Introduction
PLGA nanoparticles synthesis has revolutionized drug delivery systems in pharmaceutical research and clinical applications, offering biodegradable, biocompatible polymeric carriers that enable controlled release of therapeutic agents and making them invaluable for modern medicine. At ResolveMass Laboratories Inc., we have supported hundreds of researchers and pharmaceutical companies in developing robust PLGA nanoparticles synthesis protocols that meet regulatory standards and achieve precise drug delivery objectives, providing this comprehensive guide that walks you through the entire process from material selection to quality control with practical insights gained from years of hands-on laboratory experience. Whether you’re a graduate student beginning your nanotechnology research or a pharmaceutical scientist scaling up formulations, this step-by-step approach will help you understand the critical parameters that determine nanoparticle quality and performance.
PLGA (poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid)) nanoparticles are widely used in drug delivery due to their biocompatibility, biodegradability, and controlled-release properties. The synthesis of PLGA nanoparticles is a crucial step in pharmaceutical and biomedical research, ensuring efficient encapsulation and targeted delivery of therapeutic agents. This comprehensive guide walks beginners through the step-by-step process of PLGA nanoparticle synthesis, highlighting key considerations, challenges, and applications.
Summary
- PLGA nanoparticles synthesis is a process that creates biodegradable drug delivery systems using poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid)
- The synthesis involves four main methods: emulsion-solvent evaporation, nanoprecipitation, double emulsion, and microfluidics
- Critical parameters include polymer concentration (1-10% w/v), surfactant selection, stirring speed (500-15,000 RPM), and temperature control
- Size control ranges from 50nm to 500nm depending on application requirements
- Quality control requires dynamic light scattering (DLS), zeta potential measurement, and encapsulation efficiency testing
- ResolveMass Laboratories provides comprehensive analytical services for nanoparticle characterization and development support
1: What Are PLGA Nanoparticles?
PLGA nanoparticles are submicron-sized carriers composed of poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid), a copolymer approved by the FDA for medical applications. These nanoparticles can encapsulate drugs, proteins, or other bioactive molecules, providing sustained release and improved bioavailability.
PLGA is synthesized from lactic acid and glycolic acid monomers, with varying copolymer ratios affecting degradation rates and release kinetics. A higher glycolic acid content accelerates degradation, making PLGA adaptable for different therapeutic needs.
PLGA nanoparticles are spherical polymeric structures ranging from 50 to 500 nanometers in diameter, composed of poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid). They are FDA-approved biodegradable polymers that degrade into non-toxic lactic acid and glycolic acid, which the body naturally metabolizes through the Krebs cycle.
Key Characteristics:
- Biodegradability: Complete degradation within weeks to months
- Biocompatibility: Non-toxic degradation products
- Versatility: Can encapsulate hydrophobic and hydrophilic drugs
- Controlled release: Tunable release profiles from days to months
- Surface modifiability: Easy functionalization for targeted delivery
Advantages of PLGA Nanoparticles
- Biodegradability: Degrades into non-toxic lactic and glycolic acid byproducts.
- Biocompatibility: Safe for use in humans.
- Controlled Drug Release: Enables sustained and targeted drug delivery.
- Versatile Applications: Used in cancer therapy, vaccine delivery, and gene therapy.
- Improved Stability: Protects encapsulated drugs from degradation.
Methods of PLGA Nanoparticle Synthesis
PLGA nanoparticles can be synthesized using several techniques, each with specific advantages and limitations. The most commonly used methods include:
1. Single Emulsion-Solvent Evaporation Method
This method is widely used for hydrophobic drug encapsulation.
Steps:
- Dissolve PLGA in an organic solvent (e.g., dichloromethane or acetone).
- Add the drug to the PLGA solution.
- Emulsify in an aqueous solution containing a surfactant (e.g., PVA) using ultrasonication or high-speed homogenization.
- Remove the organic solvent through evaporation under reduced pressure.
- Collect nanoparticles by centrifugation and wash to remove excess surfactant.
- Lyophilize for long-term storage.
Advantages:
- Simple and reproducible.
- Effective for hydrophobic drugs.
Limitations:
- Risk of organic solvent residues.
- Poor efficiency for hydrophilic drugs.
2. Double Emulsion-Solvent Evaporation Method
Ideal for encapsulating hydrophilic drugs, proteins, and peptides.
Steps:
- Dissolve PLGA in an organic solvent.
- Dissolve the hydrophilic drug in water and emulsify into the PLGA solution to form a water-in-oil (W/O) emulsion.
- Emulsify the W/O emulsion in an aqueous surfactant solution to form a water-in-oil-in-water (W/O/W) emulsion.
- Remove the organic solvent via evaporation.
- Collect and purify the nanoparticles.
Advantages:
- Suitable for hydrophilic molecules.
- Protects bioactive molecules from degradation.
Limitations:
- Complex process.
- Possible loss of drug during emulsification.
3. Nanoprecipitation (Solvent Displacement) Method
A straightforward method for producing nanoparticles without harsh processing conditions.
Steps:
- Dissolve PLGA and drug in a water-miscible organic solvent (e.g., acetone).
- Add the solution dropwise to an aqueous surfactant solution under constant stirring.
- Allow nanoparticles to precipitate as the solvent diffuses.
- Collect and purify the nanoparticles.
Advantages:
- Simple and fast.
- No need for high-energy emulsification.
Limitations:
- Limited to hydrophobic drugs.
- Requires careful solvent selection.
4. Spray Drying Method
An industrial-scale method for large-scale nanoparticle production.
Steps:
- Dissolve PLGA and drug in an organic solvent.
- Atomize the solution into a hot drying chamber using a spray nozzle.
- Rapid solvent evaporation results in solidified nanoparticles.
- Collect nanoparticles using a cyclone separator.
Advantages:
- Suitable for large-scale production.
- High drug loading efficiency.
Limitations:
- Requires specialized equipment.
- High temperatures may degrade heat-sensitive drugs.
2: Understanding the Fundamentals of PLGA Nanoparticles Synthesis
PLGA nanoparticles synthesis relies on creating polymer-drug solutions and converting them into stable nanoparticle suspensions through controlled precipitation. The synthesis success depends on understanding polymer chemistry, thermodynamics, and colloidal stability principles.
Critical Material Selection
| Material Component | Purpose | Typical Specifications |
|---|---|---|
| PLGA Polymer | Core matrix material | Molecular weight: 5-100 kDa, LA:GA ratio: 50:50 to 85:15 |
| Organic Solvent | Polymer dissolution | Dichloromethane, ethyl acetate, or acetone |
| Surfactant/Stabilizer | Prevents aggregation | PVA (0.5-5% w/v), Poloxamer, or TPGS |
| Aqueous Phase | Dispersion medium | Deionized water or buffer (pH 5-8) |
Polymer Selection Guidelines:
- 50:50 LA:GA ratio: Faster degradation (1-2 months), higher drug release rates
- 75:25 LA:GA ratio: Moderate degradation (4-5 months), balanced release
- 85:15 LA:GA ratio: Slower degradation (5-6 months), extended release
Higher molecular weight PLGA creates larger particles with slower degradation, while lower molecular weight produces smaller particles with faster drug release.
Step-by-Step PLGA Nanoparticles Synthesis Methods
Method 1: Single Emulsion-Solvent Evaporation (O/W)
This is the most common method for PLGA nanoparticles synthesis with hydrophobic drugs. The method creates stable oil-in-water emulsions that form nanoparticles as the organic solvent evaporates.
Step-by-Step Process:
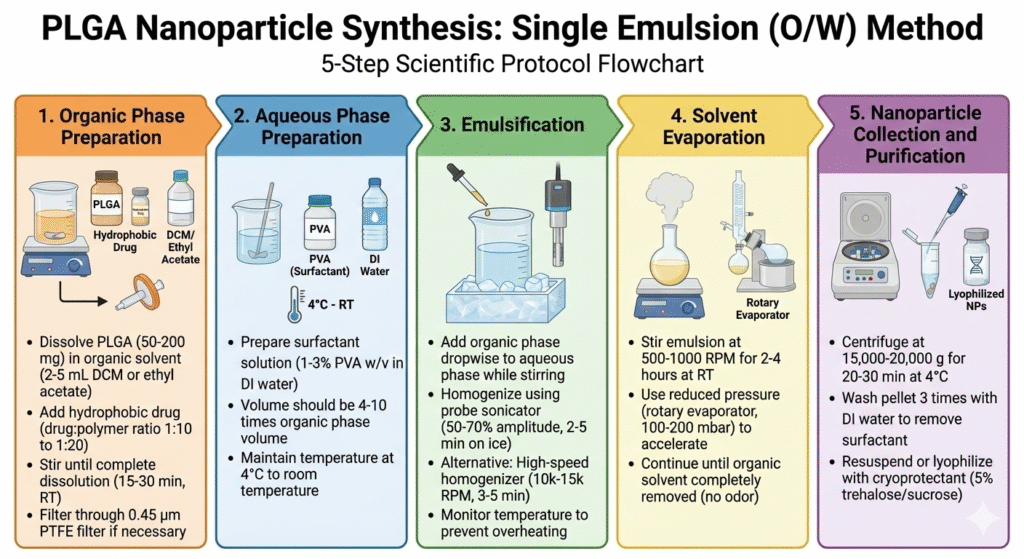
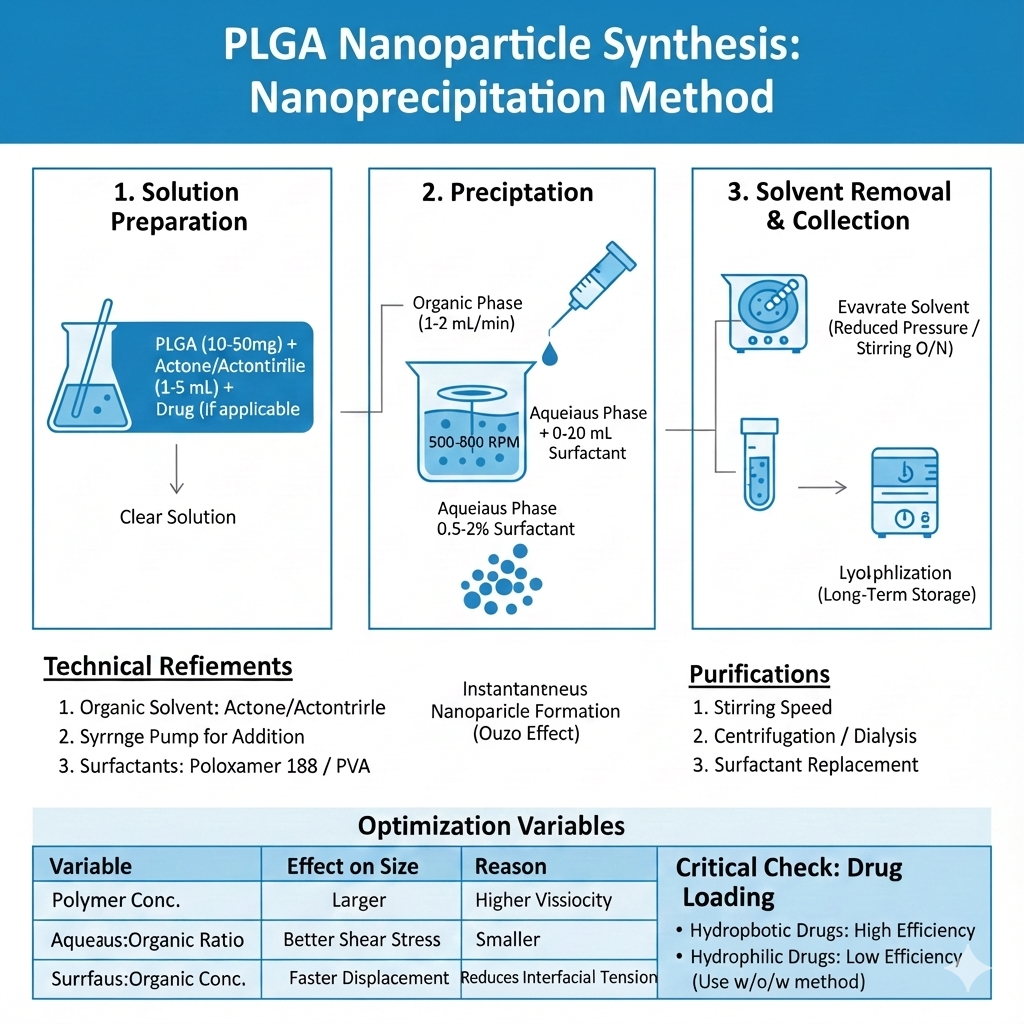
Method 2: Nanoprecipitation (Solvent Displacement)
Nanoprecipitation is ideal for rapid PLGA nanoparticles synthesis and produces smaller, more uniform particles. This method works through rapid desolvation when water-miscible organic solvent containing PLGA encounters aqueous phase.
Step-by-Step Process:
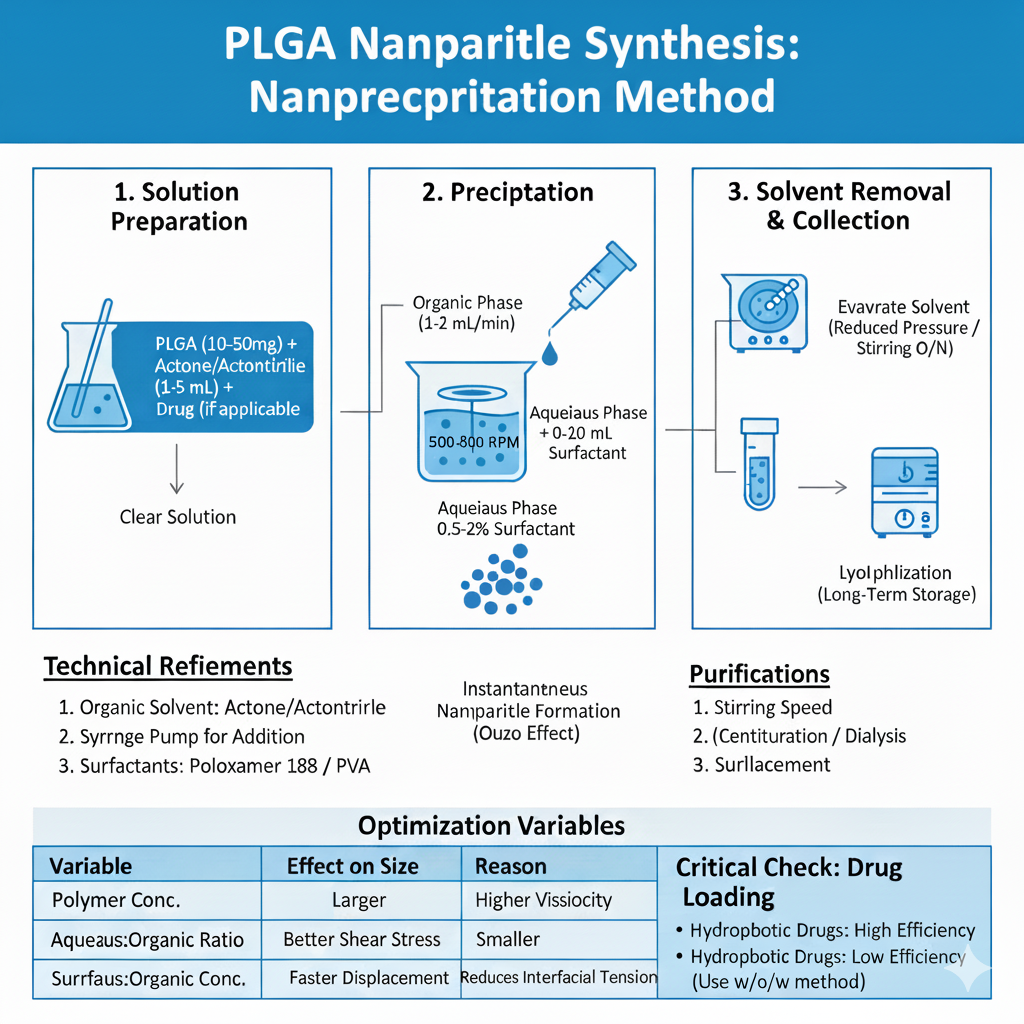
Advantages: Simple equipment, rapid formation, narrow size distribution, high reproducibility
Method 3: Double Emulsion (W/O/W)
For PLGA nanoparticles synthesis with hydrophilic drugs, proteins, or nucleic acids, double emulsion provides superior encapsulation efficiency.
Step-by-Step Process:
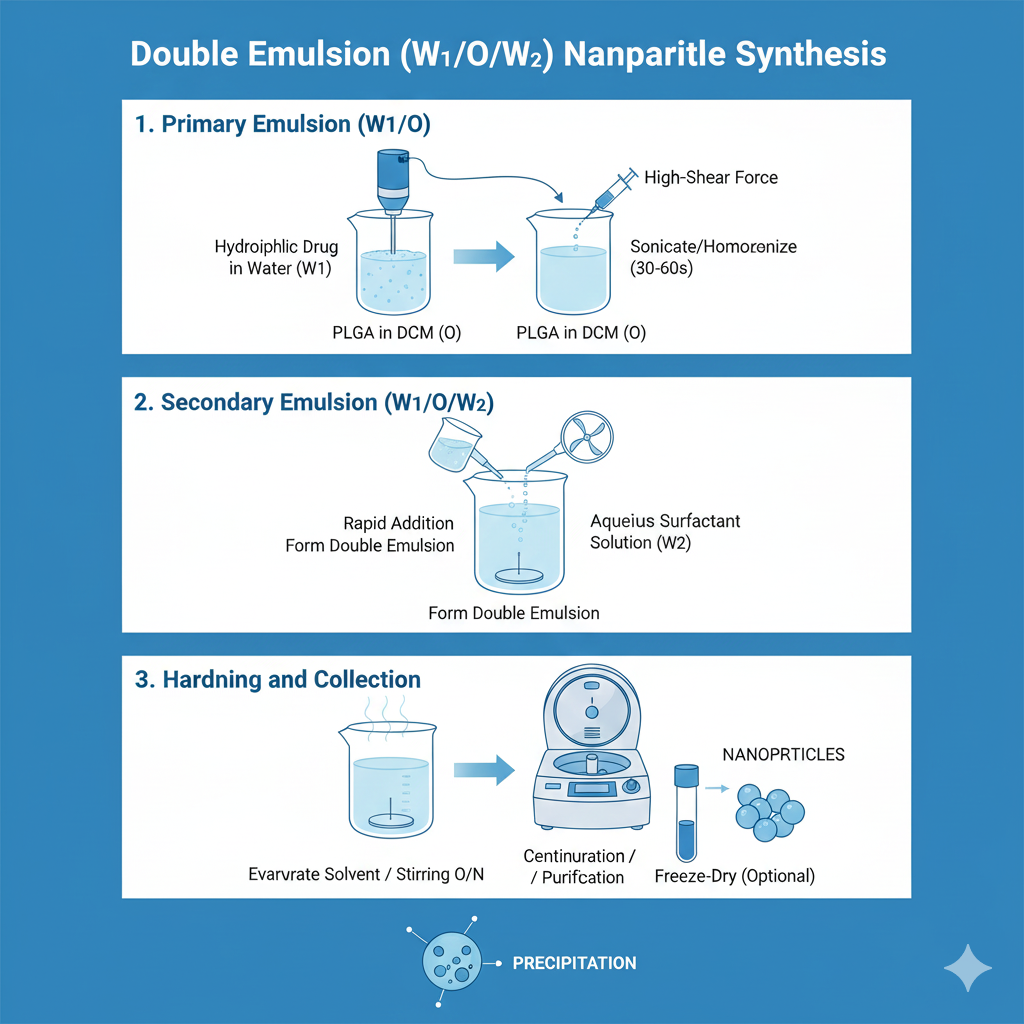
Method 4: Microfluidics-Based Synthesis
Microfluidic PLGA nanoparticles synthesis offers precise control over particle size and high batch-to-batch reproducibility, ideal for clinical translation.
Key Features:
- Continuous flow synthesis
- Precise control of flow rate ratios (typically 1:5 to 1:10 organic:aqueous)
- Monodisperse particle populations
- Scalable for GMP manufacturing
3: Critical Parameters Affecting PLGA Nanoparticles Synthesis
Size Control Parameters
| Parameter | Effect on Particle Size | Optimal Range |
|---|---|---|
| PLGA Concentration | Higher concentration → Larger particles | 1-10% w/v |
| Surfactant Concentration | Higher concentration → Smaller particles | 0.5-5% w/v |
| Homogenization Speed | Higher speed → Smaller particles | 10,000-20,000 RPM |
| Organic:Aqueous Ratio | Higher ratio → Larger particles | 1:5 to 1:10 |
| Molecular Weight | Higher MW → Larger particles | 5-100 kDa |
Drug Loading and Encapsulation
- Theoretical drug loading: (Mass of drug / Mass of PLGA + drug) × 100%
- Actual drug loading: Determined by HPLC or UV-Vis after nanoparticle dissolution
- Encapsulation efficiency: (Actual drug loading / Theoretical drug loading) × 100%
Typical encapsulation efficiencies range from 40% to 95% depending on drug properties, with hydrophobic drugs achieving higher efficiency in single emulsion methods.
Quality Control and Characterization
At ResolveMass Laboratories Inc., we emphasize rigorous characterization to ensure reproducible PLGA nanoparticles synthesis. Every batch should undergo comprehensive analysis.
Essential Characterization Techniques:
1. Size and Size Distribution
- Method: Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS)
- Parameters: Z-average diameter, polydispersity index (PDI)
- Target: PDI < 0.3 for homogeneous populations
2. Surface Charge
- Method: Zeta potential measurement
- Typical values: -20 to -40 mV for stable suspensions
- Importance: Predicts storage stability and in vivo behavior
3. Morphology
- Methods: Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM), Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
- Purpose: Confirms spherical shape, surface characteristics, and absence of aggregation
4. Drug Loading and Encapsulation Efficiency
- Method: HPLC, UV-Vis spectroscopy, or LC-MS
- Process: Dissolve nanoparticles in organic solvent, quantify drug content
- Critical for dose calculations
5. In Vitro Release Studies
- Method: Dialysis in physiological buffer (pH 7.4, 37°C)
- Duration: 1-30 days depending on formulation
- Analysis: Sample at intervals and quantify drug release
4: Troubleshooting Common Synthesis Challenges
Problem: Large Particle Size (>500 nm)
Solutions:
- Increase homogenization speed or duration
- Decrease PLGA concentration
- Increase surfactant concentration
- Use lower molecular weight PLGA
- Ensure complete polymer dissolution before emulsification
Problem: High PDI (>0.3)
Solutions:
- Optimize homogenization parameters for uniform energy input
- Filter organic phase before emulsification
- Control temperature more precisely
- Use more efficient surfactants (Pluronic F-127, TPGS)
Problem: Low Encapsulation Efficiency
Solutions:
- Optimize drug:polymer ratio (typically 1:10 to 1:20)
- For hydrophilic drugs, use double emulsion or modify drug solubility
- Increase organic phase viscosity (higher PLGA concentration)
- Work at lower temperatures to reduce drug partitioning into aqueous phase
- Add salt to aqueous phase to reduce drug solubility
Problem: Nanoparticle Aggregation
Solutions:
- Increase surfactant concentration
- Add cryoprotectants before lyophilization (trehalose, sucrose, mannitol at 5-10% w/v)
- Optimize zeta potential to ±30 mV range
- Store as suspension at 4°C rather than lyophilized powder
- Use gentle resuspension techniques (avoid vortexing)
5: Scale-Up Considerations for PLGA Nanoparticles Synthesis
Translating laboratory-scale PLGA nanoparticles synthesis to pilot or manufacturing scale requires careful planning and process validation.
Key Scale-Up Strategies:
- Maintain Geometric Similarity: Keep vessel dimensions, impeller types, and mixing patterns consistent
- Control Energy Input: Calculate and maintain constant power per unit volume (P/V)
- Temperature Control: Install jacketed vessels with precise temperature regulation
- Process Analytical Technology (PAT): Implement real-time monitoring of particle size
- Aseptic Processing: For clinical applications, establish clean room protocols and sterilization methods
GMP Compliance:
- Document all critical process parameters (CPPs) and critical quality attributes (CQAs)
- Validate analytical methods for drug content and particle characterization
- Establish stability protocols (typically 3-12 months at 4°C, 25°C, and accelerated conditions)
- Implement change control procedures
6: Factors Affecting PLGA Nanoparticle Properties
Several parameters influence the size, drug encapsulation efficiency, and release profile of PLGA nanoparticles:
- Polymer composition: PLGA ratio determines degradation rate.
- Solvent selection: Affects nanoparticle size and drug loading.
- Surfactant concentration: Controls nanoparticle stability and dispersion.
- Emulsification parameters: Ultrasonication and homogenization affect particle uniformity.
- Solvent removal rate: Impacts drug retention and nanoparticle formation.
Applications of PLGA Nanoparticles
PLGA nanoparticles have vast applications in pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, and materials science.
1. Drug Delivery
- Sustained release formulations for chemotherapy.
- Targeted delivery in cancer therapy .
- Oral and transdermal drug carriers.
2. Vaccine Delivery
- Antigen-loaded PLGA nanoparticles enhance immune response.
- Used for COVID-19 and tuberculosis vaccines.
3. Gene Therapy
- PLGA nanoparticles facilitate gene silencing and CRISPR-based treatments
4. Biomedical Imaging
- Used as contrast agents in MRI and fluorescence imaging.
Future Prospects
Advancements in PLGA nanoparticle synthesis aim to improve drug loading efficiency, targeting capabilities, and bioavailability. Innovations such as surface modification, stimuli-responsive nanoparticles, and hybrid nanocarriers are shaping the future of nanomedicine.
Reference
- Han Z, Jiang X. Microfluidic synthesis of functional nanoparticles. Nanotechnology and Microfluidics. 2020 Mar 9:319-45.
- Avilez HR, Casadiego DC, Avila AV, Perez OP, Almodovar J. Production of chitosan coatings on metal and ceramic biomaterials. InChitosan Based Biomaterials Volume 1 2017 Jan 1 (pp. 255-293). Woodhead Publishing.
- Ansar R. Synthesis of Polymer Coated Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Drug Release by Applying Alternating Magnetic Field (Doctoral dissertation, School of Chemical and Material Engineering SCME, NUST).
How to Choose the Right CDMO for Generic Drug Development in Canada
Introduction: Choosing the right CDMO for generic drug development in Canada is one of the…
Why Early Drug Development Programs Fail Without Strong Bioanalytical Strategy
Introduction: A well-planned Bioanalytical Strategy Drug Development framework is critical for the success of early…
From Discovery to First-in-Human: The Role of Bioanalytical CROs
Introduction: The journey from drug discovery to human clinical trials is complex, expensive, and highly…
Scale-Up Synthesis of Peptide-Oligonucleotide Conjugates
Introduction The Scale Up of Peptide Oligonucleotide Conjugates is an essential step in moving nucleic…
CMC Support for Peptide-Oligonucleotide Conjugates (POCs)
Introduction CMC Services for Peptide Oligonucleotide Conjugates are essential for advancing peptide-oligonucleotide therapeutics from early…
Bioanalytical CRO Partnerships That Support Key Value Inflection Points
Introduction: A Bioanalytical CRO Partnership is often the backbone of successful drug development programs. Pharmaceutical…