Introduction
Challenges in bioanalytical method development are among the most critical hurdles faced during drug discovery, preclinical studies, and clinical trials. A poorly developed or inadequately validated bioanalytical method can compromise data integrity, delay regulatory submissions, and increase overall development costs.
Bioanalytical methods are used to quantify drugs, metabolites, and biomarkers in complex biological matrices such as plasma, serum, urine, and tissues. Due to increasing molecular complexity, ultra-low concentration requirements, and evolving regulatory expectations, overcoming challenges in bioanalytical method development has become more demanding than ever.
At ResolveMass Laboratories Inc., bioanalysis is performed using a science-first, regulatory-aligned, and quality-driven approach, delivering reliable and reproducible data across the drug development lifecycle. Our integrated capabilities span bioanalytical services in drug development, from early discovery through regulatory submission and post-marketing support
👉 https://resolvemass.ca/bioanalytical-services-in-drug-development/
Summary
- The challenges in bioanalytical method development can significantly impact drug discovery and pharmaceutical research timelines. This comprehensive guide addresses:
- Matrix Effects: Complex biological matrices interfering with analyte detection and quantification
- Sensitivity and Detection Limits: Achieving ultra-low quantification levels for trace analytes
- Method Validation Complexities: Meeting stringent regulatory requirements across multiple parameters
- Metabolite Identification: Characterizing complex metabolic profiles and transformation products
- Sample Stability Issues: Maintaining analyte integrity throughout collection, storage, and analysis
Each challenge is paired with proven solutions, best practices, and expert insights derived from ResolveMass’ extensive experience in bioanalytical quantification of small and large molecules
👉 https://resolvemass.ca/bioanalytical-quantification/
👉 https://resolvemass.ca/bioanalytical-services-small-large-molecule-quantification/
Explore our biomarker bioanalytical services
👉 https://resolvemass.ca/biomarker-bioanalytical-services/
Learn more about our PK/PD bioanalysis capabilities
👉 https://resolvemass.ca/pk-pd-bioanalysis/
Challenge 1: Matrix Effects in Complex Biological Samples
Matrix effects occur when components in biological samples interfere with analyte ionization, leading to signal suppression or enhancement that compromises quantification accuracy. This represents one of the most prevalent challenges in bioanalytical method development, particularly when working with plasma, serum, urine, or tissue homogenates.
Understanding Matrix Effects
Biological matrices contain thousands of endogenous compounds including:
- Proteins and peptides
- Lipids and phospholipids
- Salts and ionic compounds
- Metabolites and cellular debris
These components may co-elute with analytes during chromatographic separation, impacting ionization efficiency and quantification accuracy—especially in small molecule vs large molecule bioanalysis workflows
👉 https://resolvemass.ca/small-molecule-vs-large-molecule-bioanalysis/
Proven Solutions for Matrix Effects
| Solution Strategy | Implementation | Expected Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Sample Preparation Optimization | Protein precipitation, solid-phase extraction (SPE), or liquid-liquid extraction | 70-90% reduction in matrix interference |
| Chromatographic Resolution | Extended gradients, alternative stationary phases | Baseline separation of analytes from matrix components |
| Matrix-Matched Calibration | Calibration standards in blank biological matrix | Compensation for unavoidable matrix effects |
| Stable Isotope Internal Standards | Deuterated or C13-labeled analogs | Complete correction for matrix-induced variability |
These approaches are routinely applied across our bioanalytical services portfolio
👉 https://resolvemass.ca/bioanalytical-services/
Challenge 2: Achieving Adequate Sensitivity and Detection Limits
Detecting and quantifying analytes at picogram or femtogram levels in biological samples requires advanced instrumentation and optimized method parameters. The challenges in bioanalytical method development often intensify when dealing with low-dose drugs, early-time-point pharmacokinetics, or trace biomarkers.
Why Sensitivity Matters
Modern pharmaceutical development demands:
- Detection of therapeutic proteins at ng/mL concentrations
- Quantification of metabolites representing <1% of parent drug
- Biomarker measurement in early disease detection
- Pediatric formulation analysis with limited sample volumes
These requirements are routinely addressed through advanced bioanalytical method development strategies
👉 https://resolvemass.ca/bioanalytical-method-development-2/
Strategies to Enhance Sensitivity
Instrumental Optimization:
- High-resolution mass spectrometry (HRMS) for improved signal-to-noise ratios
- Triple quadrupole MS/MS with optimized collision energies
- Enhanced ionization sources (APCI, nano-ESI, DESI)
- Detector voltage and dwell time optimization
Sample Concentration Techniques:
- Evaporation and reconstitution in smaller volumes
- Online SPE concentration
- Large-volume injection techniques
- Derivatization to enhance ionization efficiency
Chromatographic Enhancement:
- Narrow-bore columns for increased peak concentration
- Gradient optimization for peak sharpening
- Temperature control for improved peak shape
- Flow rate optimization for maximum sensitivity
Challenge 3: Meeting Regulatory Validation Requirements
Bioanalytical method validation must demonstrate that an analytical procedure is suitable for its intended purpose through rigorous evaluation of accuracy, precision, selectivity, sensitivity, reproducibility, and stability. This is consistently cited as one of the most time-intensive challenges in bioanalytical method development.
Regulatory Framework
Method validation must comply with:
- FDA Bioanalytical Method Validation Guidance (2018)
- EMA Guideline on Bioanalytical Method Validation (2011)
- ICH M10 Bioanalytical Method Validation and Study Sample Analysis (2022)
- Industry-specific guidelines (biomarkers, immunogenicity, cell and gene therapy)
Key Validation Parameters
Critical Parameters to Address:
- Selectivity/Specificity: Demonstrate no interference from endogenous compounds, metabolites, or concomitant medications
- Accuracy and Precision: Meet ±15% criteria (±20% at LLOQ) across calibration range
- Linearity: Establish concentration-response relationship with r² ≥ 0.99
- Sensitivity: Confirm LLOQ with acceptable precision and accuracy
- Recovery: Document consistent extraction efficiency
- Matrix Effects: Quantify ion suppression/enhancement
- Stability: Establish storage conditions and handling procedures
Validation Best Practices
Our validation approach includes:
- Thorough pre-validation experiments to identify potential issues early
- Risk-based validation strategies focusing resources on critical parameters
- Automation and electronic data capture to minimize human error
- Comprehensive documentation meeting regulatory expectations
- Cross-validation studies when transferring methods between laboratories
Common Validation Pitfalls and Solutions
| Validation Challenge | Root Cause | ResolveMass Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Failing carry-over assessment | Inadequate wash sequences | Multi-step needle wash optimization |
| Poor QC reproducibility | Sample preparation variability | Automated liquid handling systems |
| Matrix lot variability | Biological matrix heterogeneity | Testing 6-10 matrix lots during validation |
| Stability failures | Inadequate initial assessment | Comprehensive stability study design |
With over 500 successfully validated bioanalytical methods supporting regulatory submissions, our team brings deep expertise in navigating validation requirements efficiently while maintaining scientific rigor.
ResolveMass offers regulatory-ready bioanalytical method validation services for global submissions
👉 https://resolvemass.ca/bioanalytical-method-validation/
We also support IND and NDA bioanalytical requirements
👉 https://resolvemass.ca/bioanalytical-services-for-ind-nda-submissions/
Challenge 4: Metabolite Identification and Characterization
Comprehensive metabolite profiling requires identifying, characterizing, and often quantifying transformation products that may represent safety concerns or contribute to pharmacological activity. The challenges in bioanalytical method development expand significantly when metabolite characterization becomes necessary for regulatory submissions.
The Metabolite Identification Challenge
Drug metabolism studies must address:
- Identification of all major metabolites (>10% of drug-related material)
- Structural elucidation of unknown metabolites
- Distinguishing between closely related isomers
- Quantifying metabolites without reference standards
- Assessing reactive metabolite formation
Advanced Analytical Approaches
High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry Techniques:
- Accurate mass measurement for molecular formula determination
- MS/MS fragmentation for structural characterization
- Isotope pattern analysis for elemental composition confirmation
- Mass defect filtering for systematic metabolite detection
- Neutral loss and precursor ion scanning for metabolite class identification
Complementary Techniques:
- Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy for definitive structure elucidation
- Ion mobility spectrometry for isomer separation
- Radiolabeled studies for comprehensive mass balance
- Reactive metabolite trapping studies
ResolveMass applies HRMS-based metabolite identification workflows alongside complementary techniques such as NMR and radiolabeled studies, supporting both small and large molecule bioanalysis
👉 https://resolvemass.ca/large-molecule-bioanalysis/
Challenge 5: Sample Stability Throughout the Analytical Workflow
Analyte degradation during sample collection, processing, storage, and analysis can compromise data integrity and lead to incorrect pharmacokinetic or safety conclusions. Understanding and controlling stability represents a critical component of addressing challenges in bioanalytical method development.
Types of Stability to Assess
Comprehensive stability evaluation includes:
- Bench-top stability: Room temperature exposure during sample processing
- Freeze-thaw stability: Multiple freeze-thaw cycles
- Long-term storage stability: Extended frozen storage (-20°C, -80°C)
- Post-preparative stability: Processed samples in autosampler
- Stock solution stability: Reference standards and working solutions
- Blood/plasma stability: Collection to separation timeframe
Common Stability Issues
Analytes may degrade through:
- Enzymatic metabolism in biological fluids
- Chemical hydrolysis or oxidation
- Photodegradation during handling
- Adsorption to collection containers
- pH-dependent degradation
Stability Solutions and Best Practices
Immediate Stabilization Measures:
- Enzyme inhibitors (protease inhibitors, esterase inhibitors)
- pH adjustment immediately after collection
- Rapid cooling and processing
- Light-protective containers
- Appropriate anticoagulants for blood collection
Storage Optimization:
- Validated storage temperatures and durations
- Single-use aliquots to avoid freeze-thaw cycles
- Inert storage containers (polypropylene preferred)
- Controlled thaw procedures
- Documented storage conditions
Analytical Workflow Controls:
- Processing under controlled temperature
- Minimized light exposure
- Prompt analysis after preparation
- Quality control samples throughout runs
Our stability strategies are integrated into end-to-end bioanalytical services, ensuring reliable data generation across preclinical and clinical programs
👉 https://resolvemass.ca/resolvemass-bioanalytical-services-overview/
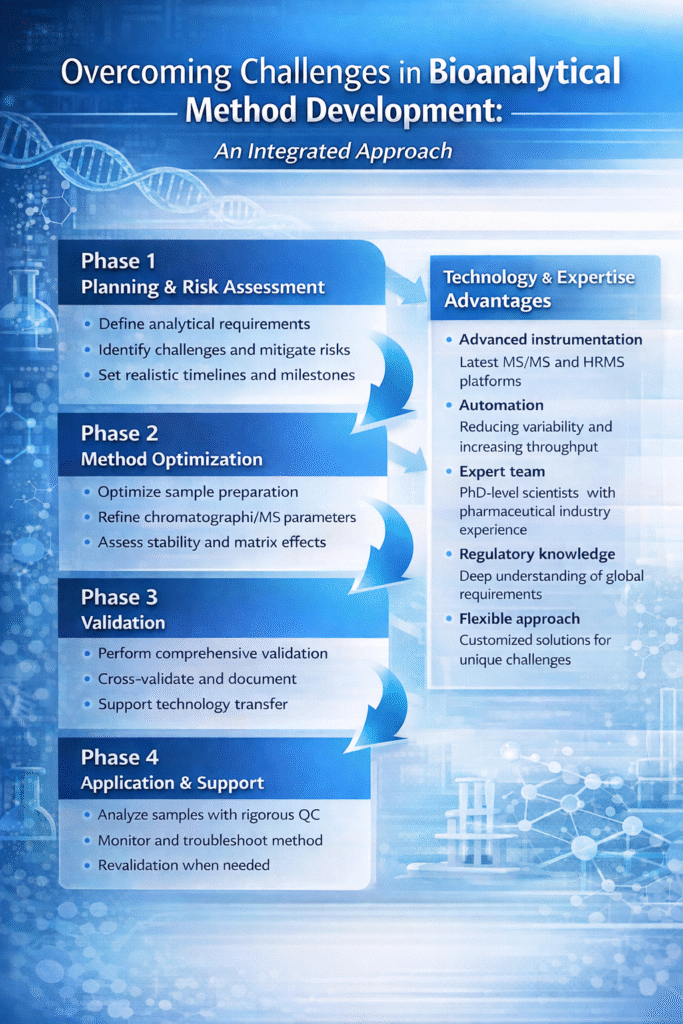
Overcoming Challenges in Bioanalytical Method Development: An Integrated Approach
Successfully navigating the challenges in bioanalytical method development requires more than addressing individual obstacles—it demands an integrated, systematic approach that considers the interplay between various analytical parameters.
Our Method Development Philosophy
At ResolveMass Laboratories Inc., we implement a structured development pathway:
Phase 1: Planning and Risk Assessment
- Define analytical requirements and acceptance criteria
- Identify potential challenges specific to the analyte and matrix
- Develop risk mitigation strategies
- Establish project timelines with realistic milestones
Phase 2: Method Optimization
- Systematic optimization of sample preparation
- Chromatographic and mass spectrometric parameter refinement
- Preliminary stability and matrix effect assessment
- Internal standard selection and evaluation
Phase 3: Validation
- Comprehensive validation following regulatory guidelines
- Documentation meeting submission standards
- Cross-validation when needed
- Technology transfer support
Phase 4: Application and Support
- Study sample analysis with rigorous QC
- Ongoing method performance monitoring
- Troubleshooting support
- Method revalidation as needed
Technology and Expertise Advantages
Our capabilities enable efficient resolution of method development challenges:
- Advanced instrumentation: Latest MS/MS and HRMS platforms
- Automation: Reducing variability and increasing throughput
- Expert team: PhD-level scientists with pharmaceutical industry experience
- Regulatory knowledge: Deep understanding of global requirements
- Flexible approach: Customized solutions for unique challenges
This approach enables efficient execution for pharma, biotech, and emerging startups, including access to affordable bioanalytical services
👉 https://resolvemass.ca/affordable-bioanalytical-services-for-biotech-startups/
We also support outsourced bioanalytical programs
👉 https://resolvemass.ca/bioanalytical-services-outsourcing-for-pharma/
Conclusion
The challenges in bioanalytical method development—from matrix effects and sensitivity limitations to validation complexity, metabolite characterization, and stability concerns—require specialized expertise, advanced technology, and systematic problem-solving approaches. At ResolveMass Laboratories Inc., we’ve built our reputation on successfully navigating these challenges for pharmaceutical companies, biotechnology firms, and research institutions worldwide.
Our comprehensive capabilities in addressing challenges in bioanalytical method development have supported numerous regulatory submissions and accelerated drug development programs. Whether you’re facing a specific analytical obstacle or need end-to-end method development and validation services, our team is ready to provide solutions tailored to your project requirements.
By partnering with experienced bioanalytical specialists who understand both the scientific and regulatory landscape, you can overcome development hurdles more efficiently, reduce project timelines, and generate high-quality data that supports confident decision-making throughout the drug development lifecycle.
🔗 Learn more about our complete bioanalytical services
👉 https://resolvemass.ca/bioanalytical-services/
FAQs regarding Bioanalytical Method Development:
Bioanalytical method development is the process of designing and optimizing analytical methods to accurately measure drugs, metabolites, or biomarkers in biological matrices such as plasma, serum, urine, or tissue.
Bioanalytical assay development focuses on creating and validating specific assays to quantitatively or qualitatively detect biological analytes using techniques such as LC-MS/MS or ligand-binding assays.
Bioanalytical techniques are analytical tools and methods used to analyze compounds in biological samples, including:
-LC-MS/MS
-HPLC
-GC-MS
-ELISA
-RIA
-qPCR
The four main types of analytical methods are:
-Qualitative methods
-Quantitative methods
-Semi-quantitative methods
-Structural (characterization) methods
Analytical methods deal with the measurement and characterization of chemicals in non-biological matrices, whereas bioanalytical methods are specifically designed to measure drugs, metabolites, or biomarkers in biological matrices such as blood or tissues.
Reference
- Bioanalytical method development and validation: Critical concepts and strategies.https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1570023216308881
- Challenges in the development of bioanalytical liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry method with emphasis on fast analysis.https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0021967312013386
- Bioanalytical Method Development and Validation: from the USFDA 2001 to the USFDA 2018 Guidance for Industry.https://www.researchgate.net/publication/326495876_Bioanalytical_Method_Development_and_Validation_from_the_USFDA_2001_to_the_USFDA_2018_Guidance_for_Industry
- A REVIEW ON BIOANALYTICAL METHOD DEVELOPMENT AND VALIDATION.https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Lokesh-Tijare/publication/316004889_A_review_on_bioanalytical_method_development_and_validation/links/5d8c5276a6fdcc25549a54b5/A-review-on-bioanalytical-method-development-and-validation.pdf

