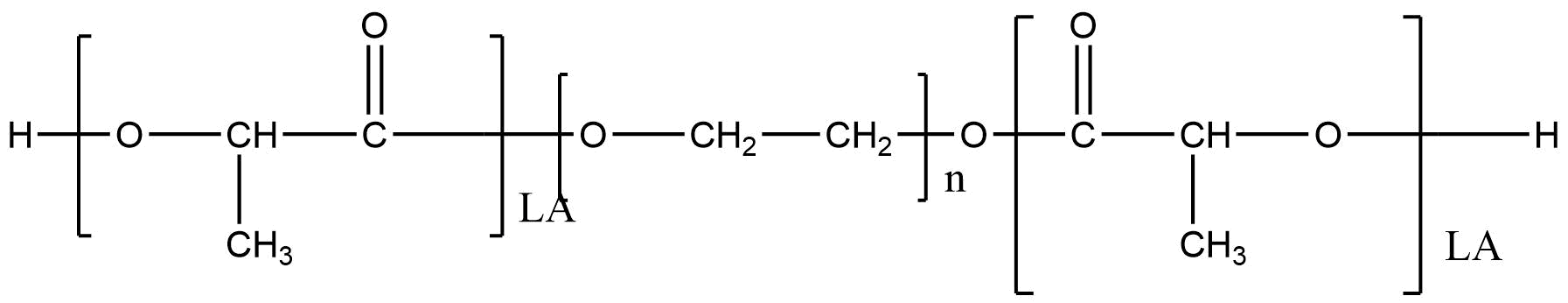
Poly(D,L-lactide)-b-poly(ethylene glycol)-b-poly(D,L-lactide) | PLA: mPEG: PLA (Mw 25000: 4000: 25000)
OVERVIEW
Poly(D,L-lactide)-b-poly(ethylene glycol)-b-poly(D,L-lactide) | PLA: mPEG: PLA (Mw 25000: 4000: 25000) is a biocompatible, biodegradable ABA triblock copolymer widely used in advanced drug delivery, formulation science, and biomedical engineering. With a molecular weight configuration of PLA 25,000 : mPEG 4,000 : PLA 25,000, this amphiphilic polymer combines the hydrophobic features of poly(D,L-lactide) with the hydrophilic, steric-stabilizing properties of PEG, resulting in a highly versatile material suitable for nanocarriers, injectable depots, implantables, and targeted delivery formulations.
The polymer’s architecture gives it exceptional self-assembly behavior, controlled biodegradability, and tunable physicochemical characteristics. These properties make PLA–mPEG–PLA an ideal excipient, particularly for hydrophobic drug encapsulation and long-acting release applications. ResolveMass Laboratories Inc. provides high-quality, research-grade PLA–mPEG–PLA with consistent molecular weight profiles, narrow dispersity, and excellent purity for reliable performance across formulations.
CHEMICAL INFORMATION
Chemical Name: Poly(D,L-lactide)-b-poly(ethylene glycol)-b-poly(D,L-lactide)
Abbreviation: PLA–mPEG–PLA
Block Structure: ABA triblock copolymer
Molecular Weight (approx.): 25,000 : 4,000 : 25,000
Polymer Type: Amphiphilic, biodegradable triblock
Backbone Features:
-
PLA segments: Provide hydrophobicity, mechanical strength, and controlled hydrolytic degradation.
-
PEG center block: Enhances hydrophilicity, solubility, biocompatibility, and steric stabilization.
PLA–mPEG–PLA is typically synthesized through ring-opening polymerization (ROP), ensuring well-defined block lengths and reproducible performance characteristics. The D,L-lactide configuration ensures amorphous polymer segments, enabling smoother degradation kinetics and improved drug dispersion within the hydrophobic PLA domains.
KEY FEATURES & BENEFITS
-
Amphiphilic Self-Assembly: Forms micelles, nanospheres, and polymeric vesicles upon dispersion, enabling sophisticated drug carrier designs.
-
Biodegradable & Biocompatible: All blocks degrade into physiologically tolerated products (lactic acid and PEG).
-
Stable Nanocarrier Formation: PEG mid-block confers steric shielding, reduces aggregation, and enhances colloidal stability.
-
High Drug Loading Capacity: Particularly suited for hydrophobic small molecules and poorly water-soluble actives.
-
Controlled Release Behavior: PLA degradation rate governs sustained release, ideal for long-acting injectable systems.
-
Low Immunogenicity: PEGylated structure minimizes opsonization, helping prolong systemic circulation times.
MECHANISM OF PERFORMANCE
PLA–mPEG–PLA triblock copolymers self-assemble in aqueous media due to the hydrophobic nature of the PLA end blocks and the hydrophilic nature of PEG. The PLA domains aggregate to form the micelle or nanoparticle core, while PEG forms the outer corona. This architecture:
-
Creates core–shell nanostructures with enhanced drug encapsulation efficiency.
-
Protects sensitive payloads from degradation.
-
Modulates drug release through PLA chain hydrolysis.
-
Enables tuning of nanoparticle size by adjusting polymer concentration, temperature, and solvent conditions.
With PLA segments at 25 kDa each, the hydrophobic sections are significantly long, enabling formation of stable, slow-degrading depots and nanostructures. The 4 kDa PEG block provides balanced hydrophilicity without overly increasing particle size or reducing encapsulation efficiency.
APPLICATIONS of Poly(D,L-lactide)-b-poly(ethylene glycol)-b-poly(D,L-lactide) | PLA: mPEG: PLA (Mw 25000: 4000: 25000)
PLA–mPEG–PLA (25k:4k:25k) is widely used across pharmaceutical, biomedical, and advanced materials research. Typical applications include:
1. Drug Delivery Systems
-
Micelles and nanocarriers for hydrophobic drugs
-
Controlled-release injectable formulations
-
Depot systems for long-acting therapeutics
-
Enhanced-stability formulations for sensitive APIs
-
Dual-drug encapsulation architectures
2. Nanomedicine & Therapeutic Platforms
-
Targeted delivery nanoparticles
-
Tumor-responsive nanocarriers
-
Polymer–drug conjugate scaffolds
-
Combination therapy platforms
3. Tissue Engineering
-
Biodegradable scaffolds
-
Smart hydrogels incorporating PLA–mPEG–PLA
-
Cell-compatible matrices with tunable degradation
4. Biomedical Coatings & Surface Modification
-
PEGylated surface treatments
-
Bio-stealth coatings
-
Slow-release protective layers for implants
PHYSICOCHEMICAL PROPERTIES
-
Appearance: White to off-white solid
-
Amphiphilicity: Allows solubility in organic solvents and dispersibility in aqueous systems
-
Glass Transition (PLA): Typically 45–55°C
-
Degradation Profile: Hydrolytic breakdown into lactic acid and PEG; rate can be modulated via formulation factors
-
Nanoparticle Formation: Produces uniform micelles typically 20–120 nm depending on preparation
These attributes ensure predictable performance in nanoparticle and controlled-release applications.
WHY CHOOSE RESOLVEMASS LABORATORIES INC.
ResolveMass Laboratories Inc. prioritizes consistency, reliability, and scientific support. Our PLA–mPEG–PLA triblock copolymers are produced with controlled polymerization conditions and undergo stringent analytical characterization, including:
-
Molecular weight verification
-
Polydispersity assessment
-
Purity and residual monomer analysis
-
Structural confirmation via NMR/FT-IR
We support researchers with detailed COAs and technical guidance to ensure smooth integration into formulation workflows.
Read below Learn with Us Articles:
PLGA Nanoparticles Synthesis: A Step-by-Step Guide for Beginners
The Science Behind GPC: A Deep Dive into Analyzing PLA, PLGA, and PCL for Research
Reviews
There are no reviews yet.