🧪 Introduction: Direct Injection vs. Headspace Techniques for Nitrosamine Volatiles in APIs
When discussing Direct Injection vs. Headspace Techniques for Nitrosamine Volatiles in APIs, the main goal is to identify which method provides reliable, reproducible, and defensible data across different pharmaceutical matrices. Given the regulatory scrutiny surrounding nitrosamines, many sponsors begin by strengthening their overall nitrosamine analysis strategy to ensure compliance and data integrity (learn more).
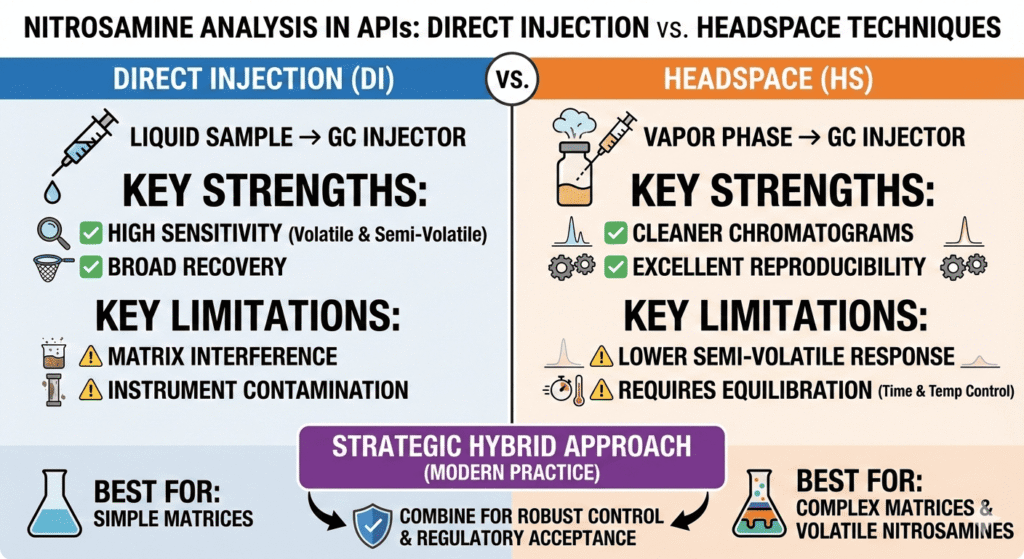
Both techniques are well established and have distinct advantages. Direct Injection involves injecting a prepared liquid sample directly into the GC system, which supports detection of both volatile and semi-volatile nitrosamines. Headspace sampling, on the other hand, analyzes only the vapor above the sample, reducing matrix-related effects and aligning well with modern nitrosamine testing for pharmaceutical drugs (explore testing approaches).
The decision is never random. Factors such as API solubility, thermal stability, matrix complexity, and expected nitrosamine levels play a major role. Since regulatory limits are often in the nanogram-per-gram range, analytical methods must be carefully optimized and fully validated in line with evolving global guidelines for nitrosamine testing (understand current expectations).
🔍 Summary (Key Insights Up Front)
- ResolveMass Laboratories Inc. applies both methods within cGMP frameworks to ensure regulatory compliance and analytical accuracy.
- Direct Injection and Headspace techniques are the two primary analytical strategies for quantifying nitrosamine volatiles in APIs.
- Direct Injection offers higher sensitivity and broader analyte recovery but is prone to matrix interference and instrument contamination.
- Headspace sampling provides superior cleanliness and reproducibility for volatile nitrosamines, especially in complex matrices and finished products.
- Selection depends on API matrix complexity, nitrosamine volatility, method validation requirements, and regulatory expectations.
- An integrated dual-approach validation strategy is emerging as the best practice for robust nitrosamine control.
⚖️ Analytical Principle Comparison: Direct Injection vs. Headspace Techniques for Nitrosamines
Understanding the analytical principles behind Direct Injection vs. Headspace Techniques for Nitrosamines helps clarify why both methods are often used together, particularly when addressing diverse nitrosamine impurities in pharmaceuticals (read more).
Direct Injection introduces the liquid extract directly into GC-MS or GC-MS/MS systems. This allows broad analyte coverage but also exposes the instrument to matrix components, making robust GC-MS method development for nitrosamine testing essential (learn how methods are optimized).
Headspace sampling measures only volatile compounds that partition into the gas phase, keeping non-volatile matrix materials out of the system.
Key Comparison Overview
- Sample Phase: Liquid (Direct Injection) vs. Gas/Vapor (Headspace)
- Matrix Impact: Higher in Direct Injection, minimal in Headspace
- Sensitivity: Better for semi-volatile compounds with Direct Injection; stronger for volatile nitrosamines with Headspace
- Instrument Cleanliness: More maintenance with Direct Injection; cleaner operation with Headspace
These complementary strengths allow laboratories to achieve complete nitrosamine coverage when both techniques are applied strategically.
🧫 Sample Matrix Considerations in Direct Injection vs. Headspace Techniques for Nitrosamines
Matrix behavior strongly influences the choice between Direct Injection vs. Headspace Techniques for Nitrosamines and is a core component of a robust nitrosamine risk assessment (see a practical guide).
Simple API matrices often perform well with Direct Injection, delivering strong recoveries and broader nitrosamine detection. However, APIs with complex excipients, oily components, or residual solvents can interfere with liquid injection methods—an issue frequently encountered during nitrosamine testing for excipients (learn more).
Headspace techniques are better suited for complex matrices because the vapor phase is separated from non-volatile materials. For water-soluble APIs, careful control of equilibrium conditions is essential, as some nitrosamines may remain strongly dissolved in the liquid phase.
Effective method development must consider boiling point, vapor pressure, solvent choice, and gas-liquid partition behavior to ensure accurate and consistent results.
⚗️ Direct Injection Techniques: Strengths and Limitations for Nitrosamine Analysis
Direct Injection remains a powerful tool in Direct Injection vs. Headspace Techniques for Nitrosamines, especially when high sensitivity is required and when validated LC-MS/MS or GC-MS/MS nitrosamine methods are available (view validated approaches).
✅ Advantages of Direct Injection
- Detects a wide range of nitrosamines, including semi-volatile species
- Simple workflow for samples already in suitable solvents
- High recovery rates when matrices are well characterized
- Effective for screening and confirmatory testing
⚠️ Limitations of Direct Injection
- Higher risk of matrix interference and ion suppression
- Increased injector contamination and carryover potential
- More frequent instrument maintenance required
- Manual injection variability can impact precision
Direct Injection works best when sample preparation is tightly controlled and maximum sensitivity is essential.
💨 Headspace Techniques: Preferred Approach for Volatile Nitrosamines
Headspace analysis has become the modern standard in Direct Injection vs. Headspace Techniques for Nitrosamines, especially for volatile compounds regulated at extremely low acceptable intake levels (understand acceptable intake limits).
✅ Advantages of Headspace Techniques
- Cleaner chromatograms with minimal matrix interference
- Excellent reproducibility using automated systems
- Reduced instrument contamination
- Highly effective for volatile nitrosamines such as NDMA and NDEA
⚠️ Limitations of Headspace Techniques
- Lower response for semi-volatile nitrosamines
- Requires precise temperature and equilibration control
- Longer equilibration times may reduce throughput
For highly volatile nitrosamines, Headspace techniques offer unmatched consistency and instrument protection.
🔬 Regulatory and Method Validation Considerations
Both approaches within Direct Injection vs. Headspace Techniques for Nitrosamines are acceptable under ICH M7 and USP <1469>, provided validation requirements are met and documented for regional submissions, including Health Canada nitrosamine impurity limits (review submission expectations).
Regulatory expectations typically include:
- Limits of detection ≤ 0.03 ppm
- Precision ≤ 10% RSD
- Strong linearity across low-level concentration ranges
Headspace methods generally show higher specificity and reproducibility, while Direct Injection excels in sensitivity for low-volatility compounds. Many submissions now include both methods to strengthen regulatory acceptance.
⚙️ Hybrid Analytical Strategy: Combining Direct Injection vs. Headspace Techniques for Nitrosamines
Modern laboratories increasingly adopt hybrid strategies when applying Direct Injection vs. Headspace Techniques for Nitrosamines.
Typical workflows include:
- Initial screening using Headspace GC-MS
- Confirmatory analysis using Direct Injection GC-MS/MS
- Cross-verification under varied conditions
This dual-method approach improves confidence in results and aligns well with regulatory expectations.
🧭 Strategic Method Selection Guidelines
Choosing between Direct Injection vs. Headspace Techniques for Nitrosamines should be based on scientific evaluation.
- Volatile nitrosamines favor Headspace
- Semi-volatile nitrosamines favor Direct Injection
- Complex matrices benefit from Headspace isolation
- High-throughput testing favors automated Headspace systems
Method selection should always follow a risk-based, science-driven approach.
🧩 Conclusion: Direct Injection vs. Headspace Techniques for Nitrosamine Control
In evaluating Direct Injection vs. Headspace Techniques for Nitrosamine Volatiles in APIs, no single method is universally superior.
Direct Injection remains critical for semi-volatile nitrosamines and confirmation testing, while Headspace dominates for volatile compounds with superior cleanliness and reproducibility.
At ResolveMass Laboratories Inc., both techniques are applied together within validated GMP workflows to ensure accurate, reliable, and regulatory-ready nitrosamine data—helping sponsors proactively manage risk and avoid the consequences of nitrosamine detection (learn why early control matters).
📞 Analytical Support and Method Consultation
👉 Contact ResolveMass Laboratories Inc.
❓ FAQs: Direct Injection vs. Headspace Techniques for Nitrosamine Analysis
The main difference between headspace and direct injection lies in how the sample enters the instrument. Direct Injection introduces the liquid sample directly into the GC system, meaning both the analyte and matrix components are analyzed together. Headspace analysis, in contrast, only measures volatile compounds present in the vapor phase above the sample, keeping most matrix materials out. This makes headspace cleaner, while direct injection offers broader analyte coverage.
Sensitivity depends on the type of nitrosamine being analyzed. Direct Injection generally provides higher sensitivity for semi-volatile nitrosamines because the entire sample extract is injected. Headspace is more sensitive and consistent for highly volatile nitrosamines, as these compounds readily move into the vapor phase. Many laboratories use both techniques to cover all sensitivity needs.
Regulatory bodies favor headspace analysis because it reduces matrix interference and minimizes contamination of analytical instruments. Since only volatile compounds are analyzed, the results are typically more reproducible and robust. This leads to better long-term method performance and stronger data reliability. As a result, headspace methods are commonly accepted in regulatory submissions.
Yes, using both methods together is considered a best practice in many laboratories. Headspace is often used for initial screening of volatile nitrosamines, while Direct Injection is applied for confirmation or semi-volatile compounds. This combined approach improves confidence in results and supports regulatory expectations. It also reduces the risk of missing low-level impurities.
The sample matrix plays a major role in choosing between Direct Injection vs. Headspace Techniques for Nitrosamines. Simple and clean matrices usually perform well with Direct Injection. Complex matrices containing excipients, oils, or residual solvents are better suited for headspace analysis. Selecting the right method helps avoid interference and improves accuracy.
Direct Injection generally requires more frequent maintenance because matrix components enter the GC inlet and column. Over time, this can lead to contamination and signal instability. Headspace analysis keeps non-volatile materials out of the system, significantly reducing maintenance needs. This makes headspace more suitable for high-throughput testing.
Headspace techniques are not suitable for non-volatile or poorly volatile nitrosamines. These compounds do not easily transfer into the vapor phase and may be underestimated or missed. In such cases, Direct Injection is required to ensure accurate quantification. Method selection must always consider analyte volatility.
Key validation parameters include accuracy, precision, specificity, linearity, and limits of detection and quantification. Both Direct Injection and Headspace methods must meet regulatory acceptance criteria. Consistent performance across multiple runs is especially important. Proper validation ensures data reliability and compliance.
Temperature directly affects how efficiently nitrosamines move into the vapor phase during headspace analysis. If the temperature is too low, volatilization may be incomplete. If it is too high, sample degradation can occur. Careful temperature optimization is essential for consistent and reproducible results.
References
- Wichitnithad, W., Sudtanon, O., Srisunak, P., Cheewatanakornkool, K., Nantaphol, S., & Rojsitthisak, P. (2021). Development of a sensitive headspace gas chromatography–mass spectrometry method for the simultaneous determination of nitrosamines in losartan active pharmaceutical ingredients. ACS Omega, 6(16), 11048–11058. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.1c00982
- Wichitnithad, W., Sudtanon, O., Srisunak, P., Cheewatanakornkool, K., Nantaphol, S., & Rojsitthisak, P. (2021). Development of a sensitive headspace gas chromatography–mass spectrometry method for the simultaneous determination of nitrosamines in losartan active pharmaceutical ingredients. ACS Omega, 6(16), 11048–11058. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.1c00982
- Zheng, J., Kirkpatrick, C. L., Lee, D., Han, X., Martinez, A. I., Gallagher, K., Evans, R. K., Mudur, S. V., Liang, X., Drake, J., Buhler, L. A., & Mowery, M. D. (2022). A full evaporation static headspace gas chromatography method with nitrogen phosphorous detection for ultrasensitive analysis of semi-volatile nitrosamines in pharmaceutical products. AAPS Journal, 24(1), 23. https://doi.org/10.1208/s12248-021-00669-8
- Amayreh, M. (2019). Determination of N-nitrosamines in water by automated headspace solid-phase microextraction. Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering, 44(2), 269–278. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-018-3567-6
- Balfour, H. (2022, June 16). Advancing nitrosamines analysis with gas chromatography. European Pharmaceutical Review. https://www.europeanpharmaceuticalreview.com/news/172292/advancing-nitrosamines-analysis-with-gas-chromatography/


