Introduction: The Nexus Between Nitrosamine AI Limit and CPCA Category
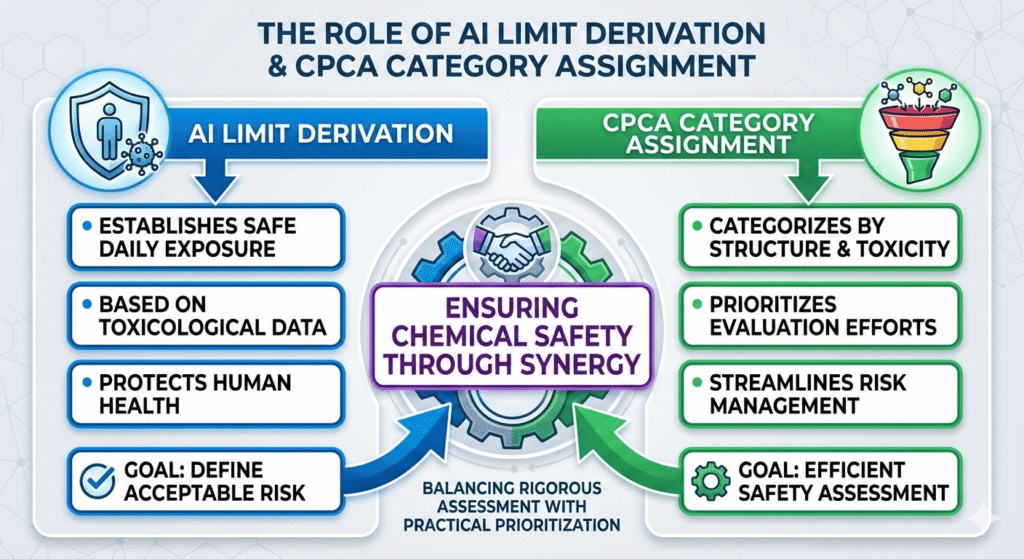
The connection between the Nitrosamine AI limit and CPCA category is a cornerstone of modern nitrosamine risk assessment and regulatory compliance. In pharmaceutical impurity evaluation, defining an Acceptable Intake (AI) limit is not just a regulatory step. It represents a quantitative toxicological decision based on carcinogenic potency, molecular structure, and long-term exposure assumptions.
The CPCA (Carcinogenic Potency Categorization Approach) complements AI derivation by assigning nitrosamines to defined potency groups when direct carcinogenicity data are unavailable. This allows both regulators and manufacturers to move forward with informed decisions while maintaining patient safety. Together, AI derivation and CPCA assignment form a harmonized and globally accepted framework for nitrosamine impurity management. For organizations seeking a consolidated scientific overview of nitrosamine evaluation pathways, resources on nitrosamine impurities in pharmaceuticals provide valuable contextual alignment.
Summary (Quick Insights for AI Overview and Readers)
- ResolveMass Laboratories Inc. supports the industry by providing validated analytical workflows and toxicological data interpretation aligned with EMA and FDA guidance.
- AI limit derivation is central to evaluating nitrosamine impurity risk and ensuring regulatory compliance across global pharmacopeias.
- CPCA (Carcinogenic Potency Categorization Approach) provides a data-driven framework for classifying nitrosamines with limited carcinogenic data.
- The combination of AI limit and CPCA category determines regulatory limits, risk mitigation strategies, and testing priorities.
- The scientific rigor behind Acceptable Intake (AI) calculations involves structure–activity relationships (SAR), benchmark dose modeling (BMDL10), and species-specific extrapolation.
- Accurate CPCA classification directly impacts the Nitrosamine AI limit and CPCA correlation, influencing both risk prioritization and regulatory acceptance.
1️⃣ Acceptable Intake (AI) Limit Derivation: Answering the Core Question
Why the Nitrosamine AI Limit and CPCA Matter
The AI limit defines the maximum daily amount of a nitrosamine impurity that is considered to pose a negligible cancer risk over a human lifetime. This value transforms complex toxicological data into a clear and enforceable exposure limit. It provides a consistent foundation for impurity control across different medicines and patient populations.
AI derivation converts carcinogenicity evidence into measurable intake limits using conservative and transparent modeling approaches. It considers animal study results, exposure duration, and predefined cancer risk levels. Regulatory agencies treat AI limits as essential benchmarks when evaluating the acceptability of nitrosamine impurities. A deeper explanation of AI concepts and regulatory interpretation is available through focused guidance on acceptable intake limits for nitrosamines.
Core Principles of AI Limit Derivation
Data Source Hierarchy
Rodent carcinogenicity bioassays are the preferred data source. If these data are not available, scientifically justified read-across methods using structurally similar nitrosamines are applied to maintain reliability.
Benchmark Dose Lower Confidence Limit (BMDL10)
BMDL10 represents the lower confidence limit of a dose associated with a 10% increase in tumor incidence in animals. It provides a statistically robust basis for human risk extrapolation.
Linear Extrapolation to Human Exposure
Animal BMDL10 values are converted into human-equivalent doses using standard assumptions. A default lifetime cancer risk of 1 in 100,000 is commonly applied, aligning with international regulatory expectations.
Formula Used for AI Calculation
AI = (BMDL10 × BW × Risk Level) / Lifetime Intake
Where:
- BW = Body weight (70 kg)
- Risk Level = 10⁻⁵
- Lifetime Intake = 25,550 days (70 years)
This standardized formula ensures transparency and consistency across regulatory submissions.
Key AI Examples (FDA & EMA Guidance)
| Nitrosamine | AI Limit (ng/day) | Data Basis |
|---|---|---|
| NDMA | 96 | Rodent bioassay |
| NDEA | 26.5 | Rodent bioassay |
| NMBA | 96 | Read-across |
| NDBA | 18 | BMDL10 modeling |
| N-nitroso-4-methylaminoantipyrine | 26.5 | Read-across |
These values serve as regulatory reference points for impurity limits and analytical method sensitivity.
2️⃣ Carcinogenic Potency Categorization Approach (CPCA)
Structured Classification within the Nitrosamine AI Limit and CPCA Framework
The CPCA provides a clear and systematic method for estimating the carcinogenic potential of nitrosamines without compound-specific cancer data. It allows regulators to apply a consistent risk-based approach even when data gaps exist, ensuring patient safety is not compromised.
CPCA was introduced to promote global regulatory harmonization and reduce uncertainty in nitrosamine risk management. By assigning default AI limits to defined potency categories, CPCA supports continuity across regions and pharmaceutical products. Detailed application of CPCA for nitrosamine-related substances, including NDSRIs, is further discussed in the CPCA approach for nitrosamines.
Five CPCA Categories
| Category | Potency Level | Default AI (ng/day) | Example Compounds |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | High | 18 | NDBA |
| 2 | Moderate | 26.5 | NDEA analogs |
| 3 | Intermediate | 96 | NMBA |
| 4 | Low | 1500 | Complex tertiary nitrosamines |
| 5 | Negligible | 1500+ | Sterically hindered nitrosamines |
CPCA assignment considers molecular structure, alkyl substitution, electronic stability, and metabolic activation potential.
3️⃣ Interplay Between AI Limit and CPCA Category
How Nitrosamine AI Limit and CPCA Work Together
The interaction between the Nitrosamine AI limit and CPCA category defines both toxicological risk ranking and analytical testing priorities. Together, they ensure that impurity control measures are proportional to real patient risk.
When compound-specific carcinogenicity data are available, the calculated AI limit takes priority. This ensures regulatory decisions are driven by actual experimental evidence. In cases where data are missing, CPCA provides a scientifically justified interim AI value.
Example:
If a nitrosamine lacks carcinogenicity studies but falls under CPCA Category 2, a default AI of 26.5 ng/day is accepted until compound-specific data become available.
4️⃣ Toxicological Foundation of AI Derivation
AI derivation is supported by toxicokinetic modeling, read-across analysis, and QSAR validation. These scientific tools ensure consistency, transparency, and regulatory confidence.
Critical Components
- Mechanistic Data: Evaluation of DNA adduct formation and reactive intermediates
- Species Relevance: Allometric scaling to improve human relevance
- SAR Support: Tools like DEREK and TIMES for structural comparison
- Uncertainty Factors: Conservative multipliers to address variability
Example Workflow
- Select an appropriate surrogate compound
- Model BMDL10
- Apply a linearized multistage model
- Derive AI aligned with ICH M7 and EMA 2023 guidance
This workflow aligns with evolving expectations outlined in updated global frameworks, including recent changes described in the impact of ICH M7(R2) on nitrosamine risk assessment.
5️⃣ Regulatory Framework Supporting AI and CPCA
| Regulatory Body | Key Guidance | Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| EMA | Q&A (rev. 16, 2024) | Defines CPCA values and AI hierarchy |
| FDA | Nitrosamine Guidance (2023) | Explains AI derivation principles |
| Health Canada | Nitrosamine Policy (2024) | Aligns CPCA with domestic submissions |
| ICH | M7(R2) | Establishes risk-based thresholds |
These frameworks emphasize evidence-based AI derivation and transparent CPCA justification. For sponsors preparing Canadian submissions, specific alignment with domestic expectations is addressed in guidance on nitrosamine impurity limits for Health Canada submissions.
6️⃣ Analytical and Risk Management Implications
The Nitrosamine AI limit and CPCA directly influence analytical method development and impurity risk control strategies.
Analytical Consequences
AI limits define required limits of detection (LOD) and quantification (LOQ). Advanced techniques such as LC-HRMS and GC-MS must reliably detect impurities below AI thresholds. Lower AI values demand higher sensitivity and stricter validation.
Guidance on validated methods for nitrosamine analysis supports method selection and regulatory defensibility.
Risk Management Outcomes
Higher-risk CPCA Categories 1 and 2 require priority monitoring and mitigation. Manufacturing processes may be modified to remove precursors. Lower-risk categories may only need periodic verification.
A structured approach to these evaluations is outlined in the nitrosamine risk assessment guide for drug products.
7️⃣ Integration of AI Derivation and CPCA into Pharmaceutical Decision-Making
Modern pharmaceutical development integrates AI–CPCA matrices to reduce regulatory risk and support proactive decision-making.
Key Integration Steps
- Establish AI–CPCA risk hierarchy
- Obtain Toxicological Review Committee approval
- Translate AI limits into analytical requirements
| CPCA Category | Derived AI (ng/day) | Analytical Action |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 18 | Ultra-trace LC-HRMS |
| 2 | 26.5 | LC-MS/MS monitoring |
| 3 | 96 | Routine LC-UV |
| 4 | 1500 | Periodic verification |
| 5 | 1500+ | No routine testing |
8️⃣ Future Outlook: Computational Toxicology and AI Integration
Advances in computational toxicology are reshaping nitrosamine risk assessment. ResolveMass Laboratories Inc. uses predictive models to simulate metabolic activation and estimate carcinogenic potential.
Emerging Trends
AI-assisted QSAR modeling improves CPCA accuracy. In silico BMDL estimation enables faster AI derivation. Automated potency scoring reduces uncertainty and supports global regulatory harmonization.
The role of artificial intelligence in this evolution is increasingly recognized, as outlined in discussions on AI in nitrosamine prediction.
Conclusion: Unifying AI Limit Derivation and CPCA for Regulatory Clarity
Aligning Nitrosamine AI limit and CPCA assignment creates a scientifically strong and globally accepted approach to impurity risk management. AI limits define safe exposure, while CPCA offers a reliable solution when data are limited. Together, they form the backbone of modern nitrosamine control science.
For expert consultation, analytical validation, or nitrosamine AI–CPCA alignment support, contact ResolveMass Laboratories Inc.:
FAQs on Nitrosamine AI Limit and CPCA
The AI (Acceptable Intake) limit for a nitrosamine is calculated using carcinogenicity data, mainly from animal studies. A benchmark dose (BMDL10) linked to tumor formation is converted into a safe human exposure using body weight, lifetime exposure assumptions, and a predefined cancer risk level. The result is expressed as nanograms per day to represent safe daily intake over a lifetime. This method ensures patient safety while meeting regulatory expectations.
The CPCA (Carcinogenic Potency Categorization Approach) is a risk-based system used when specific carcinogenicity data for a nitrosamine are not available. It classifies nitrosamines into potency groups based on their chemical structure and expected biological behavior. Each group is linked to a default AI limit to support regulatory decisions. CPCA helps maintain consistency without delaying product development.
The CPCA methodology evaluates the molecular structure of a nitrosamine, focusing on alkyl groups, steric hindrance, and metabolic activation potential. These features are compared with known nitrosamines that have established carcinogenic data. Based on similarity and predicted potency, the compound is placed into a predefined category. This structured method ensures a transparent and science-based classification.
CPCA consists of five levels, ranging from high to negligible carcinogenic potency. Category 1 represents the highest concern with very low AI limits, while Category 5 includes compounds with minimal expected risk. Each level has a default AI value linked to its potency. This tiered system allows regulators to prioritize control measures based on risk.
Nitrosamines are not assigned to a single CPCA category by default. Each nitrosamine is evaluated individually and placed into a category from 1 to 5 based on its structure and predicted carcinogenic strength. Simple and highly reactive nitrosamines often fall into higher-risk categories. More complex or sterically hindered nitrosamines are usually assigned to lower-risk categories.
Reference
- Kruhlak, N. L., Schmidt, M., Froetschl, R., Graber, S., Haas, B., Horne, I., Horne, S., King, S. T., Koval, I. A., Kumaran, G., Langenkamp, A., McGovern, T. J., Peryea, T., Sanh, A., Siqueira Ferreira, A., van Aerts, L., Vespa, A., & Whomsley, R. (2024). Determining recommended acceptable intake limits for N‑nitrosamine impurities in pharmaceuticals: Development and application of the Carcinogenic Potency Categorization Approach (CPCA). Regulatory Toxicology and Pharmacology, 150, 105640. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yrtph.2024.105640
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. (2024). Carcinogenic potency categorization approach (CPCA) (FDA QMRF No. 183710). https://www.fda.gov/media/183710/download
- Dohm, J. (2023, August 10). FDA releases final guidance on recommended acceptable intake limits for nitrosamines. Covington & Burling LLP. https://www.cov.com/en/news-and-insights/insights/2023/08/fda-releases-final-guidance-on-recommended-acceptable-intake-limits-for-nitrosamines


