OVERVIEW
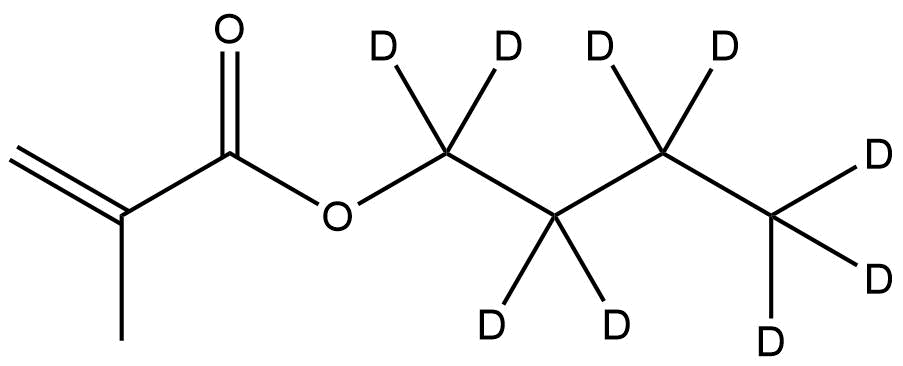
Deuterated n-Butyl-d9 Methacrylate is a fully deuterium-labeled methacrylate monomer widely used in advanced polymer research, mechanistic studies, kinetic isotope analyses, materials characterization, and high-precision NMR or mass-spectrometry-based investigations. With nine deuterium atoms incorporated on the n-butyl side chain, this monomer provides a stable isotopic signature, enabling researchers to trace polymer growth pathways, quantify copolymer composition, improve analytical resolution, and investigate degradation behaviors with exceptional clarity.
At ResolveMass Laboratories Inc., we support high-purity isotopic monomers for academic and industrial researchers working in polymer chemistry, biomaterials, nanoscale coatings, radiative shielding materials, and controlled-release systems. Deuterated n-Butyl-d9 methacrylate is synthesized using stringent quality standards to ensure lot-to-lot consistency, making it ideal for reproducible experimental design, mechanistic polymer studies, and applications requiring isotopic fidelity.
CHEMICAL INFORMATION
Chemical Name: Deuterated n-Butyl-d9 Methacrylate
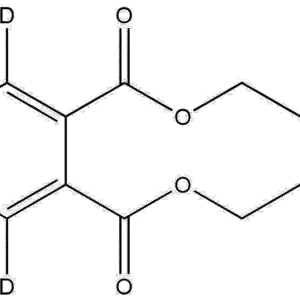
General Formula: C₈H₅D₉O₂
Isotopic Labeling: 9× D (deuterium substitution on n-butyl chain)
Class: Deuterated methacrylate monomer
Functional Group: Vinyl / methacrylate ester
Appearance: Typically clear to pale liquid (varies by grade and storage)
Typical Purity: High-purity analytical or polymer-grade (≥98%, depending on specification)
The incorporation of nine deuterium atoms significantly reduces proton-signal overlap in NMR spectroscopy and provides a strong isotopic shift in MS-based analysis. For polymer scientists, this enables precise chain-growth profiling, copolymer ratio measurements, and structural elucidation that is not possible using non-deuterated analogues.
KEY FEATURES AND BENEFITS
• Isotopic precision – Strong D-labeling minimizes proton background, ideal for NMR and MS quantification.
• Enhanced analytical resolution – Deuterium substitution introduces a predictable mass shift (9 Da), allowing clear differentiation in complex matrices.
• Ideal for mechanistic polymer studies – Trace monomer incorporation in copolymer systems, study chain transfer reactions, or evaluate block sequence distribution.
• High chemical stability – Deuterated side chains often show reduced reactivity toward certain degradation pathways, improving performance in long-term studies.
• Compatibility with standard polymerization techniques – Suitable for free-radical polymerization, ATRP, RAFT, and anionic routes.
• Excellent for diffusion, mobility, and degradation studies – The D-label enables tracking of polymer segments in bulk materials, films, and biological environments.
APPLICATIONS of Deuterated n-Butyl-d9 methacrylate
1. Polymerization Mechanism Research
Deuterated n-Butyl-d9 methacrylate is widely used to dissect polymerization behavior at the molecular level. Scientists can track monomer consumption, chain growth, branching, and termination events with high resolution using ^1H NMR suppression techniques or MS-based monitoring.
2. Copolymer Composition Analysis
In multicomponent systems, deuterium provides a measurable spectral gap, allowing accurate quantification of monomer incorporation ratios—critical for designing materials with targeted mechanical, thermal, or diffusion properties.
3. Kinetic Isotope Effect (KIE) Studies
The presence of deuterium modifies vibrational energies and bond dissociation characteristics. Researchers exploit this for evaluating reaction rates, radical stability, polymer degradation kinetics, and solvent interaction mechanisms.
4. Thin-Film and Coating Technologies
Because of its hydrophobic n-butyl backbone, this monomer is used to create deuterated polymer films for neutron reflectometry, advanced coatings, and nanoscale interfacial studies where isotopic contrast dramatically improves data interpretation.
5. Biomedical and Drug-Delivery Research
Deuterated polymers allow scientists to track polymer degradation, drug diffusion, and biodistribution using MS or isotope-sensitive imaging modalities. While the monomer itself is not a therapeutic, its deuterated signature enables precise mapping within complex biological systems.
6. Materials Science and Nanotechnology
Used in self-assembled materials, block copolymer patterning, and polymer blends requiring distinct isotopic domains, deuterated n-butyl methacrylate enhances the visibility and interpretability of nanoscale structures.
ANALYTICAL ADVANTAGES
• NMR: Deuterium labeling significantly reduces proton spectral crowding, enabling clearer quantification of polymer microstructure.
• Mass Spectrometry: Predictable isotopic mass increase supports tracing polymer fragments, verifying monomer conversion, and analyzing degradation pathways.
• Spectroscopy and Scattering: Deuterated materials enhance contrast for neutron scattering, reflectometry, and structural analysis.
STORAGE AND HANDLING
Deuterated n-Butyl-d9 methacrylate should be stored under an inert atmosphere, protected from light, heat, and radical initiators. As with all methacrylate monomers, inhibitor presence may be required to prevent premature polymerization. Proper laboratory PPE and handling protocols are recommended.
Learn more through,
Deuterated Polymers: A Cornerstone Guide to Synthesis, Applications, and Future Trends
Availability of All the Deuterated Chemicals at ResolveMass Laboratories Inc.
ResolveMass Laboratories: Leading Deuterated Chemical Synthesis Company in the United States.
Deuterated Internal Standards for LC-MS: Selection & Custom Synthesis
How to Choose the Right Deuterated Labelled Chemical Synthesis Company in Canada
How to Choose the Right Deuterium Labelled Compounds Supplier for Your Lab
Deuterium-Labelled Compounds — Synthesis, Applications & Ordering
Custom Synthesis of Deuterated Chemicals
Reviews
There are no reviews yet.