OVERVIEW
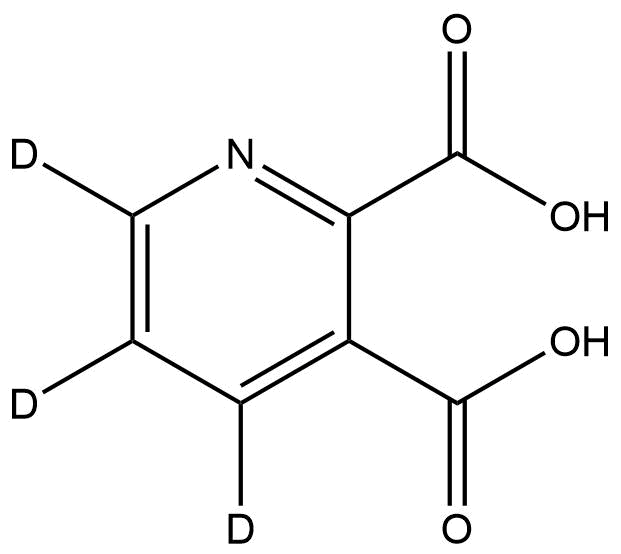
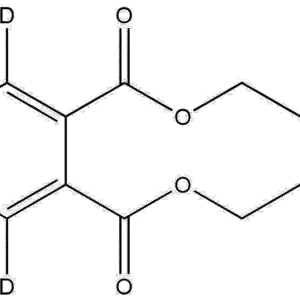
Quinolinic-4,5,6-d₃ Acid is a selectively deuterated isotopologue of quinolinic acid, an endogenous metabolite within the kynurenine pathway of tryptophan degradation. In this compound, three hydrogen atoms at the 4, 5, and 6 positions of the quinoline ring are replaced with deuterium atoms, resulting in a +3 Da molecular mass shift. This modification preserves the molecule’s chemical and biological behavior while enhancing its analytical utility for isotopic and tracer-based applications.
Deuterated quinolinic acid plays a crucial role in neurochemical, biochemical, and pharmacological research. It serves as a stable isotope-labeled internal standard for mass spectrometry (MS) and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) analyses, allowing precise quantification and kinetic profiling of quinolinic acid in biological matrices. Given quinolinic acid’s involvement in neuroinflammatory and neurodegenerative conditions, its deuterated form is a valuable analytical tool in neurobiological and metabolomic studies.
CHEMICAL INFORMATION
-
Name: Quinolinic-4,5,6-d₃ Acid
-
Molecular Formula: C₇H₂D₃NO₄
-
Molecular Weight: 170.04 g/mol
-
CAS Number: 138946-42-6
-
Isotopic Enrichment: ≥ 98 atom % D
-
Chemical Class: Deuterated heteroaromatic dicarboxylic acid
-
Functional Groups: Carboxylic acids (-COOH), aromatic nitrogen heterocycle
-
Stability: Chemically stable under standard conditions; protect from moisture and light
APPLICATIONS of Quinolinic-4,5,6-d3 Acid | CAS 138946-42-6
-
Mass Spectrometry (MS) Internal Standard:
Quinolinic-4,5,6-d₃ Acid is extensively employed as an isotopically labeled internal standard for LC-MS/MS and GC-MS analyses. The +3 Da mass difference allows clear differentiation from native quinolinic acid, enabling accurate quantification of this neuroactive metabolite in plasma, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), and tissue extracts. -
NMR Spectroscopy:
The deuterium substitution significantly reduces proton background signals, making it suitable for NMR-based kinetic and structural studies. Researchers use this compound to investigate isotopic exchange processes, metabolic pathways, and reaction intermediates involving quinolinic acid. -
Neurochemical and Metabolomic Research:
Quinolinic acid is a potent NMDA receptor agonist and neurotoxin implicated in various neuropathological disorders, including Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and Huntington’s disease. The deuterated version enables precise tracing and quantitation of quinolinic acid within the kynurenine pathway, supporting studies on neuroinflammation and oxidative stress. -
Stable Isotope Tracing:
Quinolinic-4,5,6-d₃ Acid is valuable for isotope tracing experiments, helping to elucidate metabolic flux and turnover rates within tryptophan catabolism. It is frequently used in labeled metabolite profiling to distinguish endogenous formation from exogenous administration. -
Calibration and Analytical Validation:
Utilized as a reference compound for validating analytical methods that quantify quinolinic acid and related metabolites. Its chemical stability and isotopic purity ensure reproducible results in both routine and advanced bioanalytical workflows.
ADVANTAGES of Quinolinic-4,5,6-d3 Acid | CAS 138946-42-6
-
High isotopic enrichment (≥ 98 atom % D) for enhanced analytical precision.
-
Chemically identical to native quinolinic acid—maintains equivalent reactivity and solubility.
-
Ideal for use as an internal standard in LC-MS/MS and GC-MS assays.
-
Reduces signal overlap in NMR, improving spectral clarity and accuracy.
-
Non-radioactive, safe, and environmentally stable isotope label.
-
Enhances accuracy in quantification of endogenous metabolites across biological matrices.
HANDLING
Quinolinic-4,5,6-d₃ Acid should be handled with standard laboratory precautions. Although it has low acute toxicity, quinolinic acid and its derivatives can act as neuroactive agents, so appropriate safety measures should be observed:
-
Avoid inhalation of dust and contact with skin or eyes.
-
Use gloves, lab coats, and safety goggles.
-
Handle in a well-ventilated area or fume hood.
-
Store in airtight containers protected from heat, light, and moisture.
-
In case of contact, wash thoroughly with water and seek medical advice if irritation occurs.
QUALITY & SPECIFICATION
Each batch of Quinolinic-4,5,6-d₃ Acid undergoes comprehensive analytical characterization to confirm identity, purity, and isotopic enrichment.
Characterization techniques include:
-
¹H / ²H NMR Spectroscopy: Verification of deuterium incorporation and positional labeling.
-
Mass Spectrometry (HRMS): Confirmation of isotopic mass distribution and molecular weight.
-
Infrared (IR) Spectroscopy: Structural verification through characteristic functional group absorption.
-
Chemical Purity: ≥ 98 %
-
Isotopic Enrichment: ≥ 98 atom % D
A detailed Certificate of Analysis (COA) accompanies each lot, providing analytical validation and traceability for research use.
SUMMARY
Quinolinic-4,5,6-d₃ Acid (CAS 138946-42-6) is a high-purity, deuterium-labeled derivative of quinolinic acid, specifically designed for use in isotope tracing, neurochemical, and analytical research. Maintaining the same biochemical behavior as its non-deuterated counterpart, it offers superior analytical precision through isotopic differentiation. Ideal for LC-MS/MS, NMR, and metabolic studies, this compound is a critical tool in elucidating the kynurenine pathway and studying the role of quinolinic acid in neurodegenerative and inflammatory diseases.
Learn more about,
Deuterated Polymers: A Cornerstone Guide to Synthesis, Applications, and Future Trends
Availability of All the Deuterated Chemicals at ResolveMass Laboratories Inc.
ResolveMass Laboratories: Leading Deuterated Chemical Synthesis Company in the United States.
Deuterated Internal Standards for LC-MS: Selection & Custom Synthesis
How to Choose the Right Deuterated Labelled Chemical Synthesis Company in Canada
How to Choose the Right Deuterium Labelled Compounds Supplier for Your Lab
Deuterium-Labelled Compounds — Synthesis, Applications & Ordering
Reviews
There are no reviews yet.