🔍 Summary: Key Insights
- The Nitrosamine CPCA approach for NDSRIs enables a structured and scientifically validated method to assess carcinogenic risk of structurally diverse nitrosamine drug substance-related impurities.
- It bridges the data gap between untested nitrosamines and those with established carcinogenicity data through structure–activity relationships (SARs).
- Implementation involves categorization, read-across, potency adjustment, and regulatory alignment steps.
- Analytical precision, data transparency, and scientific defensibility are critical for regulatory acceptance.
- ResolveMass Laboratories Inc. provides end-to-end analytical and toxicological support in applying the CPCA framework for global regulatory submissions.
Introduction: Why the Nitrosamine CPCA Approach for NDSRIs Matters
The Nitrosamine CPCA approach for NDSRIs (Carcinogenic Potency Categorization Approach for Nitrosamine Drug Substance-Related Impurities) provides a reliable method to establish acceptable intake (AI) limits for complex nitrosamines that lack direct carcinogenicity studies. This is especially important as many newly detected NDSRIs have limited historical toxicology data and require both predictive toxicology and high-sensitivity analytical confirmation. Organizations evaluating these impurities often rely on advanced nitrosamine analysis strategies to ensure trace-level detection and regulatory compliance (Learn more: https://resolvemass.ca/nitrosamine-analysis/).
Unlike generic threshold-based methods, CPCA applies data-driven, category-specific potency values. This ensures that risk assessments reflect the actual carcinogenic potential of each impurity rather than relying on worst-case assumptions that may not be scientifically justified. Such differentiation is increasingly critical as regulators tighten expectations around nitrosamine impurities in pharmaceuticals.
By combining molecular structure, electronic characteristics, and predicted metabolic behavior, CPCA improves regulatory confidence while continuing to protect patient safety. It enables consistent and balanced decision-making across products and therapeutic classes.
Overall, this methodology aligns impurity control strategies with modern toxicological science and evolving regulatory expectations. It represents a shift away from one-size-fits-all limits toward evidence-based, structure-guided risk management supported by comprehensive nitrosamine risk assessment frameworks.
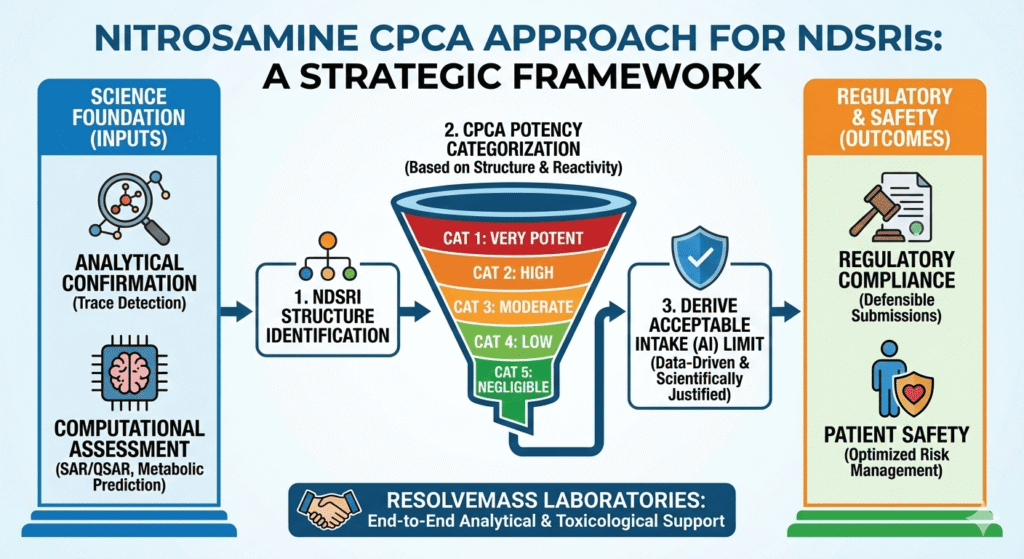
1. Foundation of the Carcinogenic Potency Categorization Approach (CPCA) for NDSRIs
The CPCA framework was developed to compare carcinogenic potency across a wide range of nitrosamine structures found in pharmaceutical products. These structures can differ greatly in size, reactivity, and metabolic activation potential.
CPCA divides nitrosamines into five categories based on molecular reactivity, steric effects, electronic features, and likelihood of metabolic activation. This structured grouping allows systematic comparison between known nitrosamines and untested NDSRIs, particularly those emerging from NDSRI-specific nitrosamine testing programs (Detailed overview: https://resolvemass.ca/ndsris-in-nitrosamine-testing/).
By focusing on shared mechanistic features, CPCA reduces uncertainty when experimental carcinogenicity data are not available. It also supports scientifically sound read-across from structurally similar compounds.
This categorization system creates a strong and transparent basis for predicting relative carcinogenic risk in NDSRIs.
Key Principle:
Each CPCA category represents a defined carcinogenic potency range. This allows prediction of cancer risk for untested NDSRIs using data from structurally related nitrosamines with established carcinogenic profiles. As a result, AI limits remain protective but not unnecessarily restrictive.
CPCA Categories Overview:
- Category 1 (Very Potent): TD₅₀ < 0.01 mg/kg/day (e.g., NDMA, NDEA)
- Category 2 (High): TD₅₀ 0.01–0.1 mg/kg/day (e.g., NMPA)
- Category 3 (Moderate): TD₅₀ 0.1–1 mg/kg/day (certain alkyl/aryl nitrosamines)
- Category 4 (Low): TD₅₀ 1–10 mg/kg/day (bulky or sterically hindered nitrosamines)
- Category 5 (Negligible): TD₅₀ > 10 mg/kg/day (non-reactive or unstable nitrosamines)
AI Derivation:
Once the CPCA category is confirmed, the acceptable intake is calculated using the lowest TD₅₀ value within that category. Appropriate uncertainty and safety factors are applied to ensure long-term patient protection.
2. Integrating the Nitrosamine CPCA Approach for NDSRIs into Risk Assessment
Applying the Nitrosamine CPCA approach for NDSRIs requires close coordination between computational chemistry, toxicology, and analytical science. Each discipline provides critical input to the final risk assessment.
This integrated workflow ensures that structural predictions are supported by analytical confirmation. It also helps identify inconsistencies early, reducing delays during regulatory review.
A harmonized approach improves reproducibility and strengthens communication between technical teams and regulators, especially when supported by experienced CRO services for nitrosamine risk evaluation (See how experts support this process: https://resolvemass.ca/nitrosamine-cro-support-for-effective-risk-evaluation/). When executed correctly, CPCA becomes a practical and defensible tool for impurity risk management.
Implementation Steps:
- Structural Classification: Identify the nitrosamine group within the molecule and understand its chemical environment.
- Electronic Descriptor Analysis: Calculate parameters such as LUMO energy and electrophilicity to estimate DNA reactivity.
- Metabolic Activation Prediction: Use QSAR models to evaluate α-hydroxylation potential and reactive intermediate formation.
- Category Assignment: Assign the impurity to a CPCA category based on combined evidence.
- AI Calculation: Derive acceptable intake limits using category-specific TD₅₀ values.
- Regulatory Documentation: Prepare a clear and traceable justification package for agencies such as the FDA, EMA, and Health Canada.
3. Advantages of the Nitrosamine CPCA Approach for NDSRIs Over Traditional Methods
The Nitrosamine CPCA approach for NDSRIs offers major improvements compared to older methods that relied on default NDMA- or NDEA-based limits.
Traditional approaches often applied overly strict limits that did not reflect the true risk of structurally different nitrosamines. CPCA corrects this by introducing scientific differentiation based on structure and mechanism.
By using mechanistic understanding, CPCA improves both accuracy and regulatory trust. It also helps prevent unnecessary recalls, manufacturing disruptions, and downstream consequences associated with nitrosamine detection in drug products (Understand potential impacts: https://resolvemass.ca/consequences-of-nitrosamine-detection/).
Key Advantages:
- Improved scientific precision with category-based potency values
- Greater regulatory transparency and traceability
- Flexibility for diverse nitrosamine structures
- Faster risk resolution without new animal studies
- Strong alignment with ICH M7 principles
4. Data Requirements and Computational Methods Supporting CPCA
Successful CPCA implementation depends on high-quality data and validated computational tools. The reliability of AI limits is directly linked to the strength of these inputs.
Computational methods allow evaluation of properties that are difficult to measure experimentally. When paired with analytical confirmation, they create a robust scientific foundation. Emerging digital tools, including AI-driven nitrosamine prediction models, are further strengthening CPCA justifications by improving consistency and explainability (Explore AI applications: https://resolvemass.ca/ai-in-nitrosamine-prediction/).
Regulators increasingly review both data quality and modeling assumptions in CPCA submissions.
Essential Data Inputs:
- Quantum chemical descriptors such as HOMO/LUMO energies and bond dissociation energies
- Structural analog databases with known carcinogenicity data
- Metabolic simulation models for P450 activation pathways
- QSAR and read-across tools for mutagenicity prediction
Analytical Role:
ResolveMass Laboratories supports CPCA through GC-MS/MS and LC-HRMS analysis of trace NDSRIs. Their services also include in-silico profiling and validation packages aligned with ICH Q2(R2).
5. Regulatory Adoption and Industry Practices
Global regulators now recognize CPCA as the preferred approach for nitrosamines without direct carcinogenicity data. This reflects increased confidence in structure-based toxicology.
Since late 2023, CPCA has shifted from an optional method to a regulatory expectation. Manufacturers are updating internal procedures to remain compliant with global nitrosamine testing guidelines and evolving authority expectations (Regulatory overview: https://resolvemass.ca/global-guidelines-for-nitrosamine-testing/).
Recent Guidance Updates:
- EMA Q&A (Version 10, 2024) formally adopted CPCA
- FDA (2024) encouraged replacing default NDMA limits with CPCA-based values
- Health Canada accepted CPCA with transparent computational justification
6. Challenges and Critical Considerations in CPCA Implementation
Despite its benefits, CPCA requires careful and consistent scientific execution. Variability in methods can weaken regulatory confidence.
Some nitrosamines show complex metabolic behavior that is hard to predict. These cases require additional supporting evidence and expert interpretation.
Key Challenges:
- Complex metabolic activation pathways
- Variability between computational tools
- High expectations for documentation and transparency
Mitigation Strategies:
- Cross-validate results using multiple in silico tools
- Maintain detailed records of models and assumptions
- Partner with experienced analytical laboratories
Partnering with laboratories experienced in advanced LC-MS/MS nitrosamine testing helps mitigate these challenges and ensures defensible submissions (Learn more: https://resolvemass.ca/lc-ms-ms-nitrosamine-testing/).
7. Implementation Roadmap for Laboratories and MAHs
A clear roadmap ensures consistent application of the Nitrosamine CPCA approach for NDSRIs. Defined roles and early coordination reduce review delays.
Typical Stages:
- Identification of potential NDSRIs
- Analytical confirmation and quantification
- Computational potency categorization
- AI derivation and justification
- Regulatory submission and review
8. Practical Example: Applying CPCA to a Tertiary NDSRI
Consider an NDSRI from a tertiary amine API with bulky substituents. Traditional methods would assign the same AI as NDMA, usually 96 ng/day.
This ignores steric hindrance and reduced metabolic activation. CPCA directly accounts for these factors.
Using the Nitrosamine CPCA approach for NDSRIs, this impurity would likely fall into Category 4. This could justify an AI near 1500 ng/day, pending analytical and computational confirmation.
This approach protects patients while avoiding unnecessary supply disruptions.
9. Role of Analytical Science in Supporting CPCA
Strong analytical data are essential for CPCA credibility. Accurate trace-level quantification supports meaningful risk assessment.
Advanced LC-HRMS and GC-MS methods detect NDSRIs below 10 ppb. Results must align with computational predictions to support category assignment.
ResolveMass Laboratories’ validated workflows ensure analytical accuracy, regulatory alignment, and toxicological defensibility.
10. Future Directions: AI-Enhanced CPCA for NDSRIs
Emerging AI tools will further strengthen CPCA. Machine learning models can refine predictions as new data become available.
Molecular simulations will improve understanding of reactivity and metabolism, while explainable AI will support regulatory review.
Together, these advances will make CPCA more predictive and adaptive.
Conclusion
The Nitrosamine CPCA approach for NDSRIs is the most advanced and globally accepted framework for assessing carcinogenic risk from nitrosamine impurities. It combines scientific rigor, transparency, and patient safety.
As regulatory expectations evolve, accurate analytics and clear documentation remain essential. ResolveMass Laboratories Inc. plays a key role in supporting compliant, evidence-based CPCA implementation.
👉 Contact us for CPCA support and analytical consultation:
https://resolvemass.ca/contact/
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
The CPCA approach is a science-based method used to assess the carcinogenic risk of nitrosamines when direct animal or human data are not available. It estimates risk by comparing the chemical structure and reactivity of an impurity with known nitrosamines. This approach helps derive acceptable intake limits that are protective but not overly conservative. It is widely used for evaluating nitrosamine drug substance-related impurities (NDSRIs).
Under CPCA, NDSRIs are classified into five potency categories based on their molecular structure, electronic properties, and likelihood of metabolic activation. Each category represents a different carcinogenic potency range. This classification allows regulators and manufacturers to predict cancer risk using structurally similar nitrosamines. It ensures consistent and proportionate risk control for diverse NDSRIs.
The CPCA assessment for nitrosamine evaluates its potential to cause cancer by analyzing structural features, DNA-reactive potential, and metabolic behavior. Computational tools and read-across data are used to assign the nitrosamine to a specific potency category. Based on this category, an acceptable intake limit is calculated. This assessment provides a transparent and reproducible scientific justification for regulatory review.
CPCA stands for Carcinogenic Potency Categorization Approach. It is a structured toxicological framework used to group chemicals, especially nitrosamines, based on their predicted carcinogenic strength. The full form reflects its focus on categorizing potency rather than applying a single default limit. This makes risk assessment more accurate and science driven.
The CPCA methodology involves structural analysis, electronic descriptor evaluation, and prediction of metabolic activation pathways. These factors are combined to assign a compound to a defined carcinogenic potency category. Once categorized, acceptable intake limits are derived using established toxicological principles. The methodology emphasizes transparency, reproducibility, and regulatory alignment.
Nitrosamines do not belong to a single CPCA category; instead, they can fall into different categories depending on their structure and reactivity. Simple nitrosamines like NDMA are placed in the highest potency category, while bulky or sterically hindered nitrosamines fall into lower categories. The category is determined through scientific evaluation, not by name alone. This ensures a realistic assessment of actual carcinogenic risk.
Reference
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. (2025, January 10). Determining recommended acceptable intake limits for N‑nitrosamine impurities in pharmaceuticals: Development and application of the carcinogenic potency categorization approach (CPCA). U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/spotlight‑cder‑science/determining‑recommended‑acceptable‑intake‑limits‑n‑nitrosamine‑impurities‑pharmaceuticals
- American Pharmaceutical Review. (2024, May 15). Using the carcinogenic potency categorization approach (CPCA) to classify N‑nitrosamine impurities. American Pharmaceutical Review. https://www.americanpharmaceuticalreview.com/Industry‑Expert‑Hub/613138‑Using‑the‑Carcinogenic‑Potency‑Categorization‑Approach‑CPCA‑to‑Classify‑N‑nitrosamine‑Impurities/


