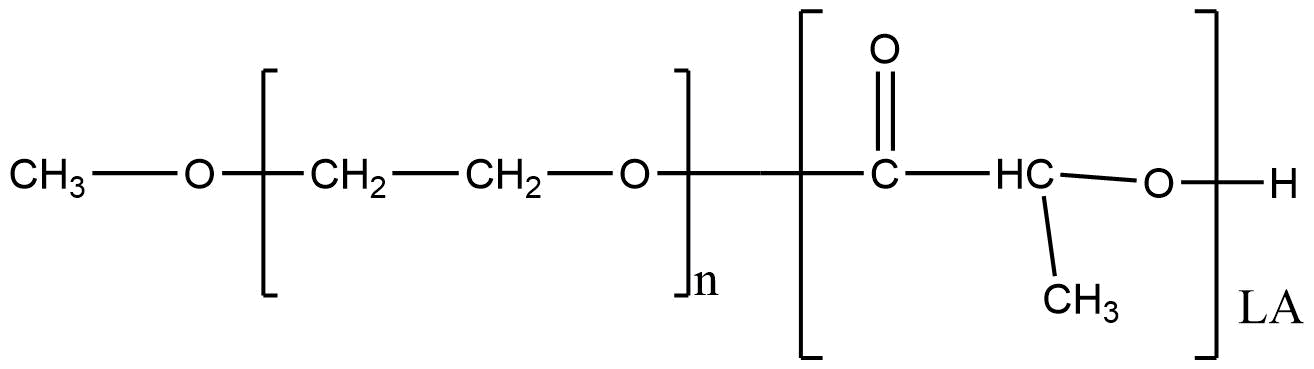
Methoxy (polyethylene glycol)-b-poly(L-lactide) | mPEG: PLA (Mw 1500: 10000)
OVERVIEW
Methoxy (polyethylene glycol)-b-poly(L-lactide) | mPEG: PLA (Mw 1500: 10000) is a high-performance amphiphilic block copolymer widely used in advanced drug delivery, nanomedicine formulation, and biodegradable material development. The polymer combines the hydrophilic, biocompatible characteristics of mPEG with the hydrophobic, semicrystalline biodegradability of poly(L-lactide) (PLA). In the configuration mPEG:PLA = 1500:10000 Da, this material provides a strongly asymmetric block ratio, creating micelles and nanoparticles with highly stable hydrophobic cores suitable for carrying poorly water-soluble drugs.
At ResolveMass Laboratories Inc., mPEG-PLA is produced with high synthetic precision, excellent lot-to-lot reproducibility, and premium purity to meet demanding R&D, formulation development, and preclinical research requirements. Its well-defined molecular architecture and predictable degradation behavior make it a preferred excipient for long-circulation nanosystems, sustained-release technologies, and tissue-engineering applications.
CHEMICAL INFORMATION
-
Chemical Name: Methoxy poly(ethylene glycol)-b-poly(L-lactide)
-
Abbreviation: mPEG-PLA
-
Structure: Amphiphilic AB block copolymer
-
Composition: mPEG block (1500 Da) + PLA block (10000 Da)
-
PLA Orientation: Poly(L-lactide), optically pure, semicrystalline
-
Functional Group: Terminal methoxy on PEG
-
Biodegradation Mechanism: Hydrolysis of ester linkages
The molecular weight arrangement of 4000:50000 places the polymer firmly in the category of long-chain PLA systems with substantial hydrophobic mass. This configuration encourages strong core-forming capability, slower degradation kinetics, and reliable encapsulation efficiency for lipophilic molecules.
KEY PROPERTIES
Amphiphilicity and Self-Assembly
The hydrophilic mPEG shell enables the polymer to self-assemble in aqueous environments into well-defined micellar structures. The PEG corona increases colloidal stability, reduces aggregation, and enhances systemic circulation time by minimizing opsonization.
Biodegradability and Biocompatibility
PLA gradually hydrolyzes into lactic acid—a metabolite naturally processed by the human body. This controlled hydrolysis is especially useful for designing sustained-release nanoparticle systems, implants, and scaffolds.
High Hydrophobic Core Volume
With a PLA molecular weight of 50 kDa, the polymer forms a large, robust hydrophobic domain. This supports:
-
High encapsulation loading for hydrophobic APIs
-
Slow and predictable drug diffusion
-
Strong structural stability under physiological conditions
Excellent Solubility Profile
The mPEG segment (4 kDa) ensures full water dispersibility of the micelle shell, while the PLA block dissolves in common organic solvents used for nanoparticle fabrication such as DCM, THF, and ethyl acetate.
FUNCTIONAL ADVANTAGES FOR FORMULATORS
Enhanced Drug Loading Efficiency
The dominant PLA mass makes this polymer ideal for hydrophobic drug encapsulation. This is particularly advantageous for oncology drugs, corticosteroids, immunomodulators, and poorly soluble small molecules.
Controlled and Extended Release
The slow-degrading PLA block offers long-term release profiles. Release rates can be tuned through:
-
Polymer concentration
-
Nanoparticle size
-
Formulation process parameters
-
Surface modifications
This allows customization for applications requiring daily, weekly, or monthly release profiles.
Reduced Burst Release
The high PLA block length significantly lowers the risk of burst release by:
-
Reducing rapid core erosion
-
Creating thicker barriers to drug diffusion
-
Increasing micelle core packing density
Improved Pharmacokinetics
PEGylation provides stealth characteristics, helping nanoparticles:
-
Circulate longer
-
Evade rapid clearance
-
Deliver drugs more efficiently to target tissues
APPLICATIONS
Nanoparticle and Micelle Drug Delivery
mPEG-PLA (4000:50000) is a preferred polymer for preparing:
-
Polymeric micelles
-
Nanoparticles
-
Nano-suspensions
-
Long-circulation carriers
Its asymmetric structure promotes enhanced stability and encapsulation performance for hydrophobic therapeutics.
Injectable Sustained-Release Systems
The slow PLA degradation profile enables long-acting injectable formulations where consistent plasma levels are desired.
Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine
The crystalline L-lactide block contributes to mechanical stability, making this polymer suitable for:
-
Biodegradable scaffolds
-
ECM-mimicking matrices
-
Controlled-resorption biomaterials
Combination Delivery Platforms
The amphiphilic profile supports the co-delivery of hydrophobic and PEG-conjugated molecules, enabling multifunctional nanocarrier systems.
SYNTHESIS & QUALITY
ResolveMass Laboratories Inc. manufactures this polymer using controlled ring-opening polymerization (ROP) to produce narrow polydispersity and highly predictable performance. Each batch undergoes rigorous analytical verification including:
-
NMR
-
GPC Mw and PDI analysis
-
Residual monomer tests
-
Solvent residue analysis
This ensures world-class reliability for pharmaceutical and academic research applications.
Read below Learn with Us Articles:
PLGA Nanoparticles Synthesis: A Step-by-Step Guide for Beginners
The Science Behind GPC: A Deep Dive into Analyzing PLA, PLGA, and PCL for Research
Reviews
There are no reviews yet.