Introduction:
Ensuring the safety and efficacy of pharmaceutical oligonucleotides requires precise and comprehensive quality control. LCMS Analysis of oligonucleotides provides a gold-standard solution for characterizing these complex molecules, detecting impurities, and validating the therapeutic product.
At ResolveMass Laboratories Inc., we leverage decades of bioanalytical expertise to deliver reliable, inspection-ready LCMS results for pharma-grade oligonucleotide projects.
Summary:
This article explores how LCMS Analysis of oligonucleotides ensures the quality, safety, and efficacy of therapeutic oligonucleotides. Key points covered include:
- The critical role of oligonucleotide quality control (QC) in therapeutics
- Why LCMS (Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry) is essential for oligonucleotide analysis
- Step-by-step workflow of LCMS in oligonucleotide QC
- Common impurities detected and their impact on therapeutic safety
- Industry best practices for regulatory-compliant oligonucleotide QC
- Advantages of partnering with an expert bioanalytical CRO like ResolveMass Laboratories Inc.
Watch the Video: How LCMS Ensures Pharma-Grade Oligonucleotide Quality
1: What Are Oligonucleotides?
Oligonucleotides are short strands of nucleic acids used as therapeutic agents in treatments like antisense therapy, RNA interference, and CRISPR gene editing. Quality control is essential because minor impurities or sequence errors can compromise efficacy and trigger adverse immune responses.
Oligonucleotides are short strands of nucleic acids, typically ranging from 15 to 30 nucleotides in length. They are synthesized chemically and can be modified to improve stability, binding affinity, and cellular uptake. Therapeutic oligonucleotides include:
- Antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs)
- Small interfering RNAs (siRNAs)
- Aptamers
- MicroRNAs (miRNAs)
- Splice-switching oligonucleotides (SSOs)
Key QC objectives include:
- Confirming sequence integrity
- Detecting and quantifying truncated sequences
- Measuring chemical modifications (e.g., phosphorothioate linkages, 2’-O-methyl groups)
- Ensuring batch-to-batch consistency
Importance of Quality Control in Oligonucleotide Therapeutics
Unlike traditional small molecules, oligonucleotides are prone to sequence errors, incomplete synthesis, and degradation, making quality control critical. Even minor impurities can significantly affect efficacy and safety. Regulatory agencies like the FDA and EMA demand robust analytical methods for batch release and stability studies. Key QC parameters include:
- Purity and identity
- Impurity profiling
- Sequence confirmation
- Batch-to-batch consistency
2: Why LCMS is Ideal for Oligonucleotide Analysis
1. High Sensitivity and Specificity
LCMS enables the detection of oligonucleotide impurities at trace levels, offering greater sensitivity than conventional UV or fluorescence detection. It differentiates between full-length products and truncated or modified sequences.
2. Accurate Mass Determination
LCMS provides high-resolution mass data, allowing accurate molecular weight determination and identification of degradation products, conjugates, or adducts.
3. Sequence Verification
Tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS) enables oligonucleotide sequencing by fragmenting ions and analyzing their mass patterns, ensuring the correct order of nucleotides.
4. Rapid Throughput and Automation
Modern LCMS systems can analyze multiple samples with high reproducibility, supporting GMP-compliant workflows and large-scale production.
5. Structural Characterization
Advanced LCMS methods provide insight into the three-dimensional structure and post-synthetic modifications such as phosphorothioate backbones and PEGylation.
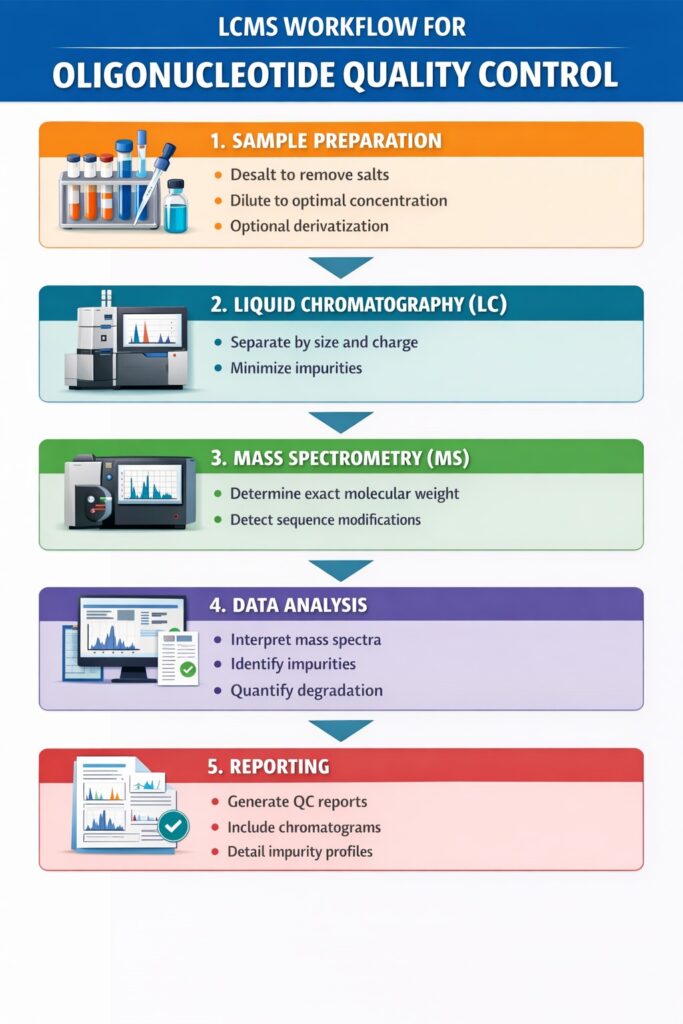
3: LCMS Workflow for Oligonucleotide Quality Control
The LCMS workflow for oligonucleotide QC involves sample preparation, separation, detection, data analysis, and reporting, each step ensuring therapeutic safety.
1. Sample Preparation
Proper sample preparation is crucial for accurate LCMS analysis. Steps include:
- Desalting oligonucleotides to remove interfering salts and buffers
- Dilution to achieve optimal concentration for LCMS detection
- Optional derivatization to enhance ionization and improve sensitivity
2. Liquid Chromatography (LC)
LC separates oligonucleotides to reduce interference and prepare them for mass analysis:
- Separation based on size, charge, and hydrophobicity
- Minimizes interference from truncated products, impurities, or degraded species
- Ensures a cleaner sample enters the mass spectrometer for precise detection
3. Mass Spectrometry (MS)
MS provides detailed molecular characterization of oligonucleotides:
- Determines exact molecular weight to confirm sequence integrity
- Detects sequence errors or chemical modifications
- MS/MS fragmentation patterns verify the structure of modified or complex oligonucleotides
4. Data Analysis
Data analysis translates raw LCMS output into actionable QC information:
- Software interprets mass spectra and generates molecular profiles
- Comparison of observed vs. expected molecular weights identifies discrepancies
- Impurity identification and quantification ensures only high-quality oligonucleotides proceed to clinical development
5. Reporting
The final step ensures QC transparency and regulatory compliance:
- Comprehensive QC reports suitable for regulatory submission
- Inclusion of chromatograms, mass spectra, and impurity profiles
- Provides documentation for batch release, audit readiness, and inspection support
4: Common Oligonucleotide Impurities Detected by LCMS
Answer upfront: LCMS Analysis of oligonucleotides detects truncations, deletions, chemical modifications, and degradation products that can compromise therapeutic safety.
| Impurity Type | Source | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Truncated sequences | Synthesis inefficiency | Reduced potency |
| Depurination | Acidic conditions | Sequence errors |
| Oxidation | Storage or handling | Reduced stability |
| Phosphorothioate modification errors | Manufacturing inconsistencies | Altered pharmacokinetics |
| Nucleobase modification errors | Chemical derivatization | Immune response risk |
By detecting these impurities early, LCMS ensures that only therapeutically safe oligonucleotides proceed to clinical use.
5: Case Studies: Real-World Applications of LCMS in Oligonucleotide QC
LCMS has been successfully applied in multiple real-world scenarios to ensure the safety, stability, and efficacy of therapeutic oligonucleotides. The following case studies illustrate its practical benefits:
1. Identification of Phosphorothioate Impurities
- Challenge: Phosphorothioate-modified antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs) can have incorrect sulfur incorporation, which may affect efficacy or safety.
- LCMS Solution: High-resolution LCMS detected trace levels of improper sulfur incorporation.
- Outcome: Enabled optimization of synthesis protocols, reducing impurity levels and ensuring therapeutic safety.
2. Monitoring siRNA Stability
- Challenge: siRNA duplexes are prone to degradation under physiological conditions, impacting potency.
- LCMS Solution: LCMS analysis tracked the degradation patterns of siRNA duplexes over time.
- Outcome: Allowed formulation scientists to predict stability issues and improve shelf-life and in vivo performance.
3. Aptamer Conjugate Verification
- Challenge: PEGylated aptamers require confirmation of successful conjugation to achieve desired bio-distribution and pharmacokinetics.
- LCMS Solution: LCMS verified PEGylation and identified any incomplete or over-conjugated species.
- Outcome: Ensured the aptamer conjugates met therapeutic specifications for diagnostic and therapeutic applications.
These case studies demonstrate that LCMS Analysis of oligonucleotides is indispensable for detecting subtle chemical variations, ensuring stability, and verifying modifications in complex oligonucleotide therapeutics.

6: Regulatory Guidelines Supporting LCMS Analysis of oligonucleotides QC
LCMS-based oligonucleotide QC aligns with regulatory expectations, including GLP/GCP compliance and inspection readiness for FDA, EMA, and Health Canada.
Best practices for compliance include:
- Complete audit trails for every sample
- Standardized SOPs for LCMS analysis
- Traceable sample handling and storage
- Batch-to-batch reproducibility testing
- Reporting impurity profiles according to ICH guidelines
ResolveMass Laboratories Inc. maintains inspection-ready QC processes, combining technical expertise with regulatory insight to support your therapeutic program.
- ICH Q6A/B: Specifications for new drug substances and products
- FDA Guidance (2021): Emphasizes orthogonal and mass-based analytical techniques for nucleic acid drugs
- EMA Guideline on oligonucleotide-based therapeutics (2022): Endorses LCMS for impurity profiling and identification
7: Challenges in LCMS Analysis of Oligonucleotides
- Ion suppression due to matrix effects
- Complex data interpretation due to charge envelopes
- Limited fragmentation for longer sequences
- Need for custom software tools
Despite these challenges, continuous advancements in instrumentation, column chemistry, and bioinformatics are addressing these limitations.
8: Emerging Trends in LCMS Analysis of oligonucleotides Therapeutics
- Native MS for studying non-covalent interactions
- Top-down sequencing for full-length oligo characterization
- Hyphenated techniques like LC-MS/MS-UV for improved detection
- Machine learning for impurity prediction and automated analysis
Conclusion
In the rapidly advancing field of oligonucleotide therapeutics, quality control is non-negotiable. LCMS Analysis of oligonucleotides provides the precision, sensitivity, and regulatory alignment necessary to confirm sequence integrity, detect impurities, and guarantee therapeutic efficacy. ResolveMass Laboratories Inc. combines decades of experience, state-of-the-art instrumentation, and inspection-ready reporting to support pharma-grade oligonucleotide QC.
Reference
- Lemaitre MM. Individualized antisense oligonucleotide therapies: how to approach the challenge of manufacturing these oligos from a chemistry, manufacturing, and control-regulatory standpoint. nucleic acid therapeutics. 2022 Apr 1;32(2):101-10.
- Aartsma-Rus A, Gagnon K, Watts J, Yu T. OTS Rare Disease N-Of-1+ Workshop Briefing Document [Internet]. 2021
- Baratta F, Simiele M, Pignata I, Iozzino MB, DE PELLEGRINI I, Torta R, Collino M, D’Avolio A, Brusa P. Cannabis FM2: optimization and standardization of galenic preparations. InAbstract book-3rd European Conference on Pharmaceutics. Bringing science into pharmaceutical practice 2019 (pp. 18-18). /.
- OTS Rare Disease N-of-1+Workshop Briefing Document.https://www.oligotherapeutics.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/07/OTS-N-of-1-Briefing-Doc_17-November-2020-FN.pdf
- Individualized Antisense Oligonucleotide Therapies: How to Approach the Challenge of Manufacturing These Oligos from a Chemistry, Manufacturing, and Control-Regulatory Standpoint.https://www.liebertpub.com/doi/abs/10.1089/nat.2021.0030
What Makes a CRO Reliable for Complex Generic Molecules?
Introduction Selecting a Reliable CRO for Generic Drugs becomes more challenging when dealing with advanced…
Analytical Method Development for Generic Drugs: CRO vs In-House Lab
Introduction Analytical Method Development for Generic Drugs is one of the most important scientific and…
Peptide Sameness Study Services in United States – How to Choose the Right CRO
Introduction: Peptide Sameness Study Services in United States are essential analytical programs designed to demonstrate…
Nitrosamine Testing for Generic Drugs: Selecting the Right CRO
Introduction Nitrosamine Testing for Generic Drugs has become a regulatory-critical and business-sensitive requirement in today’s…
Case Study: Unknown Impurity Identification in a Generic Drug Product
Introduction: The detection and characterization of unknown impurities in generic drug products is a critical…
Peptide Sameness Study Services in Canada
Introduction: Peptide Sameness Study Services in Canada are essential for pharmaceutical companies seeking regulatory approval…