Peptide Characterization Service in Canada is a critical component in the development, quality control, and regulatory approval of peptide-based therapeutics and research tools. In Canada, a robust network of academic institutions, research centers, and private companies offer comprehensive peptide characterization services. Understanding the methodologies, applications, and considerations involved in peptide characterization is essential for researchers and industry professionals aiming to ensure the efficacy, safety, and compliance of their peptide products.
👉 Explore a detailed overview of available peptide characterization services in Canadato understand how comprehensive analytical support is structured.
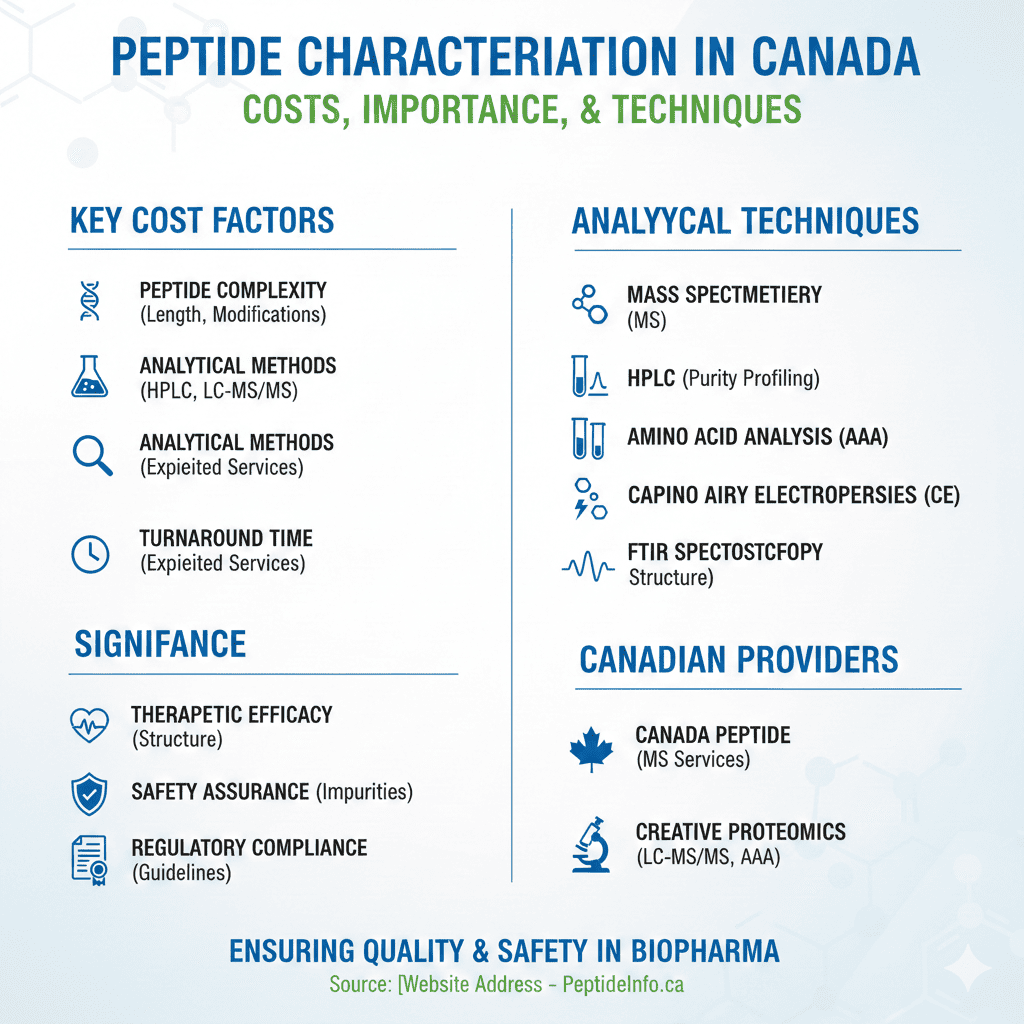
Key Cost Factors Influencing Peptide Characterization Services in Canada
The cost of peptide characterization services in Canada is influenced by several technical and operational variables. One of the most significant factors is peptide complexity, including chain length, molecular weight, and the presence of chemical modifications. Peptides with non-standard amino acids, cyclic structures, or conjugated molecules often require advanced analytical workflows, which increases both labor and instrumentation costs. The purity level required for the final application also impacts pricing, as higher sensitivity demands more sophisticated techniques.
Another major cost driver is the choice of analytical methods. Basic purity testing using HPLC is generally more economical, whereas comprehensive characterization involving LC-MS/MS, amino acid analysis, and structural studies can substantially raise expenses. Turnaround time also affects pricing, with expedited services typically incurring additional charges. Furthermore, projects requiring customized reporting or regulatory-ready documentation may involve higher service fees due to the expertise required.
👉 Learn more about commonly used peptide characterization techniques and how they influence analytical cost and scope.
Watch the full video here:
The Significance of Peptide Characterization Service in Canada
Peptides, composed of amino acids linked by peptide bonds, serve as fundamental biological molecules involved in various physiological processes. Their roles as hormones, neurotransmitters, and antibiotics underscore their importance in therapeutic applications. However, the structural complexity and susceptibility to degradation necessitate thorough characterization to confirm their identity, purity, and stability. Accurate characterization is vital for:
- Ensuring Therapeutic Efficacy: Confirming the correct sequence and structure ensures the peptide performs its intended biological function.
- Safety Assurance: Identifying and quantifying impurities or degradation products that could elicit adverse effects.
- Regulatory Compliance: Meeting stringent guidelines set by health authorities for drug approval and market release.
👉 Gain insight into impurity detection strategies by reviewing peptide impurities characterization approaches used in regulated environments.
Role of Peptide Characterization in Biopharmaceutical Development
Peptide characterization is essential throughout the biopharmaceutical development pipeline, starting from early-stage discovery through to clinical and commercial manufacturing. In the research phase, characterization confirms peptide identity, evaluates stability, and supports formulation optimization. These early analytical insights help researchers identify potential issues before advancing peptides into costly development stages.
As development progresses, peptide characterization ensures manufacturing consistency and product reproducibility. Regulatory agencies require detailed analytical evidence demonstrating that each production batch meets predefined quality standards. Comprehensive characterization minimizes the risk of regulatory setbacks and supports long-term product reliability in therapeutic applications.
👉 See how characterization supports submissions by exploring peptide characterization for IND and NDA regulatory pathways.
Analytical Techniques in Peptide Characterization Service in Canada
Several sophisticated analytical techniques are employed to characterize peptides comprehensively:
1. Mass Spectrometry (MS)
Mass spectrometry is a cornerstone technique in peptide analysis, providing precise molecular weight measurements and structural insights. Two primary ionization methods are prevalent:
- Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization (MALDI): Utilizes a laser to ionize the peptide-matrix mixture, producing predominantly singly charged ions. MALDI is renowned for its high tolerance to contaminants and rapid analysis capabilities. However, it may exhibit limitations in resolving complex peptide mixtures due to ion suppression effects.
- Electrospray Ionization (ESI): Generates multiple charged ions by applying a high voltage to a liquid sample, facilitating the analysis of large biomolecules with high sensitivity. ESI is often coupled with liquid chromatography (LC-MS) to enhance separation and analysis of complex peptide samples.
👉 Discover real-world analytical workflows through peptide characterization techniques and applications used across research and industry.
Advanced Mass Spectrometry Applications for Peptide Analysis
Advanced mass spectrometry techniques extend far beyond basic molecular weight determination. Tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS) enables peptide sequencing by fragmenting ions and analyzing their breakdown patterns. This approach is particularly valuable for confirming amino acid sequences, detecting point mutations, and identifying post-synthetic modifications that may influence biological activity.
High-resolution mass spectrometry further enhances analytical precision by distinguishing peptides with very similar masses. This capability is critical when analyzing complex mixtures or verifying therapeutic-grade peptides. As instrumentation continues to evolve, advanced MS applications remain central to accurate and reliable peptide characterization. 👉 Review an applied case study in peptide characterization of a Lanreotide generic project to see MS in action.
2. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
HPLC is instrumental in assessing peptide purity and separating complex mixtures. By passing the peptide solution through a column packed with a stationary phase, peptides are separated based on their interactions with the column material. Reversed-phase HPLC (RP-HPLC) is particularly effective for peptides, offering high resolution and sensitivity. However, factors such as column selection, mobile phase composition, and gradient conditions must be meticulously optimized to achieve reliable results.
Importance of Purity Profiling in Peptide Characterization
Purity profiling is a fundamental aspect of peptide characterization, particularly for peptides intended for clinical or pharmaceutical use. Even trace impurities can alter biological performance or introduce safety risks. HPLC-based purity analysis allows precise detection and quantification of impurities, ensuring peptides meet strict quality standards.
In addition to identifying synthetic by-products, purity profiling helps monitor degradation over time. This information is critical for determining shelf life, storage conditions, and formulation stability. When combined with complementary analytical techniques, purity data provides a comprehensive quality assessment of peptide products.
3. Amino Acid Analysis (AAA)
AAA provides quantitative data on the amino acid composition of peptides, essential for confirming sequence integrity and detecting modifications. Traditional methods involve hydrolyzing the peptide into constituent amino acids, which are then derivatized and analyzed, often by LC-MS/MS. Recent advancements have improved specificity and sensitivity, though challenges remain in handling complex biological matrices and achieving complete hydrolysis without degradation.
4. Capillary Electrophoresis (CE)
CE separates peptides based on their charge-to-mass ratio under an electric field within a capillary tube. It offers high efficiency and resolution, complementing HPLC in peptide mapping and purity assessments. However, CE’s sensitivity can be influenced by the peptide’s physicochemical properties and the composition of the running buffer.
5. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
FTIR spectroscopy is employed to analyze the secondary structure of peptides by measuring the absorption of infrared radiation at specific wavelengths corresponding to molecular vibrations. This technique is valuable for detecting conformational changes and assessing structural stability. However, interpreting FTIR spectra can be complex due to overlapping absorption bands and the influence of the peptide’s environment.
Challenges and Considerations in Peptide Characterization Service in Canada
While the aforementioned techniques provide robust tools for peptide analysis, several challenges must be addressed to ensure accurate characterization:
- Sample Preparation: Proper sample handling and preparation are crucial to prevent degradation or contamination that could skew results. Techniques such as lyophilization and the use of stabilizing agents can enhance sample stability.
- Method Validation: Analytical methods must be validated to confirm their accuracy, precision, specificity, and sensitivity. This involves rigorous testing using standard peptides and adherence to regulatory guidelines.
- Data Interpretation: Complex data sets require sophisticated software and expertise to interpret accurately. Misinterpretation can lead to incorrect conclusions about peptide identity or purity.
- Regulatory Compliance: Characterization methods must align with regulatory standards, necessitating thorough documentation and quality control measures.
👉 Understand global expectations by reviewing FDA requirements for peptide characterization and how they influence analytical strategies.
Regulatory Landscape for Peptide Characterization in Canada
Regulatory requirements significantly influence peptide characterization practices in Canada. Health Canada mandates detailed analytical documentation demonstrating peptide identity, purity, stability, and consistency. This includes validated methods, reproducible data, and thorough reporting to support product quality and safety claims.
Additionally, alignment with international regulatory frameworks, such as ICH guidelines, is often necessary for peptides intended for global markets. Canadian service providers typically design characterization workflows that meet both domestic and international expectations. This regulatory alignment helps streamline approvals and supports broader commercial deployment.
Peptide Characterization Services in Canada
Canada hosts a variety of institutions and companies offering specialized peptide characterization services. These organizations leverage advanced technologies and expertise to support both academic research and industrial applications.
Canada Peptide
Canada Peptide provides comprehensive mass spectrometry services, including peptide characterization, protein identification, and structural elucidation. Their state-of-the-art facilities and experienced team ensure high-quality analytical support for research and development projects.
Creative Proteomics
Creative Proteomics offers a range of analytical services, including amino acid analysis and protein primary structure characterization using mass spectrometry. Their expertise in LC-MS/MS techniques enables precise quantification and analysis of peptides and proteins.
Future Perspectives in Peptide Characterization Service in Canada
The field of peptide characterization is continually evolving, driven by advancements in analytical technologies and the growing complexity.
REFERENCES
- Hoofnagle AN, Whiteaker JR, Carr SA, Kuhn E, Liu T, Massoni SA, Thomas SN, Townsend RR, Zimmerman LJ, Boja E, Chen J. Recommendations for the generation, quantification, storage, and handling of peptides used for mass spectrometry–based assays. Clinical chemistry. 2016 Jan 1;62(1):48-69.
- Boutin JA, Tartar AL, Van Dorsselaer A, Vaudry H. General lack of structural characterization of chemically synthesized long peptides. Protein Science. 2019 May;28(5):857-67.
- Deutzmann R. Structural characterization of proteins and peptides. Molecular Diagnosis of Infectious Diseases. 2004:269-97.
- Miller RJ, Howlett JG, Fine NM. A novel approach to medical management of heart failure with reduced ejection fraction. Canadian Journal of Cardiology. 2021 Apr 1;37(4):632-43.
End-to-End Biomarker Bioanalytical Services Offered by a CRO: Capabilities and Expectations
Introduction Biomarker bioanalytical services CRO partnerships have become indispensable in modern pharmaceutical development, providing the…
Regulatory-Compliant Biomarker Bioanalytical Services for FDA and Health Canada Submissions
Introduction Biomarker bioanalytical services for FDA and Health Canada submissions require rigorous compliance with regulatory…
Outsourced Medicinal Chemistry for Startups: Cost, Speed, and Scientific Advantages
🔍 Summary (Key Takeaways) Outsourced medicinal chemistry for startups offers a strategic advantage by minimizing…
Why Early-Stage Biotech Companies Outsource Chemistry Services to Drug Discovery CROs
Introduction Early-stage biotech companies are increasingly adopting Outsourced Chemistry Services for Biotech to stay competitive…
Why Early-Stage Biotech Companies Outsource Bioanalytical Services to CROs
Introduction Outsourced bioanalytical services play a critical role in helping early-stage biotech companies overcome scientific,…
7 Questions to Ask Before Collaborating with a Full Service Drug Discovery CRO
Summary Before partnering with a Full Service Drug Discovery CRO, the following key questions can…