
Introduction: The Strategic Importance of PLGA Reverse Engineering for ANDA Success
PLGA reverse engineering for ANDA applications is essential for developing generic versions of complex injectable products because it enables pharmaceutical companies to precisely characterize polymer composition, drug release mechanisms, and critical quality attributes required for FDA approval. Without comprehensive reverse engineering, demonstrating pharmaceutical equivalence to reference listed drugs is virtually impossible.
PLGA-based products—including microspheres, depot injections, nanoparticles, and implants—demand sophisticated analytical characterization that goes beyond traditional generic development. Real-world examples, such as this PLGA microsphere reverse engineering case study, highlight how subtle polymer differences can determine ANDA success or failure:
👉 https://resolvemass.ca/plga-microsphere-case-study/
Summary
PLGA reverse engineering for ANDA submissions represents a critical pathway for pharmaceutical companies developing generic injectable products. This comprehensive guide explores why understanding the intricate composition and manufacturing processes of poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) formulations is essential for regulatory success.
Key Takeaways:
- PLGA reverse engineering enables precise characterization of complex generic formulations required for ANDA approval
- Regulatory agencies demand comprehensive analytical data demonstrating pharmaceutical equivalence to reference products
- Advanced characterization techniques identify critical quality attributes affecting drug release and bioavailability
- Understanding polymer composition, molecular weight, and microstructure is mandatory for demonstrating sameness
- ResolveMass Laboratories provides specialized analytical services supporting successful ANDA submissions
- Proper reverse engineering reduces development timelines and regulatory risks for generic injectable manufacturers
1: Understanding PLGA in Generic Injectable Formulations
Poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) is a biodegradable copolymer that has revolutionized controlled-release drug delivery. PLGA formulations are widely used because they provide sustained drug release over periods ranging from days to months, improve patient compliance, and maintain therapeutic drug levels.
Why PLGA Products Require Specialized Reverse Engineering
PLGA-based formulations present unique challenges:
- Complex polymer chemistry: The ratio of lactic acid to glycolic acid, molecular weight distribution, and end-group chemistry all critically affect product performance
- Manufacturing variability: Processing conditions during emulsification, spray drying, or extrusion significantly influence particle characteristics
- Release kinetics: Drug release profiles depend on multiple interdependent factors including polymer composition, particle morphology, and drug-polymer interactions
- Stability considerations: PLGA degradation pathways affect both drug stability and release characteristics
Successful generic development requires a deep understanding of:
- Polymer grade and supplier variability (e.g., PLGA 50:50 grades)
👉 https://resolvemass.ca/plga-5050-supplier/ - Drug–polymer compatibility and drug loading efficiency
👉 https://resolvemass.ca/plga-drug-loading/ - Release modulation through formulation design
👉 https://resolvemass.ca/plga-depot-formulation/
2: Why PLGA Products Require Specialized Reverse Engineering
PLGA formulations present unique challenges that demand expert reverse engineering:
Complex Polymer Chemistry
The lactide:glycolide ratio, molecular weight distribution, end-group chemistry, and polymer microstructure directly influence degradation and release. When alternative polymers such as PLA or PCL are involved, excipient equivalence becomes even more critical:
👉 https://resolvemass.ca/pla-excipient-supplier/
👉 https://resolvemass.ca/pcl-excipient-supplier/
Manufacturing Variability
Processing conditions during emulsification, solvent evaporation, or spray drying strongly impact particle morphology. Guidance on PLGA microsphere formulation design is essential to understand these effects:
👉 https://resolvemass.ca/plga-microsphere-formulation/
Release Kinetics and Stability
Drug release behavior is governed by polymer degradation, porosity, and solubility enhancement strategies:
👉 https://resolvemass.ca/plga-solubility-enhancement/
👉 https://resolvemass.ca/plga-formulation-stability/
3: The Critical Role of PLGA Reverse Engineering for ANDA Applications
PLGA reverse engineering for ANDA submissions is critical because it provides the foundational understanding necessary to demonstrate sameness to the reference product. The FDA requires generic manufacturers to prove that their products are pharmaceutically equivalent and will deliver the same clinical outcomes as the innovator product.
A structured Q1/Q2 polymer equivalence assessment helps align analytical data with regulatory expectations:
👉 https://resolvemass.ca/q1-q2-polymer-equivalence-assessment/
Regulatory Requirements Driving Reverse Engineering Needs
Generic injectable manufacturers must demonstrate:
- Qualitative and quantitative sameness in all components
- Identical or comparable release profiles under physiologically relevant conditions
- Similar physicochemical properties affecting product performance
- Equivalent impurity profiles within acceptable limits
- Comparable stability characteristics throughout shelf life
Without comprehensive reverse engineering, meeting these requirements is virtually impossible.
4: Essential Analytical Techniques for PLGA Reverse Engineering for ANDA
ResolveMass Laboratories employs a comprehensive analytical toolkit specifically designed for PLGA reverse engineering for ANDA projects:
Polymer Characterization Methods
| Analytical Technique | Critical Information Obtained | ANDA Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| Gel Permeation Chromatography (GPC) | Molecular weight distribution | Affects degradation rate and drug release |
| Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) | Lactide:glycolide ratio, end groups | Defines polymer composition and properties |
| Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) | Glass transition temperature, crystallinity | Impacts storage stability and release |
| Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA) | Thermal stability, residual solvents | Quality control and stability assessment |
| FTIR Spectroscopy | Chemical structure confirmation | Identity verification |
Particle and Formulation Analysis
Advanced characterization of the final dosage form includes:
- Particle size distribution: Laser diffraction and dynamic light scattering reveal size populations affecting release kinetics
- Morphology assessment: Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) identifies surface characteristics and internal structure
- Drug loading and distribution: HPLC and imaging techniques quantify drug content and spatial distribution
- Porosity measurements: Mercury porosimetry or nitrogen adsorption characterize pore structure influencing water penetration
Release Profile Studies
Comprehensive in vitro release testing under multiple conditions:
- Multiple pH environments simulating physiological conditions
- Temperature variations assessing stability-indicating parameters
- Extended timepoint sampling capturing complete release profiles
- Discriminatory method development identifying formulation sensitivities
In-vitro release testing under discriminatory conditions is essential to predict in-vivo performance. Scale-up introduces additional risk, making prior PLGA scale-up experience invaluable:
👉 https://resolvemass.ca/plga-scale-up-case-study/
Solvent Compatibility and Processing Insights
Understanding how PLGA dissolves during processing is critical for reproducibility and scale-up:
👉 https://resolvemass.ca/dissolving-plga-in-solvents/
5: How PLGA Reverse Engineering Reduces ANDA Development Risk
Investing in thorough PLGA reverse engineering for ANDA submissions significantly reduces regulatory and commercial risks:
Accelerated Development Timelines
Understanding the reference product’s composition and critical quality attributes allows:
- Focused formulation development targeting the right specifications
- Reduced trial-and-error experimentation
- Faster optimization of manufacturing processes
- Fewer formulation iterations before achieving equivalence
Enhanced Regulatory Success Probability
Comprehensive analytical packages demonstrate:
- Deep understanding of the reference product
- Scientific rationale for formulation choices
- Robust control strategies for critical attributes
- Confidence in pharmaceutical equivalence claims
Quality by Design Implementation
Reverse engineering data supports:
- Identification of critical material attributes
- Definition of design spaces for manufacturing
- Risk-based control strategies
- Science-based specifications aligned with product performance

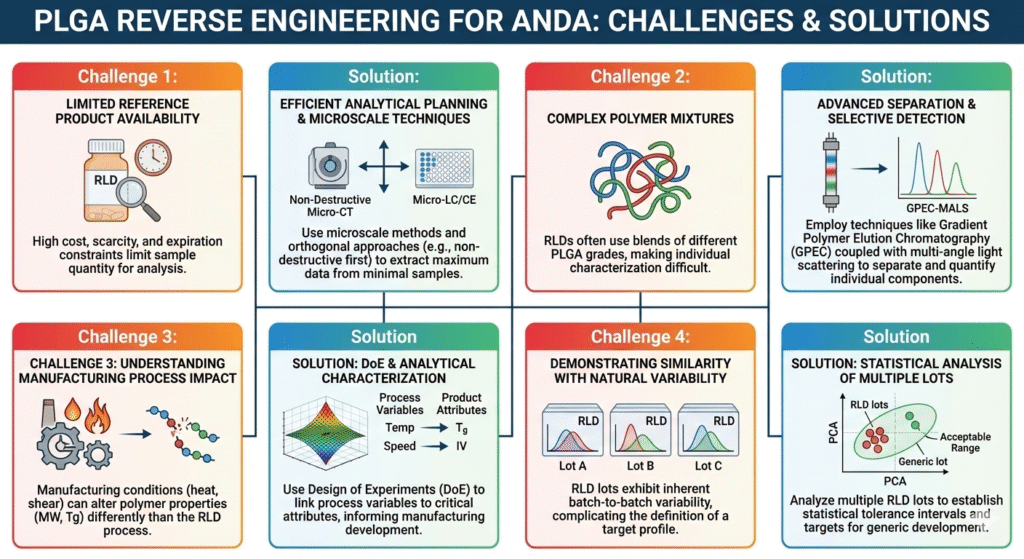
6: Common Challenges in PLGA Reverse Engineering for ANDA and How to Overcome Them
Challenge 1: Limited Reference Product Availability
Solution: Efficient analytical planning maximizes information from minimal sample quantities. Our microscale techniques and orthogonal approaches extract maximum data from each sample.
Challenge 2: Complex Polymer Mixtures
Solution: Advanced separation techniques coupled with selective detection methods identify and quantify individual components in complex PLGA blends.
Challenge 3: Understanding Manufacturing Process Impact
Solution: Design of experiments combined with analytical characterization links process variables to product attributes, informing your manufacturing development.
Challenge 4: Demonstrating Similarity with Natural Variability
Solution: Statistical analysis of multiple reference product lots establishes acceptable ranges for critical attributes, providing targets for generic development.
Future Trends in PLGA Reverse Engineering for ANDA
The field continues evolving with:
- Advanced imaging techniques: Confocal Raman microscopy and 3D X-ray tomography providing unprecedented structural insights
- In silico modeling: Computational approaches predicting release profiles from formulation parameters
- Regulatory harmonization: International guidelines creating clearer pathways for complex generic approval
- Bioequivalence considerations: Evolving approaches to demonstrating therapeutic equivalence for long-acting products
Conclusion: Partnering for ANDA Success Through Expert PLGA Characterization
PLGA reverse engineering for ANDA submissions is a critical investment that directly impacts regulatory approval success, development timelines, and commercial viability of generic injectable products. The complexity of biodegradable polymer formulations requires specialized analytical expertise, advanced instrumentation, and deep regulatory knowledge to demonstrate pharmaceutical equivalence.
ResolveMass Laboratories Inc. delivers comprehensive reverse engineering services with proven results across multiple therapeutic categories. Our combination of PhD-level scientists, state-of-the-art analytical capabilities, and regulatory-focused approach positions your ANDA for success while minimizing development risks. As generic products grow increasingly sophisticated, expert PLGA reverse engineering for ANDA becomes not just advantageous—but essential.
FAQs on Reverse Engineering of PLGA
Reverse engineering of PLGA involves systematically characterizing the innovator polymer and formulation to understand its chemical composition, molecular architecture, and performance-critical attributes. This includes lactide:glycolide ratio, molecular weight distribution, end-group chemistry, crystallinity, residual monomers, and degradation behavior. The goal is to replicate the polymer and drug release profile closely enough to meet Q1/Q2 sameness or equivalence expectations for ANDA approval.
The difference between NDA and ANDA is that an NDA is for new drugs, while an ANDA is for generic drugs, both requiring different levels of evidence and testing. NDA is for new drugs, ANDA is for generics, each with distinct evidence and testing requirements.
An abbreviated new drug application (ANDA) contains data which is submitted to FDA for the review and potential approval of a generic drug product. Once approved, an applicant may manufacture and market the generic drug product to provide a safe, effective, lower cost alternative to the brand-name drug it references.
Refusal to Receive
-Inadequate stability data;
-Incomplete information request response;
-Inadequate dissolution;
-Drug product was not qualitatively and quantitatively the same as the innovator drug; and.
-Failure to respond to information request within the prescribed timeframe.
Higher molecular weight PLGA generally degrades more slowly, leading to prolonged drug release, while lower molecular weight polymers degrade faster and may cause initial burst release. Matching the innovator’s molecular weight distribution—not just average values—is critical to achieving comparable in-vitro and in-vivo release behavior in generic products.
Reference
- Development of Complex Generics and Similar Biological Products: An Industrial Perspective of Reverse Engineering.https://link.springer.com/article/10.1208/s12249-025-03087-7
- Reverse Engineering in Complex/Combination Ophthalmic Product.https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-981-96-6306-4_7
- Current trends in PLGA based long-acting injectable products: The industry perspective.https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/17425247.2022.2075845
- Key Factor Study for Generic Long-Acting PLGA Microspheres Based on a Reverse Engineering of Vivitrol®.https://www.mdpi.com/1420-3049/26/5/1247
- Reverse Engineering in Pharmaceutical Product Development.https://www.taylorfrancis.com/chapters/edit/10.1201/9781003043164-15/reverse-engineering-pharmaceutical-product-development-rishi-paliwal-aanjaneya-mamgain-rameshroo-kenwat-shivani-rai-paliwal

