Poly(lactide-co-glycolide)-b-poly(ethylene glycol)-b-poly(lactide-co-glycolide) | PLGA: mPEG: PLGA (Mw 5000: 4000:5000 | CAS 952 111-10-3
OVERVIEW
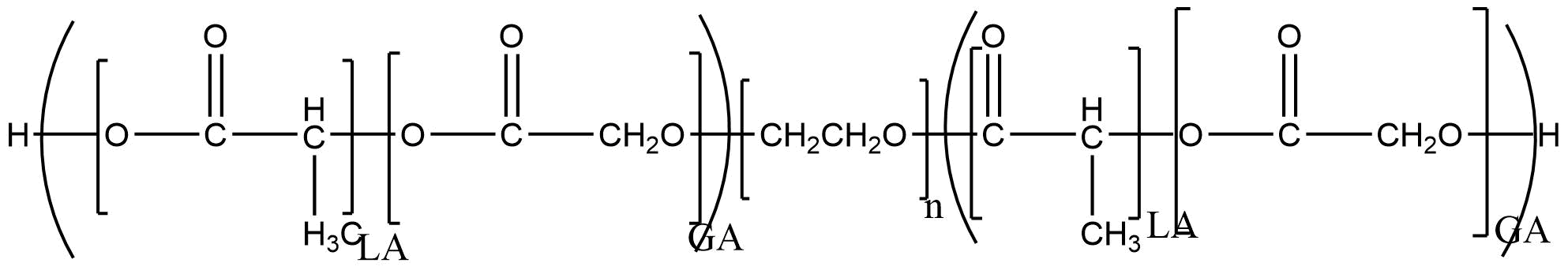
Poly(lactide-co-glycolide)-b-poly(ethylene glycol)-b-poly(lactide-co-glycolide) | PLGA: mPEG: PLGA (Mw 5000: 4000:5000 | CAS 952 111-10-3 supplied by ResolveMass Laboratories Inc. is a high-performance amphiphilic triblock copolymer engineered for advanced drug-delivery and biomedical formulations. This specific grade—PLGA : mPEG : PLGA (25,000 : 4,000 : 25,000), total nominal molecular weight ≈ 54 kDa, CAS 952-111-10-3—offers a balance of hydrophilicity and hydrophobicity optimized for controlled release, micelle formation, tissue engineering, and injectable depot systems. Its structure, featuring hydrophobic PLGA end blocks flanking a hydrophilic PEG core, enables exceptional self-assembly, predictable degradation, and formulation versatility across a wide range of APIs.
ResolveMass provides this polymer with strict analytical characterization, batch consistency, and technical support to help formulation scientists develop high-performance prototypes, preclinical systems, and translational delivery technologies.
CHEMICAL INFORMATION
-
Chemical Name: Poly(lactide-co-glycolide)-b-poly(ethylene glycol)-b-poly(lactide-co-glycolide)
-
Abbreviation: PLGA-PEG-PLGA (triblock)
-
Block Molecular Weights: PLGA 5,000 – PEG 4,000 – PLGA 5,000
-
Typical Total Mw: ~54,000 Da
-
CAS Number: 952-111-10-3
-
Polymer Type: Amphiphilic, biodegradable triblock copolymer
-
PLGA Composition: Lactic:glycolic ratio available upon request; custom ratios support tailored degradation rates.
KEY FEATURES
-
Amphiphilic triblock architecture for micelle formation and enhanced drug solubilization
-
Controlled and tunable degradation driven by PLGA block structure
-
PEG mid-block offers hydrophilicity, steric shielding, and reduced protein adsorption
-
Biocompatible and biodegradable into lactic and glycolic acid
-
Suitable for hydrophobic APIs, peptides, proteins, and imaging agents
-
Consistent molecular weight distribution verified by GPC/SEC
-
High-purity material with low residual solvent content
APPLICATIONS
This PLGA-PEG-PLGA triblock is used widely in research and development of:
-
Sustained-release injectable depots: Forms in situ gels or controlled-release matrices after solvent evaporation or aqueous self-assembly.
-
Nanoparticles and micelles: Core–shell structures capture hydrophobic drugs and protect sensitive biologics.
-
Thermoresponsive gels: Some formulations exhibit sol–gel transitions near physiological temperatures, ideal for localized delivery.
-
Protein and peptide delivery: PEG middle block minimizes aggregation and immunogenicity while PLGA controls release rates.
-
Tissue engineering hydrogels: Supports cell encapsulation, regenerative scaffolds, and controlled growth factor release.
-
Surface modification: PEG provides functional handles for ligand attachment, targeting, or stealth coating.
FORMULATION BENEFITS
-
Versatile drug loading: Compatible with small molecules, peptides, proteins, and imaging compounds.
-
Predictable release kinetics: Block lengths and PLGA composition modulate degradation from weeks to months.
-
Reduced burst release: Hydrophobic PLGA ends create a stable core that moderates initial drug diffusion.
-
Improved stability: PEG corona reduces opsonization and enhances blood circulation for nanoparticulate systems.
-
Aqueous processing compatibility: Enables thermogelling or micelle-based formulations without harsh processing conditions.
ANALYTICAL SPECIFICATIONS
ResolveMass provides full analytical documentation including:
-
GPC/SEC: Molecular weight and PDI
-
¹H NMR: Block verification and PEG content
-
FTIR: Functional group confirmation
-
Residual solvent and monomer data: GC/MS or HPLC upon request
-
Thermal analysis (DSC/TGA): Supporting data for formulation stability studies
REGULATORY & QUALITY SUPPORT
ResolveMass Laboratories Inc. supplies research-grade PLGA-PEG-PLGA with full documentation for analytical characterization, reproducibility, and traceability. Custom molecular weights, PLGA ratios, end-group types, and tailored material specifications are available to support advanced development programs, preclinical studies, and translational R&D.
Read below Learn with Us Articles:
PLGA Nanoparticles Synthesis: A Step-by-Step Guide for Beginners
The Science Behind GPC: A Deep Dive into Analyzing PLA, PLGA, and PCL for Research
Reviews
There are no reviews yet.