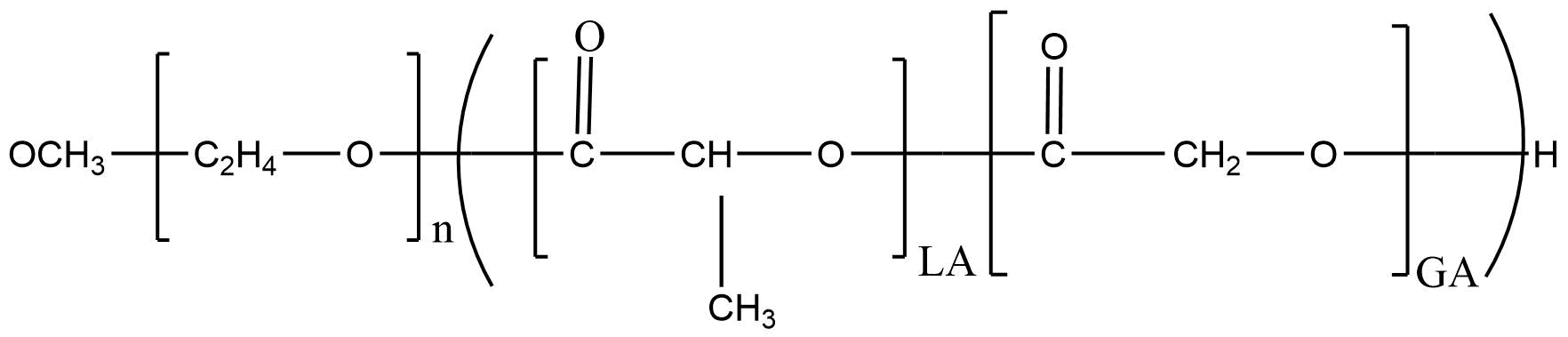
Methoxy poly(ethylene glycol)-b-poly(lactide-co-glycolide) | Ratio: 75:25 | mPEG: PLGA (Mw 1500 : 10000) | CAS 743423-15-6
OVERVIEW
Methoxy poly(ethylene glycol)-b-poly(lactide-co-glycolide) | Ratio: 75:25 | mPEG: PLGA (Mw 1500 : 10000) | CAS 743423-15-6 is a versatile amphiphilic block copolymer engineered for advanced drug delivery, solubilization enhancement, and controlled-release formulation design. Combining the hydrophilic properties of methoxy-terminated polyethylene glycol (mPEG) with the biodegradable characteristics of poly(lactide-co-glycolide) (PLGA), this polymer self-assembles into nanoscale structures suitable for encapsulating hydrophobic, hydrophilic, and amphiphilic therapeutic agents. Its tunable degradation profile, excellent biocompatibility, and regulatory acceptance make mPEG-PLGA one of the most widely adopted functional block copolymers in modern pharmaceutical R&D.
At ResolveMass Laboratories Inc., our mPEG-PLGA materials are manufactured with high structural precision, narrow molecular weight distribution, and controlled lactide:glycolide ratios to support reproducible performance in formulation development. These polymers are suitable for nanoparticle fabrication, micelle formation, depot systems, injectable formulations, and next-generation delivery platforms used across biologics, peptides, small molecules, and imaging agents.
CHEMICAL STRUCTURE & ARCHITECTURE
mPEG-PLGA consists of two chemically distinct segments:
-
mPEG block: A hydrophilic polyether chain with a terminal methoxy group that promotes aqueous solubility, reduces protein adsorption, and enhances circulation time.
-
PLGA block: A hydrophobic, biodegradable polyester composed of lactide and glycolide units, providing a customizable degradation rate based on monomer ratio and molecular weight.
This diblock architecture enables spontaneous formation of micelles or nanoparticles where the PLGA domain forms a hydrophobic core, while the mPEG chains create a stabilizing corona that prevents aggregation and reduces opsonization. The modular nature of the polymer allows customization of:
-
mPEG molecular weight
-
PLGA molecular weight
-
Lactide:glycolide ratio
-
End-group chemistry
Such structural tunability gives formulation scientists precise control over drug loading efficiency, release kinetics, particle size, and in-vivo performance.
KEY PROPERTIES
-
Biocompatible and biodegradable: Both blocks degrade into physiologically tolerated by-products (PEG, lactic acid, glycolic acid).
-
Amphiphilic behavior: Enables spontaneous self-assembly into lipophilic-core nanostructures.
-
Adjustable degradation rate: Controlled through PLGA molecular weight and LA:GA ratio.
-
High drug loading potential: Especially suitable for hydrophobic APIs sequestered in the PLGA core.
-
Extended circulation time: PEG corona reduces immune clearance, improving systemic exposure.
-
Reproducible performance: Consistent block lengths ensure formulation predictability.
MECHANISM OF DRUG ENCAPSULATION & RELEASE
mPEG-PLGA nanostructures encapsulate molecules through a combination of hydrophobic interactions, polymer–drug affinity, and core entrapment during nanoparticle or micelle self-assembly. Drug release follows a dual-mechanism pathway:
-
Diffusion Phase: At early stages, drug molecules near the nanoparticle’s surface diffuse through the PEG corona into surrounding media.
-
Degradation Phase: Hydrolytic cleavage of ester bonds in the PLGA segment gradually softens and breaks down the hydrophobic core, releasing the remaining payload in a sustained manner.
By adjusting block sizes, scientists can engineer rapid, moderate, or prolonged release profiles for diverse therapeutic modalities.
APPLICATIONS of Methoxy poly(ethylene glycol)-b-poly(lactide-co-glycolide) | Ratio: 75:25 | mPEG: PLGA (Mw 1500 : 10000) | CAS 743423-15-6
mPEG-PLGA serves numerous pharmaceutical and biomedical applications due to its amphiphilic and biodegradable nature:
-
Polymeric micelles for solubility enhancement: Improves the aqueous solubility of hydrophobic drug molecules.
-
Nanoparticles for controlled release: Ideal for small molecules, peptides, and biologics requiring predictable release kinetics.
-
Long-circulating nanocarriers: PEGylation minimizes protein adsorption and RES clearance, enabling enhanced pharmacokinetics.
-
Injectable depot systems: PLGA degradation tailors long-acting dosage forms for monthly or multi-month release.
-
Gene and RNA delivery: Surface-functionalizable PEG domain allows ligand or targeting moiety attachment.
-
Imaging and diagnostic tools: Used for contrast agent encapsulation and targeted delivery.
-
Combination therapies: Enables co-encapsulation of hydrophobic and hydrophilic drugs within a unified carrier.
The polymer’s flexibility makes it compatible with emulsification, nanoprecipitation, microfluidic assembly, and solvent evaporation processes widely used in formulation laboratories.
BENEFITS FOR DRUG DEVELOPMENT
Choosing mPEG-PLGA in early-phase or commercial formulation design offers multiple advantages:
-
Enhanced solubility and bioavailability of poorly soluble APIs
-
Reduction of burst release through controlled core structure
-
Tailored pharmacokinetic profiles aligned with therapeutic goals
-
Lower toxicity risk due to clean degradation pathways
-
Improved patient compliance through long-acting formulations
-
Versatility across multiple routes of administration, including IV, SC, and IM
ResolveMass Laboratories provides high-purity, traceable, and customizable mPEG-PLGA polymers that support these performance attributes, ensuring formulation scientists achieve consistent results from prototype to scale-up.
Read below Learn with Us Articles:
PLGA Nanoparticles Synthesis: A Step-by-Step Guide for Beginners
PLGA 50:50 Poly(D L-lactide-co-glycolide) Supplier Guide: What to Look for in a Reliable Provider
The Science Behind GPC: A Deep Dive into Analyzing PLA, PLGA, and PCL for Research
Reviews
There are no reviews yet.