9 | Quality Risk Management in analytical processes |
| USP <1225> | Validation of compendial methods |
| EU Annex 11 | Computerized systems and data integrity |
| WHO TRS 986 | Good practices for pharmaceutical quality control labs |
This integration strengthens regulatory trust and supports E-E-A-T principles.
8. Digital Transformation of QC Release Testing Service
Digital tools have significantly improved how QC release testing services operate. Manual paper-based workflows are being replaced with integrated digital systems that improve efficiency and compliance. Automation reduces errors and improves inspection readiness.
Modern solutions include LIMS-driven sample tracking, electronic laboratory notebooks, AI-supported chromatogram review, and secure digital CoA delivery. These technologies shorten turnaround time, improve accuracy, and enhance transparency for clients and regulators.
9. Common Challenges in QC Release Testing Service and Solutions
Even with strong systems, QC testing can face operational challenges. Experienced laboratories address these issues through preventive strategies and continuous improvement.
| Challenge | Typical Cause | Expert Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| OOS Results | Operator or method variability | Method requalification and retraining |
| Sample Mix-ups | Inadequate traceability | Barcode and digital sample tracking |
| Data Integrity Gaps | Manual transcription | Electronic data capture and review workflows |
| Delayed Release | Resource bottlenecks | Parallel testing and digital dashboards |
By combining scientific expertise with disciplined processes, laboratories maintain reliable QC outcomes.
10. Outsourcing QC Release Testing Service: Key Benefits
Many pharmaceutical companies outsource QC release testing to specialized laboratories. This approach reduces internal workload while providing access to advanced instruments and regulatory expertise. Outsourcing also helps shorten release timelines.
An experienced external partner supports faster market entry, cost control, and multi-regional compliance. When managed properly, outsourcing turns QC release testing into a strategic advantage rather than a bottleneck.
Conclusion: QC Release Testing Service as a Core Pillar of Pharmaceutical Quality
A QC Release Testing Service is more than a regulatory formality—it is a critical safeguard for patient safety and product quality. From sample receipt to final certification, every step supports accurate and transparent decision-making.
Leading laboratories deliver more than test results. They provide confidence backed by validated methods, digital systems, and strong regulatory alignment. This commitment reflects the Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness (E-E-A-T) expected from industry-leading QC partners.
👉 Partner with ResolveMass Laboratories Inc. for compliant, rapid, and reliable QC Release Testing Services today.
📩 Contact Us
FAQs About QC Release Testing Service
QC release testing is the final laboratory evaluation performed on a pharmaceutical batch before it is approved for market distribution. It confirms that the product meets all predefined specifications for identity, strength, purity, and safety. Only after successful QC release testing and proper documentation can a batch be released for sale or use.
A QC test in the pharmaceutical industry is an analytical or microbiological examination used to verify product quality during or after manufacturing. These tests ensure consistency, detect defects, and confirm compliance with regulatory and pharmacopoeial standards. QC testing helps protect patient safety and product reliability.
The four main types of quality control are incoming QC, in-process QC, final product QC, and stability QC. Incoming QC checks raw materials, in-process QC monitors production stages, final QC confirms finished product quality, and stability QC ensures quality over shelf life. Together, they maintain end-to-end quality control.
The seven quality control tools are flowcharts, check sheets, histograms, Pareto charts, cause-and-effect diagrams, control charts, and scatter diagrams. These tools help identify process issues, analyze data, and monitor performance trends. They support systematic problem-solving and continuous improvement.
A QA/QC checklist is a structured document used to verify that all quality and compliance activities are completed correctly. It helps ensure procedures, testing, documentation, and approvals meet regulatory and internal requirements. Checklists reduce errors and improve consistency in quality operations.
A quality control SOP is a written procedure that explains how QC activities should be performed in a standardized way. It covers testing methods, equipment use, documentation, and acceptance criteria. SOPs ensure consistency, regulatory compliance, and reliable test results.
Preparing a QC sample involves collecting a representative portion of the material using approved procedures. The sample is properly labeled, documented, and stored under defined conditions to maintain integrity. Accurate sample preparation ensures reliable and reproducible test results.
Reference
- Nutrasource. (2026). Quality control release testing. Nutrasource. Retrieved January 6, 2026, from https://www.nutrasource.ca/solutions/analytical-testing/support-your-pharmaceutical-development/quality-control-release-testing/
- Selvita. (n.d.). Quality control and QP release. Selvita. Retrieved January 6, 2026, from https://selvita.com/drug-development/small-molecules/active-substance-raw-materials-drug-product/quality-control-and-qp-release
- Beckman Coulter Life Sciences. (n.d.). QA / QC release testing. Beckman Coulter Life Sciences. Retrieved January 6, 2026, from https://www.beckman.com/resources/biologics-drug-discovery-and-development/qa-qc-testing


