Summary (Quick Insights)
- Regulatory expectations for total Acceptable Intake for Multiple Nitrosamines (Total AI) are becoming stricter across the globe.
- Effective risk mitigation requires a combined toxicological, analytical, and process-control strategy.
- Determining total AI is not a simple summation; it involves understanding structural alerts, potency ranking, and cumulative exposure.
- Strategies include advanced analytical quantitation, robust process control, and risk-based justification using structure–activity relationships (SARs).
- Scientific justification of Total AI must be integrated into product lifecycle management and regulatory filings.
- Multivariate modeling, route-specific risk mapping, and orthogonal analytical techniques are essential for compliance.
- Collaboration between toxicologists, analytical chemists, and formulation experts is critical.
Introduction
When multiple nitrosamines are detected in a single drug product, defining the Acceptable Intake for Multiple Nitrosamines becomes a complex challenge for both regulatory compliance and patient safety. Global health authorities now expect manufacturers to apply a science-based and well-documented approach rather than relying on default conservative limits. Robust nitrosamine analysis plays a critical role in accurately identifying and quantifying these trace-level impurities to support defensible Total AI justifications.
A well-planned Total AI strategy helps control carcinogenic risk while also ensuring uninterrupted patient access to essential medicines. Without a balanced approach, overly strict limits may lead to unnecessary supply disruptions.
This article outlines proven strategies used by industry leaders to manage multiple nitrosamines within a single formulation. The discussion focuses on toxicological reasoning, analytical reliability, and lifecycle-based risk management aligned with global regulatory expectations.
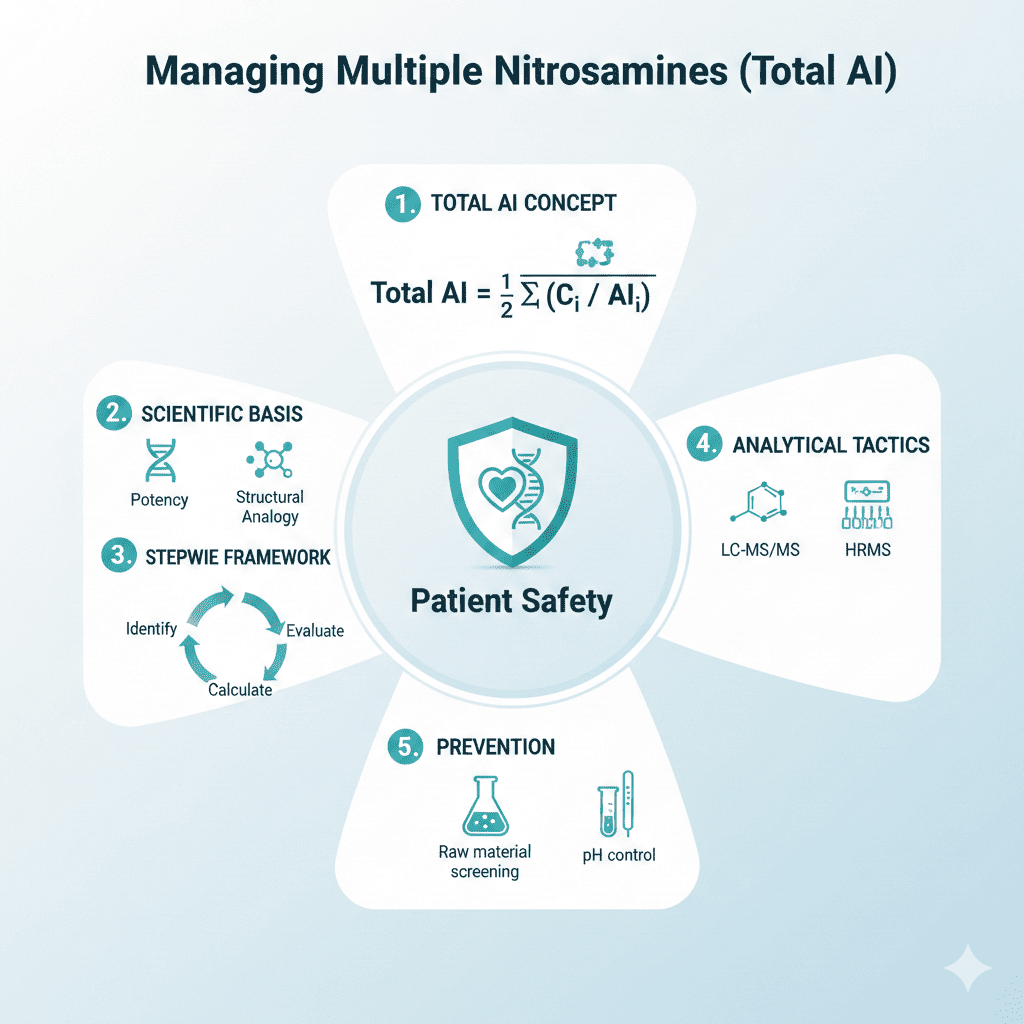
1. Understanding the Concept of Total AI in Nitrosamine Management
The Acceptable Intake for Multiple Nitrosamines (Total AI) refers to the maximum combined daily exposure to all nitrosamines present in a drug product that is considered acceptable for patient use. It is important to note that Total AI is not calculated by simply adding individual acceptable intake limits, as clarified in regulatory guidance on acceptable intake for nitrosamines.
Instead, Total AI relies on toxicological weighting and comparative carcinogenic potency. Different nitrosamines behave differently in the body, with variations in metabolic activation, DNA interaction, and tumor-forming potential.
Understanding these differences is essential for building a scientifically defensible Total AI justification. Regulatory authorities expect manufacturers to clearly explain how each impurity contributes to the overall patient risk, particularly when submitting complex impurity packages involving nitrosamine impurities in pharmaceuticals.
Key Scientific Basis for Total AI
- Potency Adjustment: Highly potent nitrosamines such as NDMA and NDEA significantly influence Total AI due to their very low acceptable intake values.
- Structural Analogy Approach: Used when compound-specific toxicology data are not available, relying on similar nitrosamines as surrogates.
- Threshold of Toxicological Concern (TTC): Applied as a conservative option when data gaps remain, ensuring acceptable lifetime cancer risk.
Regulatory Interpretation
EMA and FDA generally recommend a cumulative approach where total nitrosamine exposure does not exceed the lowest individual AI, unless strong scientific justification is provided. This interpretation is consistent with evolving global guidelines for nitrosamine testing.
Such justification often includes evidence of non-additive effects, structural differences, or low relative potency factors (RPFs).
| Parameter | Description | Regulatory Implication |
|---|---|---|
| Potency factor | TD50 or BMDL10 comparison | Guides relative toxicity |
| Exposure duration | Chronic vs. short-term | Influences Total AI |
| Mechanistic similarity | Shared metabolic pathways | Determines additivity |
2. Framework for Determining Total Acceptable Intake for Multiple Nitrosamines
The presence of multiple nitrosamines creates both analytical and toxicological challenges. A structured framework is required to ensure consistency, transparency, and regulatory acceptance, particularly during nitrosamine risk assessment activities.
This framework connects impurity identification, patient exposure estimation, and carcinogenic potency evaluation. It also helps manufacturers justify limits across complex supply chains and manufacturing sites.
Clear documentation at each step is critical for inspections and regulatory reviews, especially when supporting Health Canada or EMA submissions involving nitrosamine impurity limits.
Stepwise Framework
- Identify all detected nitrosamines in the final drug product and API using validated methods.
- Quantify patient exposure from raw materials, intermediates, solvents, and packaging components.
- Evaluate SAR data to estimate carcinogenic potency when experimental data are limited.
- Establish individual acceptable intakes using published guidance or modeling approaches.
- Apply Relative Potency Factors (RPFs) to normalize toxicity differences.
- Calculate Total AI using cumulative, potency-adjusted exposure values.
- Confirm acceptability using worst-case dosing and exposure scenarios.
Formula Example
Total AI = 1 / Σ (Ci / AIi)
Where Ci is the concentration of each nitrosamine and AIi is its individual acceptable intake.
This approach ensures cumulative cancer risk remains within the generally accepted 10⁻⁵ lifetime risk threshold.
3. Analytical Strategies to Manage Acceptable Intake for Multiple Nitrosamines
Accurate quantitation is essential when justifying the Acceptable Intake for Multiple Nitrosamines. Analytical methods must detect a wide range of nitrosamines at extremely low levels, often requiring advanced LC–MS/MS nitrosamine testing capabilities.
Sensitivity alone is not enough. Selectivity, robustness, and reproducibility are equally important. Regulatory agencies closely review validation data supporting Total AI claims.
Using orthogonal analytical techniques strengthens confidence in reported results.
Key Analytical Tactics
- Orthogonal Chromatography: Combined LC–MS/MS and GC–MS for volatile and non-volatile nitrosamines.
- Isotopic Internal Standards: Improve accuracy and correct matrix effects.
- High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry (HRMS): Confirms identity and minimizes false positives.
- Matrix-Matched Calibration: Reduces ion suppression from complex formulations.
Analytical Validation Requirements
| Parameter | Regulatory Expectation | Recommended Practice |
|---|---|---|
| LOQ | ≤30% of lowest AI | Internal standard use |
| Selectivity | Full separation | Orthogonal columns |
| Recovery | 80–120% | Spike recovery |
| Robustness | Method stability | Stress testing |
4. Process Control and Prevention of Nitrosamine Formation
Preventing nitrosamine formation is more effective than post-production mitigation. Process control strategies should focus on eliminating known precursors and high-risk conditions identified through nitrosamine degradation pathway evaluations.
Early identification of nitrosation risks reduces the need for extensive downstream testing. Regulators strongly favor preventive design over corrective action.
Continuous monitoring ensures consistent long-term control.
Key Process Control Points
- Raw material screening for nitrosating agents and secondary amines.
- Solvent purity monitoring for DMA and DEA impurities.
- Temperature optimization to slow nitrosation reactions.
- pH control and use of antioxidants to block formation pathways.
| Risk Source | Preventive Measure | Monitoring Method |
|---|---|---|
| API synthesis | Replace secondary amines | GC–MS analysis |
| Reagents | Nitrite-free grades | Supplier CoA |
| Formulation | Avoid amine excipients | Compatibility studies |
| Packaging | Migration testing | Extractables studies |
5. Toxicological Justification and Risk Assessment for Total AI
Toxicological justification is the foundation of the Acceptable Intake for Multiple Nitrosamines. Regulators expect a clear and logical explanation showing that combined exposure remains within acceptable lifetime cancer risk, often supported by specialized nitrosamine CRO support.
Assumptions should be transparent and supported by data. Conservative decisions must be clearly explained and justified.
Strong risk communication improves regulatory trust.
Approach for Justification
- Hazard characterization focusing on DNA-reactive mechanisms.
- RPF derivation using TD50 data or close structural analogs.
- Cumulative risk modeling assuming dose additivity when mechanisms overlap.
- Uncertainty analysis documenting data gaps and assumptions.
| Nitrosamine | Individual AI (ng/day) | RPF | Contribution |
|---|---|---|---|
| NDMA | 96 | 1.0 | 50% |
| NDEA | 26.5 | 3.6 | 40% |
| NMBA | 96 | 1.0 | 10% |
6. Lifecycle Management and Regulatory Communication
Managing multiple nitrosamines is an ongoing lifecycle responsibility. Changes in suppliers, formulations, or processes can introduce new risks.
Regulators expect lifecycle-based control strategies aligned with nitrosamine testing for pharmaceutical drugs and documented Total AI updates.
Clear and proactive communication reduces regulatory review timelines.
Lifecycle Approach
- Routine nitrosamine testing in stability programs.
- Impact assessments for all significant changes.
- Inclusion of Total AI justification in regulatory filings.
- Periodic updates as new toxicological data emerge.
7. Leveraging Advanced Modelling and AI-Driven Risk Prediction for Total AI
Advanced modeling tools help predict nitrosamine formation and toxicity, especially for data-poor impurities. AI-enabled platforms described in AI-driven nitrosamine prediction support faster and more informed decision-making.
Regulators increasingly accept modeling as supportive evidence when properly validated.
Applications
- QSAR and read-across modeling for potency estimation.
- Process simulations to identify high-risk steps.
- Bayesian models integrating analytical and toxicological data.
8. Case Study: Integrating Acceptable Intake for Multiple Nitrosamines Across Manufacturing Sites
A global manufacturer detected NDMA, NMBA, and NDEA at trace levels across three sites. Instead of separate limits, a unified Total AI framework was applied using RPF methodology.
Cross-functional collaboration ensured consistent evaluation and documentation.
Outcome
- Combined Total AI of 32 ng/day.
- Acceptance by EMA and Health Canada.
- Reduced testing through preventive controls.
9. Summary of Best Practices
| Strategic Element | Description | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| RPF-based Total AI | Potency-weighted exposure | Defensible limits |
| Orthogonal analytics | Confirm impurity profile | Regulatory confidence |
| Lifecycle management | Continuous oversight | Long-term compliance |
| AI-driven modeling | Predictive control | Prevention-focused |
Conclusion
The regulatory expectations for the Acceptable Intake for Multiple Nitrosamines continue to evolve rapidly. Companies that adopt a comprehensive, science-based approach can effectively manage Total AI while protecting patient safety.
Integrating toxicological modeling, advanced analytics, and preventive process controls is now essential. Transparent documentation and proactive lifecycle management are key to long-term regulatory success.
To learn how our experts can support your Total AI strategy, contact ResolveMass Laboratories Inc. today or reach out through our consultation request form for personalized guidance.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Total AI refers to the combined acceptable daily intake when more than one nitrosamine is present in a drug product. Instead of looking at each impurity in isolation, it evaluates the overall carcinogenic risk to the patient. This approach ensures patient safety while allowing scientifically justified flexibility.
The Acceptable Intake for Multiple Nitrosamines is calculated using cumulative exposure and relative potency factors. Each nitrosamine’s toxicity is weighted based on its carcinogenic strength. This method helps ensure the total cancer risk remains within globally accepted limits.
Structural similarity helps toxicologists understand whether different nitrosamines may act through similar biological pathways. When compounds share similar structures, their toxic effects are often considered additive. This information is critical for building a defensible Total AI justification.
In some cases, Total AI may exceed the lowest individual AI, but only with strong scientific evidence. This requires robust toxicological data showing differences in potency or non-additive effects. Regulators expect clear and transparent justification in such situations.
Nitrosamine monitoring should be conducted during stability studies and whenever there are significant process or supplier changes. Routine testing helps ensure continued compliance over the product lifecycle. Ongoing monitoring also supports early risk detection.
Some excipients may contain amine groups that can contribute to nitrosamine formation under certain conditions. Compatibility and risk assessments are essential during formulation development. Proper excipient selection can significantly reduce nitrosamine risk.
Reference
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. (2025). CDER nitrosamine impurity acceptable intake limits. https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents/cder-nitrosamine-impurity-acceptable-intake-limits
- GMP‑Compliance.org. (2025). How do you control multiple nitrosamine contaminants in a product? https://www.gmp‑compliance.org/gmp‑news/how‑do‑you‑control‑multiple‑nitrosamine‑contaminants‑in‑a‑product
- European Medicines Agency. (2025). Questions and answers for marketing authorisation holders/applicants on the CHMP opinion for the Article 5(3) of Regulation (EC) No. 726/2004 referral on nitrosamine impurities in human medicinal products (EMA/409815/2020 Rev. 23). https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/opinion-any-scientific-matter/nitrosamines-emea-h-a53-1490-questions-answers-marketing-authorisation-holders-applicants-chmp-opinion-article-53-regulation-ec-no-726-2004-referral-nitrosamine-impurities-human-medicinal-products_en.pdf
- United States Pharmacopeia. (2025). Calculation of limit when more than one nitrosamine is identified. https://nitrosamines.usp.org/t/calculation-of-limit-when-more-than-one-nitrosamine-is-identified/1210
- Zamann Pharma. (2024, September 25). How to calculate acceptable intake (AI) limits for nitrosamines. https://zamann‑pharma.com/2024/09/25/how‑to‑calculate‑acceptable‑intake‑ai‑limits‑for‑nitrosamines/


