Poly(caprolactone)-b-poly(ethylene glycol)-b-poly(caprolactone) | PCL: mPEG: PCL (10000: 4000: 10000)
OVERVIEW
Poly(caprolactone)-b-poly(ethylene glycol)-b-poly(caprolactone) | PCL: mPEG: PCL (10000: 4000: 10000) is a high-performance amphiphilic triblock copolymer widely used in advanced drug delivery, nanoformulation research, injectable depots, and controlled-release systems. With block molecular weights of PCL: 10,000 – PEG: 4,000 – PCL: 10,000, this polymer offers an excellent balance of hydrophobic–hydrophilic behavior, mechanical stability, and slow biodegradation. Its well-defined structure enables precise control over micelle formation, encapsulation efficiency, drug release kinetics, and material processability.
ResolveMass Laboratories Inc. supplies highly characterized PCL-b-PEG-b-PCL tailored for pharmaceutical R&D, biomedical engineering, and polymeric nanotechnology applications. Rigorous analytical-quality control ensures consistency, purity, and reproducibility for research and formulation development.
CHEMICAL INFORMATION
-
Chemical Name: Poly(caprolactone)-block-poly(ethylene glycol)-block-poly(caprolactone)
-
Synonyms:
-
PCL-PEG-PCL triblock copolymer
-
PEG-PCL amphiphilic triblock polymer
-
PEG-block-PCL-block-PEG (in reverse notation)
-
Poly(ε-caprolactone)-b-PEG-b-poly(ε-caprolactone)
-
-
Polymer Architecture: Linear triblock copolymer
-
Molecular Weight: 10 kDa – 4 kDa – 10 kDa
-
Hydrophobic/Hydrophilic Ratio: High hydrophobic fraction (PCL > PEG) enabling controlled release of hydrophobic drugs
-
Physical Form: Typically white to off-white solid
-
Solubility:
-
In water: self-assembly into micelles at elevated temperatures
-
Fully soluble in organic solvents such as DCM, THF, DMF, chloroform, or toluene
-
This molecular configuration makes the polymer particularly well suited for forming stable core–shell nanostructures, injectable hydrogels, biodegradable depots, and thermosensitive systems.
STRUCTURAL FEATURES & MATERIAL ADVANTAGES
This triblock polymer incorporates two long PCL chains flanking a central PEG segment. The design offers several advantages:
-
Amphiphilicity for Nanocarriers
The hydrophobic PCL segments form strong cores for encapsulating poorly soluble APIs, imaging agents, or hydrophobic actives. The PEG mid-block imparts water dispersibility and colloidal stability, reducing aggregation and minimizing opsonization in biological systems. -
Biodegradability & Biocompatibility
-
PCL slowly degrades through hydrolysis of ester bonds, enabling long-term release profiles ranging from weeks to months.
-
PEG improves biocompatibility, reduces protein adsorption, and enhances circulation time.
The entire copolymer is non-toxic and suitable for biomedical and pharmaceutical research applications.
-
-
Thermo-Responsive Behavior
Certain PCL-PEG-PCL compositions can form thermosensitive hydrogels that transition from sol (at room temperature) to gel (at body temperature). The selected Mw (25k-4k-25k) provides strong mechanical integrity and long-lasting gel depots. -
High Mechanical Strength
The long PCL blocks contribute to superior mechanical stability, making the polymer ideal for scaffolding, tissue-engineering matrices, and 3D-printable biomaterials. -
Versatile Processing
The polymer supports solvent casting, electrospinning, micelle/hydrogel formation, nanoprecipitation, and melt processing, offering exceptional versatility for both laboratory and preclinical R&D.
APPLICATIONS
Drug Delivery & Controlled Release
PCL-b-PEG-b-PCL is widely used for encapsulation of hydrophobic therapeutic molecules. Its high PCL content enables slow degradation, creating sustained, predictable release profiles useful for depot systems, cancer therapeutics, analgesics, peptide stabilization, and small-molecule delivery. PEG contributes stealth properties and enhances aqueous dispersibility for nano-drug carriers.
Common delivery formats include:
-
Polymeric micelles
-
Injectable thermogels
-
Nanoparticles via emulsion or nanoprecipitation
-
Implantable films and depots
Tissue Engineering & Regenerative Medicine
With strong mechanical properties and excellent biocompatibility, the polymer is suitable for:
-
Soft tissue scaffolds
-
Bone regeneration matrices
-
3D-printed biomaterials
-
Wound healing systems
The degradation rate can support tissue remodeling over extended periods.
Biomedical Hydrogels
Thermo-responsive behavior enables in situ gelling hydrogels for:
-
Localized drug release
-
Cell encapsulation
-
Minimally invasive implant delivery
-
Bio-inks for bioprinting
Hydrogels based on this polymer maintain stability while undergoing slow bioerosion.
Nanocarriers & Imaging
The amphiphilic architecture supports:
-
Stable micelles for imaging probes
-
Nanocarriers for poorly soluble dyes
-
MRI/fluorescent agent encapsulation
PEG chains enhance circulation and reduce immune clearance.
KEY BENEFITS FOR RESEARCHERS
-
High reproducibility and tight molecular weight distribution
-
Suitable for both hydrophobic drug encapsulation and hydrogel formation
-
Excellent biocompatibility and customizable degradation behavior
-
Thermally tunable systems for injectable or implantable formats
-
Compatible with a wide range of pharmaceutical solvents
-
Strong mechanical integrity for scaffold engineering
Read below Learn with Us Articles:
PLGA Nanoparticles Synthesis: A Step-by-Step Guide for Beginners
The Science Behind GPC: A Deep Dive into Analyzing PLA, PLGA, and PCL for Research
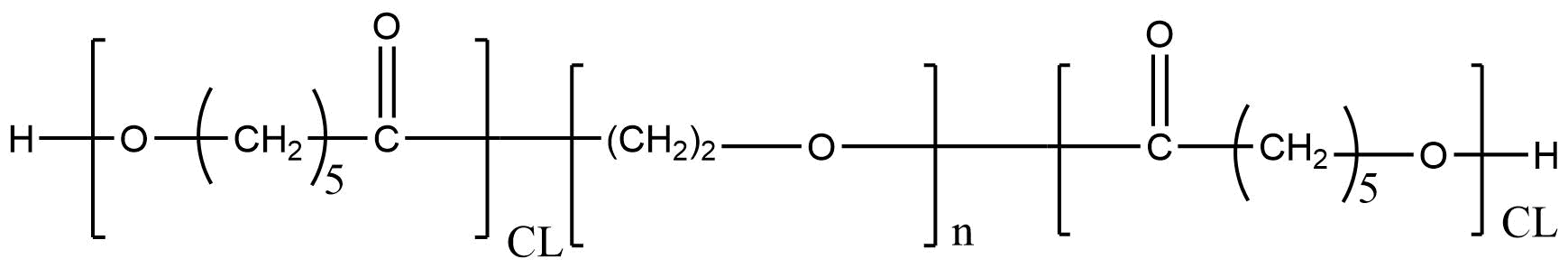

Reviews
There are no reviews yet.