
Introduction:
PLGA polymer characterization for generics represents one of the most challenging aspects of developing complex injectable drug products, yet innovator companies typically disclose only minimal characterization data in their regulatory filings. This knowledge gap creates substantial barriers for generic manufacturers attempting to demonstrate pharmaceutical equivalence and bioequivalence.
Poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) polymers serve as the backbone for numerous controlled-release formulations, including injectable microspheres, implants, and nanoparticles used in blockbuster drugs like Lupron Depot, Risperdal Consta, and Sandostatin LAR. The complexity of these polymer matrices means that even slight variations in polymer properties can dramatically affect drug release profiles, stability, and ultimately, therapeutic outcomes.
Real-world formulation challenges encountered during PLGA microsphere development are illustrated in this detailed PLGA microsphere reverse-engineering case study:
https://resolvemass.ca/plga-microsphere-case-study/
Generic manufacturers face a significant disadvantage: while innovators have spent years optimizing their PLGA polymer specifications through iterative development, generic companies must reverse-engineer these specifications with limited publicly available information. This article addresses this information asymmetry by examining what innovators don’t disclose and how generic developers can bridge these knowledge gaps through comprehensive analytical characterization.
Summary
PLGA polymer characterization for generics requires comprehensive analytical strategies that innovator companies rarely disclose in their regulatory submissions. This article reveals critical characterization gaps and provides actionable guidance for generic pharmaceutical manufacturers developing biosimilar and complex injectable formulations.
Key Takeaways:
- Critical quality attributes (CQAs) for PLGA polymers often remain undisclosed in innovator patents
- Molecular weight distribution, end-group composition, and residual monomers directly impact drug release kinetics
- Advanced analytical techniques beyond USP methods are essential for establishing bioequivalence
- Regulatory agencies increasingly demand comprehensive polymer characterization data for generic approvals
- ResolveMass Laboratories offers specialized testing protocols addressing characterization gaps
1: Understanding PLGA Polymers in Generic Drug Development
PLGA polymers are biodegradable copolymers composed of lactic acid and glycolic acid monomers that degrade through hydrolysis into metabolically safe compounds. Their degradation rate and drug release characteristics depend on numerous polymer properties that innovators carefully control but rarely fully disclose.
Practical formulation considerations such as polymer solubility, solvent compatibility, and dissolution behavior are discussed in detail in this guide on dissolving PLGA in solvents:
https://resolvemass.ca/dissolving-plga-in-solvents/
Critical Polymer Attributes Affecting Generic Equivalence
The pharmaceutical performance of PLGA-based formulations depends on several interdependent polymer characteristics:
Molecular Weight and Distribution:
- Average molecular weight (Mn, Mw, Mz)
- Polydispersity index (PDI)
- Molecular weight distribution profiles
- Impact on mechanical properties and degradation kinetics
Compositional Factors:
- Lactide-to-glycolide ratio (LA:GA ratio)
- Stereochemistry (D,L-lactide vs. L-lactide content)
- Monomer sequence distribution
- Block vs. random copolymer architecture
Structural Characteristics:
- End-group chemistry (carboxyl vs. ester terminated)
- Branching and cross-linking degree
- Crystallinity and glass transition temperature
- Residual monomer and oligomer content
Polymer attributes such as end-group chemistry and residual monomers also play a critical role in long-term formulation stability, as outlined in this technical resource on PLGA formulation stability:
https://resolvemass.ca/plga-formulation-stability/
Each of these parameters influences drug encapsulation efficiency, release kinetics, degradation rate, and ultimately, the bioequivalence potential of generic formulations.
2: What Innovators Disclose vs. What They Don’t
Publicly Available Information
Innovator regulatory submissions typically include:
- Basic lactide-to-glycolide ratio specifications
- General molecular weight range (often very broad)
- Manufacturing process descriptions (heavily redacted)
- Final product specifications and release testing methods
The Critical Information Gap
What innovators rarely disclose includes detailed specifications for PLGA polymer characterization for generics, leaving manufacturers to determine these parameters independently:
| Disclosed Information | Undisclosed Critical Details |
|---|---|
| LA:GA ratio (e.g., 50:50) | Exact ratio tolerance limits (±2%, ±5%?) |
| Molecular weight range | Precise Mn, Mw targets and acceptance criteria |
| “Biodegradable polymer” | End-group composition and ratio specifications |
| General manufacturing process | Catalyst type, residual levels, purification methods |
| Standard USP testing | Advanced characterization methods used for batch release |
| Degradation behavior | Specific degradation pathway and intermediate products |
This information asymmetry creates substantial development challenges for generic manufacturers pursuing abbreviated new drug applications (ANDAs) or 505(b)(2) pathways.
3: Advanced Analytical Techniques for PLGA Polymer Characterization
PLGA polymer characterization for generics demands analytical methods that go beyond standard compendial testing to fully understand polymer structure-function relationships. ResolveMass Laboratories employs comprehensive testing protocols addressing these characterization needs.
Molecular Weight Characterization
Gel Permeation Chromatography (GPC/SEC):
- Multi-detector systems (RI, UV, MALS, Viscometry)
- Absolute molecular weight determination
- Molecular weight distribution profiling
- Detection of high molecular weight aggregates
- Low molecular weight oligomer quantification
Critical Parameters Measured:
- Number-average molecular weight (Mn)
- Weight-average molecular weight (Mw)
- Z-average molecular weight (Mz)
- Polydispersity index (Mw/Mn)
- Mark-Houwink parameters
Compositional Analysis
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy:
- Precise LA:GA ratio determination
- Monomer sequence distribution analysis
- End-group identification and quantification
- Stereochemistry characterization (D,L vs. L-lactide)
- Residual monomer detection at trace levels
Proton and Carbon-13 NMR provide quantitative data on:
- Exact copolymer composition (±0.5% accuracy)
- Block length distribution in the polymer chain
- Terminal group chemistry (hydroxyl, carboxyl, ester)
- Impurities and degradation products
Thermal and Physical Property Analysis
Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) and Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA):
- Glass transition temperature (Tg) determination
- Crystallinity assessment
- Thermal degradation profiles
- Residual solvent quantification
- Moisture content analysis
Dynamic Mechanical Analysis (DMA):
- Viscoelastic property characterization
- Mechanical strength assessment
- Temperature-dependent behavior
- Long-term stability prediction
Chemical Purity and Impurity Profiling
PLGA polymer characterization for generics must include comprehensive impurity analysis:
Residual Monomer Quantification:
- Lactic acid and glycolic acid residuals
- Detection limits: <0.01% by HPLC or GC-MS
- Impact on degradation kinetics and stability
Residual Catalyst Analysis:
- Tin, zinc, or aluminum catalyst residues
- ICP-MS analysis for trace metal detection
- Regulatory compliance with ICH Q3D guidelines
Oligomer Profiling:
- Low molecular weight species characterization
- Potential impact on biocompatibility
- Correlation with manufacturing process control
In addition to PLGA, alternative biodegradable polymers such as polycaprolactone (PCL) are increasingly evaluated for long-acting injectables. Supplier and polymer selection considerations are discussed here:
https://resolvemass.ca/pcl-excipient-supplier/
4: Establishing Polymer Specifications for Generic Development
Generic developers must establish polymer specifications that ensure pharmaceutical equivalence without access to innovator’s internal specifications. This requires a systematic approach combining analytical characterization with formulation development.
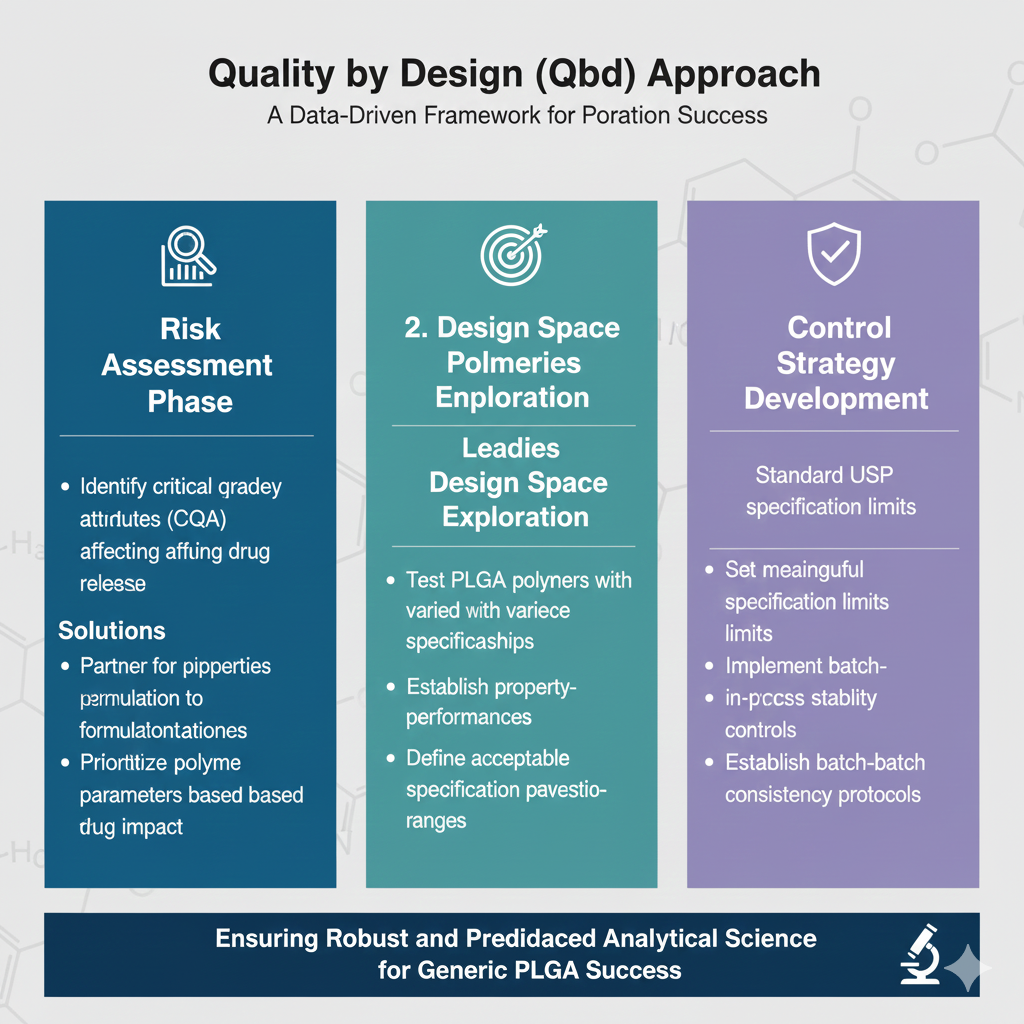
Quality by Design (QbD) Approach
1. Risk Assessment Phase:
- Identify critical quality attributes (CQAs) affecting drug release
- Link polymer properties to formulation performance
- Prioritize characterization parameters based on impact
2. Design Space Exploration:
- Test PLGA polymers with varied specifications
- Establish property-performance relationships
- Define acceptable specification ranges
3. Control Strategy Development:
- Set meaningful specification limits
- Implement in-process controls
- Establish batch-to-batch consistency protocols
Comparative Analysis Strategy
For PLGA polymer characterization for generics, comparative studies against reference listed drug (RLD) batches provide critical insights:
Recommended Approach:
- Extract and isolate PLGA polymer from multiple RLD batches
- Perform comprehensive analytical characterization
- Identify batch-to-batch variability in polymer properties
- Establish target specifications based on RLD polymer characteristics
- Validate that generic polymer falls within RLD variability range
This comparative approach demonstrates pharmaceutical equivalence to regulatory agencies by showing that the generic product’s polymer properties match those of the innovator product.
Establishing Q1/Q2 equivalence at the polymer level is a regulatory cornerstone for complex generics and is discussed in detail in this Q1/Q2 polymer equivalence assessment guide:
https://resolvemass.ca/q1-q2-polymer-equivalence-assessment/
5: Regulatory Considerations and Requirements
FDA Expectations for Complex Generics
The FDA’s guidance on complex drug products explicitly states that comprehensive polymer characterization is essential for demonstrating sameness in PLGA-based formulations. Regulatory submissions must include:
Required Polymer Characterization Data:
- Complete molecular weight characterization (Mn, Mw, Mz, PDI)
- Precise LA:GA ratio with tight specification limits
- End-group composition and quantification
- Residual monomer and catalyst levels
- Comparative data vs. reference product polymer
In Vitro Release Testing (IVRT):
- Drug release kinetics in physiologically relevant media
- Multiple time points covering entire release duration
- Statistical comparison to reference product
- Correlation between polymer properties and release profiles
Global Regulatory Landscape
Different regulatory agencies have varying expectations for PLGA polymer characterization for generics:
EMA (European Medicines Agency):
- Requires detailed polymer specifications
- Emphasizes quality-by-design approaches
- Demands comprehensive comparative studies
Depot-based long-acting injectables require additional polymer and release-control considerations, which are discussed in this guide on PLGA depot formulation development:
https://resolvemass.ca/plga-depot-formulation/
PMDA (Japan):
- Strict requirements for polymer identity and purity
- Detailed impurity profiling expectations
- Stability study requirements for polymer degradation
Health Canada:
- Aligned with FDA expectations
- Additional focus on biocompatibility data
- Process validation requirements
6: Common Challenges in Generic PLGA Formulation Development
Challenge 1: Polymer Sourcing and Variability
Generic manufacturers face significant challenges in sourcing PLGA polymers that match innovator specifications because polymer suppliers typically offer standard grades with broad specification ranges. Custom polymer synthesis may be required, adding time and cost to development.
Solutions:
- Partner with specialized polymer manufacturers for custom synthesis
- Establish long-term supply agreements with multiple vendors
- Implement rigorous incoming polymer testing protocols
- Develop robust formulation designs less sensitive to polymer variability
Supplier selection and specification control for commonly used grades such as PLGA 50:50 are explored in this technical overview:
https://resolvemass.ca/plga-5050-supplier/
Challenge 2: Incomplete Characterization Leading to Bioequivalence Failures
Inadequate PLGA polymer characterization for generics has led to numerous bioequivalence study failures where formulations appeared equivalent in vitro but demonstrated different pharmacokinetic profiles in vivo.
Root Causes:
- Subtle differences in molecular weight distribution
- Undetected variations in end-group composition
- Residual impurities affecting degradation pathways
- Inadequate understanding of polymer degradation kinetics
Prevention Strategies:
- Comprehensive polymer characterization before formulation development
- Multiple pilot batches with varied polymer specifications
- Accelerated stability studies to understand degradation behavior
- Predictive modeling of in vivo performance
Strategies to improve drug loading efficiency and polymer–drug compatibility are discussed in this resource on PLGA drug loading optimization:
https://resolvemass.ca/plga-drug-loading/
Challenge 3: Analytical Method Limitations
Standard USP methods often lack the sensitivity and specificity needed for complete polymer characterization.
Advanced Analytical Solutions:
- Multi-dimensional chromatography techniques
- High-resolution mass spectrometry
- Advanced NMR methods (2D NMR, solid-state NMR)
- Coupled techniques (LC-MS, GC-MS, GPC-MALS-Viscometry)

7: Best Practices for PLGA Polymer Characterization
Based on decades of experience supporting generic pharmaceutical development, ResolveMass Laboratories recommends the following best practices:
1. Comprehensive Characterization Protocol
Implement a multi-technique approach for PLGA polymer characterization for generics:
- Molecular weight analysis: GPC-MALS-Viscometry
- Composition analysis: ¹H-NMR and ¹³C-NMR
- Purity assessment: HPLC, GC-MS, ICP-MS
- Thermal properties: DSC, TGA, DMA
- Chemical structure: FTIR, end-group titration
2. Statistical Quality Control
- Establish control charts for critical polymer attributes
- Monitor batch-to-batch consistency
- Implement statistical process control (SPC)
- Define process capability indices (Cpk)
3. Degradation Study Design
Understanding PLGA degradation behavior is critical for predicting drug release and stability:
Recommended Studies:
- Accelerated degradation under physiological conditions
- Real-time degradation monitoring
- Identification of degradation products
- Mass loss kinetics
- Molecular weight decrease over time
4. Correlation Studies
Establish relationships between:
- Polymer properties and drug loading efficiency
- Molecular weight and release kinetics
- End-group ratio and initial burst release
- Residual monomers and stability
Formulation-level strategies for enhancing polymer performance are further discussed in this guide on PLGA solubility enhancement:
https://resolvemass.ca/plga-solubility-enhancement/

8: ResolveMass Laboratories’ Approach to PLGA Characterization
ResolveMass Laboratories specializes in comprehensive PLGA polymer characterization for generics, offering pharmaceutical manufacturers the analytical expertise needed to overcome innovator disclosure gaps. Our laboratory employs state-of-the-art instrumentation and methodology development expertise to address the most challenging characterization requirements.
Our Service Capabilities
Complete Polymer Characterization Package:
- Advanced molecular weight determination by GPC-MALS
- Quantitative compositional analysis by NMR
- Trace impurity profiling by LC-MS and GC-MS
- Thermal and physical property characterization
- Comparative studies against reference products
- Regulatory support and documentation
Specialized Testing:
For highly potent molecules, additional containment and formulation controls are required, as outlined in this article on formulating highly potent APIs using PLGA microspheres:
https://resolvemass.ca/formulating-highly-potent-apis-using-plga-polylactic-co-glycolic-acid-microspheres/
- Custom method development for unique formulations
- Forced degradation studies
- Extractable and leachable studies
- Biocompatibility testing support
- Regulatory submission packages
Consultative Support:
- Polymer specification development
- Quality-by-design study planning
- Regulatory strategy consultation
- Troubleshooting bioequivalence failures
9: Case Study: Successful Generic Development Through Comprehensive Characterization
A related example highlighting scale-up challenges and polymer variability control is available in this PLGA scale-up case study:
https://resolvemass.ca/plga-scale-up-case-study/
A recent generic manufacturer approached ResolveMass Laboratories after experiencing bioequivalence study failures for a PLGA microsphere formulation. Despite matching the innovator’s stated LA:GA ratio and general molecular weight range, their product showed faster drug release and different pharmacokinetic profiles.
Our comprehensive PLGA polymer characterization for generics revealed:
- End-group composition significantly different from innovator (70:30 vs. 50:50 COOH:OH ratio)
- Higher residual glycolic acid monomer content
- Broader molecular weight distribution (PDI 1.8 vs. 1.4)
- Presence of low molecular weight oligomers not detected by standard methods
Resolution: After adjusting polymer specifications based on our detailed characterization and sourcing polymer matching these tighter specifications, the generic manufacturer successfully achieved bioequivalence in their subsequent clinical study and received FDA approval.
10: Future Trends in PLGA Polymer Characterization
The field of polymer characterization continues to evolve with emerging technologies:
Emerging Analytical Techniques:
- Ultra-high-resolution mass spectrometry for oligomer characterization
- 2D-LC techniques for comprehensive polymer profiling
- Machine learning-based predictive modeling
- Real-time degradation monitoring systems
- Advanced imaging techniques (AFM, SEM, TEM)
Regulatory Evolution:
- Increased emphasis on polymer characterization in generic submissions
- Harmonization of global requirements
- Post-approval change protocols for polymer specifications
- Quality-by-design expectations becoming standard
Conclusion:
PLGA polymer characterization for generics requires sophisticated analytical strategies that go well beyond what innovator companies disclose in their regulatory submissions. Generic manufacturers must invest in comprehensive characterization programs to establish polymer specifications that ensure pharmaceutical equivalence and bioequivalence.
Success in developing complex PLGA-based generic formulations depends on:
- Comprehensive analytical characterization using advanced techniques
- Understanding the relationship between polymer properties and drug performance
- Implementing robust quality control systems
- Partnering with specialized laboratories equipped to address characterization challenges
The information asymmetry between innovators and generic developers need not be an insurmountable barrier. Through systematic characterization, quality-by-design approaches, and partnership with experienced analytical laboratories, generic manufacturers can successfully navigate the complexities of PLGA polymer characterization for generics and bring high-quality, cost-effective medications to patients.
ResolveMass Laboratories stands ready to support pharmaceutical manufacturers with the analytical expertise, advanced instrumentation, and regulatory knowledge needed to overcome the challenges of complex generic development. Our commitment to scientific excellence and customer success has made us a trusted partner for pharmaceutical companies worldwide.
For developers evaluating alternative biodegradable excipients, PLA polymer sourcing and excipient considerations are discussed here:
https://resolvemass.ca/pla-excipient-supplier/
FAQs on Polymer Characterization for Generic Drug Development
PLGA is not a single, well-defined material but a family of polymers with variations in lactide:glycolide ratio, molecular weight, end groups, crystallinity, and polymer architecture. These attributes directly control drug release kinetics, degradation rate, particle morphology, and in vivo performance. Innovator products rarely disclose full polymer specifications. For generics, insufficient PLGA characterization can lead to bio-inequivalence, altered release profiles, or regulatory rejection, making in-depth analytical characterization essential for Q1/Q2/Q3 matching.
Innovators usually disclose only high-level information such as “PLGA 50:50” or “PLGA-based microspheres.” Critical attributes often missing include:
-Exact molecular weight distribution (Mn, Mw, PDI)
-End-group chemistry (acid vs ester terminated)
-Polymer sequence distribution
-Residual monomers and oligomers
-Stabilizers, residual solvents, or processing aids
These hidden parameters significantly impact degradation behavior and drug release.
Higher molecular weight PLGA degrades more slowly, resulting in extended drug release and reduced initial burst. Lower molecular weight PLGA degrades faster, which may cause premature drug release, higher burst effects, and stability issues. Matching only the average molecular weight is insufficient; polydispersity and molecular weight distribution shape also influence formulation performance and must be characterized using techniques like GPC/SEC.
Acid-terminated PLGA accelerates hydrolytic degradation and may increase initial burst release, while ester-terminated PLGA degrades more slowly and provides smoother release profiles. End-group chemistry also affects polymer–drug interactions and particle stability. Innovators rarely disclose this information, yet regulators increasingly expect generics to understand and control it.
Beyond composition, polymer microstructure—including randomness of monomer distribution and blockiness—affects water uptake, autocatalysis, and degradation uniformity. Differences in microstructure can result in dose dumping or delayed release, even if bulk parameters appear similar. Advanced NMR techniques are often required to uncover these differences.
Reference
- FORMULATION FORUM – PLGA – A Versatile Copolymer for Design & Development of Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery.https://drug-dev.com/formulation-forum-plga-a-versatile-copolymer-for-design-development-of-nanoparticles-for-drug-delivery/
- FDA’s Regulatory Science Program for Generic PLA/PLGA-Based Drug Products.https://www.americanpharmaceuticalreview.com/Featured-Articles/339677-FDA-s-Regulatory-Science-Program-for-Generic-PLA-PLGA-Based-Drug-Products/
- PLGA-based nanoparticles: A new paradigm in biomedical applications.https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0165993615300121

